-
What Is Oracle RMAN Configuration?
-
Why Configure Oracle RMAN?
-
Pre-Configuration Checklist
-
Method 1: Basic Oracle RMAN Configuration Steps
-
Method 2: Advanced Oracle RMAN Configuration Options
-
Vinchin Backup & Recovery Enhances Enterprise Database Protection
-
Oracle RMAN Configuration FAQs
-
Conclusion
Oracle RMAN (Recovery Manager) is the standard tool for backing up and recovering Oracle databases. To ensure reliable backups and fast recovery, you must configure RMAN correctly from the start. This guide explains how to set up Oracle RMAN configuration step by step—from basic settings to advanced options—so you can protect your data with confidence.
What Is Oracle RMAN Configuration?
Oracle RMAN configuration refers to persistent settings that control how RMAN performs backups and restores. These parameters include backup storage locations, retention policies, compression methods, encryption rules, channel parallelism, and more. Once you set these values in RMAN, they stay active until you change them again—saving time on every backup job.
When you run SHOW ALL; in an RMAN session, it displays both user-defined settings and system defaults. For example, by default CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP is OFF unless you enable it yourself—a detail many overlook at first.
Why Configure Oracle RMAN?
Configuring RMAN is not just about convenience—it’s essential for reliable database protection. With proper settings:
Backups become automated.
Storage use is optimized.
Security standards are met.
Recovery becomes faster when disaster strikes.
A well-configured environment also helps meet compliance needs by keeping backups as long as required—and no longer than necessary. Wouldn’t you want peace of mind knowing your backups are always done right?
Pre-Configuration Checklist
Before changing any Oracle RMAN configuration parameters or running your first backup job, take time to prepare your environment properly.
First, make sure there is enough disk or tape storage available for all planned backups—including fulls and incrementals—and that these locations are mounted with correct permissions for the Oracle user account.
Next, check if your database runs in ARCHIVELOG mode using SQL*Plus:
ARCHIVE LOG LIST;
If not enabled yet but point-in-time recovery is needed later on (a common requirement), switch modes before proceeding:
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE STARTUP MOUNT ALTER DATABASE ARCHIVELOG; ALTER DATABASE OPEN;
Plan out a directory structure where all backup pieces will reside—using clear naming conventions helps with future management tasks.
Finally, decide which retention policy fits your business needs: do you want to keep a certain number of full backups (redundancy) or retain everything needed within a specific number of days (recovery window)?
By preparing these details ahead of time, you avoid surprises during setup or restore operations down the road.
Method 1: Basic Oracle RMAN Configuration Steps
Let’s begin with essential steps every administrator should know when setting up an initial Oracle rman configuration:
Start by connecting to your target database using:
rman target /
To review current settings—including both custom values and defaults—run:
SHOW ALL;
Here’s how to configure key options:
1. Set the Retention Policy
Decide how long old backups should be kept before deletion.
To keep only the last two full backups:
CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY TO REDUNDANCY 2;
To retain everything needed for point-in-time recovery within seven days:
CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY TO RECOVERY WINDOW OF 7 DAYS;
2. Set Default Device Type
By default RMAN writes backups to disk.
Confirm or set this explicitly:
CONFIGURE DEFAULT DEVICE TYPE TO DISK;
If using tape (with media manager configured):
CONFIGURE DEFAULT DEVICE TYPE TO SBT;
3. Enable Control File Autobackup
Protect control files automatically after each backup operation.
Turn autobackup ON:
CONFIGURE CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP ON;
Set a custom location (recommended: fast local storage):
CONFIGURE CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP FORMAT FOR DEVICE TYPE DISK TO '/backups/ORCL/cf_%F';
4. Configure Backup Compression
Save space by compressing backup sets.
Enable compressed backupsets on disk:
CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK BACKUP TYPE TO COMPRESSED BACKUPSET;
Use BASIC compression algorithm (included in standard licenses):
CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'BASIC' AS OF RELEASE 'DEFAULT' OPTIMIZE FOR LOAD TRUE;
5. Enable Backup Optimization
Skip unchanged files during incremental jobs:
CONFIGURE BACKUP OPTIMIZATION ON;
6. Set Snapshot Control File Location
Specify where temporary snapshot control files are stored during jobs (use fast local disks—not shared network drives—for best performance):
CONFIGURE SNAPSHOT CONTROLFILE NAME TO '/u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1/dbs/snapcf_ORCL.f';
7. Clear a Configuration Setting
If you need to reset any parameter back to its default state:
CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY CLEAR;
With these basics complete, most environments can handle routine backup and restore tasks smoothly.
Method 2: Advanced Oracle RMAN Configuration Options
Once comfortable with basic setup steps above—or if managing larger production systems—you may need advanced controls over performance or security:
1. Configure Channel Parallelism & Formats
Channels let multiple streams run at once; increasing parallelism speeds large jobs but requires enough CPU/I/O bandwidth.
Set two channels writing in parallel on disk:
CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK PARALLELISM 2;
Customize file name format so each piece has a unique name (%U ensures uniqueness):
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '/backups/ORCL/db_%U.bkp';
Be careful not to set parallelism higher than what hardware supports; too many channels can slow things down due to contention.
2. Set Archivelog Deletion Policy
Archived redo logs support point-in-time recovery but fill up storage quickly if unmanaged.
Delete logs after being backed up twice (often paired with RECOVERY WINDOW retention policy):
CONFIGURE ARCHIVELOG DELETION POLICY TO BACKED UP 2 TIMES TO DEVICE TYPE DISK;
Keep all archivelogs until manually deleted if strict audit/compliance rules apply:
CONFIGURE ARCHIVELOG DELETION POLICY TO NONE;
3. Enable Backup Encryption
Protect sensitive data at rest by encrypting all new backups automatically.
Enable encryption globally for future jobs:
CONFIGURE ENCRYPTION FOR DATABASE ON; CONFIGURE ENCRYPTION ALGORITHM 'AES256';
Note: You must manage encryption keys/wallets outside of these commands—for example using Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) or password-based wallets—to ensure restores work later even after hardware changes.
4. Set Maximum Backup Piece Size
Avoid filesystem limits or optimize tape usage by capping file sizes per piece.
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE DISK MAXPIECESIZE 2G;
This ensures no single file exceeds size limits imposed by OS or storage devices.
5. Exclude Tablespaces from Backups
Skip tablespaces containing test data or other non-essential information from regular jobs.
Exclude one named EXAMPLE from future automatic backups:
CONFIGURE EXCLUDE FOR TABLESPACE EXAMPLE;
Re-enable inclusion later if needed:
CONFIGURE EXCLUDE FOR TABLESPACE EXAMPLE CLEAR;
6. Configure Multiple Backup Copies
Increase safety by making more than one copy per job—store copies on different disks if possible.
CONFIGURE DATAFILE BACKUP COPIES FOR DEVICE TYPE DISK TO 2;
7. Use Advanced Compression Levels
If licensed for Advanced Compression Option (ACO), choose higher levels like ‘HIGH’ instead of ‘BASIC’—but note that only ‘BASIC’ comes standard without extra cost.
CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'HIGH';
8. Manage Settings for Data Guard Environments
For multi-site setups using Data Guard replication features, set parameters separately per site using unique DB names, like so:
CONFIGURE FOR DB_UNIQUE_NAME <name>;
These advanced tools let experienced admins fine-tune performance, security, and flexibility across complex clusters—or simply automate routine maintenance further.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery Enhances Enterprise Database Protection
For organizations seeking streamlined enterprise-level protection beyond native tools like Oracle RMAN, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers comprehensive support for today’s leading databases—including robust integration with Oracle as well as MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB environments. As an enterprise-grade solution designed specifically for modern IT infrastructures, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers powerful features such as batch database backup management, multiple level data compression options tailored for efficiency and speed, granular data retention policies including GFS strategies for compliance needs, log/archived log backup capabilities supporting any-point-in-time recovery scenarios—even cloud/tape archiving integration—all while ensuring integrity checks and ransomware-resistant storage protection are built into every workflow.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your Oracle database simple:
Step 1—Select the Oracle database to back up;
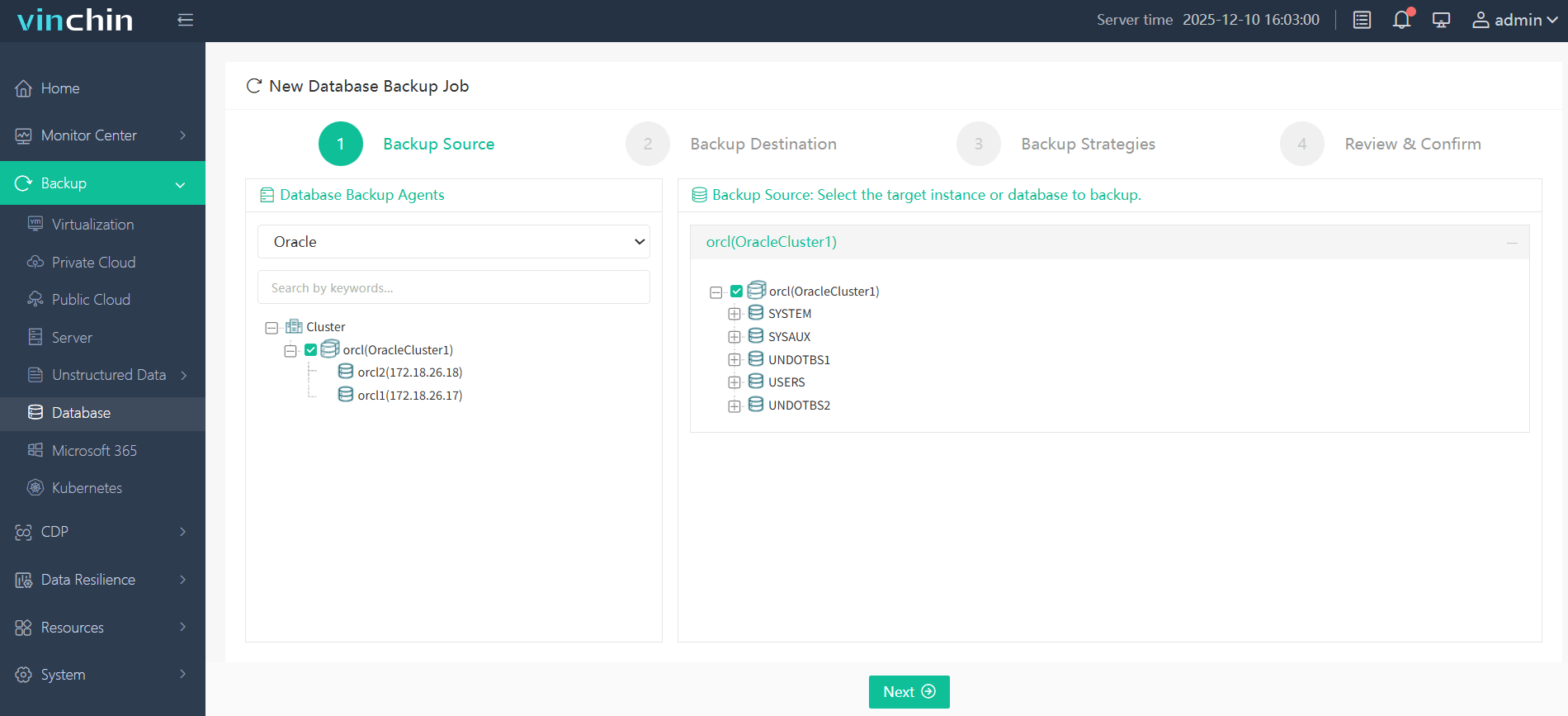
Step 2—Choose the desired backup storage location;
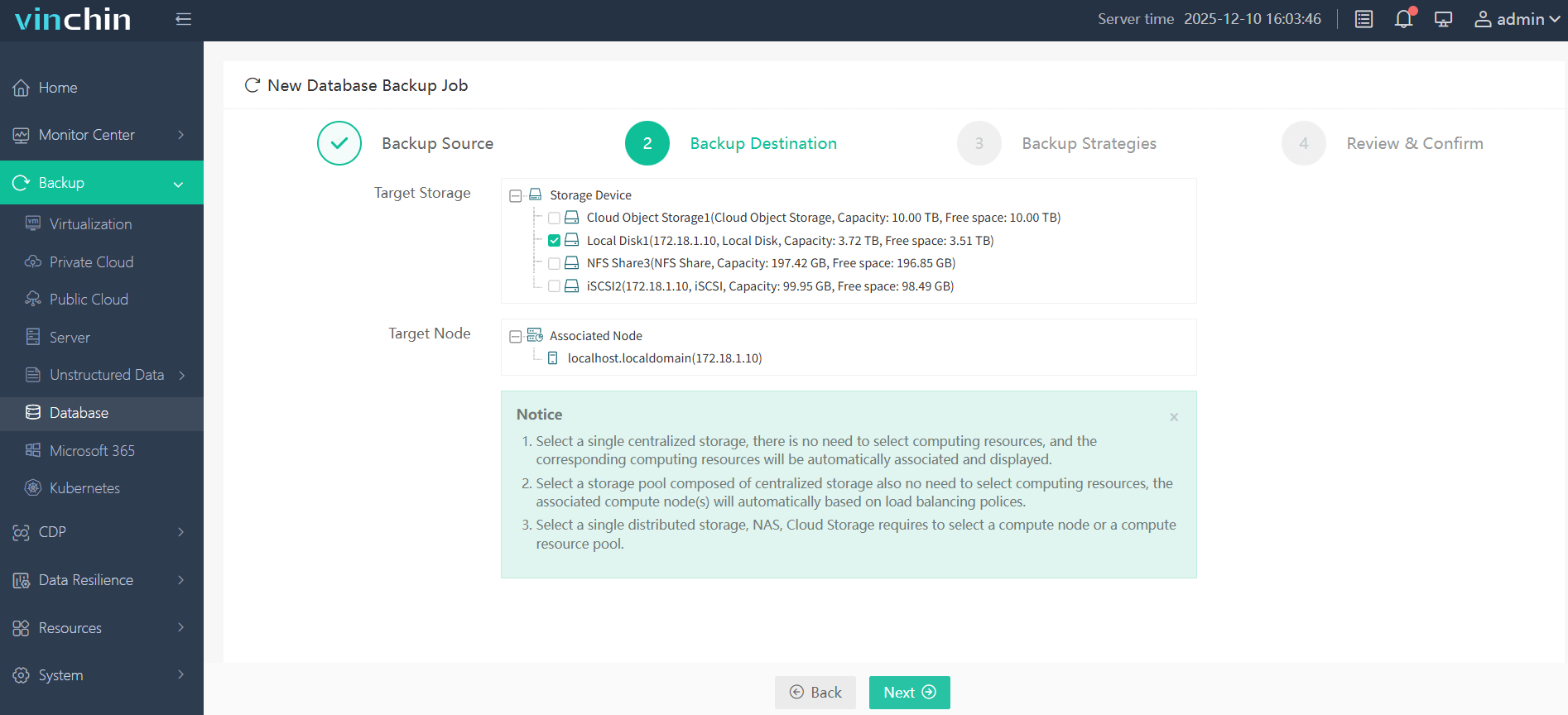
Step 3—Define a suitable backup strategy based on business requirements;
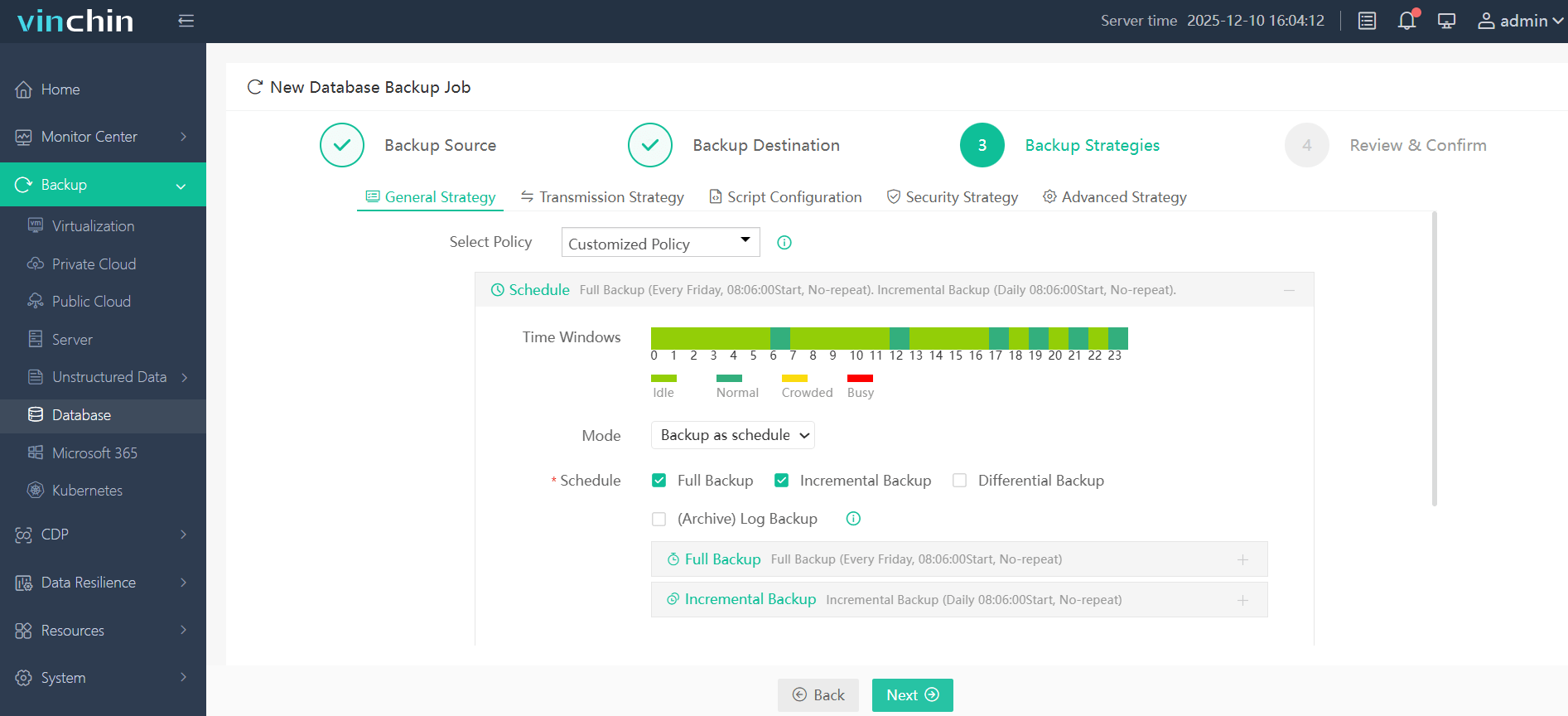
Step 4—Submit the job with just a few clicks.
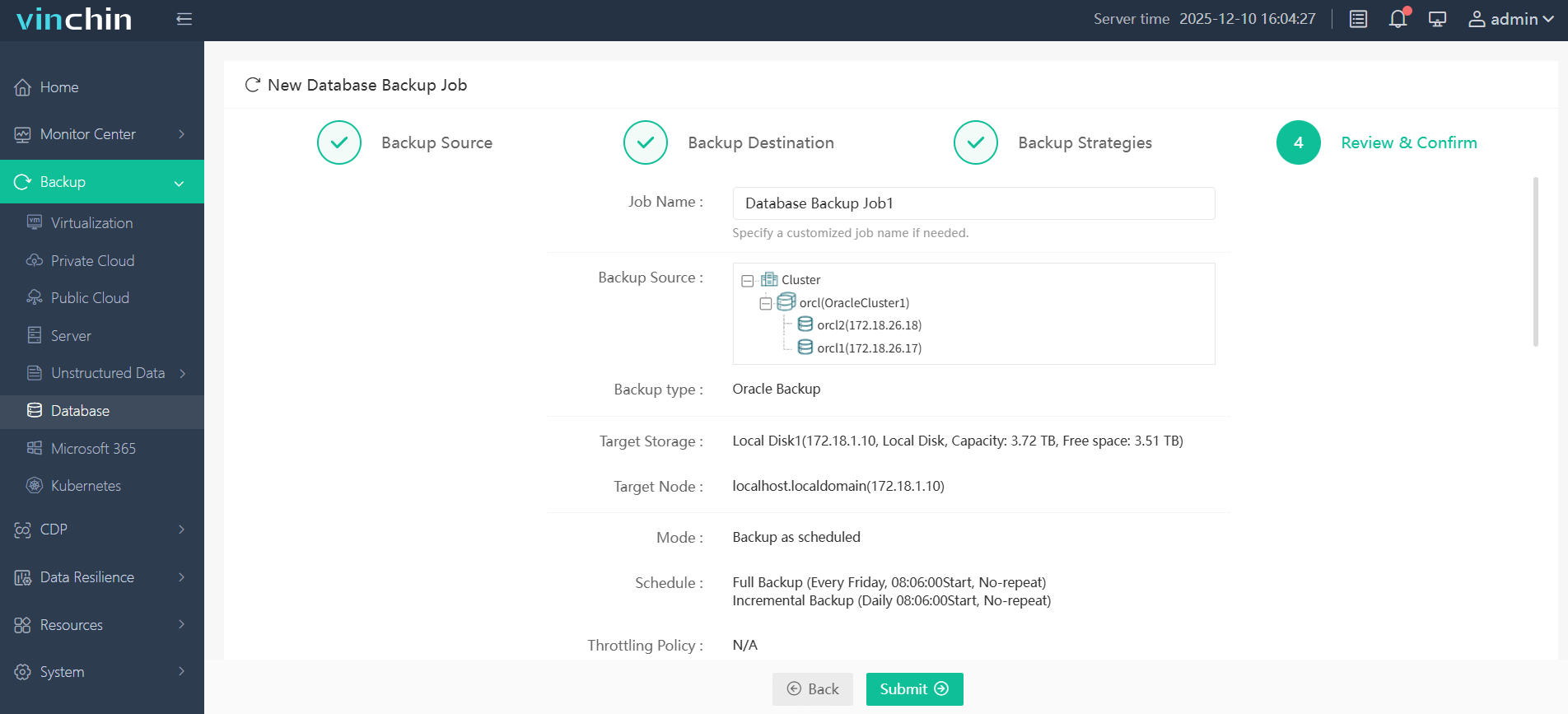
Vinchin Backup & Recovery enjoys global recognition among enterprises—with high customer satisfaction ratings worldwide—and offers a risk-free 60-day full-featured trial so you can experience its advantages firsthand.
Oracle RMAN Configuration FAQs
Q1: How can I schedule daily full backups using my rman configuration?
A1: Use either an OS-level scheduler like cron/Task Scheduler—or create a recurring job inside the database itself via DBMS_SCHEDULER—to call an rman script referencing persistent config values.
Q2: What should I do if my compressed backups fail due to lack of space?
A2: Monitor free space daily at all destinations shown in SHOW ALL; delete obsolete files promptly after confirming recent successful jobs have completed safely.
Q3: How do I migrate my rman configuration between databases?
A3: Script out relevant CONFIGURE commands from SHOW ALL output on source system then run them line-by-line against target instance after initial setup.
Conclusion
A well-configured Oracle rman environment forms the backbone of reliable enterprise data protection—automating routine work while meeting compliance goals as needs evolve over time.
For even greater simplicity plus centralized control across platforms, try Vinchin’s enterprise-grade solution today with its free trial offer!
Share on:







