-
What Is a Kubernetes Registry?
-
Why Use a Private Registry in Kubernetes?
-
Method 1: Setting Up Docker Hub Registry
-
Method 2: Using Harbor as Your Registry
-
Access Control And Authentication
-
Image Security Practices
-
Registry Performance Optimization
-
How to Protect Kubernetes With Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
Kubernetes Registry FAQs
-
Conclusion
Kubernetes runs applications using container images stored in registries. These registries act as central hubs that hold your application code in packaged form—ready to deploy at scale across clusters worldwide. You may have heard of Docker Hub or enterprise solutions like Harbor or Azure Container Registry; all serve this purpose but differ in features and control.
Why does this matter? Public registries can limit your pull requests per hour or expose you to risks if an image gets compromised upstream—a real headache when uptime counts most. That’s why understanding how to set up, secure, optimize, and troubleshoot a kubernetes registry is essential for any operations administrator managing modern workloads.
What Is a Kubernetes Registry?
A kubernetes registry is a service that stores container images used by your clusters’ pods and deployments. Think of it as a warehouse: every time you launch an app in Kubernetes, it pulls its image from this warehouse using an address like myregistry.com/app:1.0. Registries can be public (open to everyone) or private (restricted within your organization).
Registries do more than store images—they handle versioning so you can roll back if needed; enforce access controls so only trusted users push new versions; support scanning for vulnerabilities; and keep audit trails for compliance. Without a reliable kubernetes registry strategy, managing large-scale deployments becomes risky fast.
Why Use a Private Registry in Kubernetes?
Private registries give you more control than public ones—and that matters when uptime or data privacy are on the line. With a private kubernetes registry:
You decide who can upload (“push”) or download (“pull”) images
Sensitive apps stay inside your network
Compliance rules are easier to enforce
Performance improves because images travel shorter distances within your infrastructure
Public services like Docker Hub often throttle traffic during peak hours—imagine production pods failing because you hit those limits! Private registries also let you scan images before use and keep detailed logs of every change—a must-have for regulated industries or anyone serious about security.
Method 1: Setting Up Docker Hub Registry
Many teams start with Docker Hub since it’s widely known—but even here you need proper setup for private images in Kubernetes environments.
First log into Docker Hub locally using docker login. This creates credentials stored in config.json. Next create a secret inside Kubernetes:
kubectl create secret docker-registry regcred \ --docker-server=https://index.docker.io/v1/ \ --docker-username=YOUR_USERNAME \ --docker-password=YOUR_PASSWORD \ --docker-email=YOUR_EMAIL
Verify creation by running kubectl get secrets—you should see regcred listed under your namespace’s secrets.
To allow pods access to private images add this snippet under your deployment spec:
spec: containers: - name: myapp image: yourusername/yourimage:tag imagePullSecrets: - name: regcred
When deploying across namespaces remember secrets are namespace-scoped—repeat creation as needed elsewhere. If authentication fails check both credentials validity and secret reference spelling!
Method 2: Using Harbor as Your Registry
Harbor offers enterprise-grade features like vulnerability scanning, role-based access control (RBAC), replication policies—and full ownership over where data lives.
To install Harbor via Helm chart:
1. Add repository then update charts:
helm repo add harbor https://helm.goharbor.io helm repo update
2. Install Harbor into its own namespace:
helm install harbor harbor/harbor --namespace harbor --create-namespace
For production always configure persistent storage so no data is lost on pod restarts—set values under persistence.enabled=true during installation.
After deployment open the web console (https://<harbor-domain>) to set up projects/users/policies as needed.
To push an image:
docker login harbor.yourdomain.com docker tag myapp:1.0 harbor.yourdomain.com/project/myapp:1.0 docker push harbor.yourdomain.com/project/myapp:1.0
Create a pull secret inside Kubernetes:
kubectl create secret docker-registry harborcred \ --docker-server=harbor.yourdomain.com \ --docker-username=YOUR_USER \ --docker-password=YOUR_PASSWORD \ --docker-email=YOUR_EMAIL
Check success with kubectl get secrets then reference it just like before:
spec: containers: - name: myapp image: harbor.yourdomain.com/project/myapp:1.0 imagePullSecrets: - name: harborcred
If accessing externally through Ingress/LB make sure DNS points correctly—and certificates are valid (self-signed certs require extra trust configuration on nodes). Troubleshoot connectivity issues by checking pod logs (kubectl logs) plus ingress controller events (kubectl describe ingress). For multi-cluster setups ensure firewall rules allow traffic between clusters and registry endpoints!
Access Control And Authentication
Controlling who accesses what is fundamental when running any kubernetes registry at scale—even more so if multiple teams share resources across namespaces or clusters.
Always enable strong authentication mechanisms such as username/password combos—or better yet integrate with LDAP/OAuth providers supported by many enterprise registries including Harbor. Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) within both Kubernetes itself (via ServiceAccounts) and at the registry level to restrict permissions tightly—for example only allowing CI/CD pipelines push rights while developers have read-only access.
Rotate credentials regularly using tools like Secrets Manager integrations wherever possible—and never hardcode passwords directly into manifests! Instead leverage Kubernetes Secrets resource which encrypts sensitive info at rest.
Image Security Practices
Protecting against malicious code starts long before deployment—it begins with how you manage container images themselves inside any kubernetes registry environment.
Enable automated vulnerability scanning wherever available (Harbor includes native scanners)—flagging outdated libraries before they reach production. Require signed images using Notary/TUF frameworks so only verified builds are accepted downstream by cluster nodes.
Regularly clean out unused tags/layers via garbage collection jobs—which frees disk space and reduces attack surface area if old vulnerable versions linger unseen.
Registry Performance Optimization
Performance bottlenecks can cripple large-scale deployments especially when hundreds of nodes try pulling big base layers simultaneously from one kubernetes registry endpoint!
Optimize throughput by enabling layer caching on worker nodes—so repeated pulls fetch local copies instead of hitting remote servers each time. Place your main registry close network-wise to major clusters—or deploy geo-replicated mirrors if operating globally across regions/clouds.
Run regular garbage collection tasks especially after mass deletions—to reclaim space instantly rather than waiting days/weeks for automatic cleanup cycles. Monitor disk I/O metrics closely since slow disks translate directly into longer pod startup times!
How to Protect Kubernetes With Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
Beyond securing your kubernetes registry, robust backup is vital for safeguarding workloads against threats such as ransomware, accidental deletion, or system failure. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-level solution designed specifically for comprehensive Kubernetes protection. It delivers full and incremental backups, fine-grained restore options down to the cluster, namespace, application, PVC, or resource level; supports policy-based automation alongside one-off backups; enables encrypted transmission and storage; allows cross-version recovery between heterogeneous clusters; and accelerates PVC backup throughput through configurable multithreading—all ensuring operational continuity while simplifying management overhead.
The intuitive Vinchin Backup & Recovery web console streamlines backup workflows into four straightforward steps tailored for Kubernetes environments:
Step 1. Select the backup source

Step 2. Choose the backup storage
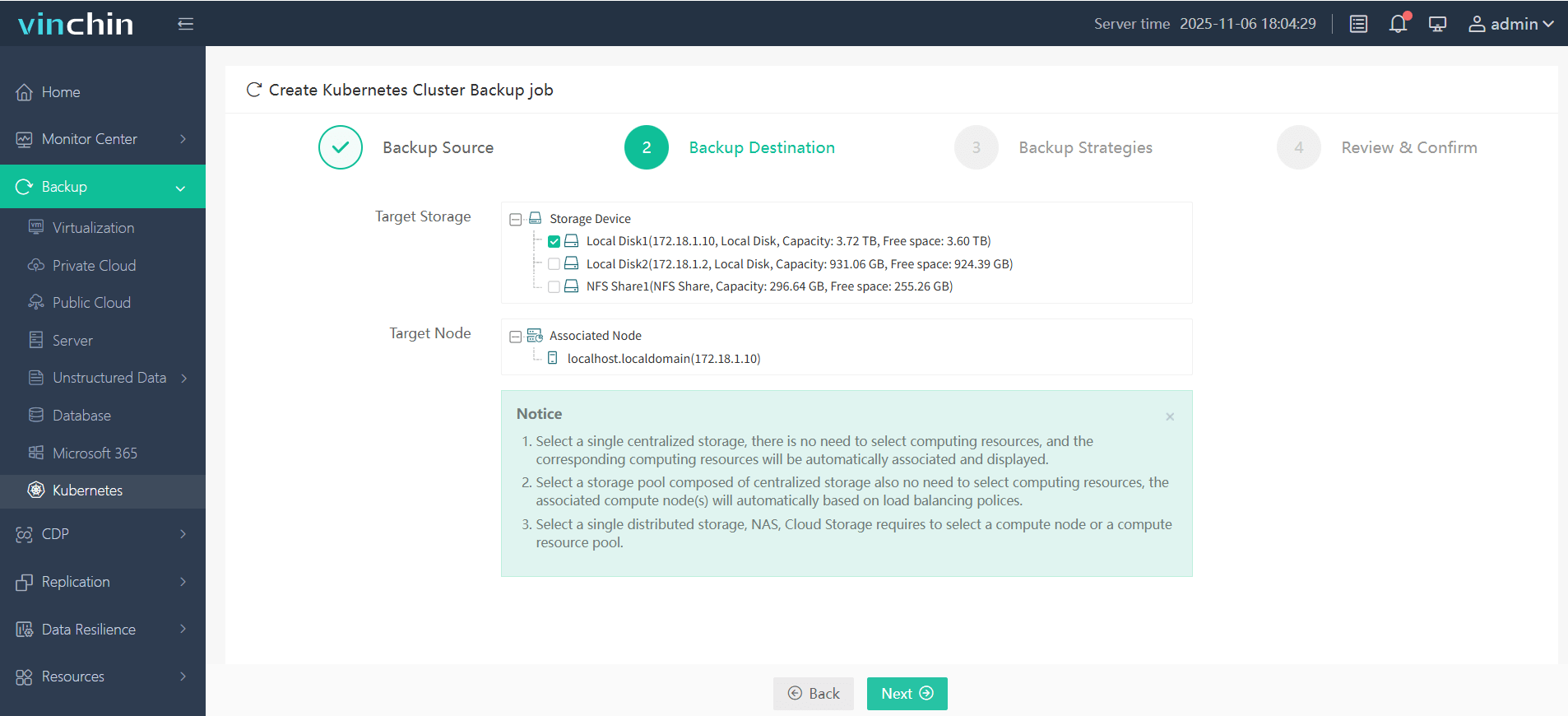
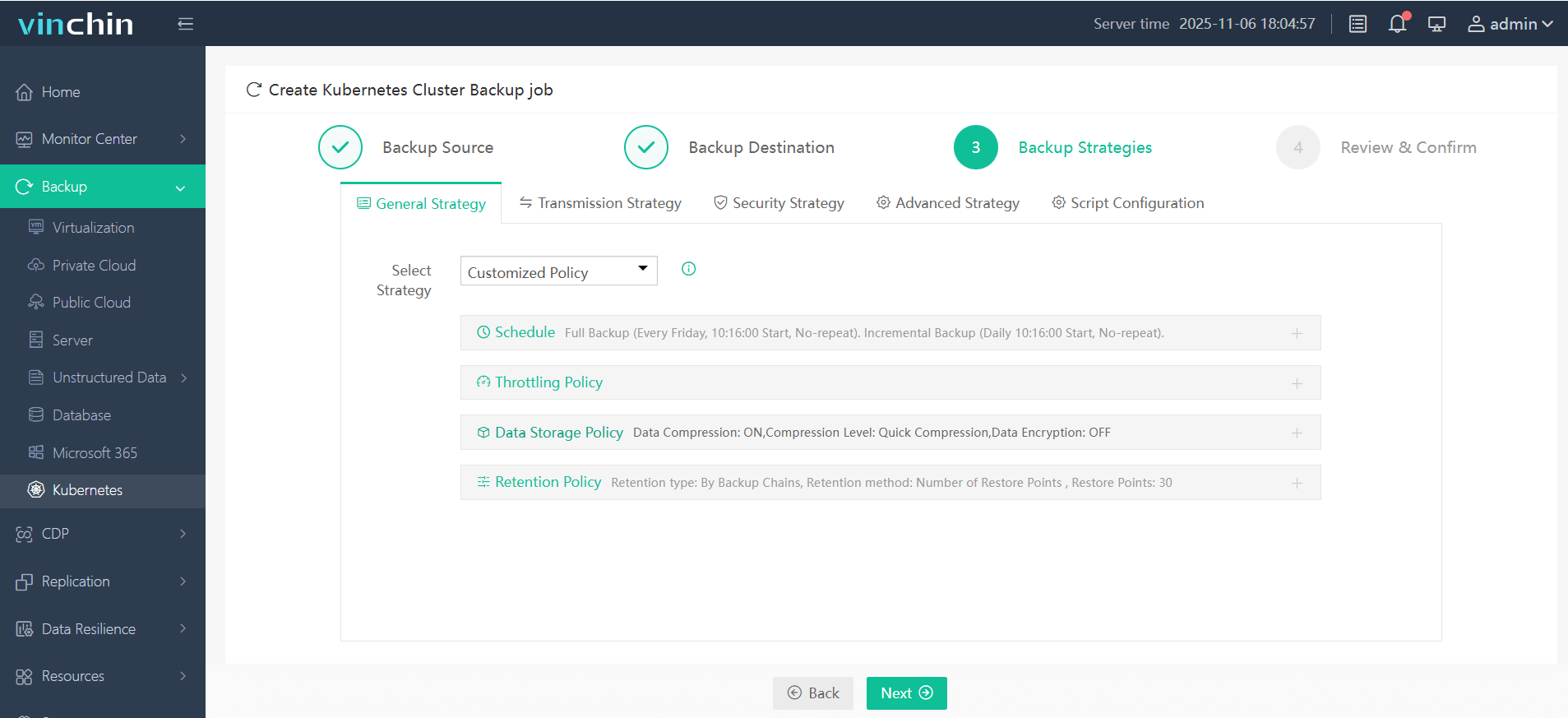
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
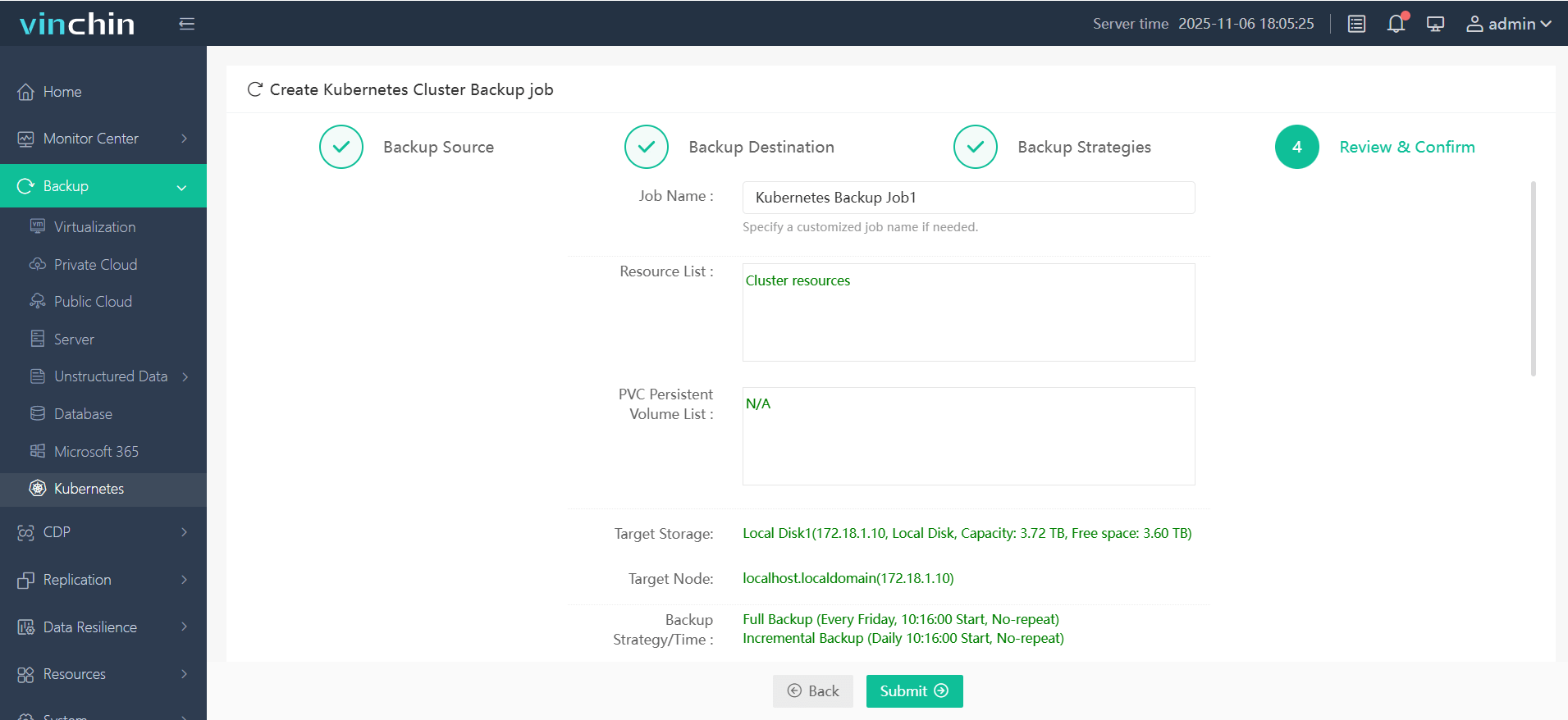
Step 4. Submit the job
Recognized globally with top customer ratings and trusted by thousands of enterprises, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured free trial for 60 days—click below to experience industry-leading data protection firsthand.
Kubernetes Registry FAQs
Q1: How do I recover quickly if my main kubernetes registry goes down?
A1: Switch deployments temporarily to use cached local node layers or failover mirror endpoints until primary service returns online stability.
Q2: What’s the best way to migrate all existing repositories from one kubernetes registry platform to another?
A2: Export current repositories using built-in export tools then import them onto new platform ensuring tag/version consistency throughout transition period.
Q3: How can I improve pull speeds when scaling up new worker nodes rapidly?
A3: Pre-populate commonly used base layers onto node caches ahead of time—or deploy regional mirrors closer physically/network-wise to target clusters.
Conclusion
A robust kubernetes registry strategy ensures secure delivery of containerized apps at scale—from basic setup through advanced optimization/troubleshooting techniques covered above.
For complete peace-of-mind protection—including disaster recovery—try Vinchin’s advanced backup solution free today!
Share on:








