-
What Is Oracle RMAN Backup As Copy?
-
Image Copies vs. Backup Sets: A Practical Comparison
-
Why Use Backup As Copy in Oracle?
-
How to Create Backup As Copy with RMAN?
-
How to Restore from Backup As Copy with RMAN?
-
Vinchin: Enterprise-Level Oracle Database Protection Made Simple
-
Oracle RMAN Backup As Copy FAQs
-
Conclusion
Protecting your Oracle database is a top priority for any operations administrator. You need backups that are fast, reliable, and easy to restore. Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) offers several backup options, but one of the most straightforward is the Backup As Copy method. This article explains what RMAN Backup As Copy is, why you might use it, and how to create and restore these backups step by step.
What Is Oracle RMAN Backup As Copy?
Oracle RMAN Backup As Copy creates an exact, byte-for-byte image of your database files. Unlike backup sets, which store data in a proprietary format, image copies are direct file copies. They can be used for quick restores and are easy to manage. When you run the BACKUP AS COPY command in RMAN, the resulting files are identical to those created by operating system copy commands but with the added benefit that RMAN tracks them in its repository. Image copies are ready-to-use files—meaning you can mount or switch to them directly without extra processing.
Image Copies vs. Backup Sets: A Practical Comparison
Understanding the difference between image copies and backup sets helps you choose the right tool for each job. Image copies are exact replicas of your datafiles or control files; they keep their original format so you can use them instantly when needed. In contrast, backup sets compress data into proprietary blocks—saving space but requiring extraction during recovery.
For example:
Restore Speed: Image copies allow instant switching; backup sets require extraction first.
Format: Image copies match original files; backup sets use special formatting.
Use Cases: Choose image copies for fast disaster recovery or critical tablespaces; pick backup sets for long-term storage or tape archiving.
Do you want immediate access after a failure? Go with image copies.
Why Use Backup As Copy in Oracle?
Choosing Backup As Copy offers several advantages. First, restores are faster because you can switch to the image copy without having to extract files from a backup set. Second, these copies are not locked into RMAN’s format—you can even work with them using other tools if needed. Third, image copies support strategies like incrementally updated backups that keep your recovery window short while reducing downtime.
Another benefit is transparency: since these backups look just like regular database files on disk, troubleshooting becomes easier if something goes wrong during recovery. Do you want a backup that is both simple and flexible? Backup As Copy is a strong choice.
How to Create Backup As Copy with RMAN?
Creating a Backup As Copy with RMAN is straightforward but requires attention to detail for best results. Before starting an online backup using this method on a production system, make sure your database runs in ARCHIVELOG mode so all changes get captured safely during operation.
Start by connecting to your Oracle database using RMAN:
# Connects locally as target rman target /
To create a full database image copy while online:
BACKUP AS COPY DATABASE;
If your environment allows downtime—or you're performing maintenance—you may shut down the instance cleanly then start it in MOUNT state before running this command for an offline (cold) consistent copy:
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; STARTUP MOUNT; BACKUP AS COPY DATABASE;
Want more control? Back up specific tablespaces or datafiles like this:
BACKUP AS COPY TABLESPACE users; BACKUP AS COPY DATAFILE 4 FORMAT '/backup/users01.dbf';
You can also specify custom locations using FORMAT clauses:
BACKUP AS COPY DATABASE FORMAT '/backup/%U';
Here %U ensures each file gets a unique name—avoiding accidental overwrites—and %d adds your DB_NAME if desired ('/backup/%d_%U'). For better tracking over time or across jobs add tags:
BACKUP AS COPY DATABASE TAG 'FULL_IMG_COPY';
Tags help identify particular backups later when listing or deleting old images—a lifesaver when managing many jobs at scale.
After completion RMAN records all new images in its catalog so they're easy to find later:
LIST COPY;
This lists every known image copy along with location details—making audits simple.
Validating Your Backup Copy
Once you've created an image copy it's wise to check its integrity before relying on it for disaster recovery. Validation detects physical corruption early so there are no surprises during restoration.
Run this command from within RMAN after creating your copy:
RESTORE DATABASE VALIDATE;
This simulates restoring from your latest available images without actually writing any data back—confirming everything needed exists and works as expected.
For individual datafiles try:
RESTORE DATAFILE 4 VALIDATE;
Regular validation should be part of every admin's routine—it saves headaches down the road!
How to Restore from Backup As Copy with RMAN?
Restoring from a Backup As Copy is fast and efficient—but knowing exactly how matters when time counts most! There are two main approaches depending on whether you're recovering single components or entire environments.
If just one datafile fails—and its corresponding image remains accessible locally—you can switch over quickly by following these steps:
1. Take affected datafile offline
SQL 'ALTER DATABASE DATAFILE 4 OFFLINE';
2. Switch pointer from lost/corrupt file directly onto valid image
SWITCH DATAFILE 4 TO COPY;
3. Apply archived redo logs as needed
RECOVER DATAFILE 4;
4. Bring restored file back online
SQL 'ALTER DATABASE DATAFILE 4 ONLINE';
Note: This process assumes both source path and destination remain unchanged; if moving between servers/disks use SET NEWNAME inside RUN blocks before restoring!
For full environment failures—or planned migrations—you may need complete switchover instead:
1. Shut down instance immediately
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE;
2. Mount database without opening
STARTUP MOUNT;
3. Permanently redirect all pointers within control file toward new images
SWITCH DATABASE TO COPY;
Warning: After running SWITCH DATABASE TO COPY all future operations reference these new locations until changed again! Make sure paths have enough performance/storage capacity before proceeding further!
4. Recover outstanding transactions via archived logs
RECOVER DATABASE;
5. Open environment normally once finished
ALTER DATABASE OPEN;
Always ensure required archived redo logs remain available throughout this process—they're essential for bringing everything current after switching over!
Vinchin: Enterprise-Level Oracle Database Protection Made Simple
For organizations seeking streamlined protection beyond native tools like RMAN, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers robust enterprise-grade solutions tailored specifically for Oracle databases—as well as MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB environments among others. With features such as advanced source-side compression, incremental backup capabilities, batch database management options, granular retention policy controls including GFS strategies, plus comprehensive integrity checks and WORM protection across platforms—Vinchin Backup & Recovery ensures both operational efficiency and regulatory compliance while minimizing risk of ransomware attacks or accidental loss.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your Oracle workloads effortless:
Step 1: Select the Oracle database to back up;
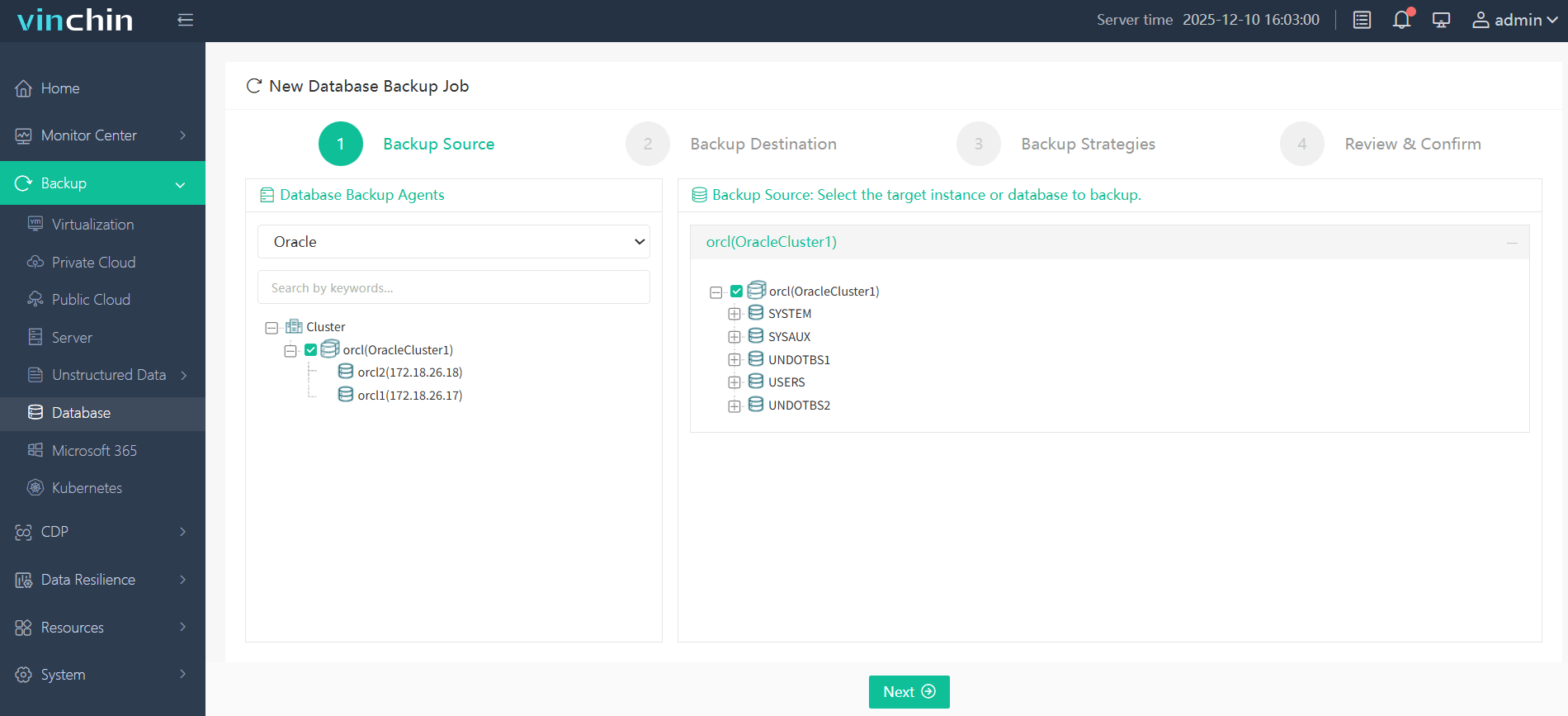
Step 2: Choose secure storage;
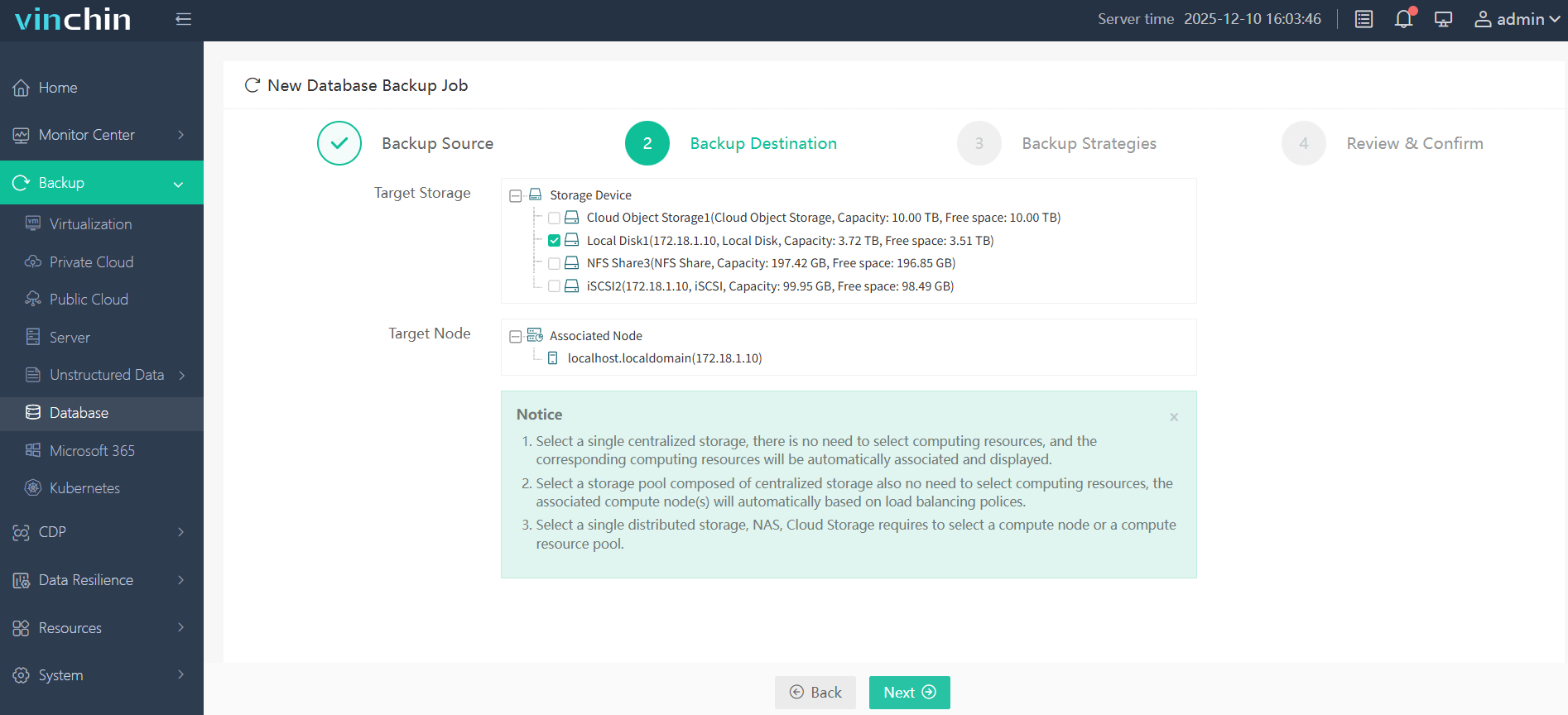
Step 3: Define scheduling and strategy parameters;
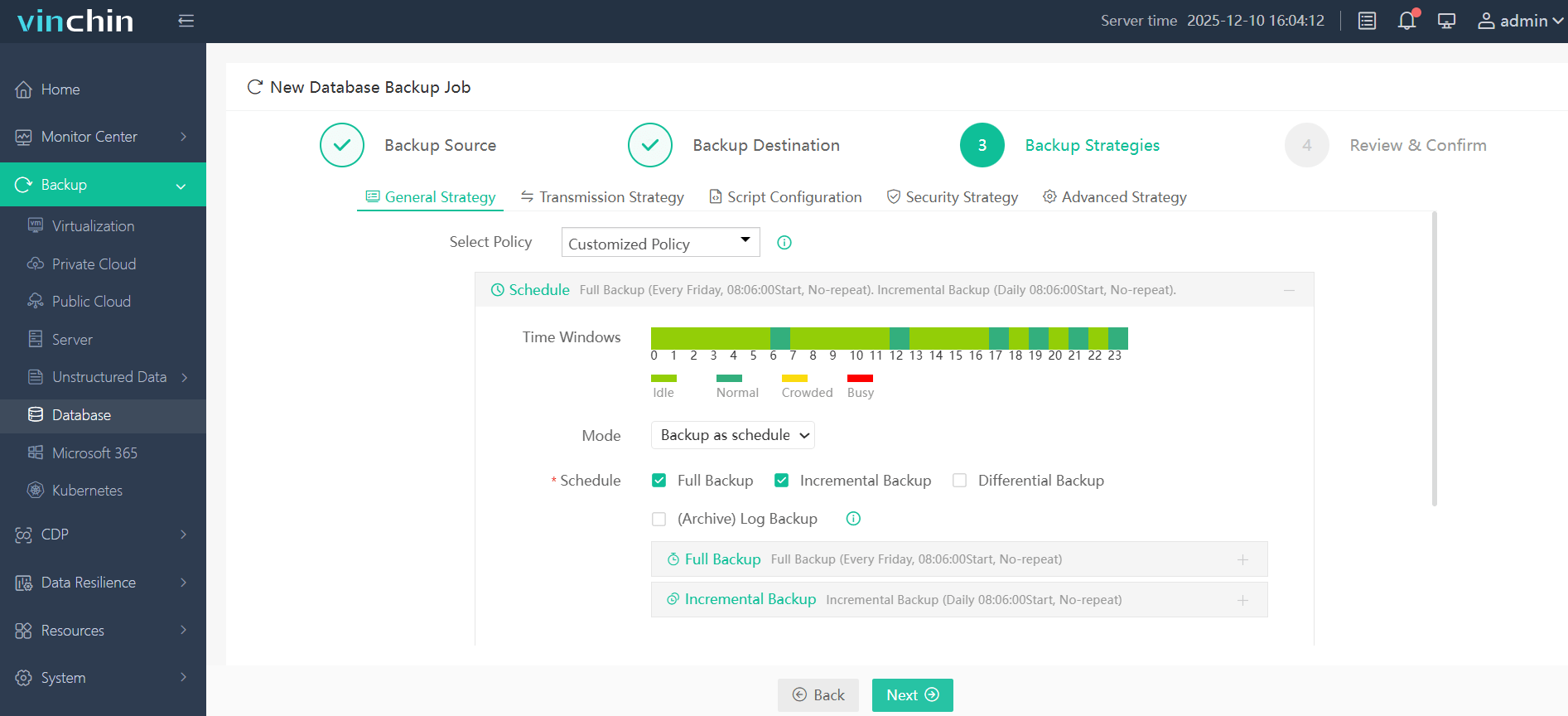
Step 4: Submit the job—all within minutes through clear guided workflows designed for administrators at any skill level.
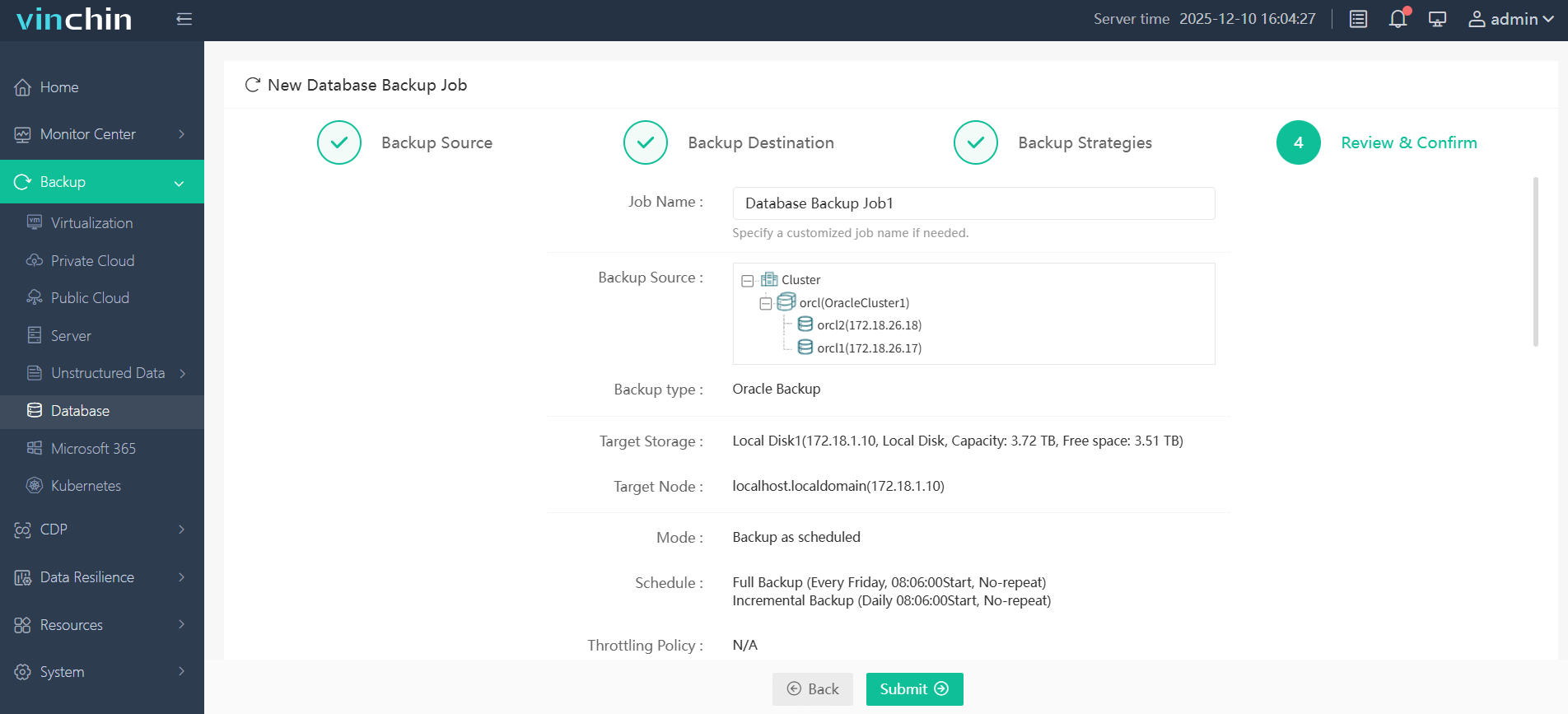
Trusted globally by thousands of enterprises—with top industry ratings—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully functional free trial (60 days). Experience world-class protection firsthand by clicking below to download today!
Oracle RMAN Backup As Copy FAQs
Q1: Can I schedule automatic RMAN BACKUP AS COPY jobs inside Oracle itself?
Yes; use DBMS_SCHEDULER within SQL*Plus or Enterprise Manager Grid Control—or call external scripts through OS schedulers like CRON (Linux) or Task Scheduler (Windows) as needed.
Q2: What's best practice for deleting outdated image copies?
First configure retention policy (CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY TO RECOVERY WINDOW OF N DAYS) then run DELETE OBSOLETE regularly—this removes only those no longer required per policy settings rather than everything blindly.
Q3: Are there space concerns compared with traditional compressed backups?
Yes; since each image copy matches original size uncompressed they consume more disk than compressed BACKUPSETs—plan storage accordingly especially when retaining multiple generations simultaneously!
Conclusion
Oracle RMAN Backup As Copy gives operations teams speed flexibility reliability—all crucial traits under pressure! It’s easy enough beginners master basics yet powerful enough experts trust daily workflows alike! Vinchin makes protecting mission-critical workloads even simpler thanks intuitive web console plus advanced automation features—try it free today see difference firsthand!
Share on:








