-
Compatibility and Limitations
-
Scalability
-
Distributed Services Engine
-
vSphere with Tanzu Kubernetes
-
Lifecycle Management
-
Enhanced vCenter Recovery
-
Improved Security
-
Facilitate AI & ML
-
vSphere vMotion and DRS
-
VMware vSAN 8
-
Wrap up

The highly visible VMware vSphere 8 is available now following the new version announcement on August 30, 2022, which includes VMware ESXi 8, VMware vCenter Server 8, and new features compared to older versions. We know that the new version is pitched as an enterprise workload platform that facilitates cloud to on-premises operations, but what else? Let's take a closer look at the new features and improvements coming in VMware vSphere 8.
Compatibility and Limitations
ESXi 8 supports the latest Intel and AMD CPUs.
vSphere 8 supports DPUs in ESXi.
ESXi 8 is compatible with ESX 3. x and later but earlier versions have to be upgraded and NSX-V is not supported.
You cannot upgrade from ESXi 6.5 directly to 8.
The minimum memory boot requirements rise from 4 to 8GB.
vSphere 8 needs a CPU license with up to 32 physical sores and doesn’t support the following guest operating systems:
eComStation
SCO Openserver
SCO Unixware
Oracle Linux 4. x
SLES9 SP4
Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
Debian 6.0
FreeBSD 7. x
FreeBSD 8. x
macOS
Scalability
The ESXi host limitations by vSphere Lifecycle Manager increase from 280 to 1,000.
VMs per cluster is now 10,000 instead of 8,000.
The number of VM DirectPath I/O devices per host has risen from 8 to 32.
The write buffer maximum in vSAN 8 increases from 600GB to 1.6 TB.
Distributed Services Engine
vSphere Distributed Services Engine (previously Project Monterey) is introduced in vSphere 8 to work with the Data Processing Units (DPUs) that offload ESXi services to it for better performance. With NSX and Distributed Switch 8, administrators can improve infrastructure security and performance without CPU overhead, and streamline the administration of DPU lifecycles.
A Data Processing Unit (DPU) is a channel controller and electronic circuit including a CPU, NIC, and programmable data acceleration engines to centrally process units. In VMware, DPU exists in the hardware layer and lives in an ESXi instance, so the ESXi services could be offloaded to the DPU to free CPU cycles.
vSphere with Tanzu Kubernetes
For administrators and DevOps using containers, Tanzu Kubernetes Grid 2.0 with Workload Availability Zones is a fantastic improvement for vSphere 8. Workload Availability Zones isolates vSphere clusters workloads and allows users to deploy Kubernetes clusters across zones, which expands Kubernetes to multi-availability zones and simplifies the multiple clusters operations and management in one place.
You can also create clusters in a simpler way with ClusterClass, the Cluster API project that specifies cluster configurations.
Lifecycle Management
vSphere 8 is the last version to support baseline lifecycle management and it has some changes:
Stage cluster images: Stage ESXi images without maintenance mode to expedite ESXi update and firmware payloads staging is also supported.
Remediate multiple hosts in parallel: Administrators can choose to remediate all ESXi hosts under maintenance mode in parallel or set the number of parallel remediations to reduce hugely the time needed for whole cluster remediation.
vSphere Configuration Profiles: The cluster configuration management tool defines desired configurations for the cluster and applies them to all hosts within the cluster, which is an alternative to VMware Host Profiles, and the latter is still supported in vSphere 8.
Besides the above new features, VMware vSphere Update Manager is deprecated in VMware 8, although you can still use it in this release.
Enhanced vCenter Recovery
Restoring vCenter from a backup ends up with the original vCenter configurations when the backup was created, which may need manual vCenter reconfigurations since the changes made since the backup were missing. VMware vSphere 8 uses the distributed key-value store to reconcile the backup state and configurations.
Improved Security
Untrusted binaries execution: ESXi 8 turns on this feature by default to prevent binaries that are installed via a VIB.
SSH timeout: Users can enable SSH access to ESXi for a set amount of time and once it expires, the access is disabled.
Sandboxed daemons: Daemons and processes running under ESXi 8 in a separate domain that is sandboxed and only grants them the bare minimum of access.
TLS 1.2: vSphere supports TLS 1.2 and higher versions and removes TLS 1.0 and 1.1.
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 1.2 is discontinued in the ESXi 8 but installation or upgrade is allowed.
Facilitate AI & ML
Device Groups allow users to logically interconnect various devices to a virtual machine for AI & ML workloads (artificial intelligence and machine learning).
Device Virtualization Extensions built on Dynamic DirectPath I/O (previously using DirectPathIO) allow users to create hardware-backed virtual devices using a new framework to support greater virtualization features such as live migration with vMotion, VM suspension, and resumption, and disk and memory snapshots. The drive needs to be installed on both the ESXi host and the guest host.
vSphere vMotion and DRS
Certain applications like time-sensitive ones, VoIP, and clustered applications, can be suffered in performance during the migration process in the previous vSphere versions. Now with vSphere 8, you can create migration-aware applications either by stopping the applications services gently or by performing a failover, or delaying the migration start time with a configured timeout.
Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) in vSphere leverages memory statistics to make optimal VM memory decisions using PMEM (Persistent Memory), which takes non-volatile media and places them onto a Memory Module to retain data after power events. vSphere Green Metrics is a set of new consumption metrics to monitor vSphere infrastructure consumption to improve energy saving.
VMware vSAN 8
The new vSAN Express Storage Architecture in vSphere 8 increases overall effectiveness and is designed to work best on current hardware. VMware vSAN in this release enables TLC storage devices for improved storage performance. Meanwhile, it also conducts deduplication, then compresses the data when transferring data from the cache to the capacity tier.
The new storage pool enables smaller fault domains, and you can get native snapshots with minimum impact on performance now. Additionally, the time needed for recreating a vSAN object and distributing it across hosts is shorter. And you can increase management flexibility with enhanced HCI that allows you to set data policies per VM.
The above features are the major changes of vSphere 8 to help VMware users to increase performance and simplify management workload. But whatever your VMware version, it is always advisable to produce agentless and frequent VMware backups via thought-out smart strategies.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a versatile backup solution that is carefully designed for 10+ virtualizations including VMware (v5.0-8.0 for vCenter, ESXi, vSphere), Hyper-V, oVirt, Oracle OLVM, OpenStack, etc., 6 databases, Linux & Windows Servers, and NAS.
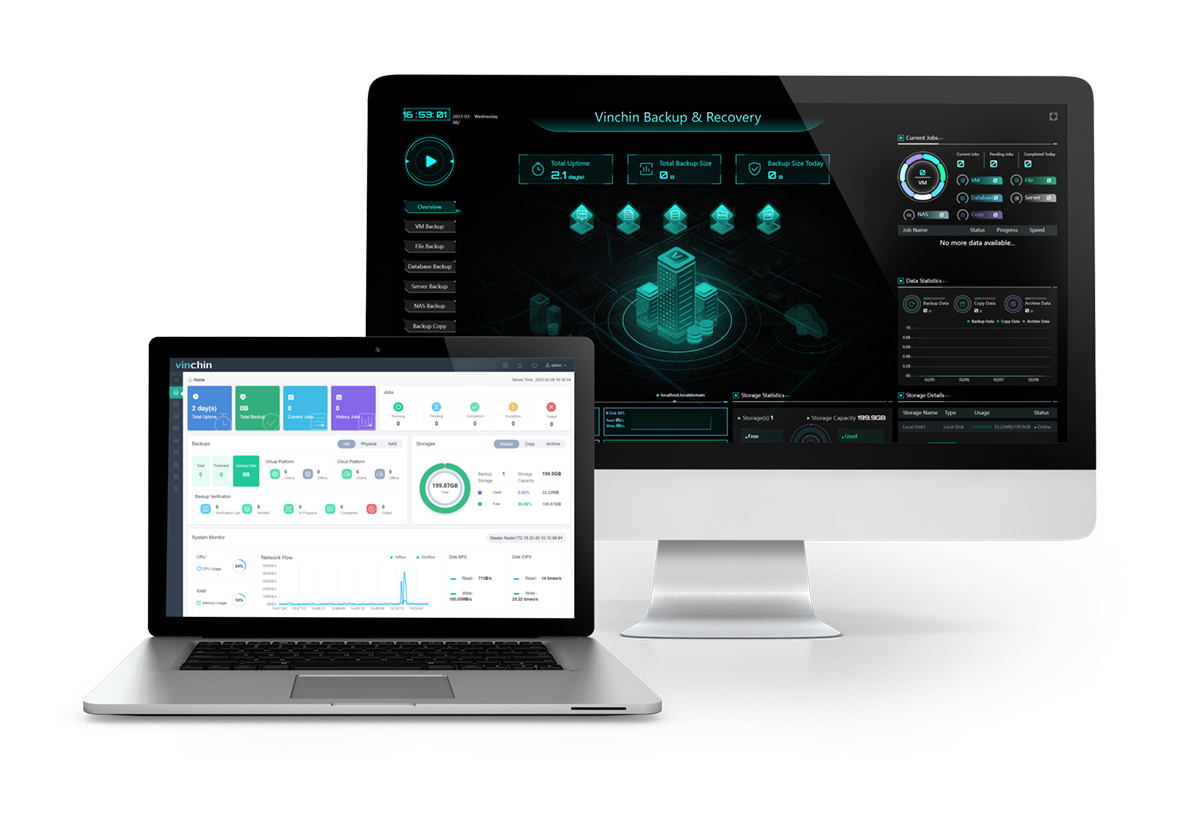
The software delivers fast backup with clear and simple options while securing the backups through multiple features and disaster recovery. The following are its key features of it:
Automatic agentless backup: perform agentless backup under preset backup schedules and mail notifications for backup automation without network consumption.
Practical backup strategies: enable CBT-supported incremental backup, full, and differential backup and transmit the data under encrypted or HotAdd mode through deduplication and compression for speedy and efficient VMware backup. Also, you can keep it under GFS.
Anti-malware protection: keep data away from outside threats with backup storage protection that safeguards backups in the server with real-time IO, double data encryption, data archiving to public clouds, frequent backups, etc.
Cross-platform V2V migration: easily migrate VMs from supported platforms to VMware or vice versa with a 3-step wizard of restoring source vitalization to the target platform.
Instant recovery with offsite backup copy: save a backup copy in a remote location for emergency based on the 3-2-1 backup rule, which could be used to establish a remote DR center combined with instant recovery that resumes VMware VM in 15s from local backups or backup copies for business continuity.
Care for more features or test those mentioned above? Here is a 60-day full-featured free trial available.
Wrap up
VMware vSphere 8 with a series of new functions for enhanced VM performance and simpler administration is available now, you can upgrade it as you needed with VMware instructions.
Regardless, VMware backup is always a priority for VMware users in case of data loss incidents. Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers designated backup and recovery solutions for VMware infrastructures.
Share on: