-
What is RMAN Compressed Backup?
-
Why Use Compressed Backups in Oracle?
-
Understanding the Trade-offs: Compression Ratio vs CPU
-
How to Create an RMAN Compressed Backup?
-
How to Restore from an RMAN Compressed Backup?
-
Enterprise-Level Oracle Database Protection With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
RMAN Compressed Backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Managing Oracle database backups can be a balancing act. Storage costs rise quickly as data grows. Network bandwidth becomes strained during large backup windows. For operations administrators tasked with keeping systems safe while controlling expenses, these are daily headaches. What if you could shrink your backup footprint without losing reliability? That’s where RMAN compressed backup comes in—a built-in Oracle feature that can cut backup size by up to 70%. This guide explains how it works, why it matters for your business, and how you can start using it today.
What is RMAN Compressed Backup?
RMAN compressed backup uses Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) to reduce the size of your database backups through binary compression. Instead of saving every data block exactly as it appears on disk, RMAN scans for repeated patterns or empty space within blocks. It then compresses this data before writing it out—either to disk or tape.
This process applies only when creating backup sets, not image copies. A backup set is an RMAN-specific format that groups multiple files into one logical unit; these files are eligible for compression. An image copy, by contrast, is a bit-for-bit duplicate of your original file—compression isn’t possible here because fidelity must be absolute.
The result? Smaller backup files that save storage space and reduce network load during both backup creation and restore operations.
Why Use Compressed Backups in Oracle?
Compressed backups help organizations manage limited resources more efficiently. When disk space runs low or when you need to send backups across slow networks—for example between remote offices or cloud storage—compression makes a real difference.
For large databases or environments where multiple copies must be kept online at once (such as production plus development), shrinking each backup saves money directly on storage hardware. It also shortens transfer times over busy networks.
However, there’s always a trade-off: Compression uses more CPU power than standard backups do. If you run backups during peak hours on heavily loaded servers, this extra demand could affect other workloads. Most teams find that scheduling compressed backups during off-hours balances these concerns well.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Compression Ratio vs CPU
Choosing the right compression level involves balancing storage savings against system performance. The default algorithm—BASIC—offers moderate compression with minimal CPU overhead; it's included in all Oracle editions at no extra cost.
If your organization has licensed the Advanced Compression Option (ACO), you unlock three additional algorithms: LOW, MEDIUM, and HIGH:
LOW: Fastest but least efficient; uses little CPU but achieves less reduction.
MEDIUM: Good balance between speed and space savings; often recommended for most environments with ACO.
HIGH: Maximum reduction in size but highest CPU usage; best reserved for non-critical systems or when minimizing storage is essential.
Monitor system load during test runs using tools like V$SESSION_LONGOPS or OS-level utilities such as top. You can also check actual savings after each job by querying V$BACKUP_SET for input/output sizes (see below).
Remember: Higher compression levels mean longer processing times but smaller files—and vice versa.
How to Create an RMAN Compressed Backup?
Setting up compressed backups in RMAN is straightforward whether you want all jobs compressed by default or just specific ones.
First, configure RMAN so future disk-based jobs use compressed sets:
RMAN> CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK BACKUP TYPE TO COMPRESSED BACKUPSET;
Or set this up for tape devices:
RMAN> CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE SBT BACKUP TYPE TO COMPRESSED BACKUPSET;
Next, choose your preferred algorithm:
RMAN> CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'BASIC';
Important: Only the BASIC algorithm comes standard with all Oracle licenses. To use LOW, MEDIUM, or HIGH settings requires purchasing the Advanced Compression Option license from Oracle
To run a one-time compressed full database backup:
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE;
You can target specific objects too:
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET TABLESPACE users; BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET ARCHIVELOG ALL;
Want archived logs deleted after they’re backed up?
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET ARCHIVELOG ALL DELETE ALL INPUT;
For faster throughput on large databases—or if you have multi-core CPUs—you may allocate several channels manually:
RUN {
ALLOCATE CHANNEL c1 DEVICE TYPE DISK;
ALLOCATE CHANNEL c2 DEVICE TYPE DISK;
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE;
RELEASE CHANNEL c1;
RELEASE CHANNEL c2;
}Note: Channel configuration can also be preset globally via CONFIGURE CHANNEL.
Keep in mind that only backup sets support compression—not image copies. Also remember that higher levels like HIGH will take longer due to increased processing demands but yield smaller output files.
How to Restore from an RMAN Compressed Backup?
Restoring from a compressed set feels just like any other recovery operation—no special flags required! During restore jobs RMAN automatically decompresses data behind-the-scenes so you don’t need extra steps or options.
To perform a full database restore:
1. Start RMAN and connect to your target instance
2. Mount if needed:
STARTUP MOUNT;
3. Restore main files:
RESTORE DATABASE;
4. Apply changes since last full:
RECOVER DATABASE;
5. Open live again:
ALTER DATABASE OPEN;
Need only certain tablespaces restored?
RESTORE TABLESPACE users; RECOVER TABLESPACE users; ALTER TABLESPACE users ONLINE;
Or just one datafile?
RESTORE DATAFILE 5; RECOVER DATAFILE 5; ALTER DATABASE DATAFILE 5 ONLINE;
Enterprise-Level Oracle Database Protection With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Beyond native tools like RMAN, organizations seeking streamlined management and advanced protection often turn to dedicated solutions designed for enterprise needs. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional platform supporting most mainstream databases—including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with robust features tailored specifically for complex environments like Oracle deployments first and foremost among them.
Key capabilities include advanced source-side compression (for Oracle), incremental backup options (also available for Oracle), batch database backup management, flexible retention policies including GFS retention strategy, and comprehensive integrity checks—all working together to maximize efficiency while ensuring reliable recoverability across diverse scenarios.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding Oracle databases straightforward:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
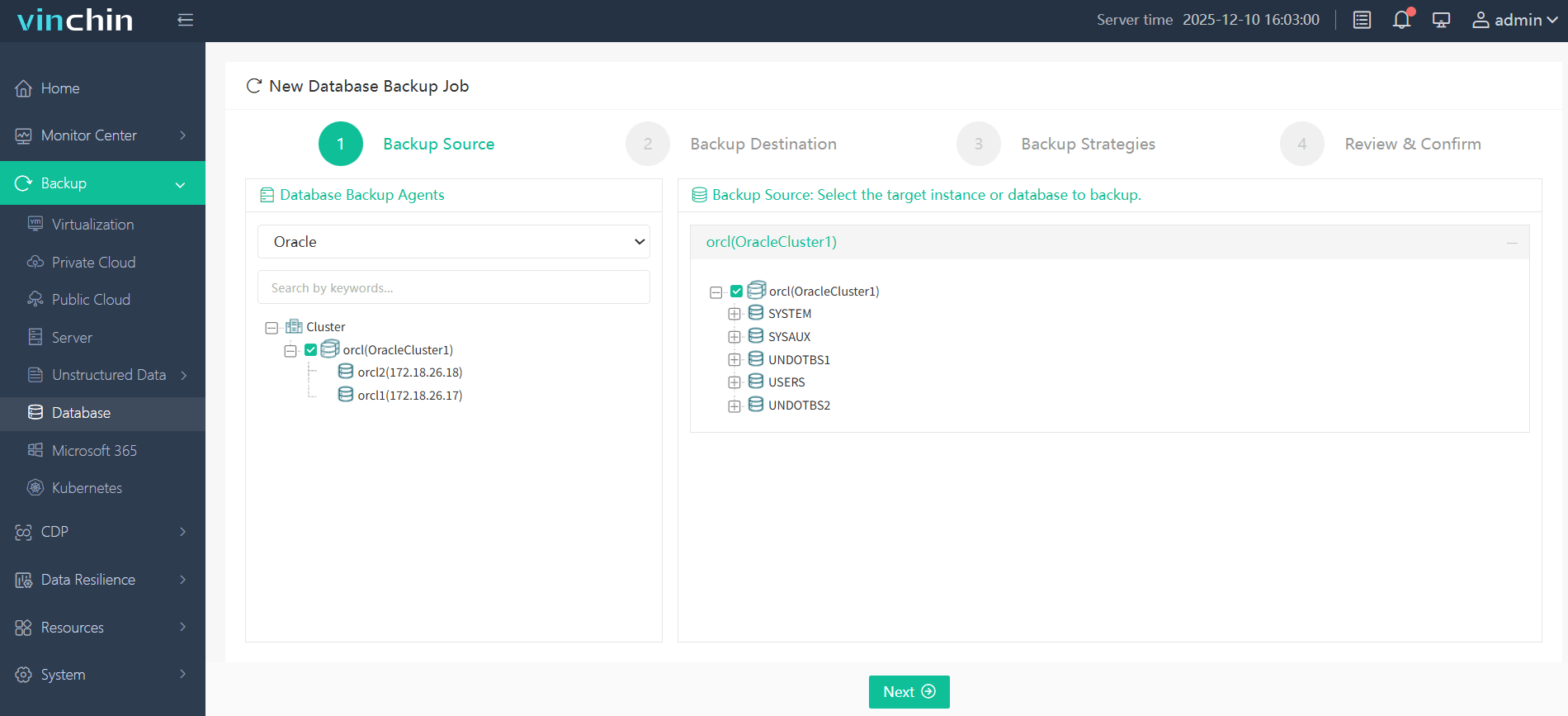
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
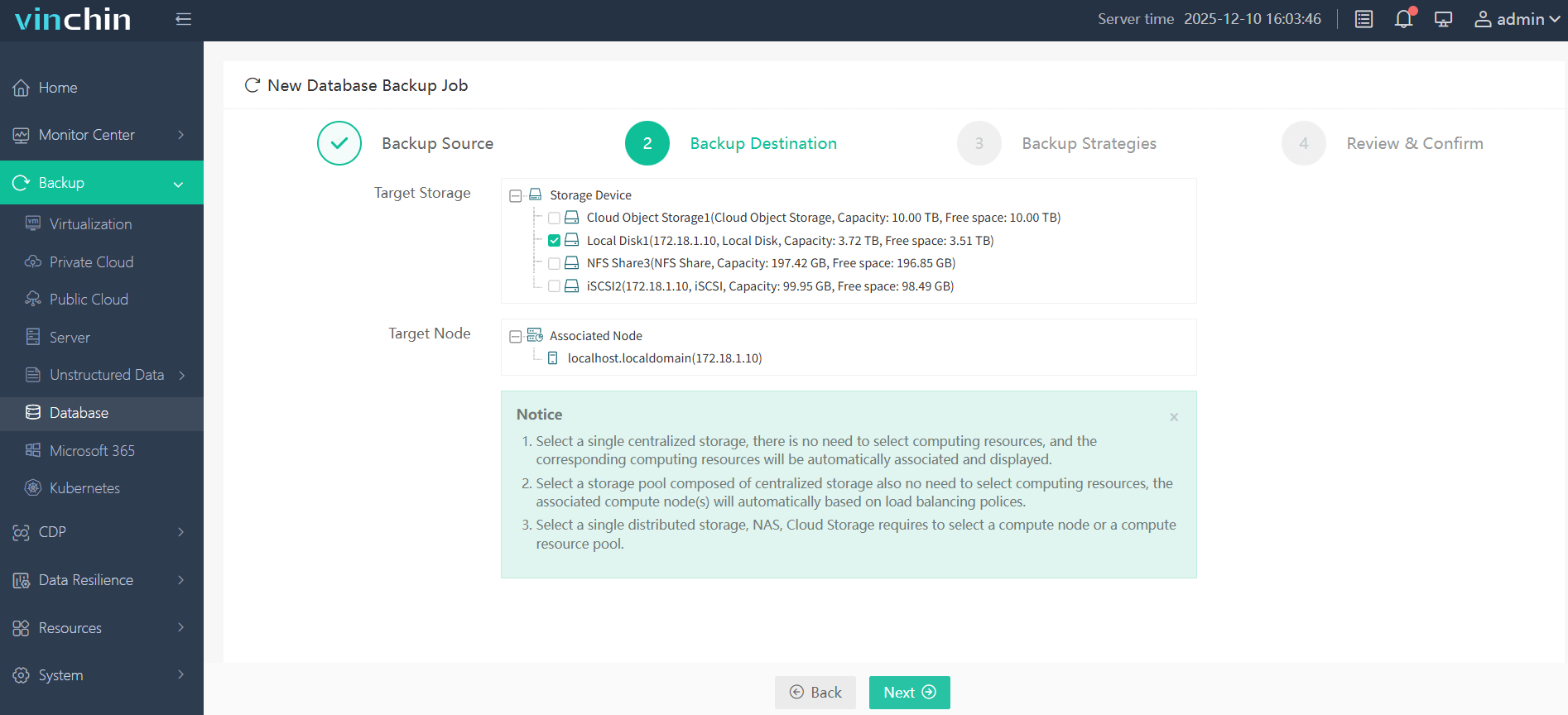
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
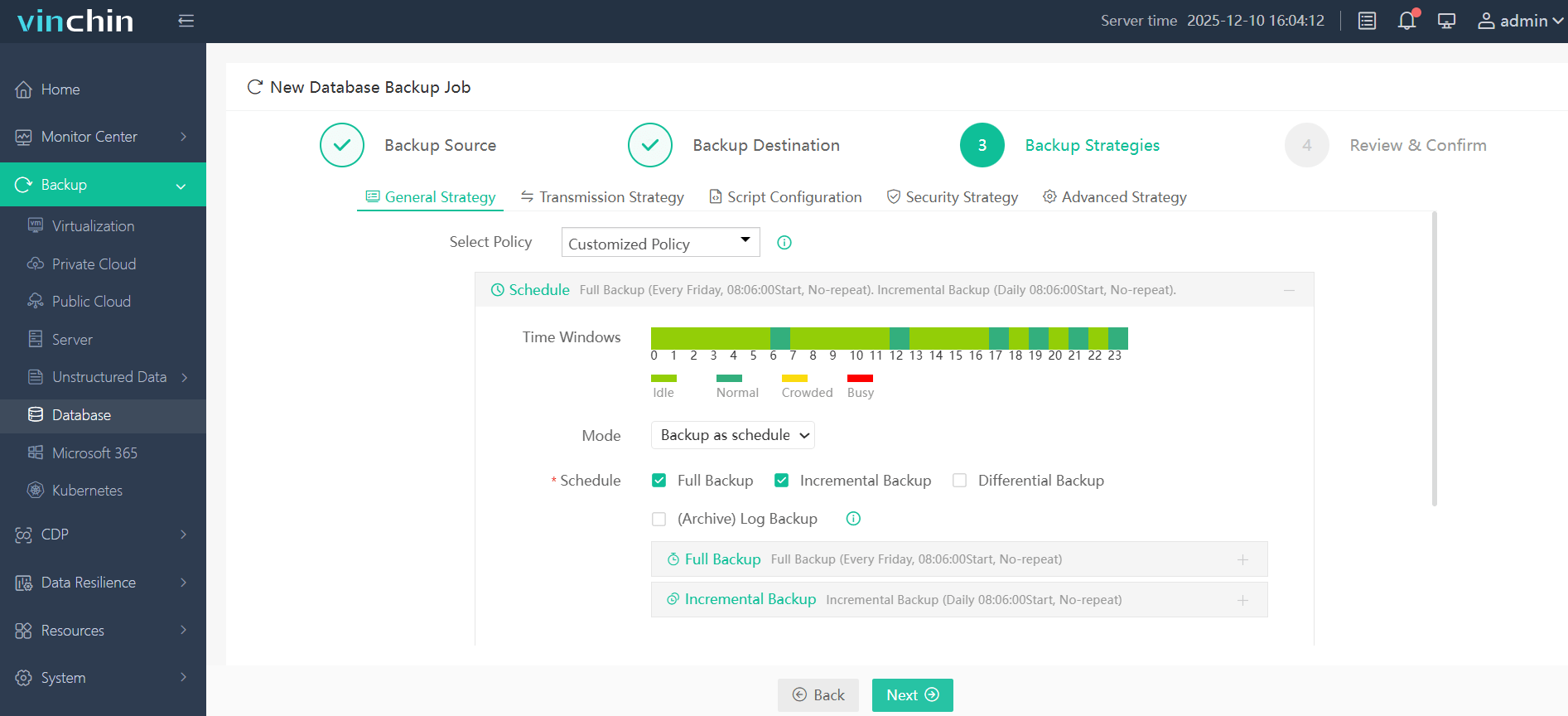
Step 4. Submit the job
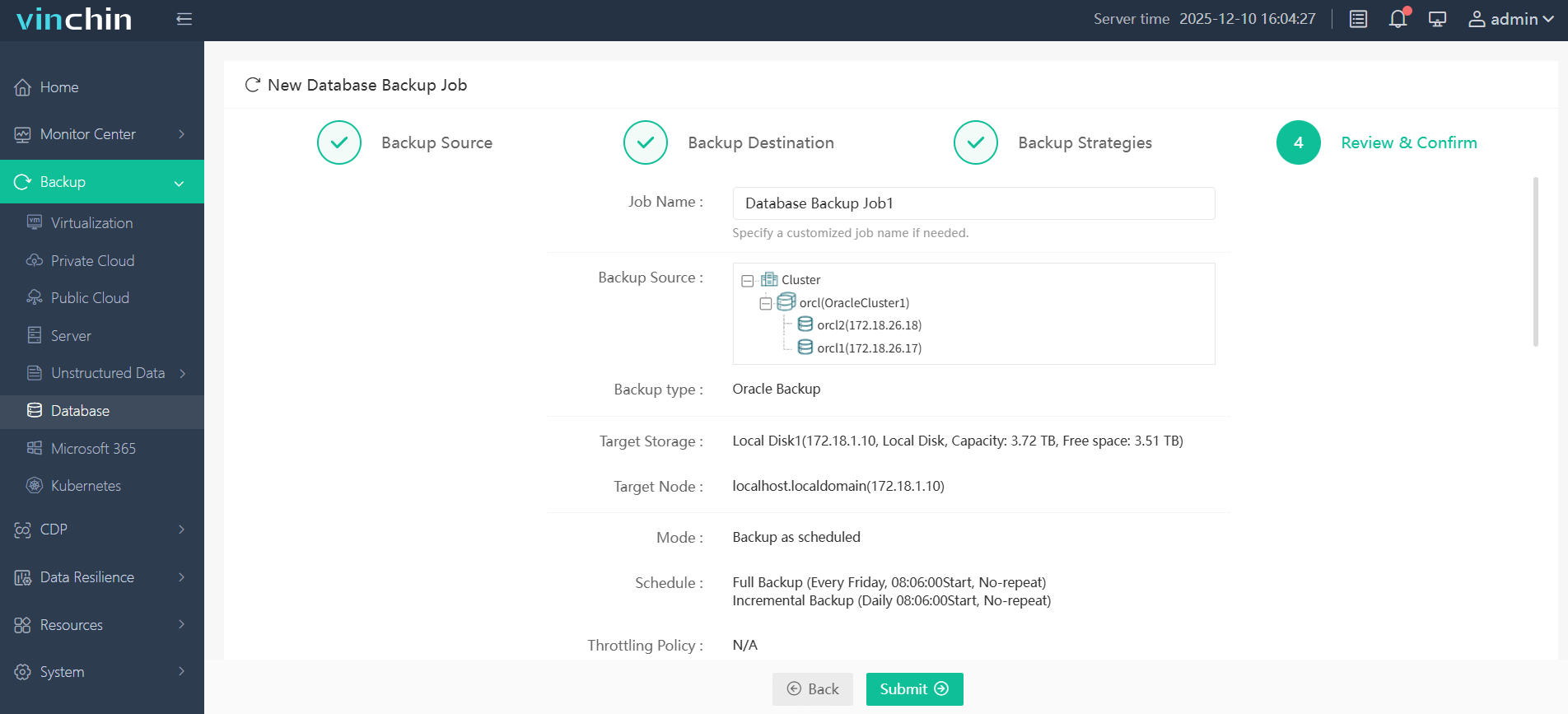
Recognized worldwide for its reliability and customer satisfaction ratings,Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured free trial lasting 60 days so IT teams everywhere can experience its benefits firsthand—click download now to get started!
RMAN Compressed Backup FAQs
Q1: Can I schedule automatic verification of my compressed backups?
Yes; use VALIDATE commands within scheduled scripts or configure periodic RESTORE VALIDATE jobs in RMAN maintenance plans.
Q2: Should I compress before encrypting my backups?
Yes; always apply COMPRESSION before ENCRYPTION since encrypted data does not compress well afterward maximizing space savings this way.
Q3: How much additional CPU should I expect when enabling BASIC versus HIGH compression?
Expect minimal impact with BASIC usually under 10% increase while HIGH may consume up to 40% more CPU depending on workload test both outside peak hours first.
Conclusion
Using RMAN compressed backup helps reduce both storage needs and network traffic while protecting critical databases efficiently—it’s easy once configured properly! For even greater flexibility consider trying Vinchin’s robust enterprise-grade solution trusted worldwide by IT professionals everywhere
Share on:






