-
What is RDM?
-
How to migrate VM with RDM?
-
Method 1. vMotion
-
Method 2. Cold Migration
-
Method 3. Storage vMotion
-
Enhancing VM migration with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Migrate VM with RDM FAQs
-
Conclusion
What is RDM?
RDM stands for Raw Device Mapping and is a special configuration in the VMware virtualization environment. It allows VMs to access storage devices directly, rather than through virtual disk files. In short, RDM provides a way for VMs to connect directly to physical storage rather than brokering it through the virtualization layer. This direct access allows some applications and scenarios, such as databases or specific storage performance requirements, to run more efficiently in a virtualized environment.
How to migrate VM with RDM?
When you need to migrate virtual machines with RDM, you need to give special consideration on how to handle RDM to ensure data continuity and accessibility. You may need to choose a migration method that is appropriate for your situation and ensure that RDM is handled correctly during the migration process.
When migrating VMware VMs with RDM, you can choose from methods such as hot migration (vMotion), cold migration, or storage migration (Storage vMotion). These migration methods automatically process the RDM and ensure that the data for the RDM is smoothly migrated to the new location during the migration process to ensure that the VMs can function properly in the new environment.
Method 1. vMotion
Hot migration (vMotion) is a method of migrating a VM from one physical host to another, where the VM remains in a running state during the migration process. During a hot migration, the system automatically handles the RDM and ensures that the data from the RDM migrates smoothly to the new location. This means that VMs have continuous access to RDM-stored data without interruption during the migration process.
Benefits: No downtime, smooth migration process, low impact on VM services.
1. In vCenter, locate the VM to be migrated and ensure that the target host has been added to the same cluster
2. Right-click the VM > choose Migrate > Migrate to Another Host
3. In the migration wizard, select the target host and follow the prompts to complete the migration process
Method 2. Cold Migration
Cold migration is a method of moving a virtual machine from one physical host to another while the virtual machine is powered off throughout the entire migration process. For migrating VM with Raw Device Mapping, cold migration can smoothly relocate them to a new physical host while maintaining the connectivity of RDM without any changes.
Benefits: Simple and reliable, suitable for scenarios where migration during runtime is not possible.
1. In vCenter, power off the VM you want to migrate.
2. Right-click the VM > select Migrate > Move to Another Datastore
3. In the migration wizard, choose the target datastore, and follow the prompts to complete the migration process
Method 3. Storage vMotion
Storage vMotion allows you to migrate the storage location associated with a virtual machine from one storage device to another while the virtual machine is running, without interrupting its service.
Benefits: No downtime required, only storage location is migrated, minimal impact on VM service, and flexibility to adjust VM storage layout between different storage devices.
1. In vCenter Server, right-click the VM > select Migrate > Storage vMotion
2. In the migration wizard, choose the target datastore > select options such as whether to change disk format
3. Follow the prompts to complete the migration process
Enhancing VM migration with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
In addition to using the migration method provided by VMware, it is recommended to consider using a third-party backup software such as Vinchin for the VM migration. Vinchin Backup & Recovery not only enables backup and recovery of VMs, but also serves as a migration tool to migrate VMs.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery provides migration solutions across multiple virtualization platforms including VMware, XenServer, Proxmox, and more than 10 other platforms. By using Vinchin for VM migration, users can easily move VMs from one platform to another, increasing the flexibility and scalability of their IT environments.
Here's how to use Vinchin to migrate VM from VMware to Proxmox:
1. Just select the backup of VMware VM > click Next
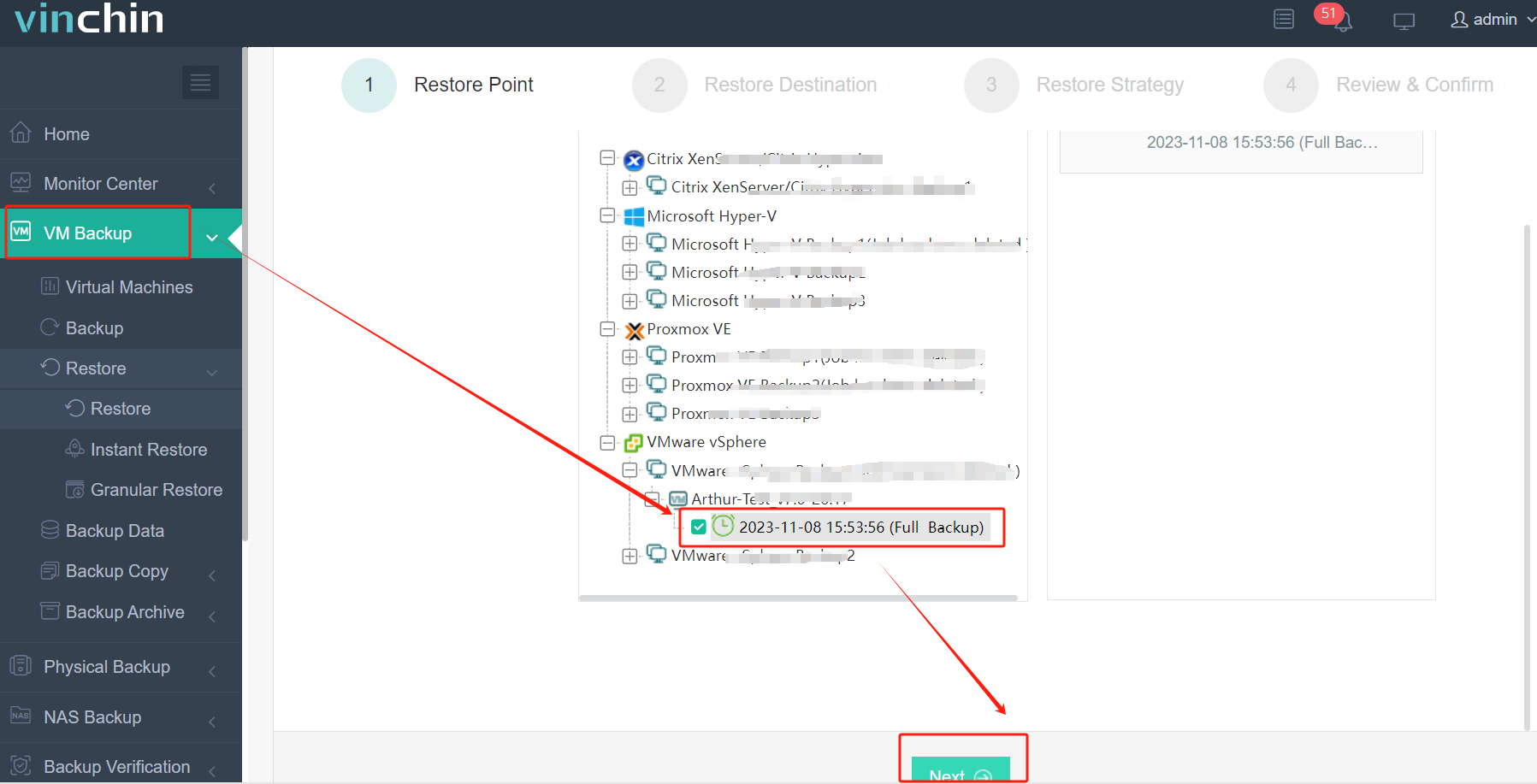
2. Select the Proxmox host as the target host > click Next
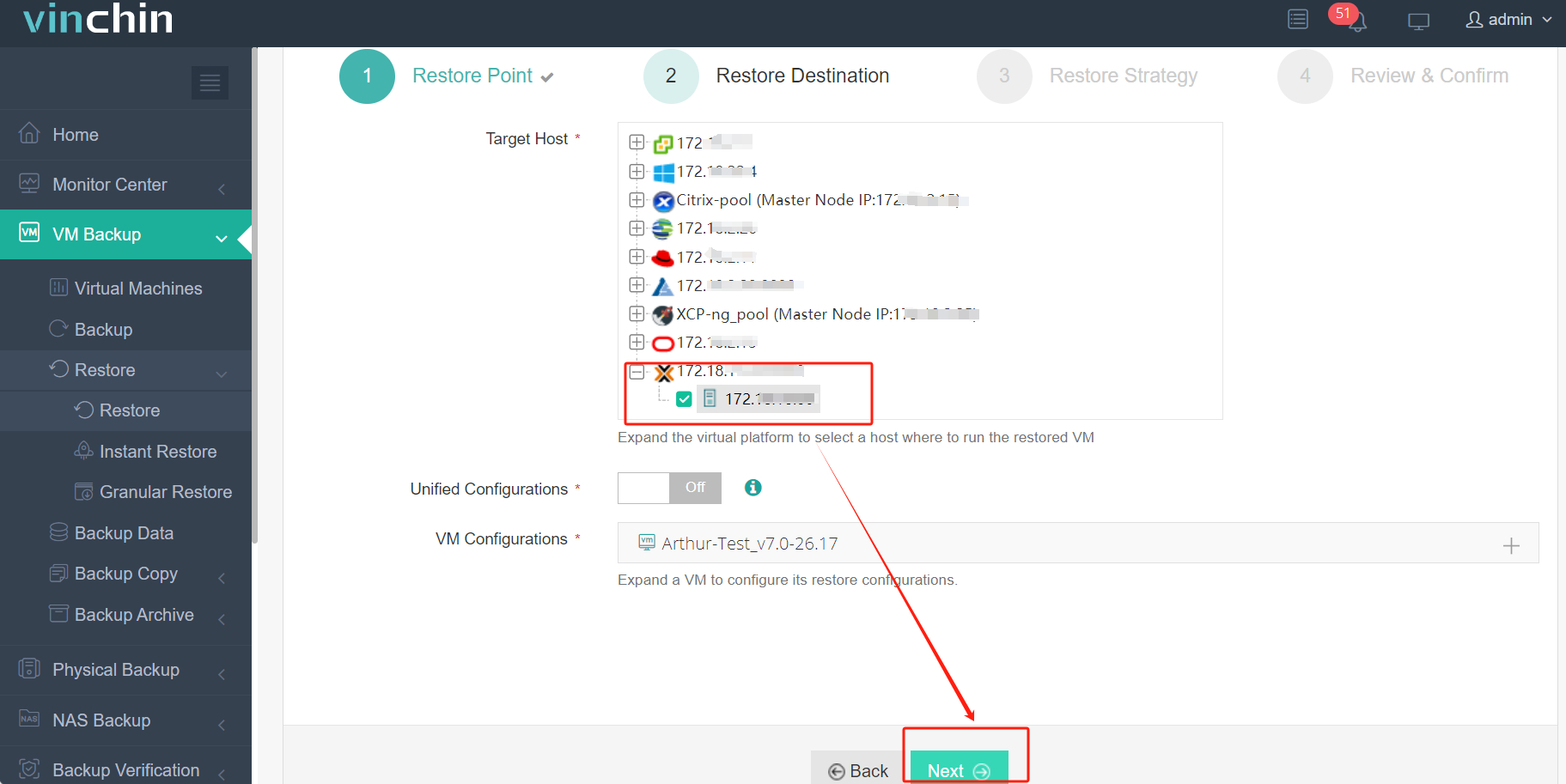
3. Select Once-off Restore > click Next
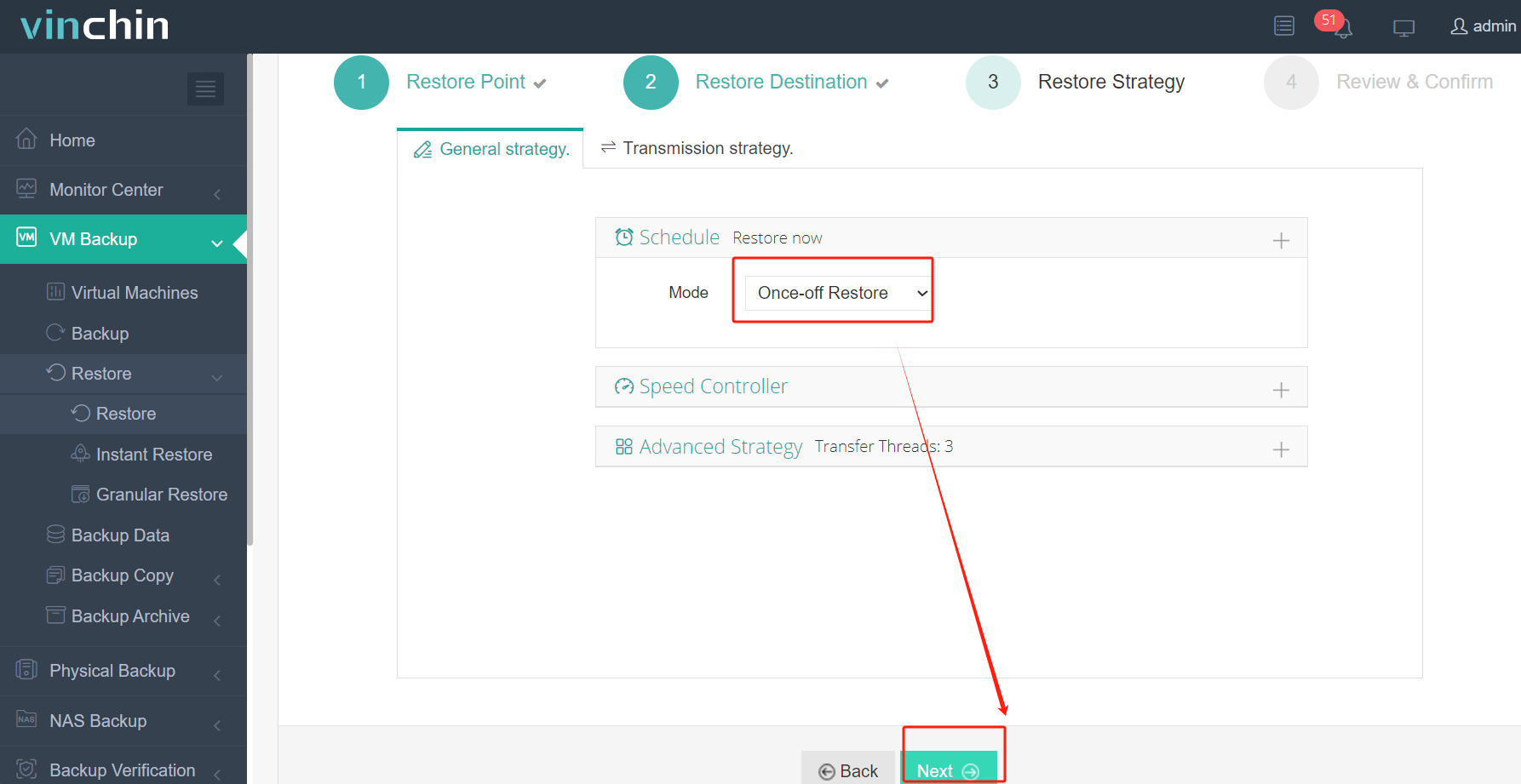
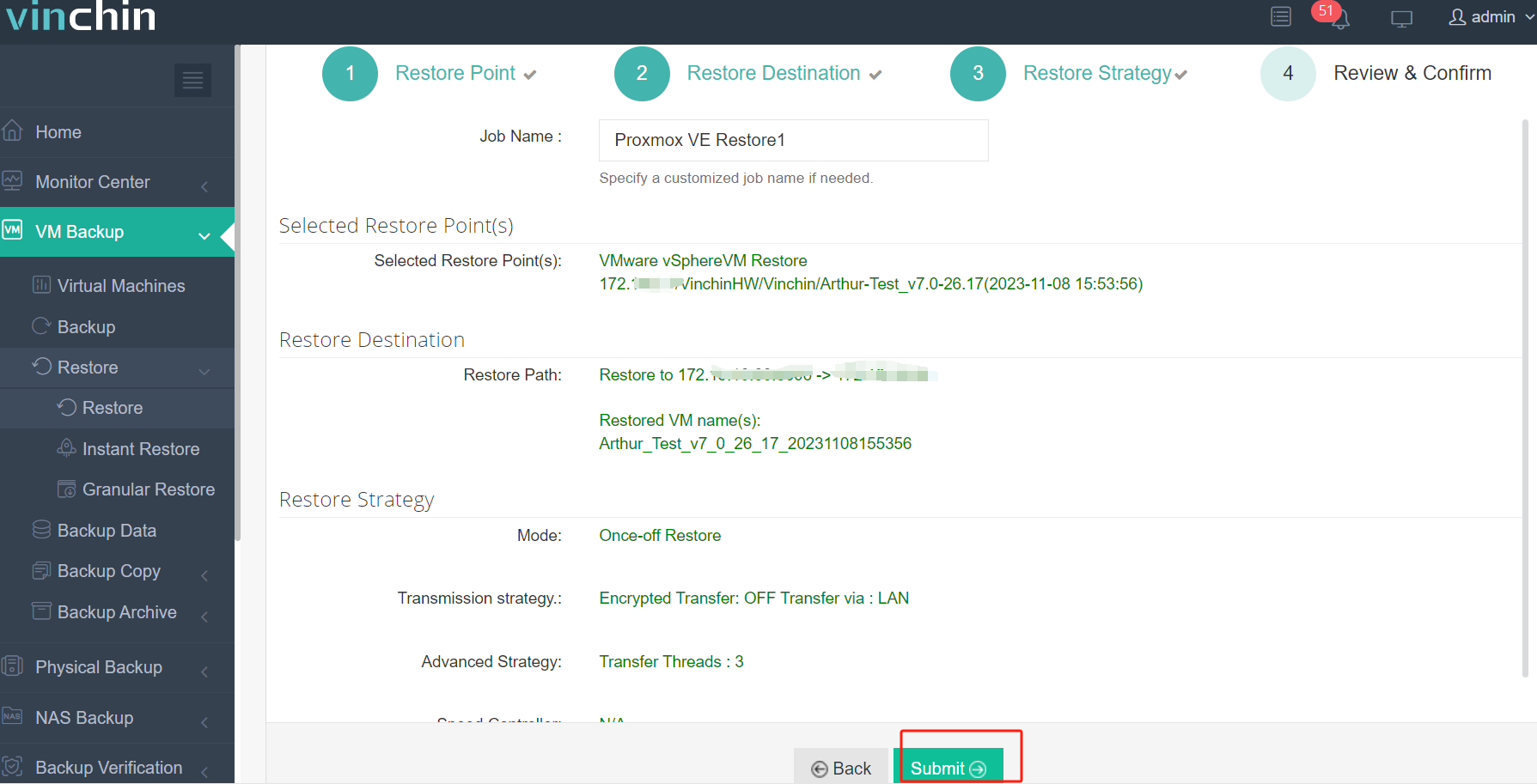
4. Submit the job
Besides, Vinchin offers a free 60-day trial for users to experience the functionality in a real-world environment. For further details, please reach out to Vinchin directly or contact our local partners for assistance.
Migrate VM with RDM FAQs
Q1: What precautions should I take before migrating VMware VM with RDM?
A1: It's essential to thoroughly plan the migration and test it in a non-production environment before performing it in production. Back up critical data and ensure that all prerequisites are met to avoid potential issues.
Q2: Are there any post-migration tasks for VMs with RDM?
A2: After migrating a VM with Raw Device Mapping, verify that the RDM mappings are correctly configured and that the VM operates as expected. Perform any necessary post-migration validation and testing to ensure a successful migration.
Conclusion
RDM, or Raw Device Mapping, provides VMs direct access to storage devices in VMware environments, enhancing performance for specific applications. Migrating VMware VMs with RDM requires careful handling. Methods like vMotion, Storage vMotion, or cold migration ensure smooth transitions while maintaining data integrity and accessibility. Consider augmenting migration with tools like Vinchin Backup & Recovery for added flexibility and scalability across multiple virtualization platforms.
Share on:








