-
What Is Oracle RMAN?
-
What Is Backup To Disk?
-
Method 1: How to Use Oracle RMAN Command Line for Backup to Disk?
-
Method 2: How to Automate RMAN Backups to Disk with OS Schedulers?
-
Method 3: How to Perform RMAN Backups to Disk Using Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM)?
-
Simplify Oracle Protection with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Oracle RMAN Backup To Disk FAQs
-
Conclusion
Protecting your Oracle database is critical for business continuity. For database administrators and system operators, Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is the built-in tool that delivers reliable backup and restore capabilities. One of the most efficient strategies is using RMAN to back up your database to disk storage. This guide explains what RMAN does, what “backup to disk” means in practice, how you can perform these backups step by step—both from the command line and through Oracle Enterprise Manager—and how to automate them safely. We’ll also cover why disk-based backups are so popular in enterprise environments and show how Vinchin can make Oracle protection even simpler.
What Is Oracle RMAN?
Oracle RMAN (Recovery Manager) is Oracle’s native utility for backup and recovery tasks. It automates many complex operations that would otherwise require manual scripting. With RMAN, you can back up databases at different levels—full or incremental—and protect tablespaces, datafiles, control files, or archived redo logs. RMAN tracks all backup metadata in its catalog or control file so you always know what has been backed up and when.
A key advantage of RMAN is its tight integration with Oracle Database itself. This ensures consistency during backup operations—even if your database stays online throughout the process.
What Is Backup To Disk?
Backing up to disk means storing your database backup files on a local drive or network-attached storage instead of tape or cloud storage services. Disk-based backups offer several advantages: they are fast to create, easy to manage day-to-day, and allow quick restores when needed most.
With RMAN’s flexibility, you can write either backup sets (which group multiple files together) or image copies directly onto disk storage. You have full control over where these files go by configuring destination directories and file naming conventions that fit your organization’s standards.
Disk-based backups also integrate well into automated workflows—making them ideal for both small teams managing a single instance as well as large enterprises running hundreds of databases.
Method 1: How to Use Oracle RMAN Command Line for Backup to Disk?
Using the command line gives you precise control over every aspect of an RMAN backup operation—from configuration through execution.
Before starting any backup job:
First ensure your database runs in ARCHIVELOG mode if you want point-in-time recovery capability—a must-have for most production systems. Check this by connecting as SYSDBA in SQL*Plus:
SQL> SELECT log_mode FROM v$database;
If it returns ARCHIVELOG, you're ready; if not, switch modes before proceeding.
Next connect to your target database using RMAN:
rman target /
Check current configuration settings by running:
RMAN> SHOW ALL;
Pay special attention here: look at parameters like RETENTION POLICY (which controls how long old backups are kept), CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP, and default device type settings—they affect both safety and storage use.
Set default device type if needed:
RMAN> CONFIGURE DEFAULT DEVICE TYPE TO DISK;
Configure a channel specifying where backups should be stored:
RMAN> CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '/u01/backups/%d_%T_%U.bkp';
Here %d inserts the DB name; %T adds today’s date; %U creates a unique identifier per file—helpful when sorting through many backups later.
To run a full database backup:
RMAN> BACKUP DATABASE;
For better recoverability include archived redo logs too:
RMAN> BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;
Want smaller files? Compress them like this:
RMAN> BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE;
Need only specific tablespaces? Try:
RMAN> BACKUP TABLESPACE users;
Tagging helps identify jobs later—for example,
RMAN> BACKUP DATABASE TAG 'WEEKLY_FULL';
After completing any backup job list summaries using:
RMAN> LIST BACKUP SUMMARY;
This approach puts you fully in charge—ideal for ad-hoc jobs or scheduled scripts alike.
Method 2: How to Automate RMAN Backups to Disk with OS Schedulers?
Manual jobs work fine—but automation ensures regular protection without relying on memory alone! Most admins use OS-level schedulers like cron (Linux/Unix) or Task Scheduler (Windows).
Begin by creating an executable shell script such as /u01/scripts/rman_backup.sh. Here’s an enhanced sample including basic logging/error handling:
#!/bin/bash
export ORACLE_SID=ORCL
export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1
export PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH
LOGFILE=/u01/scripts/logs/rman_backup_$(date +%Y%m%d).log
exec >> $LOGFILE 2>&1
echo "Backup started at $(date)"
rman target / <<EOF
RUN {
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE FORMAT '/u01/backups/ORCL_%T_%U.bkp';
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET ARCHIVELOG ALL FORMAT '/u01/backups/ORCL_ARCH_%T_%U.bkp';
BACKUP CURRENT CONTROLFILE FORMAT '/u01/backups/ORCL_CTL_%T_%U.bkp';
}
EOF
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Backup completed successfully at $(date)"
else
echo "Backup FAILED at $(date)"
# Optional: send alert email here
fi
echo "-----------------------------"Make sure it’s executable:
chmod +x /u01/scripts/rman_backup.sh
Schedule daily runs at 2 AM via cron by adding this line (crontab -e):
0 2 * /u01/scripts/rman_backup.sh
On Windows use Task Scheduler with similar logic inside a batch file (.bat).
For larger databases consider parallelizing channels inside your RUN block—for example,
ALLOCATE CHANNEL ch1 DEVICE TYPE DISK; ALLOCATE CHANNEL ch2 DEVICE TYPE DISK; ... RELEASE CHANNEL ch1; RELEASE CHANNEL ch2;
Automation reduces human error risk while ensuring fresh restore points exist every day.
Method 3: How to Perform RMAN Backups to Disk Using Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM)?
Prefer working visually? OEM provides an intuitive interface for managing all aspects of Oracle—including scheduling robust disk-based backups without typing commands manually!
To schedule a new job:
1. Log into Oracle Enterprise Manager then open your database's Home page.
2. From the Availability menu choose Backup & Recovery, followed by Schedule Backup.
3. On the Schedule Backup screen pick Customized Backup.
4. Select either entire Database, specific tablespaces/datafiles/pluggable DBs as needed.
5. Under options set type (Full/Incremental) then select destination as Disk.
6. Specify location/file format details matching site standards.
7. Define schedule frequency plus retention policy according to business needs.
8. Review everything carefully then click Submit—your job is now scheduled!
After submission monitor progress via the Job Activity page within OEM—it displays real-time status updates plus detailed logs if anything fails during unattended runs.
Simplify Oracle Protection with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Beyond native tools like RMAN, unified solutions streamline enterprise data protection across diverse environments—including complex setups involving multiple databases such as Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-level solution supporting all these mainstream platforms—with particular strength in comprehensive Oracle protection tailored for modern IT demands.
Key features include incremental backup support for efficient resource usage, batch database backup management for operational ease, granular data retention/GFS policies meeting regulatory needs, advanced source-side compression optimizing storage footprint on supported platforms like Oracle itself, and robust integrity check mechanisms ensuring recoverability confidence at scale—all designed for reliability while reducing administrative overhead across large deployments.
The web console makes setup remarkably straightforward:
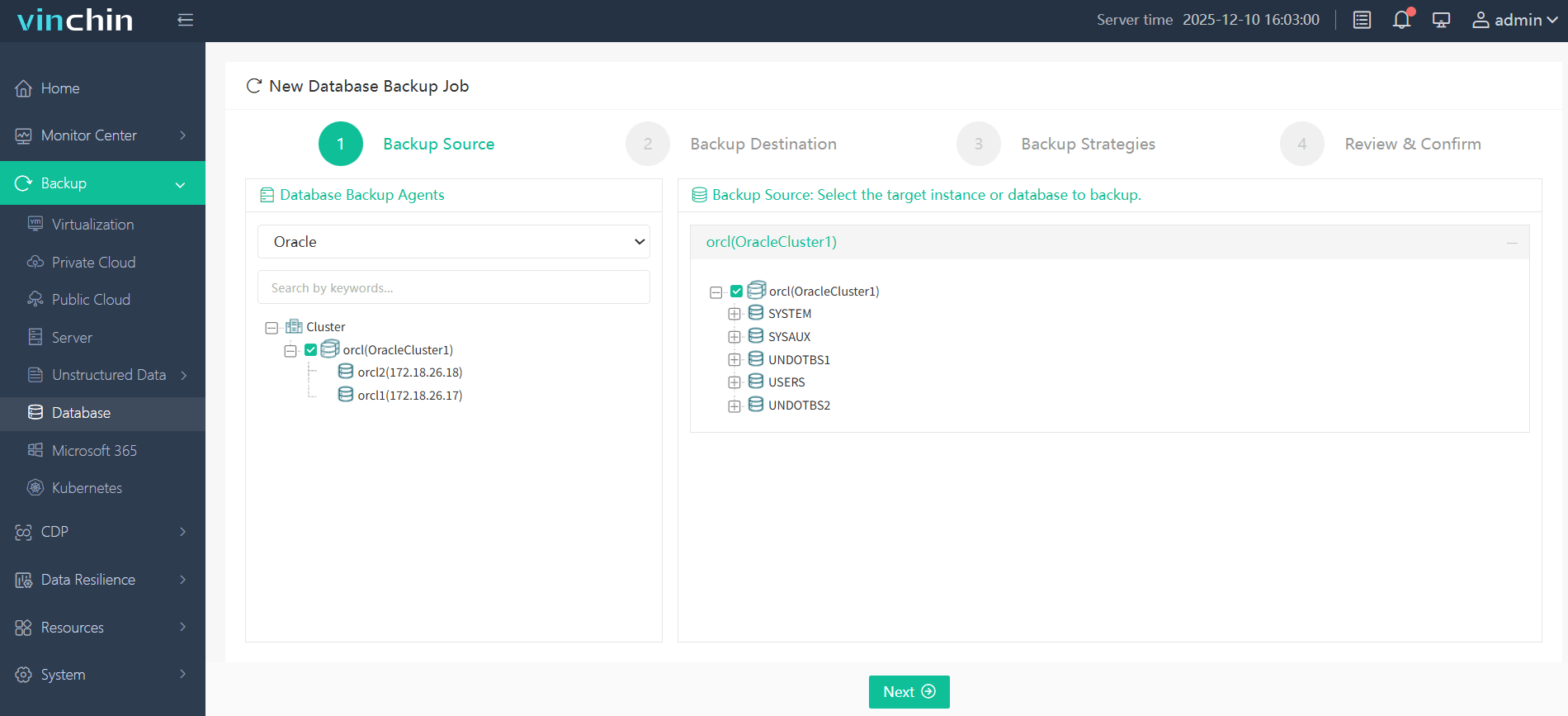
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
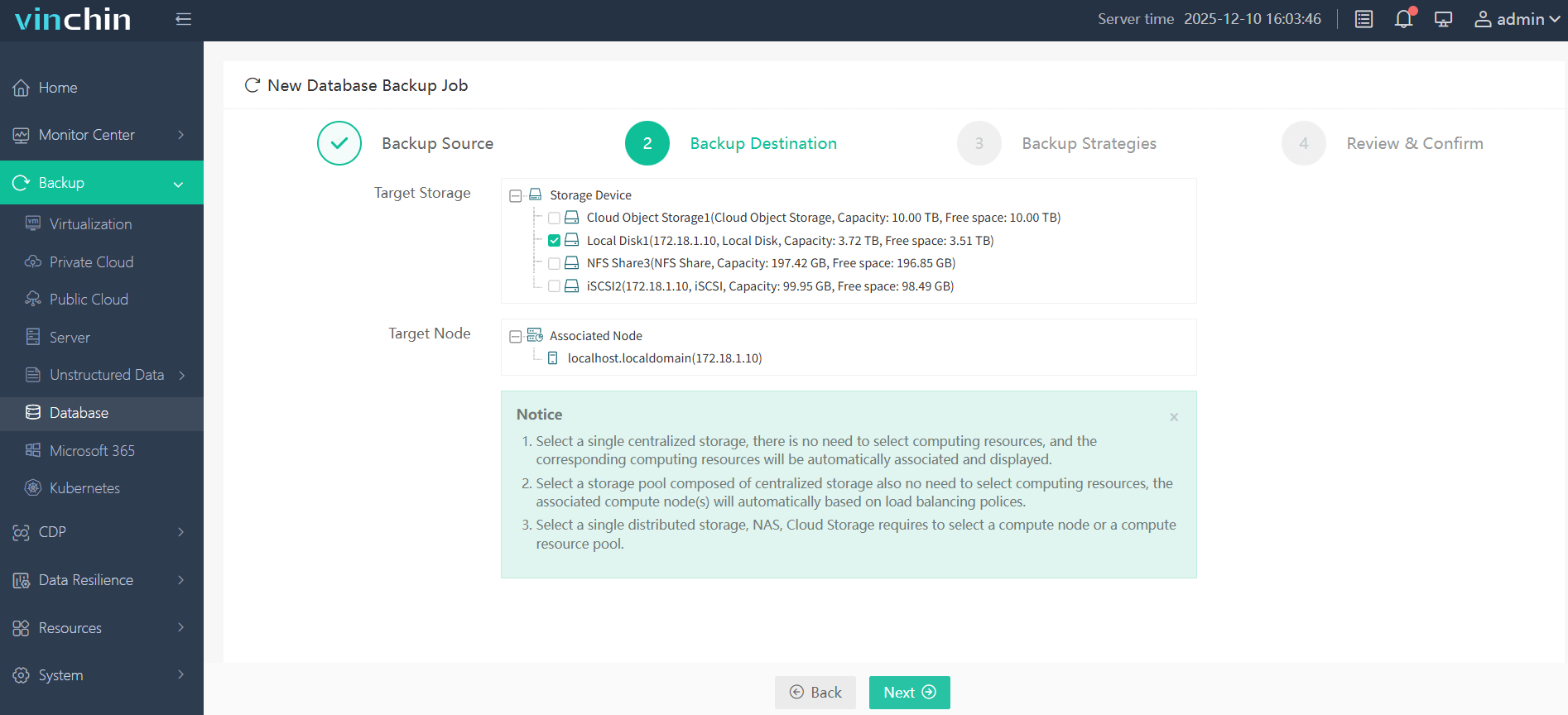
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
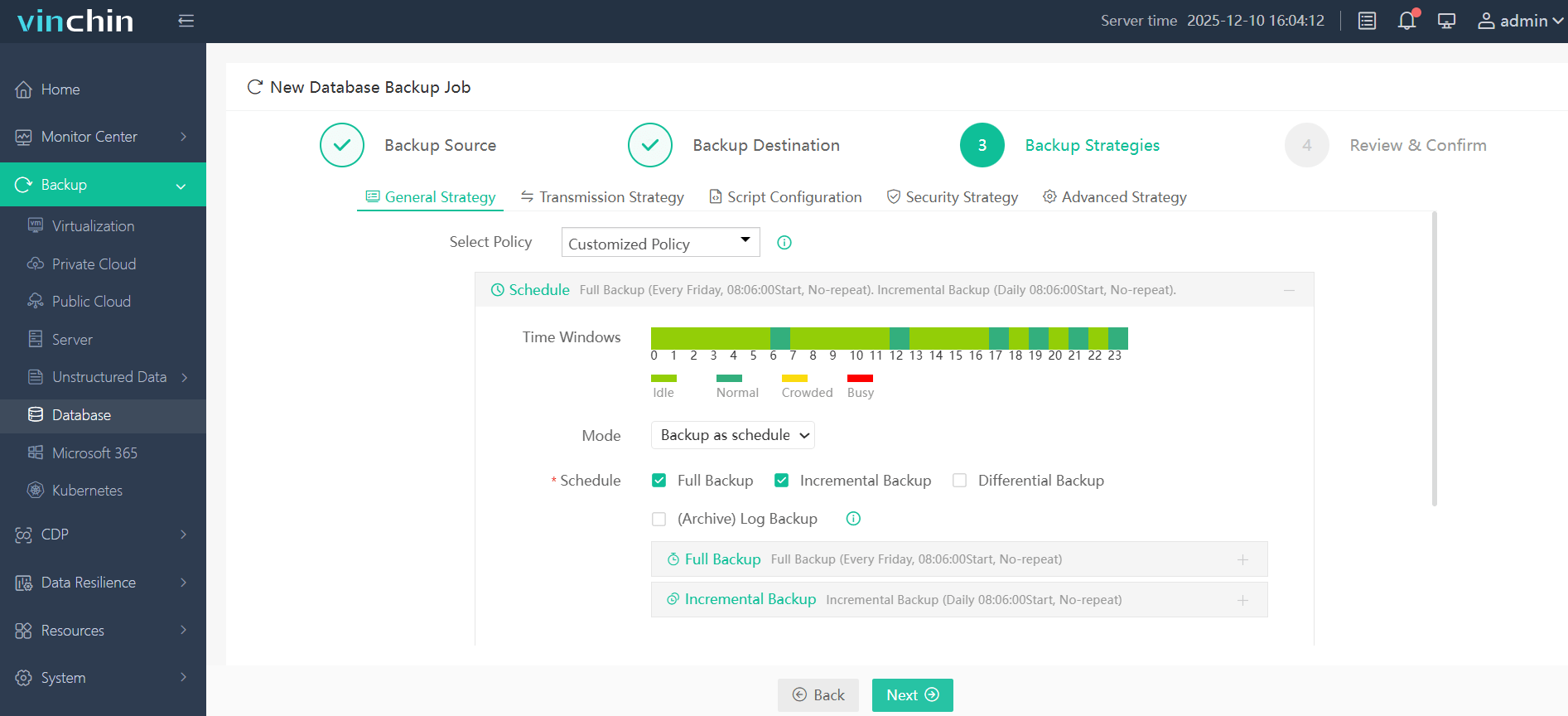
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
Step 4. Submit the job
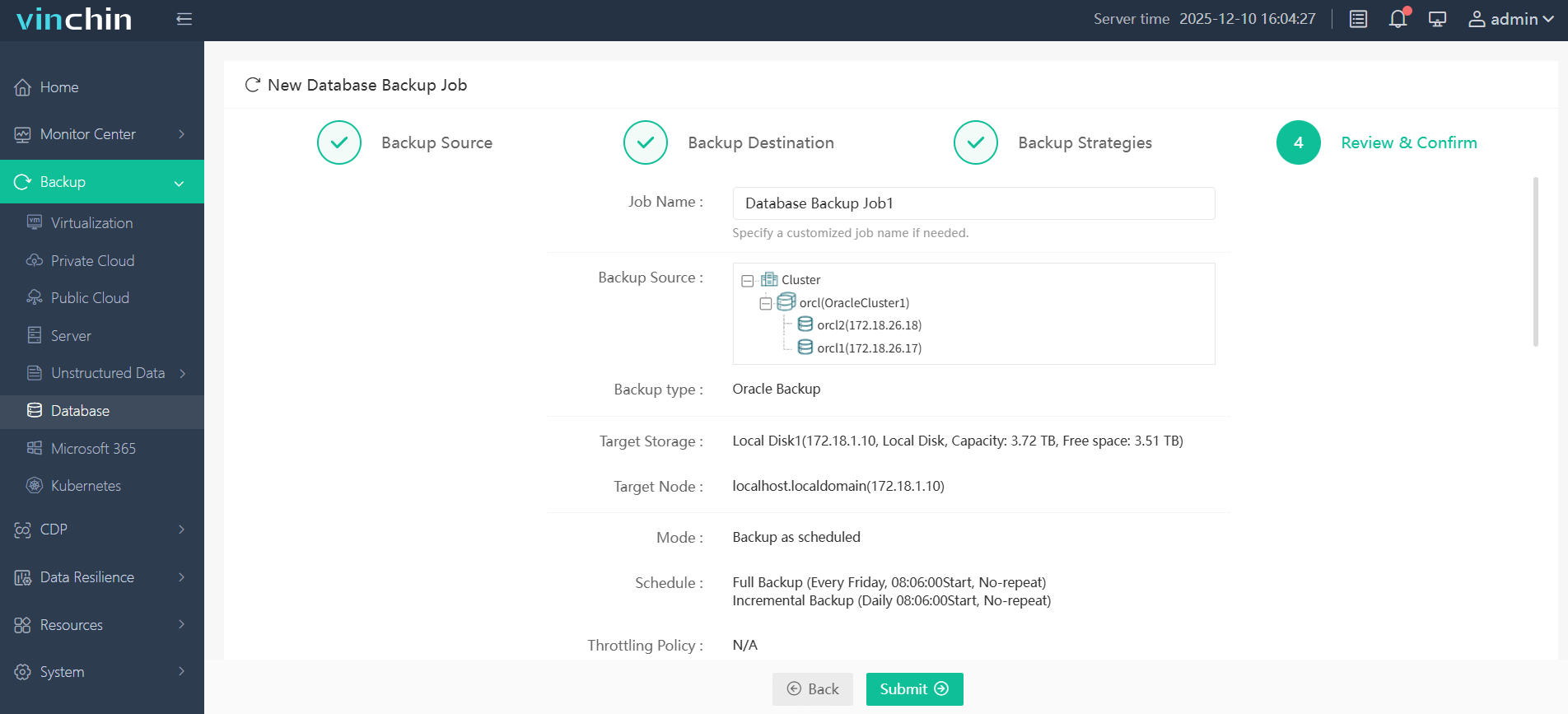
With just four steps through an intuitive interface—even non-specialists can configure secure automated protection quickly and monitor results centrally from anywhere worldwide.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is trusted globally by thousands of organizations seeking proven enterprise-grade data security solutions—with top ratings from industry analysts year after year. Try the fully featured free trial for 60 days now—click below to get started!
Oracle RMAN Backup To Disk FAQs
Q1: Can I check my last successful disk-based backup quickly?
Yes—run LIST BACKUP SUMMARY; in RMAN then check completion times shown there for confirmation.
Q2: What should I do if my scheduled script fails due to permission errors?
Check directory/file ownerships under /u01/backups, correct them using chown/chmod, then rerun manually before re-enabling automation jobs again afterward.
Q3: How do I clean up old obsolete backups automatically?
Run DELETE OBSOLETE; inside an automated script after setting proper retention policy—it removes expired sets based on configured rules.
Conclusion
Backing up Oracle databases to disk with RMAN combines speed with flexibility while supporting advanced features like compression or automation easily. Whether through command line tools, scripts, schedulers—or graphical interfaces—you have options tailored exactly toward operational needs. For unified management, Vinchin offers even greater simplicity alongside advanced enterprise-grade protections. Try the free trial today!
Share on: