-
What Is Oracle RMAN?
-
What Makes Up Oracle RMAN Architecture
-
Why Use Oracle RMAN for Backup
-
Key Processes Inside Oracle RMAN Architecture
-
How Does Vinchin Back Up Oracle Databases?
-
Oracle RMAN Architecture FAQs
-
Conclusion
Every Oracle database administrator knows that backup and recovery are not just routine tasks—they are the backbone of data protection. But how does Oracle ensure these processes are reliable, efficient, and scalable? The answer lies in Oracle RMAN architecture. If you have ever wondered what makes Oracle RMAN tick or how its components work together to safeguard your data, you are in the right place. Let’s break down the architecture step by step so you can make the most of this essential tool—and avoid costly mistakes along the way.
What Is Oracle RMAN?
Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is Oracle’s built-in utility for managing database backup, restore, and recovery operations. Unlike manual backup methods that require scripting or third-party tools, RMAN automates many tasks—reducing human error while offering advanced features like block-level corruption detection and incremental backups. Since RMAN is included with every Oracle Database installation by default, there is no need to purchase or install extra software.
RMAN works closely with the core database engine to give you a single interface for all backup-related activities. Whether you manage one database or dozens across different environments, understanding how RMAN operates is crucial for building an effective data protection strategy.
What Makes Up Oracle RMAN Architecture
Understanding Oracle RMAN architecture means knowing its main components—and how they interact during daily operations. At its core, RMAN consists of several key parts:
RMAN Client: This command-line tool lets you issue backup and recovery commands directly to your databases. You can run it locally on your server or remotely if network access is available.
Target Database: This is the actual Oracle database instance you want to back up or restore. All operations start here.
Channels: A channel represents a stream of data between your database server and a storage device (disk or tape). Each channel corresponds to a dedicated server session on your target database—enabling parallelism when multiple channels are configured.
RMAN Repository: Here’s where metadata about backups—such as copies made or structural changes—is stored. By default, this information lives in your target database’s control file; however, using a separate
Recovery Catalog provides longer retention periods and centralized management across multiple databases.
Media Management Layer: For disk-based backups this layer isn’t needed—but if you use tape storage solutions then an external media management application must be installed so that RMAN can communicate with those devices.
Fast Recovery Area (FRA): This special disk location managed by Oracle stores backup files alongside archived logs and other recovery-related files—simplifying space management through automated cleanup routines.
These components form a flexible yet robust environment for handling both simple backups as well as complex disaster recovery scenarios. While only the client tool plus target database are strictly required for basic operation—in production environments most administrators leverage additional features like parallel channels or external catalogs for greater control.
How Components Work Together
When you initiate an operation such as BACKUP DATABASE, several things happen behind the scenes:
First—the RMAN Client parses your command input before connecting securely to your chosen target database instance using credentials provided at login time.
Next—for each defined channel—a new server process starts up within that instance; these processes handle reading datafiles from disk (or archive logs/control files) according to instructions received from the client session.
As each channel reads blocks of data—it writes them out either directly onto local disk storage (using standard filesystem paths) or passes them through any configured media management layer if writing out onto tape devices instead.
Finally—as soon as all requested objects have been backed up successfully—the system updates metadata records inside both control file repositories plus any connected recovery catalog databases—ensuring future restores reference accurate information about what was saved when (and where).
This workflow allows DBAs not only fine-grained control over their backups but also visibility into historical activity—which becomes invaluable during audits or troubleshooting exercises later on.
Why Use Oracle RMAN for Backup
Why do so many organizations rely on Oracle RMAN? The answer is simple: it offers reliability plus features manual methods cannot match—even under pressure from tight SLAs or compliance requirements.
Here’s why:
Automation: With built-in scheduling options plus policy-driven retention rules—you set guidelines once then let automation handle repetitive cycles going forward.
Incremental Backups: Instead of copying everything every time—RMAN identifies changed blocks since last run—saving both time & storage space.
Corruption Detection: During every read/write cycle—including restores—each block gets checked automatically; early warnings mean less risk down the road.
Parallelism: Multiple channels allow simultaneous streams—increasing throughput dramatically especially when dealing with large datasets.
Centralized Management: Using a dedicated recovery catalog enables oversight across many databases from one console—a big win for enterprise teams juggling complex landscapes.
Integration with Core Features: Seamless compatibility exists between RMAN & technologies like Data Guard replication—or Flashback queries—all coordinated via Fast Recovery Area settings behind-the-scenes.
In short—RMAN isn’t just another utility; it forms part of an integrated framework designed specifically around high availability goals demanded by modern businesses today.
Key Processes Inside Oracle RMAN Architecture
To truly master backup strategies using oracle rman architecture—it helps seeing what happens during typical workflows:
1. When issuing commands such as BACKUP DATABASE, first connect via rman client specifying user credentials & service name (rman TARGET sys/password@prod_db).
2. Allocate channels explicitly if custom performance tuning needed (ALLOCATE CHANNEL ch1 DEVICE TYPE DISK), otherwise defaults apply based on configuration settings (CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK PARALLELISM 4).
3. As job runs—the allocated server sessions read source files chunk-by-chunk; each writes output pieces into designated locations (either FRA directory paths—or via MML interface onto tapes).
4. Upon completion—all relevant metadata updates occur automatically inside both local control file repository & remote catalog if present (RESYNC CATALOG ensures synchronization).
5. In event errors arise mid-process (for example due hardware failure)—detailed logs generated help pinpoint root cause quickly so corrective action taken without delay.
This end-to-end flow illustrates why understanding architectural roles matters—not just knowing which buttons exist but grasping their impact during real-world events such as disaster recoveries or compliance audits later on!
How Does Vinchin Back Up Oracle Databases?
For organizations seeking even more streamlined protection beyond native tools, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers professional-grade enterprise backup tailored for today’s mainstream databases—including comprehensive support for Oracle environments alongside MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB platforms. With capabilities such as advanced source-side compression and incremental backup specifically optimized for Oracle workloads—as well as batch database backup, GFS retention policies, and robust integrity checks—you gain efficient storage utilization while automating compliance-ready cycles and ensuring recoverability at scale.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out thanks to its intuitive web console that simplifies complex tasks into four clear steps:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
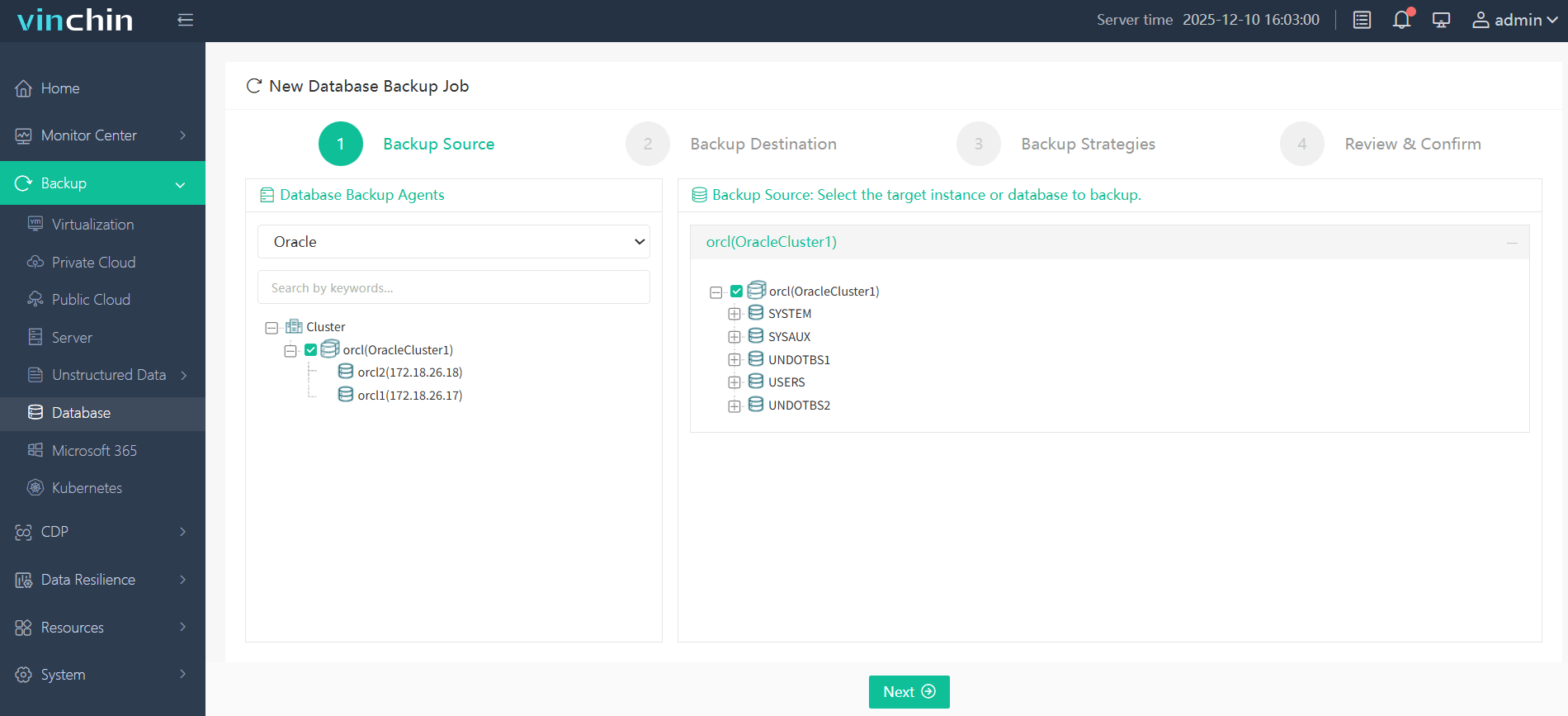
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
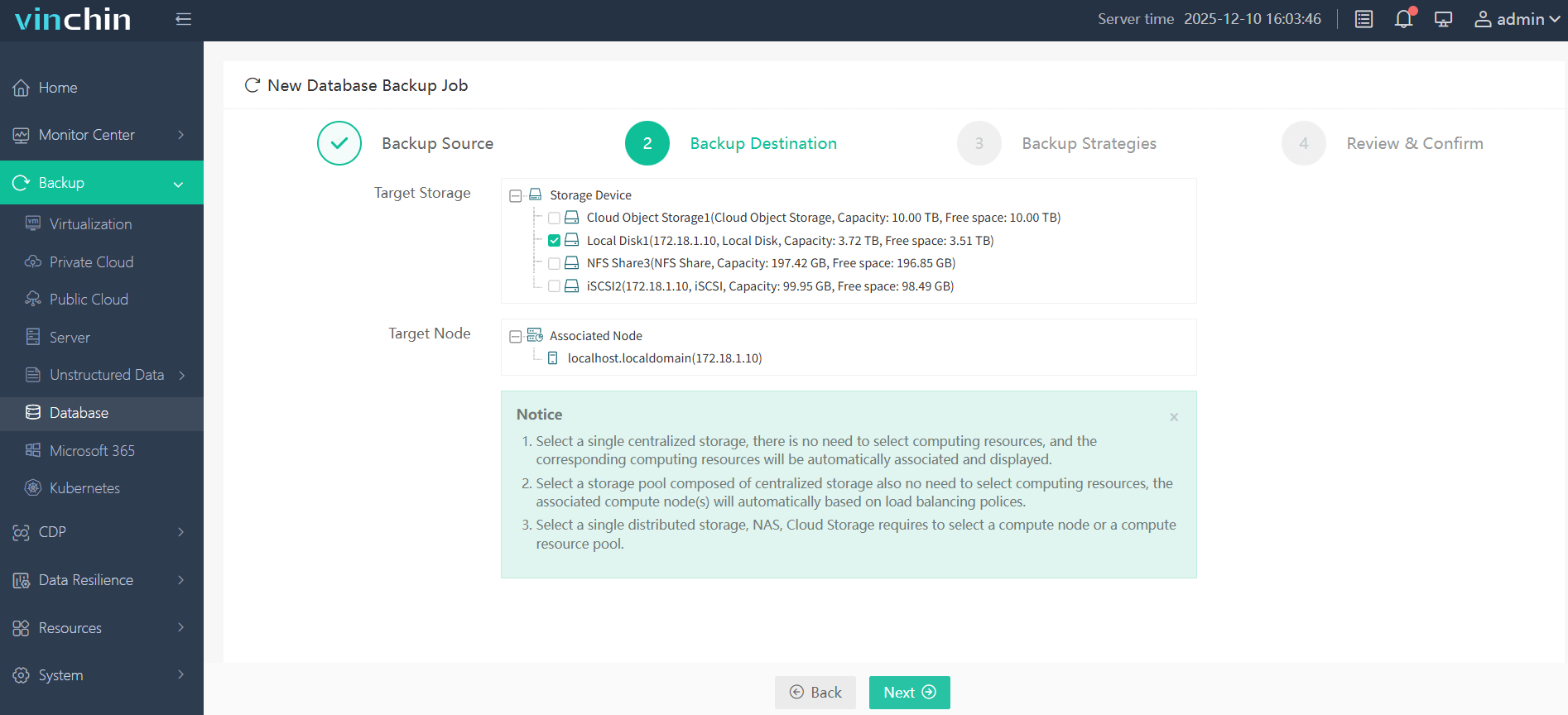
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
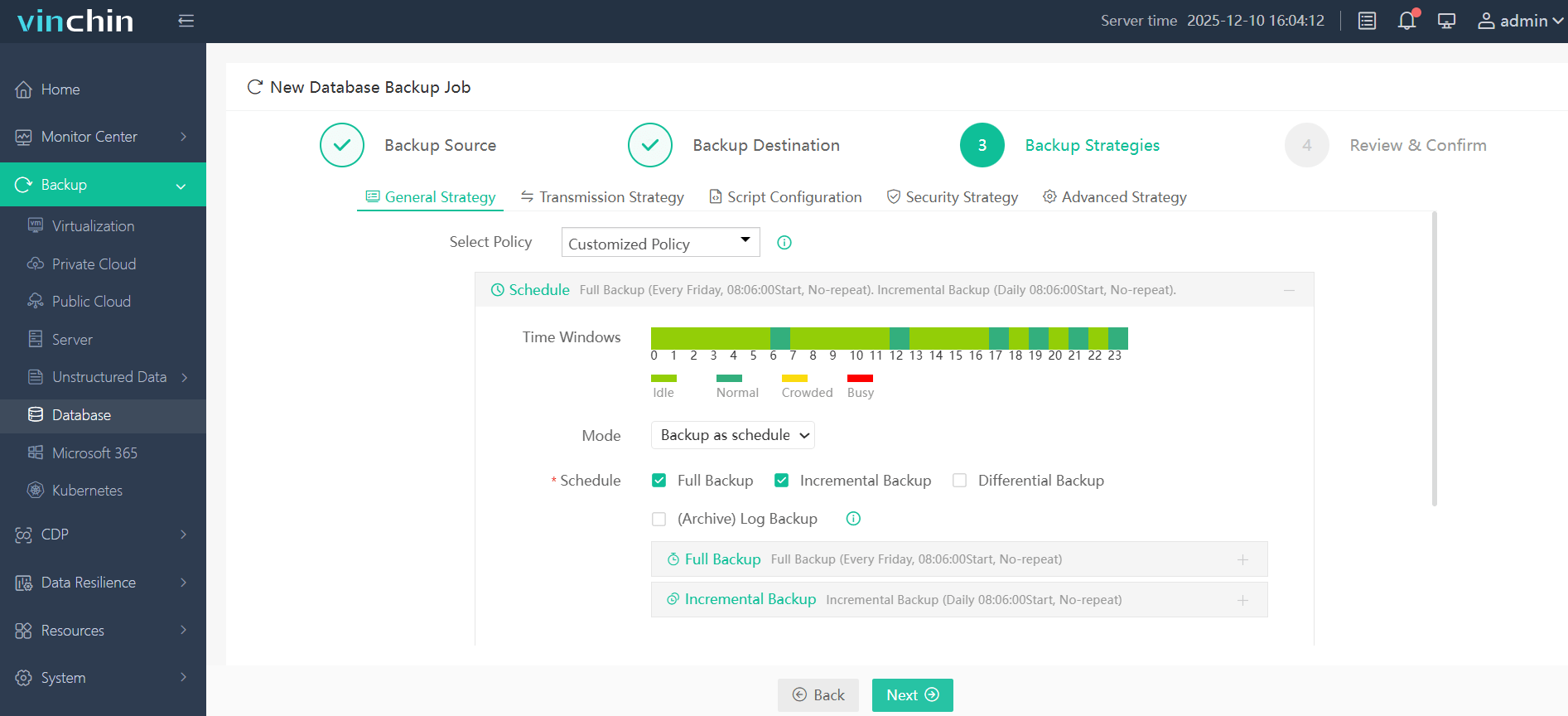
Step 4. Submit the job
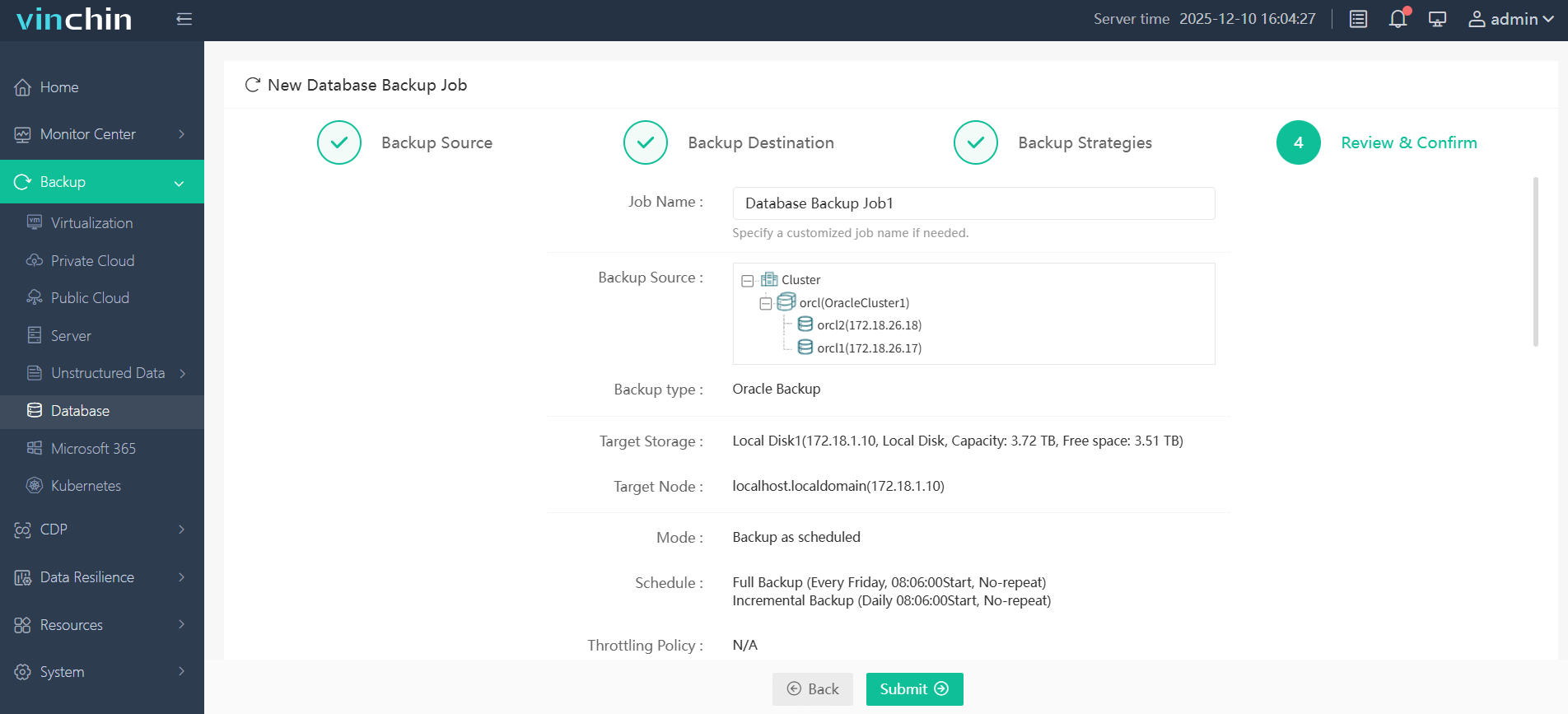
Recognized globally by thousands of enterprises for reliability and ease-of-use—with top industry ratings—you can experience all features free for 60 days by clicking below to download Vinchin Backup & Recovery now.
Oracle RMAN Architecture FAQs
Q1: Can I schedule regular automatic validation checks using only native tools?
A1: Yes; use VALIDATE BACKUPSET within scheduled scripts through OS task schedulers like cron or Windows Task Scheduler.
Q2: What should I do if my archived redo log destination fills up?
A2: Free space immediately in your archive log destination directory then consider increasing size limits via LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_SIZE.
Q3: How do I quickly list all available restore points created by previous backups?
A3: Connect with rman client then run LIST RESTORE POINT ALL.
Conclusion
Oracle rman architecture gives administrators powerful tools for reliable data protection at scale—from automation through granular controls over every aspect involved throughout lifecycle management processes overall! Vinchin further simplifies enterprise-grade oracle backups.
Share on:







