-
What Is Red Hat Kubernetes?
-
Why Choose Red Hat Kubernetes?
-
How to Deploy Red Hat Kubernetes with OpenShift?
-
How to Deploy Vanilla Kubernetes on RHEL?
-
Protecting Your Kubernetes Environment with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Red Hat Kubernetes FAQs
-
Conclusion
Kubernetes is now essential in IT operations worldwide. It automates how you deploy, scale, and manage containerized applications across clusters of servers. But what happens when your business needs more than just open source? That’s where Red Hat comes in—with enterprise-grade solutions that make Kubernetes ready for production workloads everywhere. Curious how it works? Let’s explore red hat kubernetes from basics to advanced protection.
What Is Red Hat Kubernetes?
Red hat kubernetes refers to the set of enterprise-ready Kubernetes offerings from Red Hat. At its core is OpenShift—a platform built on upstream Kubernetes but enhanced with security, automation, and management tools designed for business-critical environments.
Red Hat OpenShift gives you a tested distribution of Kubernetes plus extra features like integrated monitoring, developer tools, automated upgrades, and commercial support. This means you can run containers at scale—on-premises or in any cloud—with confidence that your platform is secure and reliable.
Some organizations also choose to run “vanilla” (unmodified) Kubernetes directly on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). This approach offers flexibility but requires more manual setup and maintenance compared to OpenShift’s streamlined experience.
OpenShift vs. Vanilla Kubernetes
It helps to understand the difference between these two approaches:
OpenShift delivers an opinionated stack—Kubernetes bundled with extras like a web console (OpenShift Console), built-in CI/CD pipelines (Pipelines), OperatorHub integration, strict security defaults (SELinux enforcement), automatic updates via Cluster Version Operator, and official support from Red Hat engineers.
Vanilla Kubernetes on RHEL is closer to upstream open source code. You install components like kubelet, kubeadm, and kubectl yourself using system packages or binaries. You get full control but also take responsibility for networking plugins, storage drivers, upgrades, monitoring setup—and troubleshooting when things go wrong.
Which should you choose? If you want rapid deployment with less risk—and expert help when needed—OpenShift is often best for enterprises. If you need maximum customization or want to experiment hands-on with every component, vanilla may suit smaller teams or test labs better.
Why Choose Red Hat Kubernetes?
Choosing red hat kubernetes isn’t just about running containers—it’s about building a foundation your business can trust as it grows into hybrid cloud operations.
Let’s break down why so many organizations rely on this platform:
Security Features
Security is baked into every layer of red hat kubernetes solutions:
SELinux integration enforces strong isolation between workloads by default.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) lets you define who can access what resources within your cluster.
Network policies restrict traffic between pods based on labels or namespaces—helping prevent lateral movement during attacks.
Built-in image scanning checks container images against known vulnerabilities before they’re deployed.
These features mean fewer surprises—and faster compliance audits—for regulated industries like finance or healthcare.
Automation Benefits
Manual cluster management takes time away from innovation. With red hat kubernetes platforms:
Automated installers handle complex tasks such as configuring networking layers (OVN-Kubernetes, Calico) or setting up persistent storage classes right out of the box.
Over-the-air updates let you patch clusters safely without downtime using tools like the Cluster Version Operator in OpenShift.
Operators automate lifecycle management of databases, caches, monitoring stacks—you name it—so admins spend less time firefighting routine issues.
Enterprise Support & Hybrid Cloud Flexibility
When problems arise—or when scaling up fast matters—you want backup from experts who know both Linux internals and cloud-native architectures:
Commercial support means access to 24x7 help desks staffed by certified professionals who resolve issues quickly.
Certified integrations ensure compatibility across major clouds (AWS/GCP/Azure), bare metal servers—even edge devices running RHEL CoreOS.
Unified management lets teams operate multiple clusters through one interface using tools like Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management—ideal for hybrid/multi-cloud strategies.
Want proof? Many global banks have adopted OpenShift because its security controls meet strict regulatory requirements while still enabling agile development practices—a rare combination!
How to Deploy Red Hat Kubernetes with OpenShift?
Deploying red hat kubernetes through OpenShift streamlines setup while giving you robust automation out-of-the-box. Here’s how most administrators get started—from planning through first login:
Infrastructure Preparation
Before installing OpenShift Container Platform (OCP), review hardware specs:
Minimum 4 CPUs per node
At least 16 GB RAM per node
Reliable network connectivity among nodes
Check official docs for updated requirements based on your chosen version/platform (bare metal vs public cloud).
You’ll also need:
1. A valid Red Hat subscription
2. DNS records configured so cluster nodes can resolve each other
3. Firewall ports opened as specified by OCP documentation
4. Optional: Load balancer if deploying highly available control plane nodes
Step-by-Step Deployment Process
1. Download the latest installer from the Red Hat Customer Portal.
2. Extract installer files onto your jump host/server; log in via SSH as root/admin user.
3. Run ./openshift-install create cluster then follow prompts:
Enter pull secret from portal
Specify base domain/DNS zone
Select infrastructure type (AWS, bare metal etc.)
Set number of worker/master nodes
4. Wait while installer provisions VMs/nodes automatically—including OS installation if using RHEL CoreOS images provided by Red Hat!
5. Once complete: retrieve kubeadmin password shown at end of install log file (auth/kubeadmin-password)
6. Access web console at https://<cluster-api-url>:6443 using browser; log in as kubeadmin user
7. Configure persistent storage classes via Storage menu; set up ingress controllers under Networking tab; assign users/groups permissions under Administration > Users menu
For advanced setups:
Integrate external identity providers under Administration > Authentication menu
Enable additional Operators via OperatorHub catalog inside web console
How to Deploy Vanilla Kubernetes on RHEL?
Running vanilla red hat kubernetes gives full control—but demands careful attention during setup! Here’s how experienced admins roll out clusters step-by-step:
Initial Setup & Package Installation
Start by preparing each node:
1. Update system packages (sudo yum update)
2. Disable swap (sudo swapoff -a) since kubelet won’t start otherwise!
3. Set SELinux mode permissive temporarily if troubleshooting startup issues (setenforce 0)
4.Add official repo file /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo containing:
[kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.x/rpm/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.x/rpm/repodata/repomd.xml.key
5.Install core components:
sudo yum install kubelet kubeadm kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes sudo systemctl enable --now kubelet
Cluster Initialization & Networking Configuration
On master/control-plane node:
1.Initialize cluster specifying pod network CIDR range:
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
2.Configure admin credentials so kubectl works non-root:
mkdir ~/.kube && sudo cp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf ~/.kube/config && sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) ~/.kube/config
3.Deploy pod network plugin—for example Flannel:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/releases/latest/download/kube-flannel.yml
(Or substitute Calico/Cilium YAML manifests depending on preference)
4.Join worker nodes using token printed after kubeadm init, e.g.:
sudo kubeadm join <master-ip>:6443 --token <token> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:<hash>
To verify health run kubectl get nodes,pods --all-namespaces. All should show Ready status before deploying apps!
Protecting Your Kubernetes Environment with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Once your Kubernetes environment is operational, ensuring comprehensive data protection becomes critical for business continuity and compliance needs in modern IT landscapes.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional enterprise-level solution purpose-built for safeguarding Kubernetes workloads at scale. Among its extensive capabilities are full/incremental backups; fine-grained restore options by cluster, namespace, application, PVC or resource; policy-based scheduling alongside one-off jobs; encrypted transmission; cross-cluster/cross-version recovery—even migration across heterogeneous storage backends—and much more.
The intuitive Vinchin Backup & Recovery web console makes protecting red hat kubernetes straightforward:
1. Simply select your backup source (cluster/workloads)

2. Choose target storage location (local/NAS/cloud/object storage)
3. Define strategy parameters such as schedule/frequency/policy settings
4. Then submit the job—all within four guided steps tailored specifically for K8S environments.
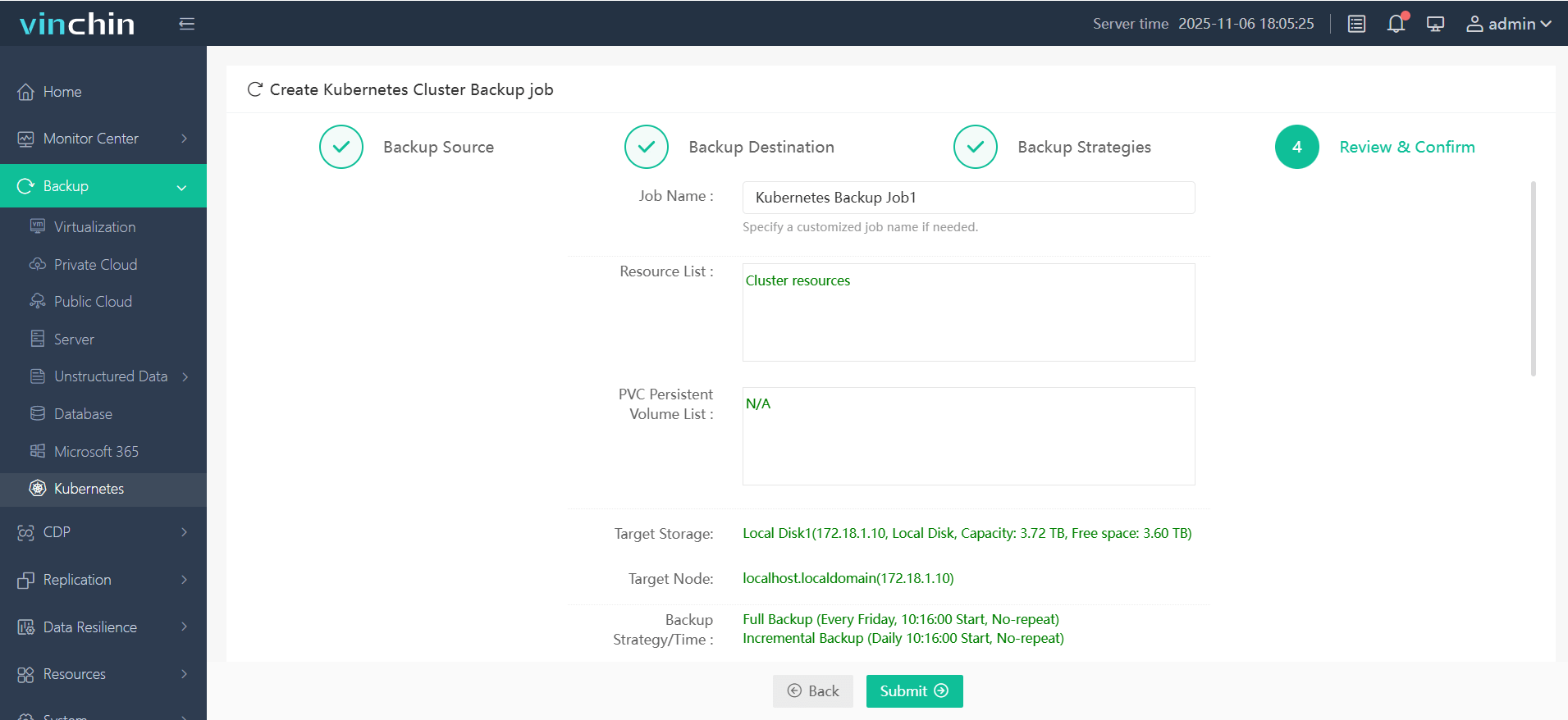
Recognized globally with top ratings among enterprise customers, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured 60-day free trial. Download now to experience trusted data protection used by leading businesses worldwide!
Red Hat Kubernetes FAQs
Q1: Can I migrate my existing Docker Compose apps into an OpenShift-based red hat kubernetes cluster?
Yes; convert Compose files into standard K8s manifests using tools like Kompose then deploy them via the web console or oc apply.
Q2: My vanilla red hat kubernetes pods are stuck Pending after install—what should I check first?
Verify that your pod network add-on was applied correctly; use kubectl get pods --all-namespaces then inspect events/logs for CNI errors before redeploying Flannel or Calico YAML manifests if needed.
Q3: How do I grant temporary admin rights in an emergency?
Use kubectl create clusterrolebinding temp-admin-binding --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=<username> then remove binding once resolved.
Conclusion
Red hat kubernetes brings together security, automation, and expert support so businesses can run containers anywhere confidently—from data center racks to public clouds worldwide. For reliable backup tailored specifically for these environments, Vinchin delivers powerful protection. Try their free trial today!
Share on:







