-
What Is RMAN Allocate Channel?
-
Why Allocate Channel for Maintenance in RMAN?
-
Method 1: Manual RMAN Allocate Channel for Maintenance
-
Method 2: Automatic RMAN Allocate Channel for Maintenance
-
How to Back Up Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
RMAN Allocate Channel for Maintenance FAQs
-
Conclusion
Oracle RMAN (Recovery Manager) is an essential tool for database backup and recovery. One of its most important features is the ability to allocate channels—connections between RMAN and your storage devices. When you perform maintenance tasks such as deleting obsolete backups or crosschecking files, allocating the right channel becomes critical. Have you ever seen errors like RMAN-06091: no channel allocated for maintenance (of an appropriate type)? If so, you know how frustrating it can be when RMAN cannot access your backup files due to missing or misconfigured channels.
In this article, we’ll explain what “rman allocate channel for maintenance” means, why it matters in daily operations, and how to use both manual and automatic methods step by step. We’ll also cover troubleshooting tips and best practices so you can manage Oracle backups confidently.
What Is RMAN Allocate Channel?
A channel in RMAN is simply a link between the Recovery Manager process and a storage device—either disk or tape. Allocating a channel means creating this connection so that RMAN can read from or write to your chosen device during backup or recovery jobs.
For maintenance operations—such as DELETE, CROSSCHECK, or CHANGE—you may need to allocate a special type of channel called a maintenance channel. This ensures that RMAN has direct access to the storage location where your backups reside. Maintenance channels are different from regular backup channels; they are used only for managing backup metadata and files rather than performing actual data movement.
When you run commands like DELETE OBSOLETE or CROSSCHECK BACKUP, allocating an appropriate maintenance channel tells RMAN exactly which device type (disk or tape) it should use during these tasks.
Why Allocate Channel for Maintenance in RMAN?
Allocating a maintenance channel is crucial whenever you need to manage backups stored on different devices. If you try running maintenance commands without specifying the correct channel, you might see errors such as RMAN-06091: no channel allocated for maintenance (of an appropriate type). This problem often appears in environments where both disk-based and tape-based backups exist—or after certain Oracle patches change default behaviors.
By allocating the right type of maintenance channel before running your command, you ensure that RMAN can find every relevant backup file across all configured devices. This keeps your backup catalog accurate and prevents wasted storage space from lingering obsolete files. In short: proper allocation makes routine cleanup safer, faster, and more reliable.
To avoid these errors—and keep your environment tidy—you have two main options: manual allocation or automatic configuration.
Method 1: Manual RMAN Allocate Channel for Maintenance
Manual allocation gives you full control over which device types RMAN uses during maintenance tasks. This approach is helpful if your environment stores backups on both disk and tape drives—or if you want to specify detailed parameters like library paths.
To manually allocate a maintenance channel:
1. Start by connecting to RMAN using your target database credentials.
2. At the RMAN prompt—not inside any RUN block—use the command ALLOCATE CHANNEL FOR MAINTENANCE, specifying either disk (DEVICE TYPE DISK) or tape (DEVICE TYPE SBT_TAPE) along with any needed parameters.
3. Run your desired maintenance command such as DELETE OBSOLETE or CROSSCHECK BACKUP.
4. Release each allocated channel using RELEASE CHANNEL once finished.
Let’s walk through some examples:
If all obsolete backups are on disk:
RMAN> ALLOCATE CHANNEL FOR MAINTENANCE DEVICE TYPE DISK; RMAN> DELETE OBSOLETE DEVICE TYPE DISK; RMAN> RELEASE CHANNEL;
If they’re on tape:
RMAN> ALLOCATE CHANNEL FOR MAINTENANCE DEVICE TYPE SBT_TAPE PARMS 'SBT_LIBRARY=/path/to/library'; RMAN> DELETE OBSOLETE DEVICE TYPE SBT_TAPE; RMAN> RELEASE CHANNEL;
For environments with both disk AND tape:
RMAN> ALLOCATE CHANNEL FOR MAINTENANCE DEVICE TYPE DISK; RMAN> ALLOCATE CHANNEL FOR MAINTENANCE DEVICE TYPE SBT_TAPE PARMS 'SBT_LIBRARY=/path/to/library'; RMAN> DELETE OBSOLETE; RMAN> RELEASE CHANNEL;
You must allocate one separate maintenance channel per device type if managing multiple locations at once—for example when cleaning up after migrations or patching.
Note: Channels allocated outside of RUN blocks are released automatically at session end—but using RELEASE CHANNEL explicitly helps avoid confusion during complex sessions.
This method also works with other commands like CROSSCHECK BACKUP or changing status flags via CHANGE BACKUPSET UNAVAILABLE; Just remember: always allocate channels at the prompt—not within RUN blocks—as Oracle does not support allocating maintenance channels inside scripts’ RUN contexts.
Method 2: Automatic RMAN Allocate Channel for Maintenance
Automatic allocation lets Oracle handle most details based on pre-set configurations—a great choice if you want fewer manual steps or have many databases under management.
With automatic allocation enabled:
1. Use configuration commands like CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK PARALLELISM 2; or set up tape libraries using similar syntax.
2. Optionally configure specific parameters per device using commands such as
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE SBT_TAPE PARMS 'SBT_LIBRARY=/path/to/library';
3. Run any supported maintenance command directly at the prompt—for example,
DELETE OBSOLETE; CROSSCHECK BACKUP;
When these commands run outside any RUN block, Oracle checks existing configurations under both disk/tape settings—and allocates matching channels automatically according to parallelism values.
This approach reduces human error because there’s no need to remember exact syntax every time—or worry about forgetting which devices hold which files after upgrades or hardware changes! It’s especially useful in large-scale environments where automation saves hours each week.
If needed—for instance when troubleshooting—you can still override automatic settings by switching back temporarily to manual allocation as shown above.
How to Back Up Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
After mastering efficient management of Oracle database backups through proper RMAN channel allocation, it's equally important to implement robust enterprise-level protection solutions tailored for modern environments. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional solution supporting mainstream databases including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with comprehensive feature coverage specifically designed for demanding workloads like Oracle databases.
Key features include incremental backup support, batch database backup capabilities, advanced source-side compression technology, flexible data retention policies including GFS retention policy options, and powerful integrity check mechanisms—all working together to optimize storage usage while ensuring rapid recovery readiness across diverse deployment scenarios. These functionalities streamline daily operations by automating cycles and safeguarding critical data against loss events without adding administrative burden.
The intuitive web console simplifies workflow dramatically:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
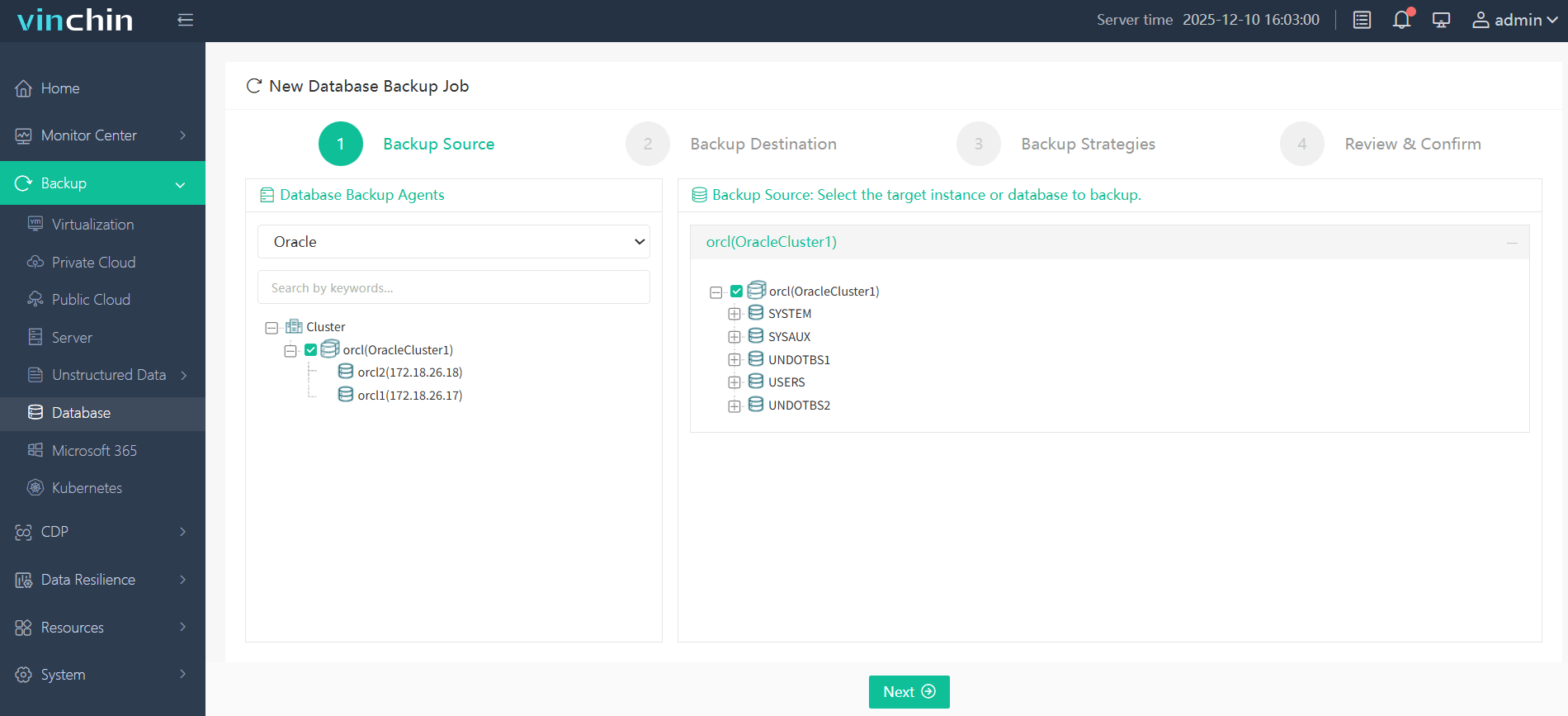
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
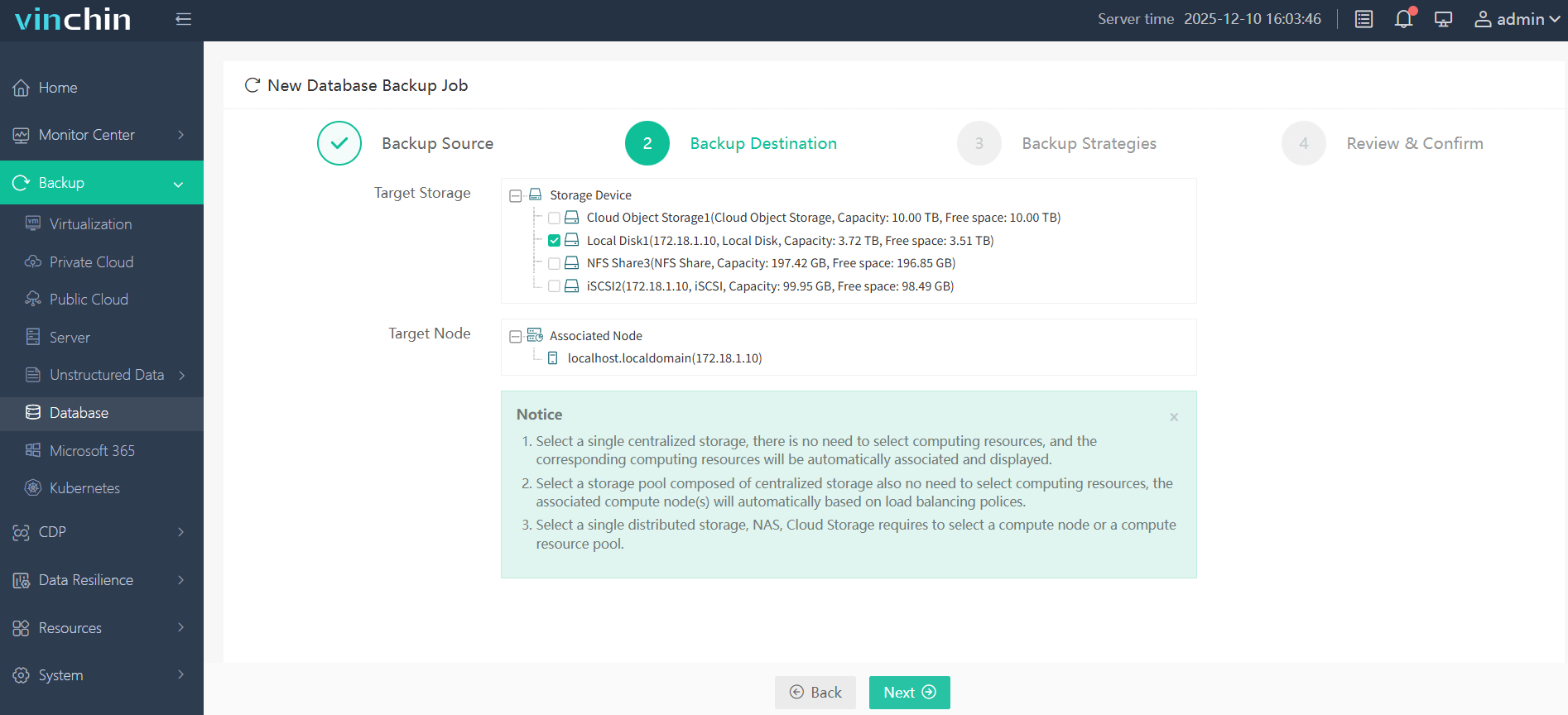
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
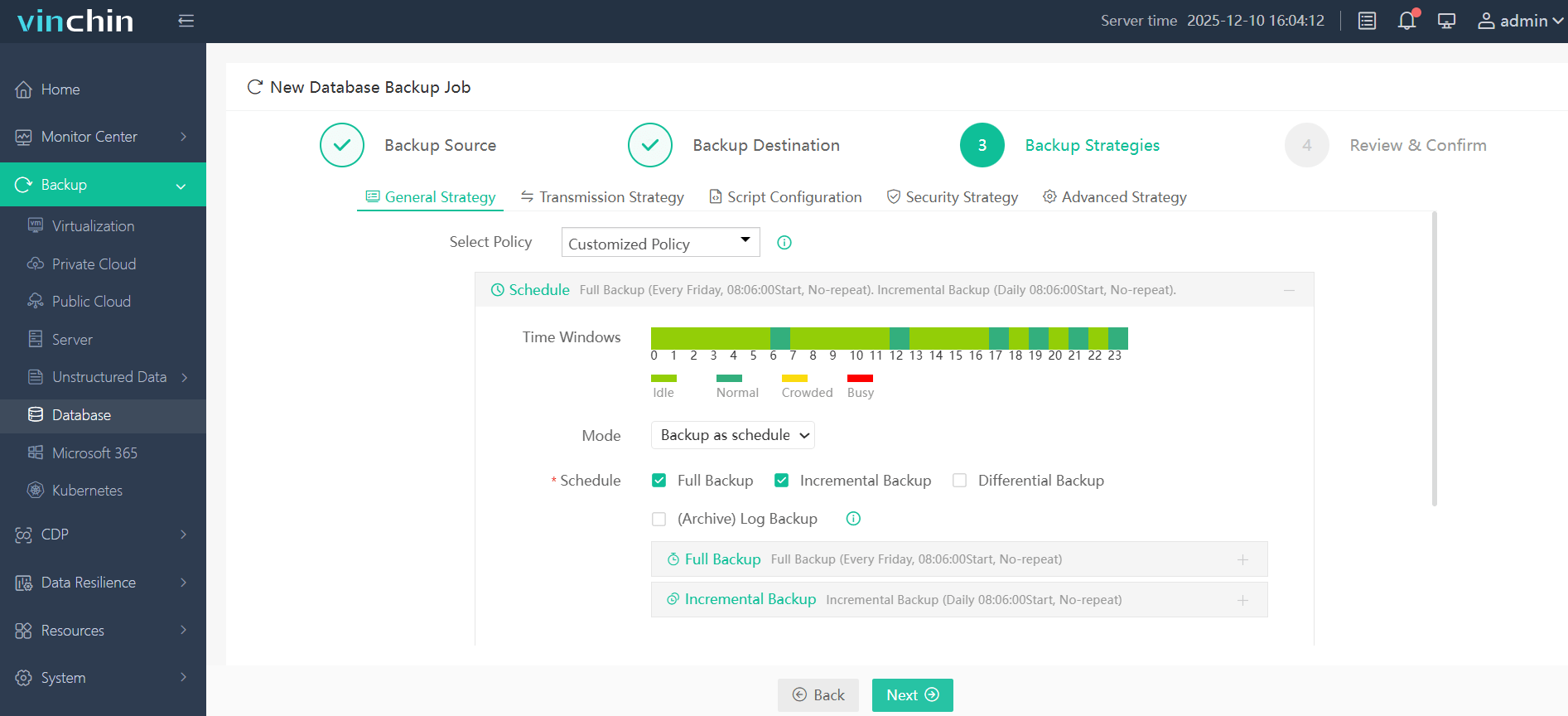
Step 4. Submit the job
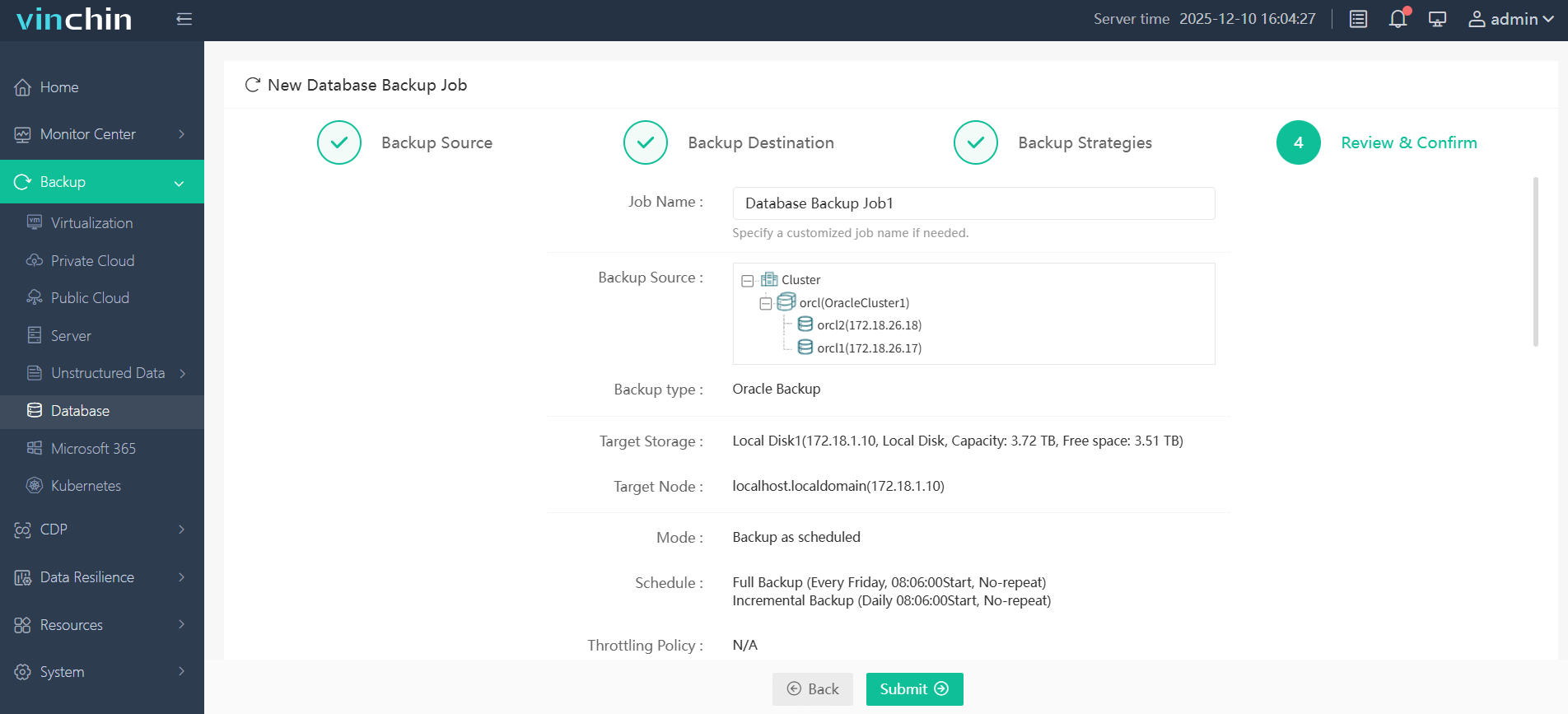
Vinchin Backup & Recovery enjoys global recognition among enterprises thanks to its reliability and ease of use—backed by thousands of satisfied customers worldwide and top industry ratings. Experience all features risk-free with a 60-day full-featured free trial; click below to download now!
RMAN Allocate Channel for Maintenance FAQs
Q1: What should I do if I get “RMAN-06091: no channel allocated for maintenance (of an appropriate type)”?
A1: Check configured device types then manually allocate required channels at prompt before rerunning DELETE/CROSSCHECK/CLEANUP commands if needed.
Q2: Can I allocate channels simultaneously for both disk AND tape?
A2: Yes—allocate one separate MAINTENANCE CHANNEL per device type then issue desired command before releasing each afterward.
Q3: How do I release a MAINTENANCE CHANNEL after use?
A3: Enter RELEASE CHANNEL at prompt following completion of all related operations—it closes connections safely before next task begins.
Conclusion
Allocating proper channels ensures smooth management of Oracle backups across disks/tapes alike—with fewer errors along the way! Use manual methods when precision matters most; rely on automation otherwise whenever possible. Vinchin further simplifies enterprise-grade protection so teams stay focused on business goals instead of routine chores!
Share on:








