-
What Are Oracle RMAN Views?
-
Essential Oracle RMAN Views Explained
-
How to Query Oracle RMAN Views?
-
Protecting Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Oracle RMAN Views FAQs
-
Conclusion
Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is essential for backup and recovery in Oracle databases. But how do you track what RMAN does behind the scenes? That’s where Oracle RMAN views come in. These special database views let you monitor, report on, and troubleshoot every part of your backup operations. Whether you’re just starting out or have years of experience as a DBA, understanding these views helps keep your data safe.
What Are Oracle RMAN Views?
Oracle RMAN views are database objects that show detailed information about backup and recovery activities. There are two main types: V$ views read from the control file of your target database; RC_ views read from the recovery catalog if you use one. With these views, you can check backup status, job history, backup piece details, validation results, and more—all using SQL queries.
Think of them as windows into RMAN’s internal repository. They help you see what has happened or is happening during backups so you can make informed decisions fast.
Essential Oracle RMAN Views Explained
Several key RMAN views provide vital information for daily operations:
V$BACKUP_SET and RC_BACKUP_SET: Show all backup sets created by RMAN with type, status, size, and completion time.
V$BACKUP_PIECE and RC_BACKUP_PIECE: List individual backup pieces along with their location on disk or tape; also indicate encryption status.
V$BACKUP_DATAFILE and RC_BACKUP_DATAFILE: Detail datafile backups including checkpoint info and System Change Numbers (SCNs).
V$RMAN_BACKUP_JOB_DETAILS and RC_RMAN_BACKUP_JOB_DETAILS: Provide job-level details such as start/end times, status codes (success/failure), throughput rates.
V$ARCHIVED_LOG and RC_ARCHIVED_LOG: Track archived redo logs—both those already backed up by RMAN and those pending backup.
The difference between these view types matters most when managing multiple databases or Data Guard environments:
Choosing Between V$ Views vs RC_ Views
Selecting which set of views to use depends on your environment:
Use V$ views for real-time status on the connected target database—ideal for immediate troubleshooting or checking current jobs.
Use RC_ views when you need historical reporting across all registered databases in your recovery catalog—for example when planning restores after failover events.
Remember that almost all RC_ queries require filtering by
DB_KEYorDBIDto focus on one specific database’s data.
This distinction becomes crucial during audits or disaster recovery drills when accuracy matters most.
How to Query Oracle RMAN Views?
Querying these views is straightforward if you know what to look for—and which view fits your needs best. You can use SQL*Plus or any compatible query tool connected as a user with proper privileges.
Start simple if you're new; dig deeper as your skills grow:
1. Checking Recent Backup Jobs
To see recent backup jobs at a glance:
SELECT SESSION_KEY, INPUT_TYPE, STATUS, TO_CHAR(START_TIME,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI') AS START_TIME, TO_CHAR(END_TIME,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI') AS END_TIME FROM V$RMAN_BACKUP_JOB_DETAILS ORDER BY SESSION_KEY DESC;
This shows each job’s type (full/incremental/archivelog), its outcome (completed/running/failed), plus timing details so you spot trends quickly.
2. Linking Backup Sets to Pieces
To connect logical sets with physical files:
SELECT BS.SET_STAMP, BS.SET_COUNT, BP.PIECE#, BP.HANDLE, BP.STATUS FROM V$BACKUP_SET BS JOIN V$BACKUP_PIECE BP ON BS.SET_STAMP = BP.SET_STAMP AND BS.SET_COUNT = BP.SET_COUNT ORDER BY BS.SET_STAMP DESC;
This links each set to its actual storage location—helpful when tracing missing files during restores.
3. Cross-Database Reporting Using RC_ Views
If using a recovery catalog:
SELECT BS_KEY,BACKUP_TYPE, COMPLETION_TIME FROM RC_DATABASE_INCARNATION i, RC_BACKUP_SET b WHERE i.DB_KEY = :db_key AND i.DB_KEY = b.DB_KEY AND i.CURRENT_INCARNATION = 'YES';
First find your DBID:
SELECT DBID FROM V$DATABASE;
Then map it to DB_KEY using catalog queries before running cross-database reports—a must-have skill in large enterprises!
Protecting Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
After exploring how to monitor Oracle backups effectively via RMAN views, it's important to ensure those backups remain secure and manageable over time. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional enterprise-level solution supporting today’s mainstream databases—including Oracle (as well as MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, TiDB). For Oracle environments specifically, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers advanced source-side compression, incremental backup capabilities, batch database backup management options, multi-level data compression strategies, plus flexible data retention policies—all designed to optimize storage efficiency while meeting compliance requirements. These features collectively enhance reliability by streamlining protection workflows without sacrificing performance or manageability.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your Oracle environment remarkably straightforward—just follow four steps:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
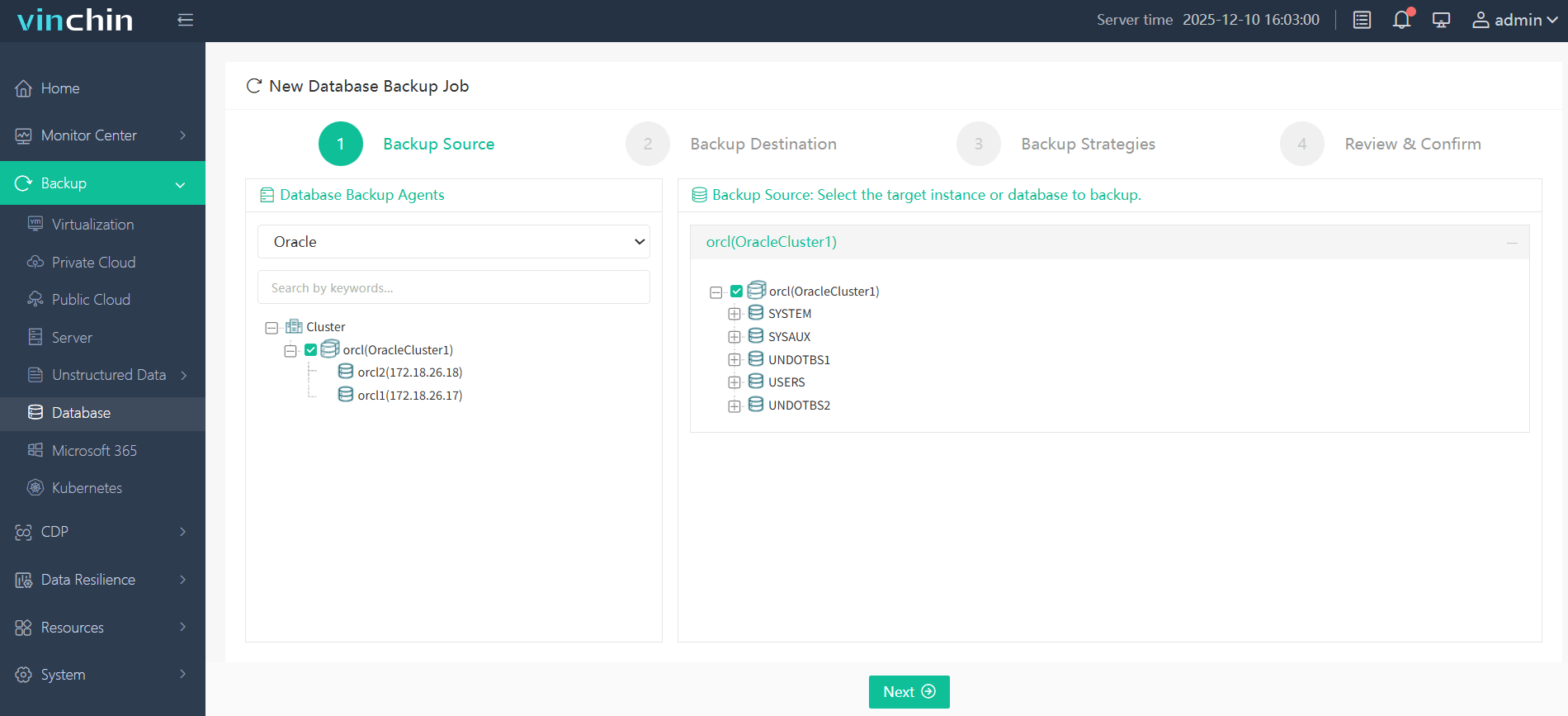
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
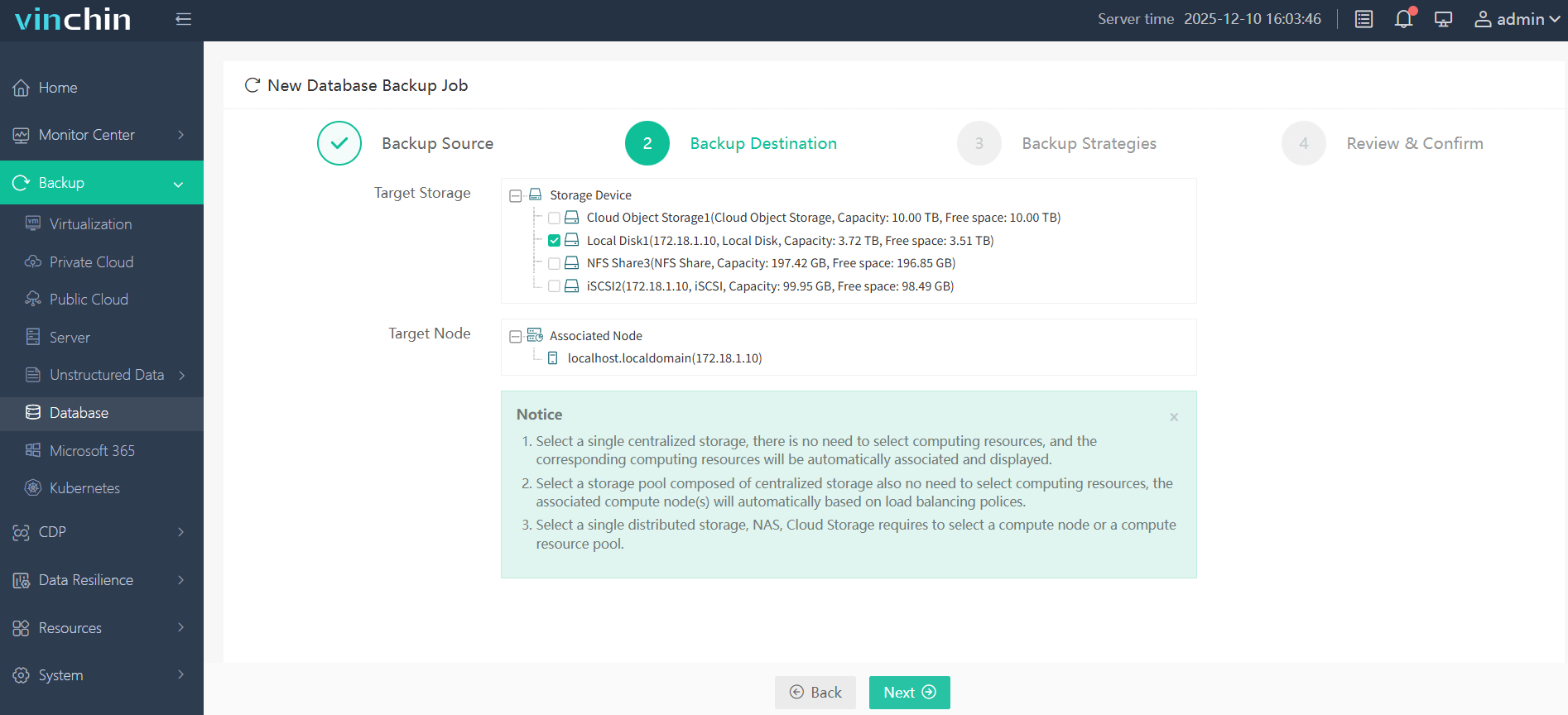
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
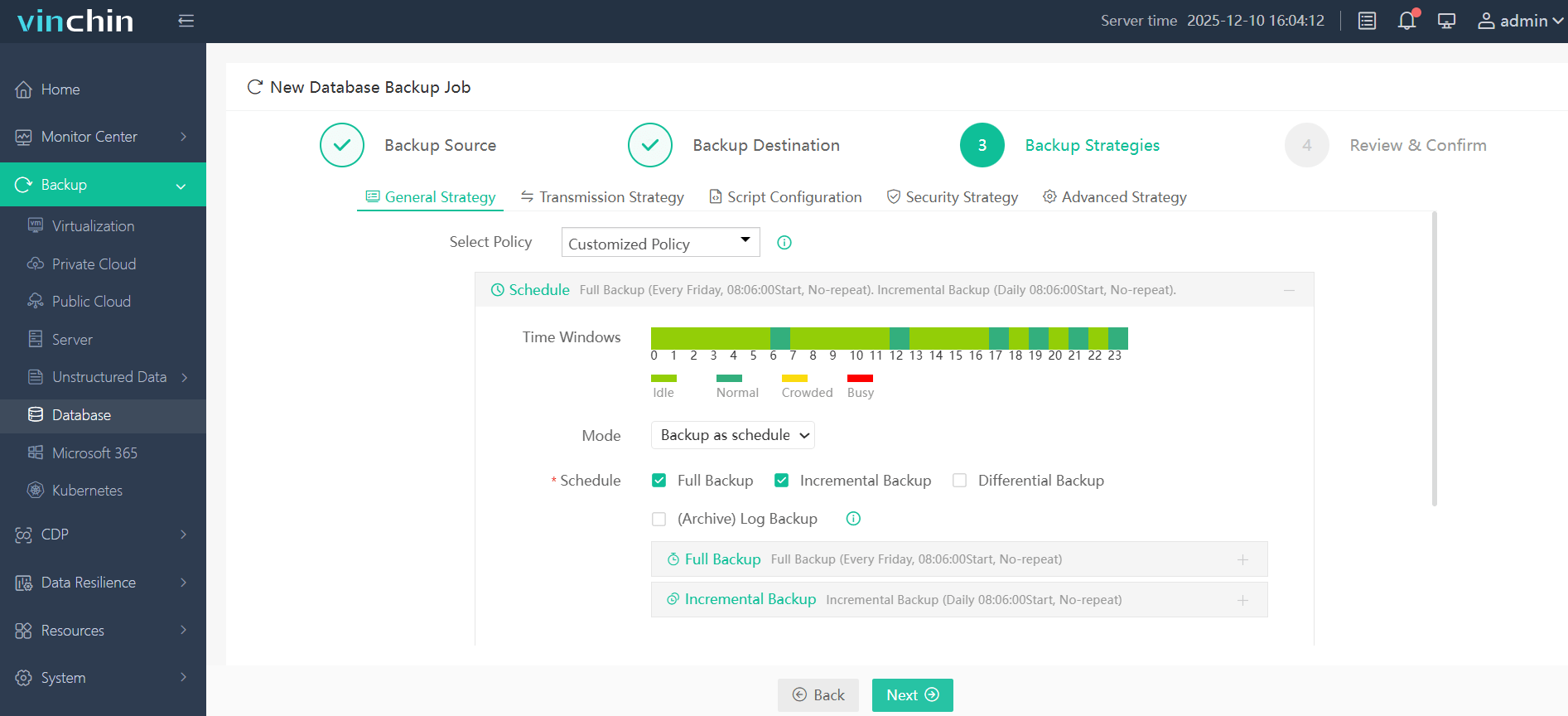
Step 4. Submit the job
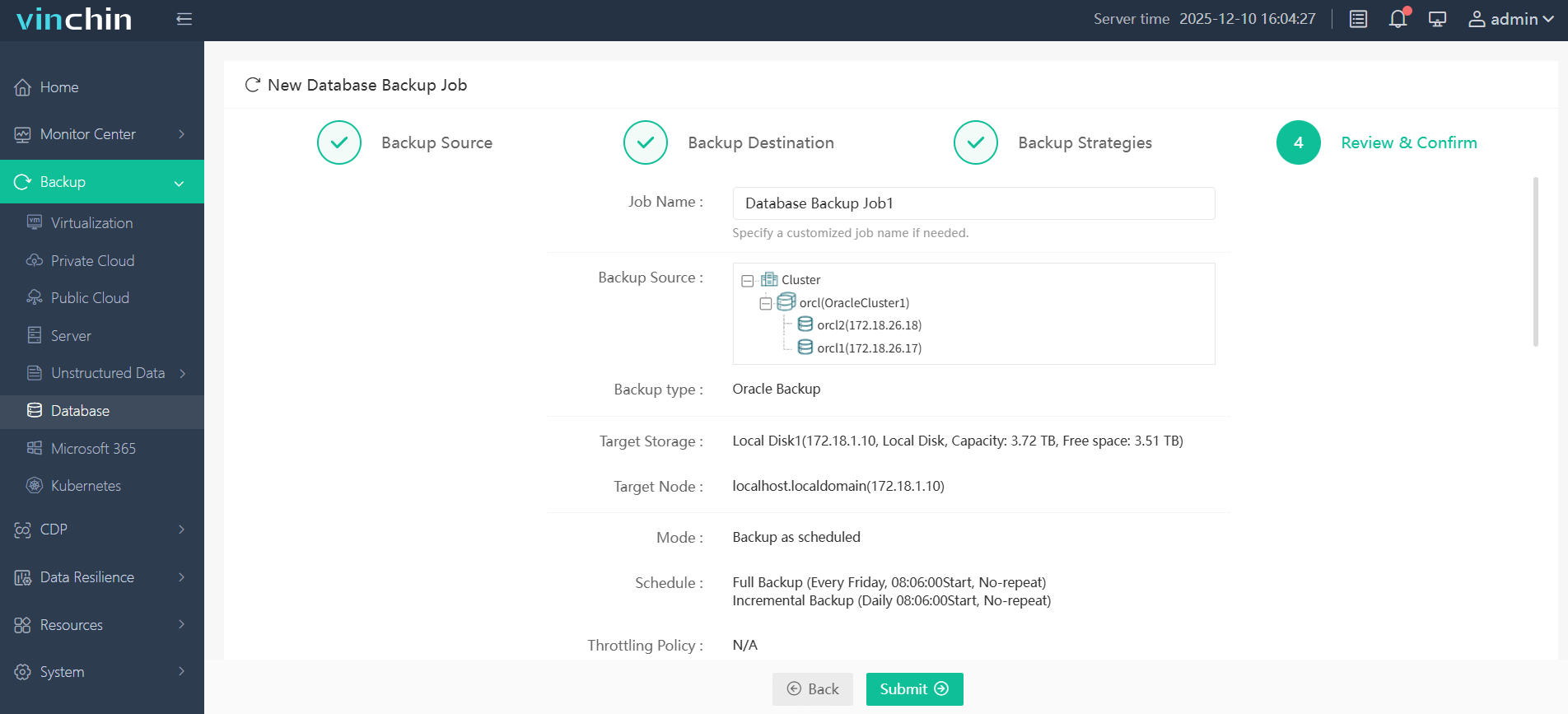
Recognized globally with top ratings from thousands of customers across industries,Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured free trial for 60 days—click download below to experience enterprise-grade protection firsthand.
Oracle RMAN Views FAQs
Q1: Can I automate daily checks of failed backups using only built-in tools?
A1: Yes; schedule SQL scripts querying V$RMAN_OUTPUT, then email results via OS-level cron jobs or Windows Task Scheduler integration.
Q2: How do I find out which archived redo logs haven’t been backed up yet?
A2: Query V$ARCHIVED_LOG WHERE BACKED_UP=0, then investigate reasons before deleting any log files from disk storage arrays.
Q3: Is there a way to preview obsolete backups before deletion without running DELETE OBSOLETE?
A3: Yes; run REPORT OBSOLETE inside an RMAN session review output in V$RMAN_OUTPUT, ensuring no needed files will be removed unexpectedly.
Conclusion
Oracle RMAN views give DBAs clear insight into every aspect of their backup environment—from basic job tracking through advanced validation checks—making proactive management possible at any scale. For even greater efficiency, considering Vinchin's enterprise-grade solution designed specifically for modern multi-database environments.
Share on:








