-
What Are Oracle RMAN Logs?
-
Why Oracle RMAN Logs Matter?
-
Where to Find Oracle RMAN Logs?
-
How to Analyze Oracle RMAN Logs Using Oracle Enterprise Manager?
-
How to Analyze Oracle RMAN Logs Using SQL*Plus or SQLcl?
-
How to Analyze Oracle RMAN Log Files on Disk?
-
Protecting Your Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Oracle RMAN Logs FAQs
-
Conclusion
Oracle RMAN logs are essential for backup and recovery troubleshooting in any serious database environment. If you manage Oracle databases, you know that tracking every backup job is not just helpful—it’s critical for compliance and disaster recovery. But how do you find these logs? What should you look for inside them? And how can you use them to improve your backup strategy? This guide covers everything from the basics to advanced log analysis so you can handle any situation.
What Are Oracle RMAN Logs?
Oracle RMAN logs record every action taken by Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) during backup or restore operations. These records include commands issued by users or scripts, job status updates, error messages, warnings, performance statistics, and detailed output about each step in the process.
These logs help verify that backups completed successfully or pinpoint where something went wrong if they did not. Detailed log entries support auditing requirements and help optimize complex backup strategies by revealing bottlenecks or recurring issues. Without these logs, diagnosing failed jobs or verifying that backups are valid would be almost impossible.
Why Oracle RMAN Logs Matter?
RMAN logs are much more than plain text files—they are your first line of defense when things go wrong with database protection. When a scheduled backup fails overnight or an urgent restore does not work as expected, the log file tells you why.
For daily operations: Reviewing recent RMAN logs helps confirm backups ran correctly without errors or warnings.
For compliance: Auditors often require proof that backups occurred as scheduled; RMAN logs provide this evidence in detail.
For optimization: By studying patterns in log files—such as frequent warnings about slow disk access—you can adjust your strategy to avoid future problems.
In short: Whether you need to troubleshoot failures today or plan improvements for tomorrow, understanding your oracle rman logs is vital at every level of experience.
Where to Find Oracle RMAN Logs?
Finding where your oracle rman logs are stored depends on how you run your jobs—interactively at the command line or through automated scripts.
If running interactively:
By default, output appears directly in your terminal window.
To save this output for later review (which is best practice), use the LOG parameter when starting RMAN:
rman target / LOG /path/to/rman.log
If running automated jobs:
Scheduled tasks (using cron jobs on Unix/Linux or Task Scheduler on Windows) rely on script settings.
The location of each log file is defined by the script itself—not by any system default.
Always check your automation scripts for lines containing LOG parameters.
Common locations include
/tmp,$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/log, custom directories set by environment variables like$RMAN_LOG_DIR, or paths hardcoded in scripts.For production environments: It’s wise to capture both standard output (what appears onscreen) and write it explicitly to a file using
tee:
rman target / | tee /var/log/oracle/rman_backup_$(date +%F).log
Pro tip: Always check exit codes after an automated job finishes so you know whether it succeeded—even before reading the log details!
If using third-party management tools:
Consult their documentation for exact log locations; some may centralize all job outputs in specific folders within their installation directory.
Remember: Consistent naming conventions make searching historical oracle rman logs much easier when investigating past incidents.
How to Analyze Oracle RMAN Logs Using Oracle Enterprise Manager?
Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) provides a graphical interface for reviewing oracle rman logs—a great choice if you prefer visuals over command lines.
After a backup job completes:
1. Log into Oracle Enterprise Manager
2. Go to Availability, then select Backup & Recovery
3. Locate your recent job in the list
4. Right-click it and choose View RMAN Log
A detailed window opens showing every command executed during that session along with timestamps and error messages if present. You can search within this view using keywords like “error” or filter results based on time ranges or job types. Exporting these results lets you share them easily with colleagues who may need input during troubleshooting sessions.
This method works well for quick checks—or when sharing information across teams who may not have direct server access but still need insight into what happened during critical maintenance windows.
How to Analyze Oracle RMAN Logs Using SQL*Plus or SQLcl?
Command-line tools like SQL*Plus and SQLcl let experienced administrators query live oracle rman log data straight from dynamic performance views inside the database itself—a powerful approach for automation and reporting tasks alike.
To get started:
1. Connect using SQL*Plus (sqlplus / as sysdba) or SQLcl
2. Query views such as V$RMAN_OUTPUT (shows current/recent session messages) and V$RMAN_STATUS (lists completed jobs)
Example beginner query—to see recent output:
SELECT * FROM V$RMAN_OUTPUT ORDER BY SESSION_RECID DESC;
Intermediate query—to check status of finished jobs:
SELECT SESSION_KEY, OPERATION, STATUS, TO_CHAR(START_TIME,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI') AS STARTED, TO_CHAR(END_TIME,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI') AS ENDED, OUTPUT FROM V$RMAN_STATUS WHERE START_TIME > SYSDATE - 1 ORDER BY SESSION_KEY DESC;
Advanced tip—for those using a Recovery Catalog database rather than just controlfile-based logging:
Use catalog views like
RC_RMAN_OUTPUTwhich store longer histories across multiple databases.
You can filter these queries further by operation type (“BACKUP”, “RESTORE”), time range (START_TIME), status (“COMPLETED”, “FAILED”), or even specific error codes found within OUTPUT.
This approach supports deep dives into historical trends—perfect if you're building custom dashboards or integrating alerts into enterprise monitoring systems!
How to Analyze Oracle RMAN Log Files on Disk?
Sometimes only raw disk-based oracle rman log files contain enough detail—especially when troubleshooting rare errors missed by summary tables inside the database itself.
To review such files:
1. Locate the correct .log file based on date/job name/script path used earlier.
2. Open it with a text editor such as vi, nano, Notepad++, etc.
3. Search within using keywords like “error”, “warning”, “failed”, specific error numbers (“ORA-xxxx”/“RMAN-xxxxx”).
Look especially near the end of each file—the final lines usually report overall success/failure plus any last-minute exceptions encountered before completion.
Want even more detail?
Add commands like
set echo oninside your script so every executed line appears verbosely in output.
Need both live feedback and persistent storage?
rman target / | tee /home/oracle/rman_backup.log
This way you see progress onscreen while keeping full records for later audits—or forensic reviews after unexpected outages!
Always double-check available disk space before launching large jobs; incomplete writes due to full partitions can result in missing crucial diagnostics right when they're needed most.
Protecting Your Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Given how crucial both data integrity and comprehensive logging are for effective disaster recovery planning, leveraging robust solutions becomes essential. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-grade platform supporting major databases—including top-tier compatibility with Oracle Database—as well as MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB environments. For organizations managing mission-critical workloads on Oracle Database specifically, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers features such as incremental backups, advanced source-side compression, batch processing capabilities, flexible retention policies including GFS options, plus built-in integrity checks—all designed to streamline protection while minimizing resource impact. These features collectively ensure reliable recoverability while optimizing storage usage and simplifying long-term compliance management needs across diverse infrastructures.
Managing backups through Vinchin Backup & Recovery’s intuitive web console is straightforward—even at scale—with just four steps required per workflow:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
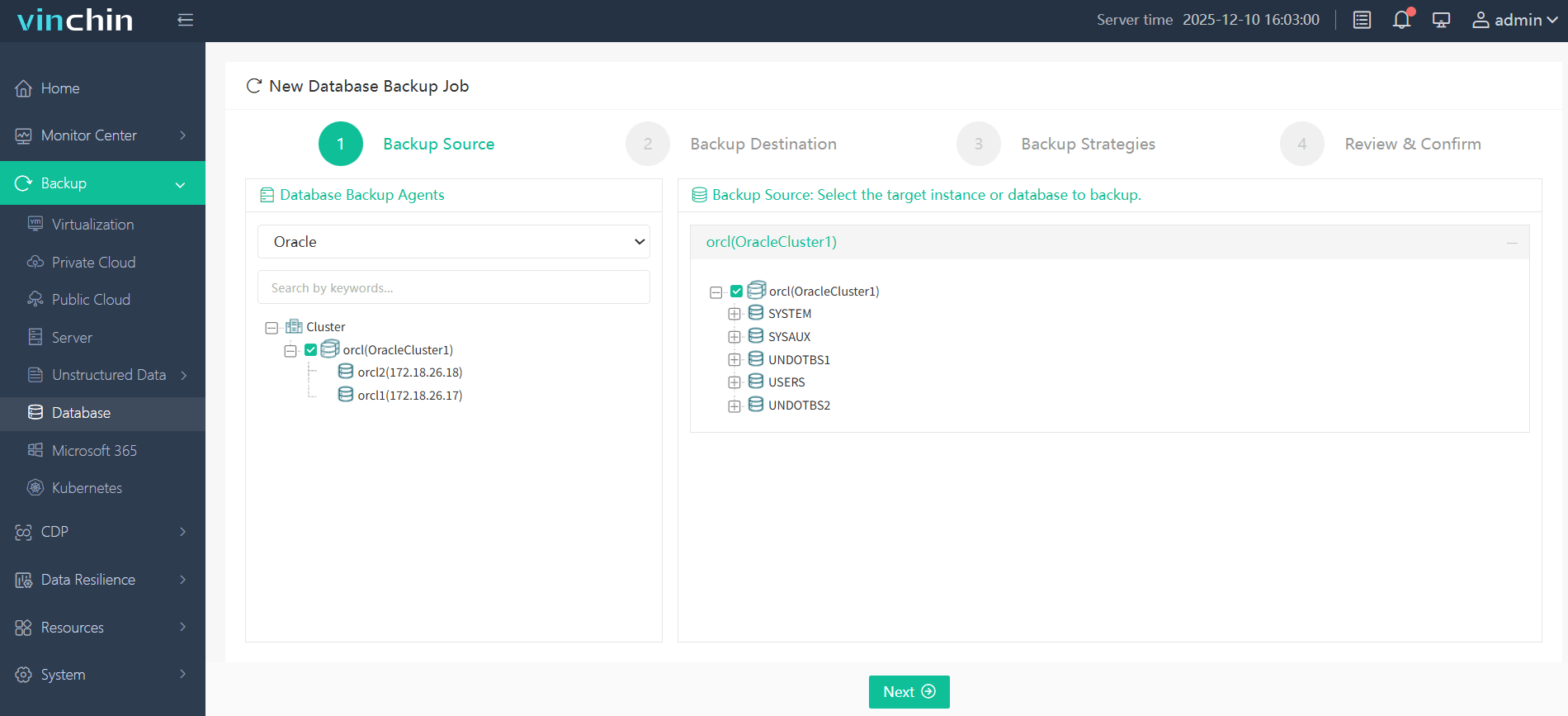
Step 2. Choose the desired backup storage location
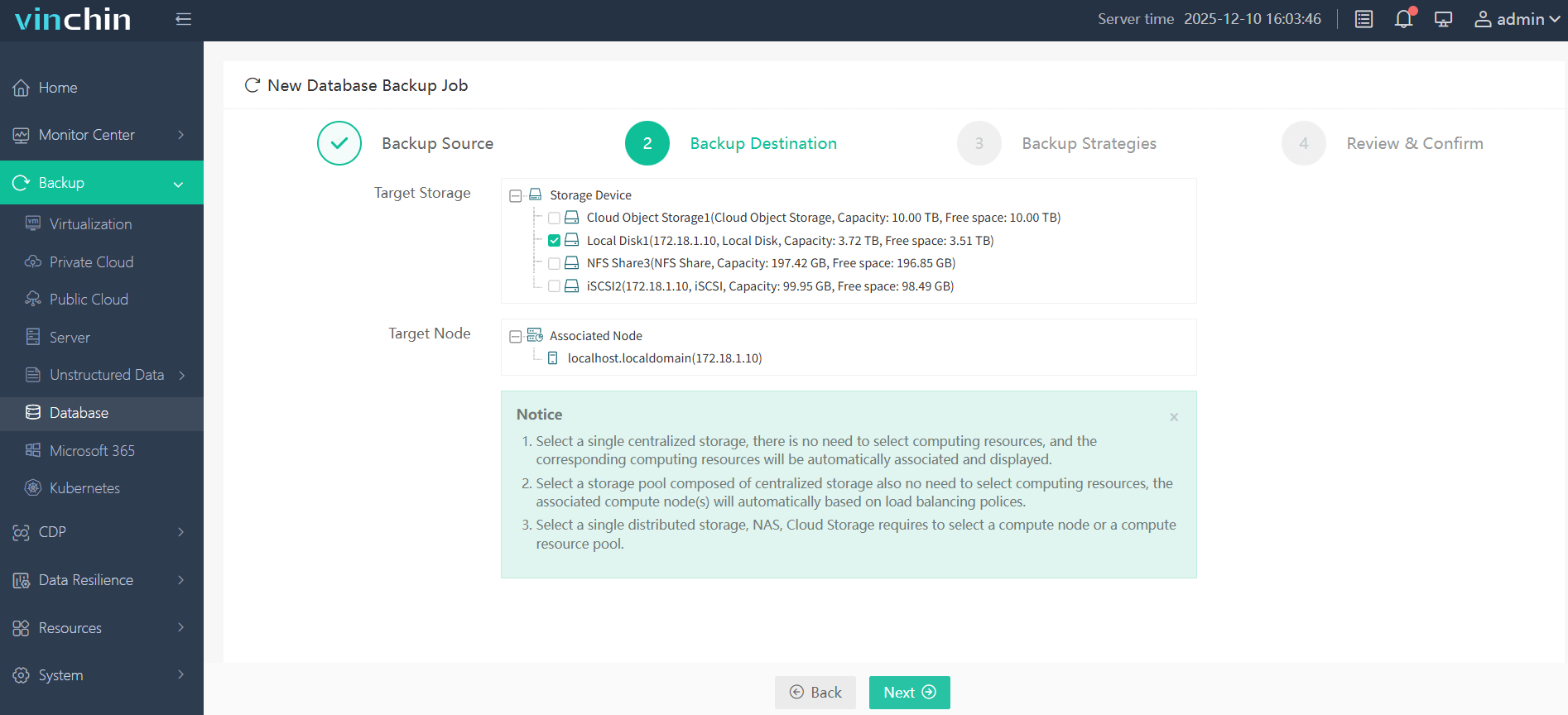
Step 3. Define scheduling rules and retention strategies
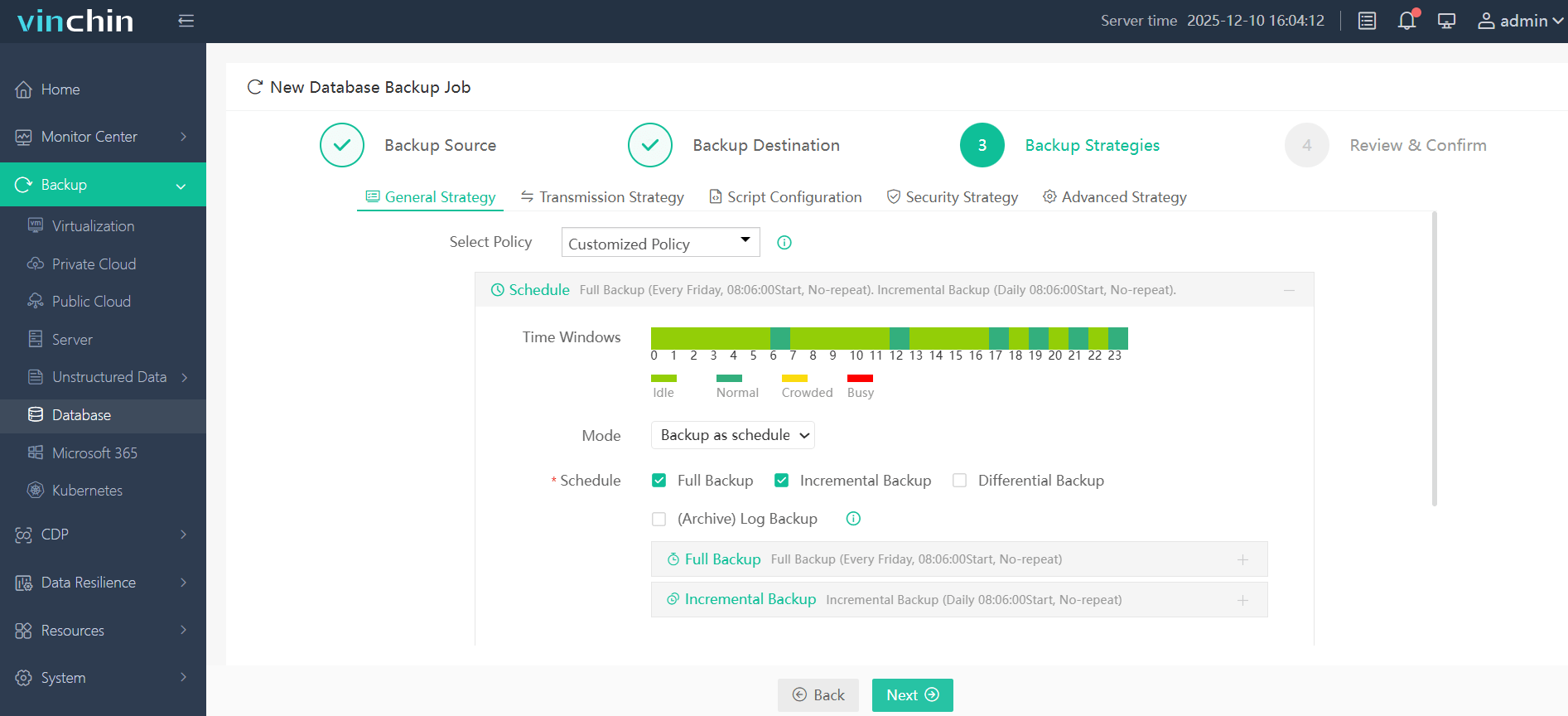
Step 4. Submit the job—all actions managed securely via browser interface
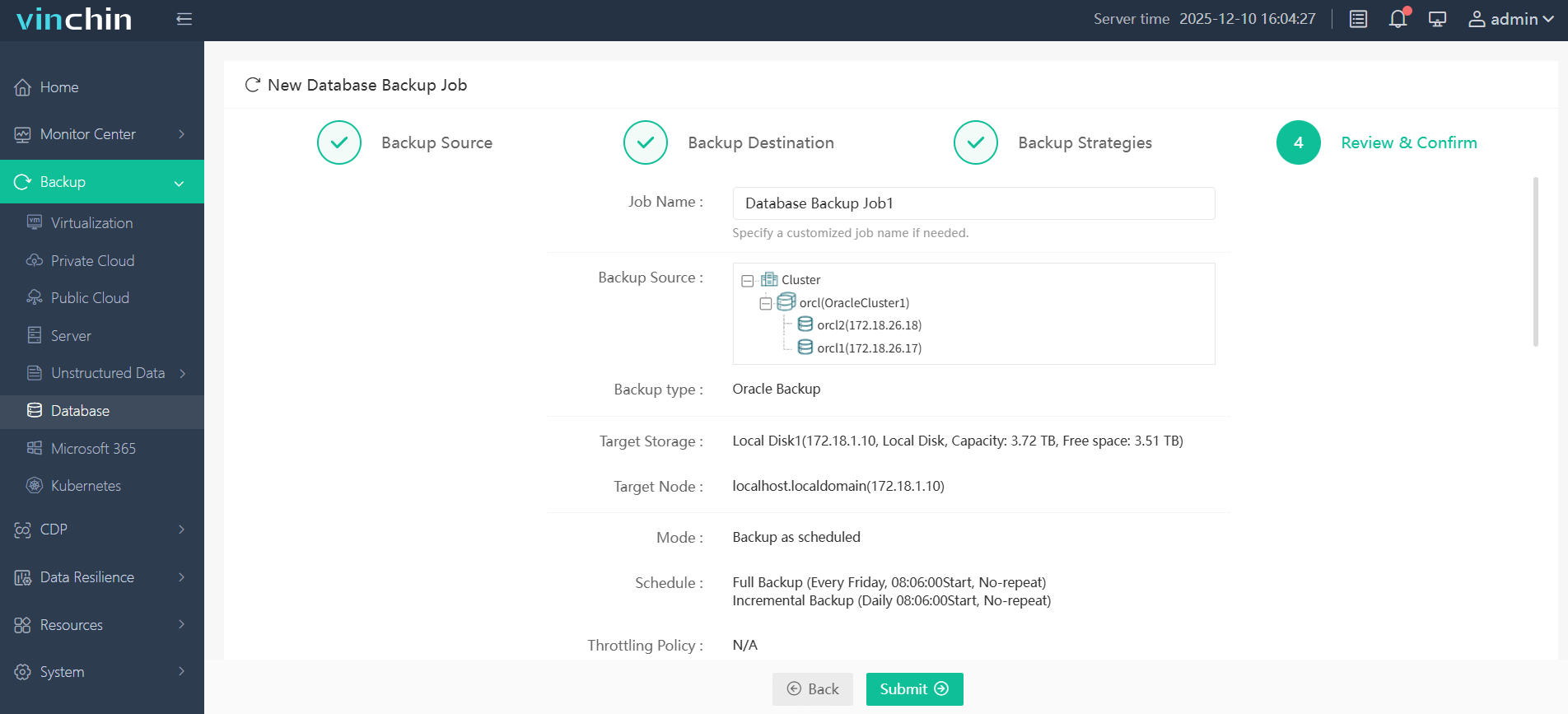
Trusted globally by thousands of enterprises—with top ratings from industry analysts—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully-featured 60-day free trial; click below to experience world-class data protection firsthand!
Oracle RMAN Logs FAQs
Q1: Can I automate email alerts based on errors found in my latest oracle rman log?
A1: Yes; use shell/Python scripts scanning new .log files post-job then send emails if keywords like "FAILED" appear—with links back to full details if needed.
Q2: Is there a way to keep only recent oracle rman logs automatically?
A2: Yes; schedule cleanup scripts removing old .log files beyond desired retention period—or compress/archive them offsite per policy requirements.
Q3: What should I do if my scheduled backup completes but no corresponding .log file exists?
A3: Check script permissions/path correctness available disk space plus ensure correct usage of LOG parameter—not just relying solely upon terminal/stdout redirection.
Conclusion
Oracle RMAN logs play a crucial role in verifying backups succeed troubleshooting failures meeting audit needs—and optimizing long-term strategies too! Whether analyzing visually via OEM querying dynamic views parsing raw disk files—or automating alerts—the right approach depends upon experience level goals involved each day. Vinchin makes protecting both databases AND their vital activity records simple secure reliable—try it now risk-free!
Share on:







