-
What Is Hyper-V Boot Failure?
-
Why Hyper-V Boot Failure Happens?
-
Method 1: Fixing Hyper-V Boot Failure via Safe Mode
-
Method 2: Repairing Virtual Hard Disk Errors in Hyper-V
-
How to Back Up Hyper-V Virtual Machines with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Hyper-V Boot Failure FAQs
-
Conclusion
Microsoft Hyper-V is a trusted virtualization platform used by organizations worldwide. Yet even reliable systems can face problems like hyper-v boot failure—a situation where a virtual machine (VM) refuses to start its operating system. This issue can halt business processes and frustrate IT teams. Let’s explore what causes this problem, how to fix it at different skill levels, ways to prevent it in the future, and why regular backups are essential.
What Is Hyper-V Boot Failure?
A hyper-v boot failure means your VM cannot load its guest operating system as expected. Instead of seeing Windows or Linux start up normally inside your VM window, you might encounter error messages such as “Boot failure. Reboot and Select proper Boot device,” “No bootable device found,” or specific codes like 0xC000000F indicating BCD corruption (Microsoft Docs). These errors signal that something is blocking the VM from finding or loading its required startup files—whether due to configuration mistakes or underlying disk issues.
Both new VMs during initial setup and long-running production VMs can experience these failures if their settings change or files become damaged.
Why Hyper-V Boot Failure Happens?
Understanding why hyper-v boot failure occurs helps you troubleshoot faster when every minute counts. Here are common reasons:
Incorrect Boot Order: If your VM tries to start from an empty DVD drive or network instead of its hard disk, it cannot find an OS.
Corrupted Boot Configuration Data (BCD): The BCD tells Windows where to find startup files; if it’s missing or damaged (often showing error code 0xC000000F), the VM fails to boot.
Inactive Partition: For Generation 1 VMs using BIOS emulation with MBR disks, the partition holding Windows must be marked active.
Generation Mismatch: Attaching a Generation 1 virtual hard disk (VHD) to a Generation 2 VM—or vice versa—can cause incompatibility since Gen2 uses UEFI while Gen1 uses BIOS.
Hardware Compatibility Issues: If assigned virtual hardware doesn’t match what your guest OS expects—such as Secure Boot enabled on unsupported systems—the result may be a failed startup.
Missing/Misconfigured Virtual Hard Disk: If you detach the wrong VHD file or point your VM at an empty one by mistake, there’s nothing for it to load.
Host-Level Storage Problems: Sometimes storage outages on the host server make VHDs temporarily unavailable until resolved.
Method 1: Fixing Hyper-V Boot Failure via Safe Mode
Safe Mode loads only basic drivers and services so you can diagnose software-related problems without interference from third-party tools or recent updates gone wrong.
To enter Safe Mode on a non-starting Hyper-V VM:
1. Attach a Windows installation ISO file to your VM’s DVD drive using Hyper-V Manager while the VM is powered off.
2. Start the VM; press any key quickly if prompted so it boots from DVD instead of hard disk.
3. On Windows Setup screen select Next, then click Repair your computer at bottom left.
4. Choose Troubleshoot, then select Advanced options, followed by Startup Settings.
5. Click Restart; when options appear choose number key (4) for Safe Mode entry.
Method 2: Repairing Virtual Hard Disk Errors in Hyper-V
Many hyper-v boot failures trace back to corrupted virtual disks or misconfigured attachments within the VM settings panel itself—especially after sudden host shutdowns or failed migrations between storage pools.
First verify correct disk attachment:
Right-click affected VM in Hyper-V Manager > select Settings > expand menu under “Hard Drive” > confirm path points at intended .vhd/.vhdx file—not an old snapshot nor empty placeholder file by mistake!
Check boot order next:
In same Settings window go under “Firmware” section;
ensure main hard drive appears first above CD/DVD drives
and network adapters unless intentionally doing PXE/network installs instead of local boots.
How to Back Up Hyper-V Virtual Machines with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
To further safeguard against data loss caused by hyper-v boot failure events, leveraging robust backup solutions is critical for business continuity. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional enterprise-level solution supporting over 15 mainstream virtualization platforms—including full support for Microsoft Hyper‑V alongside VMware, Proxmox VE, oVirt/RHV/OLVM/XCP-ng/XenServer/OpenStack/ZStack/KVM/FusionCompute/H3C CAS/UIS and more—making it suitable for diverse hybrid environments found in modern datacenters.
For protecting Hyper‑V workloads specifically, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers powerful features such as forever incremental backup, granular restore capabilities down to individual files within a backup set, efficient data deduplication and compression technologies that optimize storage usage and speed up transfers, scheduled backup automation with flexible retention policies including GFS strategy support for compliance needs—all designed to ensure rapid recovery while minimizing resource consumption across large-scale deployments.
The intuitive web console of Vinchin Backup & Recovery streamlines operations into four straightforward steps:
Step 1: Select the Hyper-V VM to back up.
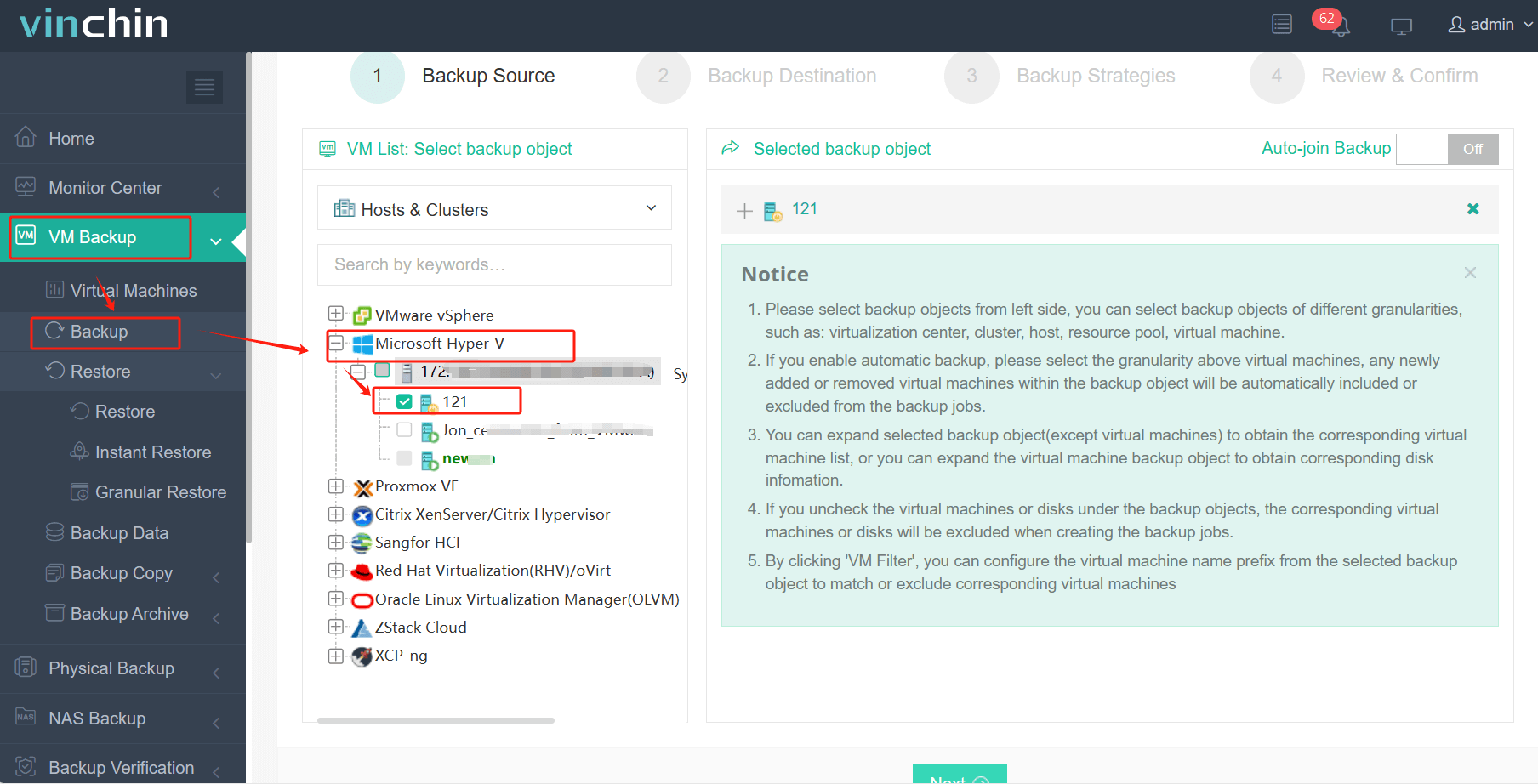
Step 2: Choose the backup storage.
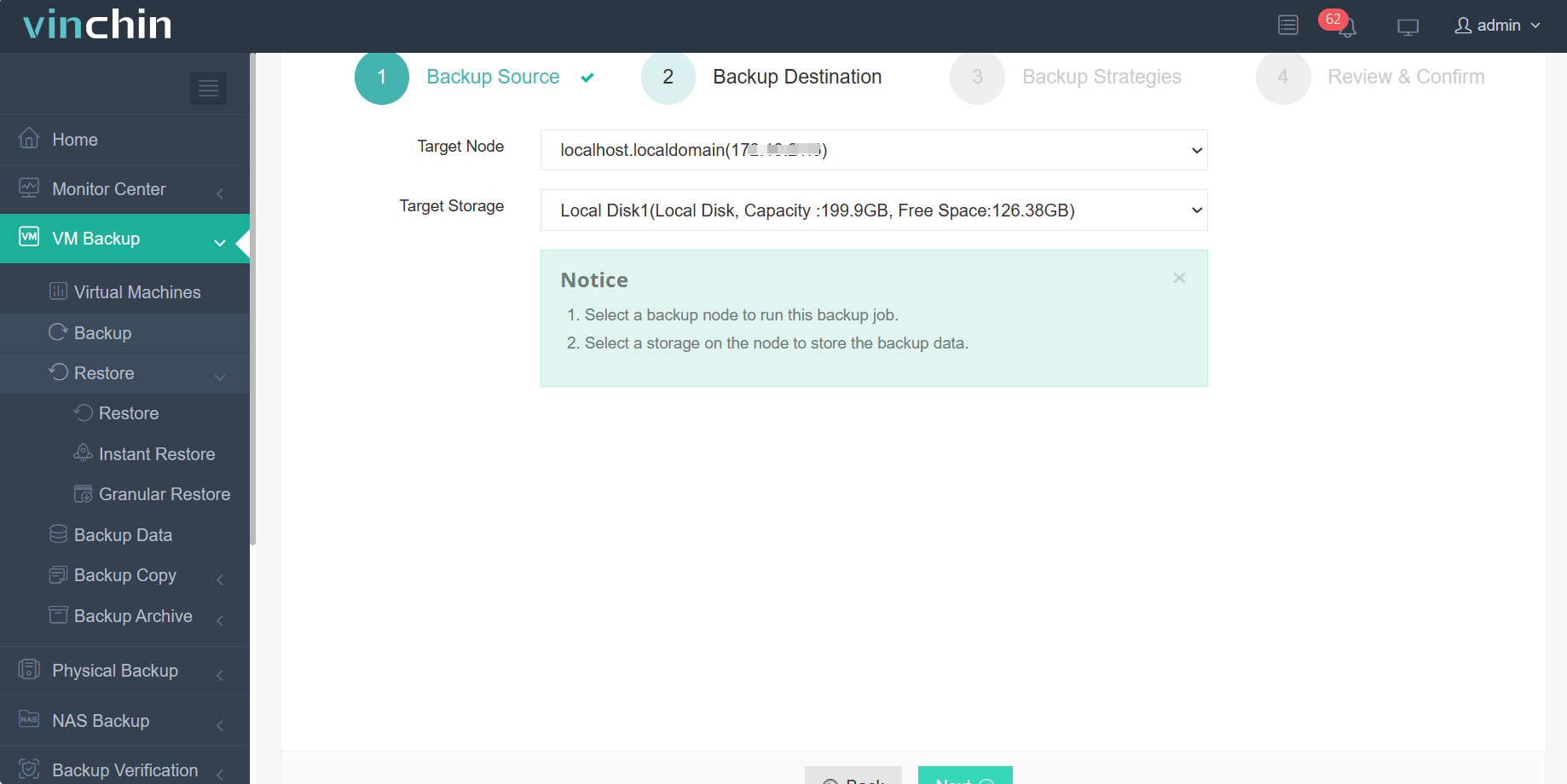
Step 3: Configure the backup strategy.
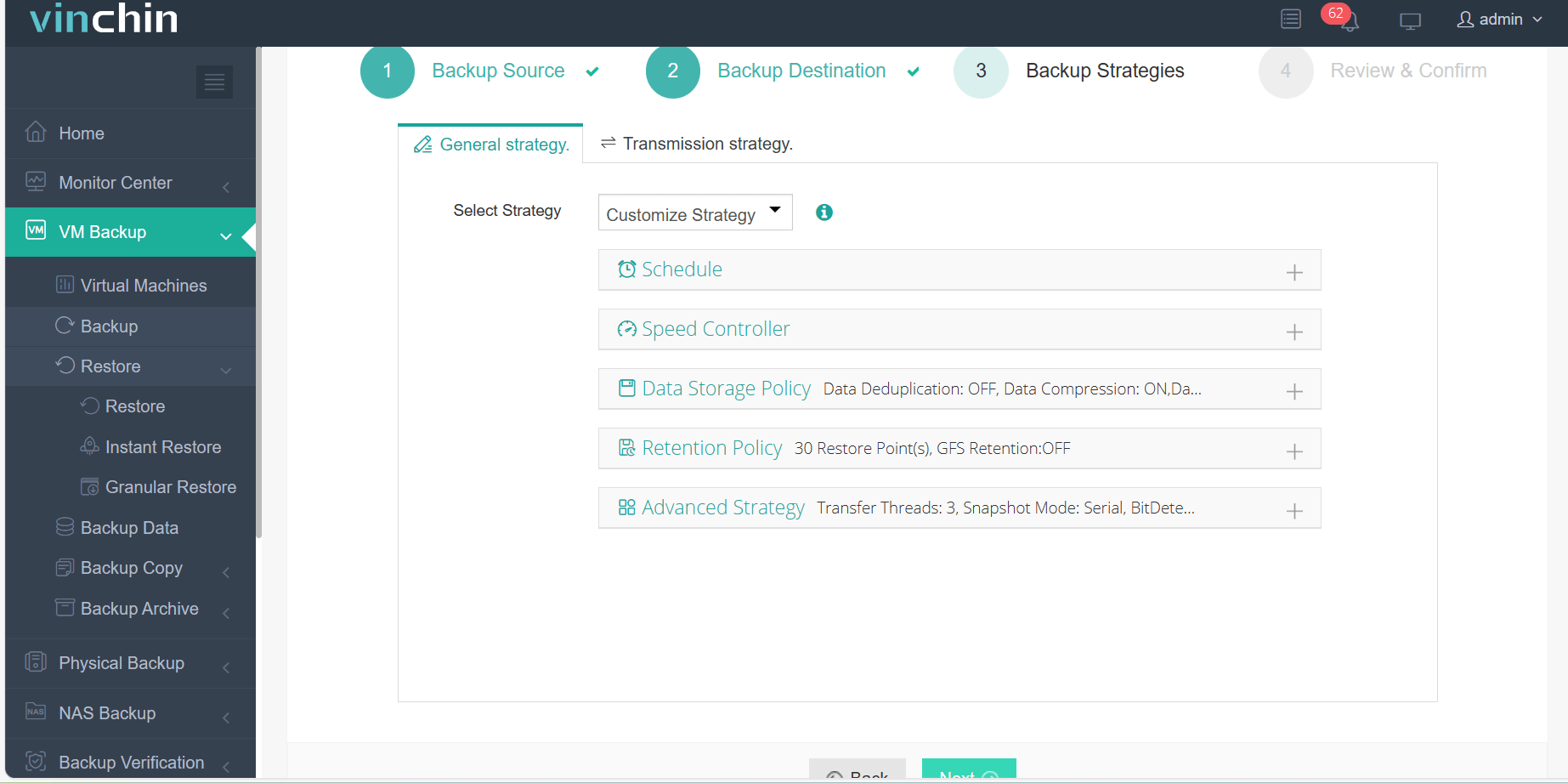
Step 4: Submit the job.
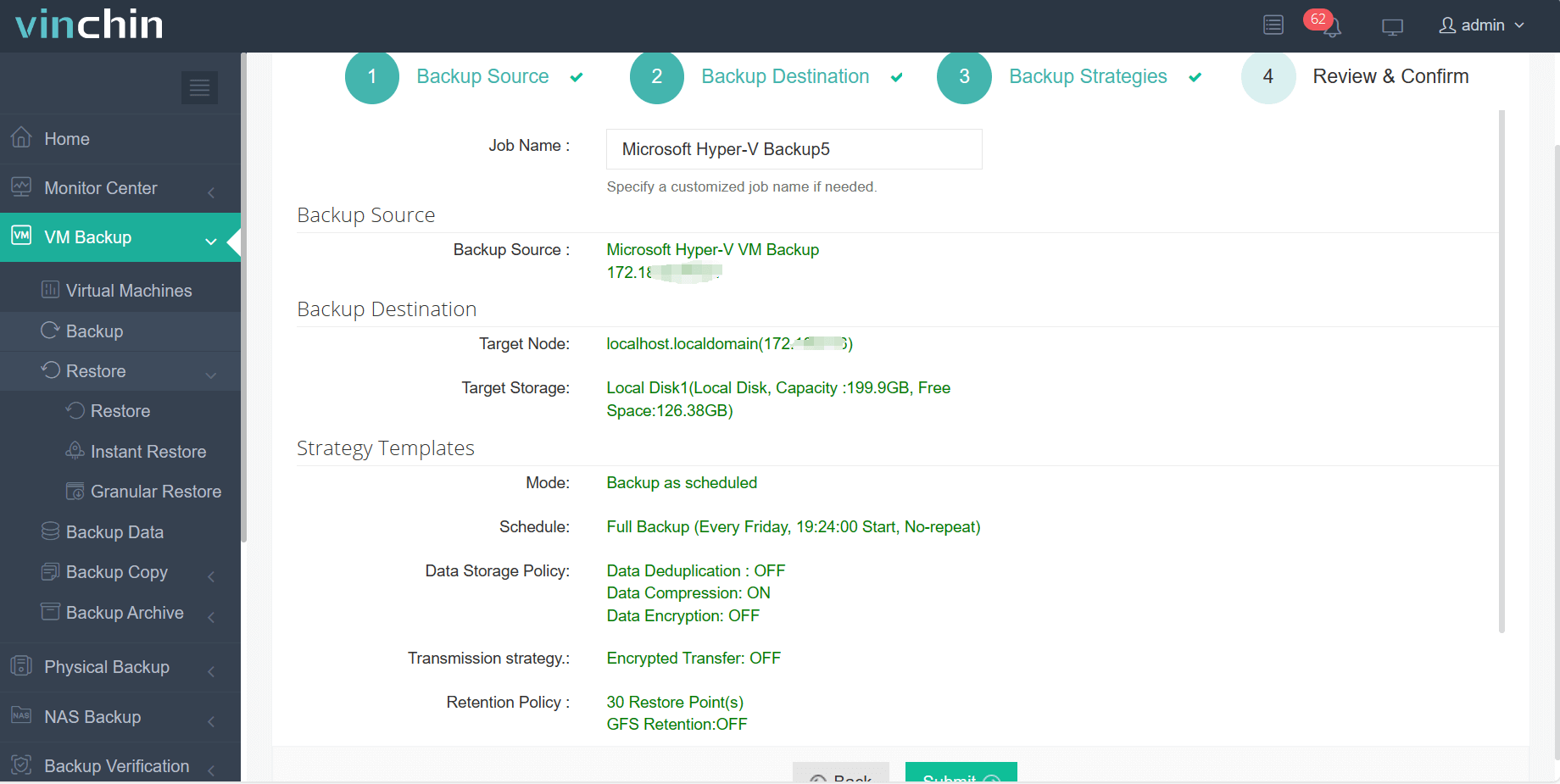
Recognized globally with top ratings among enterprise users across industries—and trusted by thousands worldwide—you can experience all features free for 60 days; click below to download Vinchin Backup & Recovery now!
Hyper-V Boot Failure FAQs
Q1: My Generation 2 Hyper-V VM fails with "Secure Boot violation." What should I do?
Disable Secure Boot under Firmware settings if guest OS does not support UEFI Secure Boot feature natively.
Q2: After updating my host server's firmware my VMs won't start anymore—is this related?
Yes; check that updated BIOS/UEFI settings still match original configuration required by each affected virtual machine profile before restarting them again successfully!
Q3: Can I script regular checks for possible hyper-v boot failure risks?
Yes; use PowerShell cmdlets like Get-VM | Get-VMFirmware | Format-Table Name,BootOrder regularly then review output logs manually.
Conclusion
Hyper‑v boot failure disrupts business but most cases are fixable with methodical troubleshooting—from Safe Mode repairs through advanced log analysis techniques described above! Always keep current backups handy; Vinchin makes protecting/restoring critical workloads simple no matter what goes wrong behind-the-scenes!
Share on:








