-
What Happens When You Delete a VM in vSphere?
-
Prerequisites Before Attempting Restore
-
Method 1: Restoring Deleted vSphere VMs from Backup
-
Method 2: Recovering Deleted vSphere VMs Using Snapshots
-
How to Prevent Accidental VM Deletion Disasters?
-
Restore Deleted vSphere VM with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
vSphere Restore Deleted VM FAQs
-
Conclusion
Have you ever deleted a virtual machine by mistake? It happens more often than you think—even to experienced admins. When it does, knowing how to recover quickly can save your day. This guide explains what really happens when you delete a VM in vSphere and shows you practical ways to bring it back using backups or snapshots. We also cover prevention tips so you can avoid this headache in the future.
What Happens When You Delete a VM in vSphere?
Deleting a VM in vSphere is not just removing an icon from your inventory—it’s much more final than that. If you use the Delete from Disk option in the vSphere Client, both the configuration files (.vmx) and all virtual disks (.vmdk) are erased from your datastore. There’s no built-in undo or recycle bin feature for this action; once confirmed, those files are gone for good at the storage level.
If instead you choose Remove from Inventory, only the reference to the VM disappears from your list—the actual files remain untouched on disk until manually deleted or overwritten later.
Why does this matter? Because if you want to perform a vsphere restore deleted vm operation after using “Delete from Disk,” your only hope is having either a valid backup or intact snapshots with their base disk files still present on storage.
This reality highlights why regular backups—and understanding exactly what each removal option does—are critical parts of any administrator’s toolkit.
Prerequisites Before Attempting Restore
Before jumping into recovery steps, pause for some quick checks:
Confirm which method applies: Did you use “Delete from Disk” or just remove from inventory?
Check if recent backups exist—these are your safest bet.
If relying on snapshots, verify whether any .vmx or .vmdk files remain on your datastore.
Make sure you have proper permissions in vSphere to perform restores.
Know your environment version; steps may differ slightly between different versions.
Having these details ready helps prevent wasted time during urgent recovery situations.
Method 1: Restoring Deleted vSphere VMs from Backup
Restoring from backup is usually the fastest way to complete a vsphere restore deleted vm task—if backups were made before deletion occurred. Backups capture everything about your VM: configuration settings, attached disks, even memory state if configured that way.
Here’s how most environments handle restoring VMs via backup:
First, log into your vSphere Web Client with admin credentials. In many setups using third-party solutions integrated with vCenter Server (such as plugins), look for options like Backup & Restore under main menus or directly within host/datastore context menus.
A typical workflow looks like this:
1. Open the vSphere Web Client.
2. Navigate to Menu > Backup & Restore (or similar plugin entry).
3. Locate available backup jobs; filter by date or name if needed.
4. Select the backup containing your lost VM.
5. Click Restore—this launches a wizard interface.
6. On the wizard screens:
Choose whether to overwrite an existing object or create as new
Pick target ESXi host/cluster
Set destination datastore
Adjust network mappings if restoring across clusters
7. Review summary details carefully; click Finish when ready
Once complete:
The restored VM appears back in inventory
Power it on via right-click > Power On
Test connectivity and application function inside guest OS
If restoring across different hardware versions or datastores:
Double-check network adapter types match expected VLANs/port groups
Validate storage policies align with production requirements
Method 2: Recovering Deleted vSphere VMs Using Snapshots
Snapshots offer another potential path—but only under specific conditions! Remember: snapshots are not full backups; they’re meant for short-term rollback before risky changes like patching software or updating drivers.
A snapshot alone cannot resurrect missing base disk files—a common misconception among newer admins! For snapshot-based recovery to work after accidental deletion:
1. Open the vSphere Web Client
2. Go to Menu > Storage
3. Select affected datastore; launch its Datastore Browser
4. Search for folders named after recently deleted VMs
5. Inside each folder check for presence of both .vmx (config) AND .vmdk (disk) files
6a.If found: Right-click .vmx file > select Register Virtual Machine...
6b.Follow prompts; assign unique name if re-registering alongside original copies
7.Once registered again: Right-click new entry > choose Snapshot > Revert to Snapshot
If successful:
Your VM returns at its last saved state per snapshot chain
Boot up normally; confirm data integrity inside guest OS
But beware! If only delta/snapshot files remain without their parent disks/configs…recovery isn’t possible through standard means—you’d need advanced file carving tools or professional help at this point.
How to Prevent Accidental VM Deletion Disasters?
Prevention beats cure every time! Here are key strategies every operations team should follow:
First, enforce strict role-based access control (RBAC)—limit who can execute dangerous actions like Delete from Disk, especially outside maintenance windows!
Second, organize VMs logically using tags/folders so bulk actions never catch critical workloads by mistake;
clear naming conventions help too (“PROD_”, “DEV_”, etc.).
Third, test all backup jobs regularly—not just creation but full restores—to guarantee usable recovery points exist!
Schedule periodic drills simulating real-world loss scenarios so staff know exactly what steps work best under pressure.
Lastly, document every change—including deletions—in ticketing systems so audit trails always exist when questions arise later!
Restore Deleted vSphere VM with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
For organizations seeking robust protection and streamlined recovery of VMware environments, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers enterprise-level virtual machine backup capabilities across over 15 mainstream virtualization platforms—including VMware vSphere first and foremost, as well as Hyper-V, Proxmox VE, oVirt/RHV/OLVM, XCP-ng/XenServer, OpenStack, ZStack and others. This solution offers comprehensive support for features such as quiesced snapshot, HotAdd transport mode, CBT tracking technology, LAN-free backup architecture and instant recovery—all tailored specifically for VMware users’ needs.
Among its extensive toolkit are forever-incremental backup strategies that optimize storage usage and speed up operations; granular restore options enabling precise data retrieval down to individual files; advanced deduplication/compression algorithms reducing overall costs; ransomware-resistant storage protection mechanisms safeguarding against malicious alteration of backups; and automated malware detection powered by Kaspersky scanning engines—all designed to ensure rapid disaster recovery while minimizing risk exposure.
Using Vinchin Backup & Recovery’s intuitive web console makes protecting VMware VMs straightforward:
Step 1: Select the VMware VM(s) you wish to back up
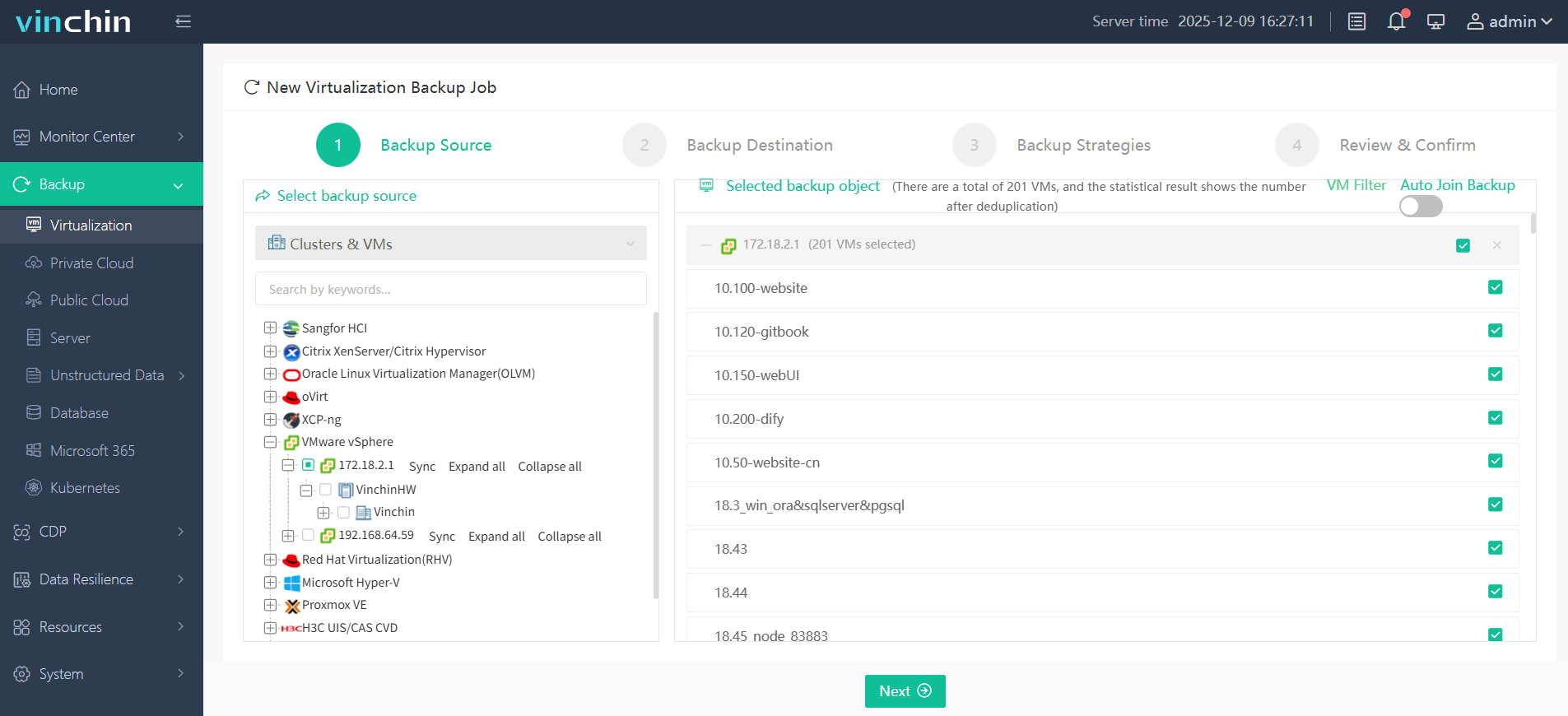
Step 2: Choose target backup storage
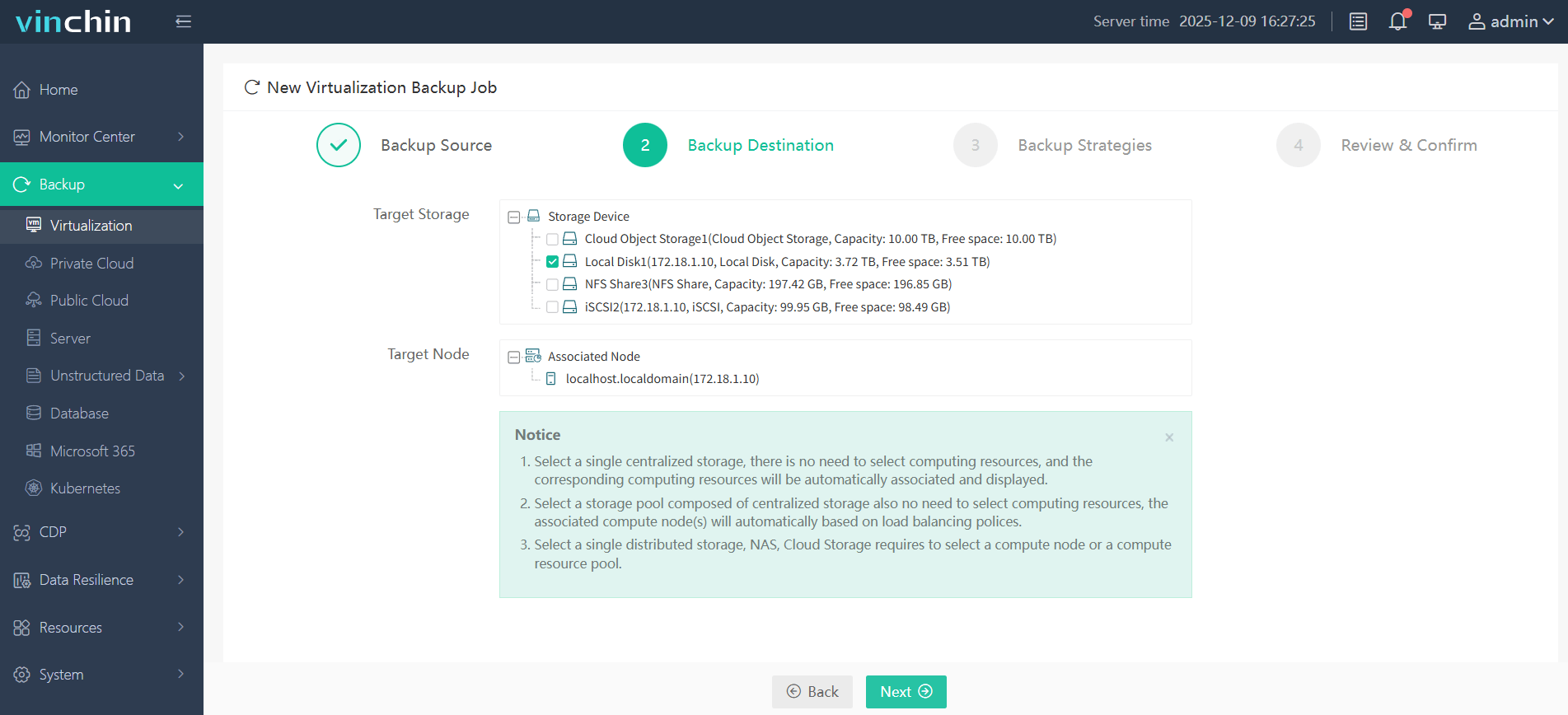
Step 3: Configure desired backup strategy (full/incremental/differential/schedule/etc.)
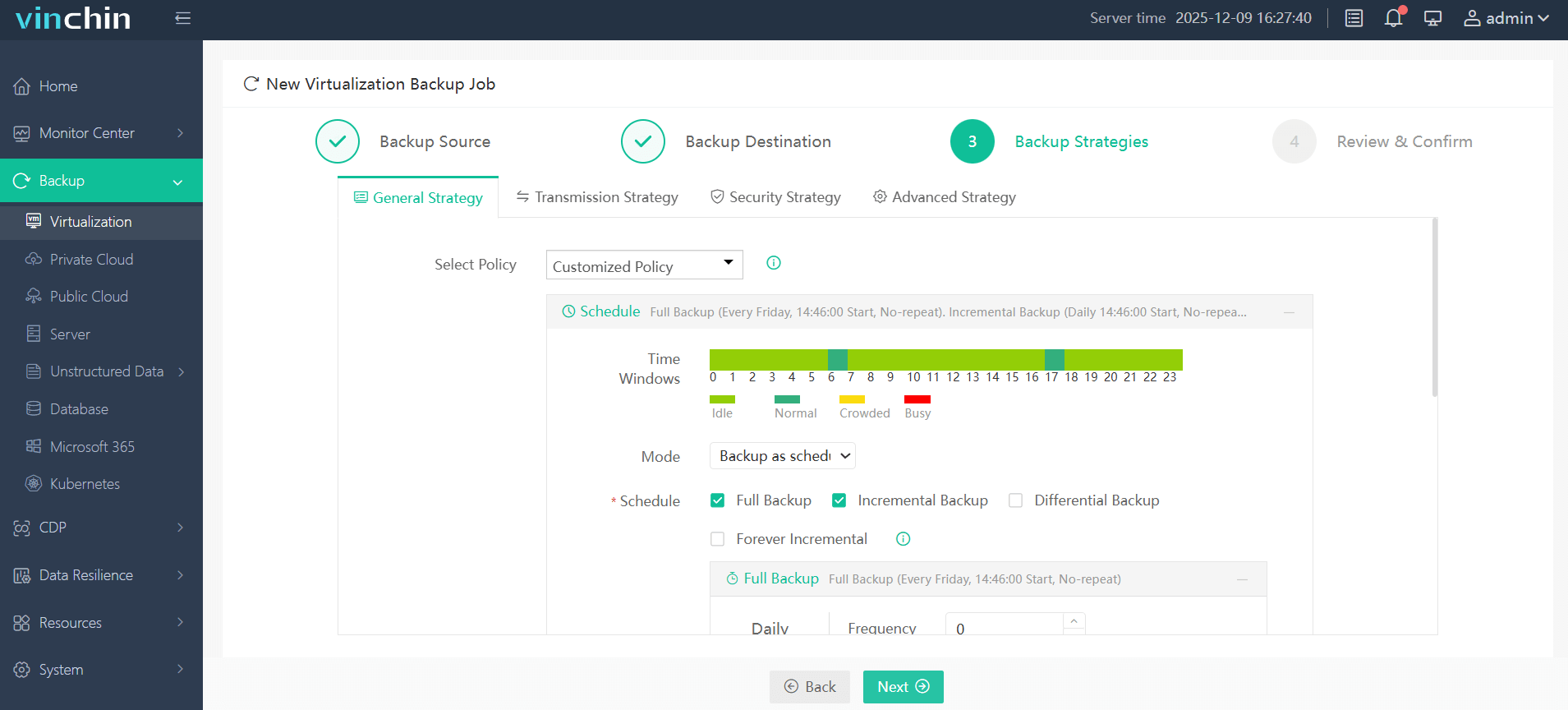
Step 4: Submit job and monitor progress
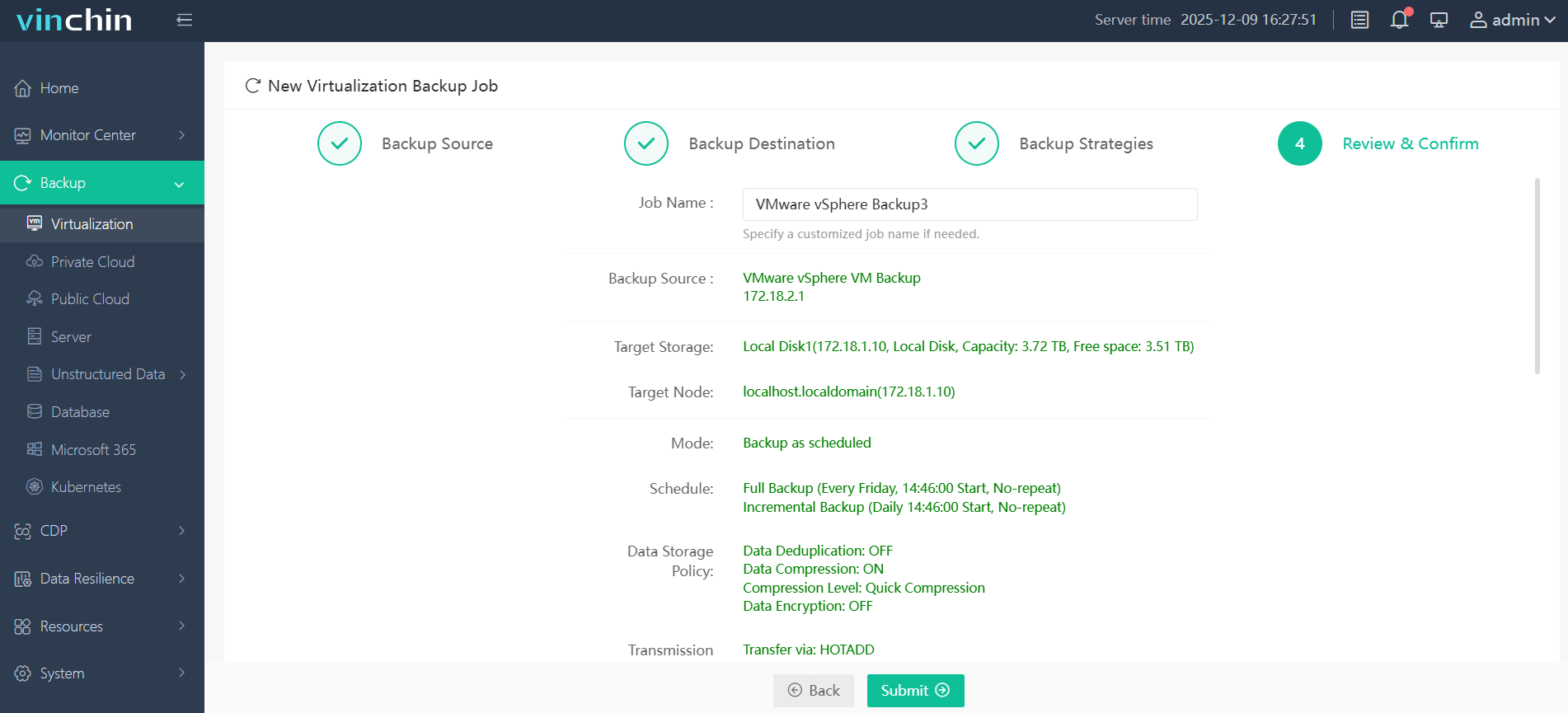
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is trusted worldwide by thousands of enterprises for reliable data protection—try all features free for 60 days now by clicking below!
vSphere Restore Deleted VM FAQs
Q1: Can I recover my deleted vSphere VM if my last scheduled backup failed?
A1: Without any valid backups or intact snapshots left on disk there’s no supported way—consider consulting data recovery specialists immediately if business-critical data was lost unexpectedly!
Q2: What should I do if my restored VM boots but cannot connect to its original network?
A2: Edit its settings post-recovery; assign correct port group/network adapter matching current cluster topology then reboot guest OS as needed!
Q3: Is it safe to reuse old folders left behind after failed restores?
A3: No—it’s best practice first verify contents aren’t required elsewhere then delete unused directories via Datastore Browser keeping environment tidy/conflict-free!
Conclusion
Losing a vital workload hurts—but fast action makes all difference! With regular backups plus careful permissions management, vSphere restore deleted vm tasks become routine rather than emergencies.
Vinchin makes protecting and recovering your virtual infrastructure simple no matter how complex things get!
Share on:








