-
What Is RMAN Duplicate From Active Database?
-
Why Use RMAN Duplicate From Active Database?
-
Method 1: Duplicating With Command Line
-
Method 2: Duplicating With Scripts
-
How to Back Up Oracle Databases With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
RMAN Duplicate From Active Database FAQs
-
Conclusion
Cloning an Oracle database is a routine task for many administrators. Whether you want to set up a test environment, refresh development data, or migrate workloads to new hardware, you need a method that is both reliable and efficient. RMAN Duplicate From Active Database offers a fast way to create an exact copy of your running Oracle database with minimal fuss. In this guide, we’ll break down what it is, why it matters, and how you can use it at beginner, intermediate, and advanced levels.
What Is RMAN Duplicate From Active Database?
RMAN Duplicate From Active Database is an Oracle feature that allows you to clone a live database directly over the network—no backup files required. Instead of restoring from disk-based backups or tapes, RMAN copies data files straight from the source instance (the primary) to the target (the auxiliary). This process uses either image copies or backup sets but always works directly from the running source. By skipping backup creation and transfer steps, this method saves time while reducing storage needs.
This approach is best suited for environments where both source and target databases run on compatible platforms with matching endianness and Oracle versions.
Why Use RMAN Duplicate From Active Database?
Why pick this method instead of traditional backup-and-restore? First off—it’s faster because there’s no need to generate or move backup files between servers. That means less disk space used on both ends. Second—the source database stays online throughout duplication; users experience no downtime during cloning operations.
Flexibility is another big win: you can duplicate databases onto different hosts or even keep them on the same server by using unique names and directory paths. For many DBAs who need quick environment refreshes or seamless migrations with little disruption, RMAN Duplicate From Active Database stands out as one of the most effective tools available.
Method 1: Duplicating With Command Line
Before diving into commands, let’s cover what must be ready before starting any duplication job.
Prerequisites and Environment Setup
Preparation makes all the difference when duplicating databases:
Both source (primary) and target (auxiliary) servers must have compatible Oracle software installed.
The source database should run in ARCHIVELOG mode.
Ensure both servers can communicate over your network—test connectivity using
tnsping.On each server:
Create necessary directories for data files (
$ORACLE_BASE/oradata/<SID>), redo logs ($ORACLE_BASE/redo), control files ($ORACLE_BASE/controlfile), audit files ($ORACLE_BASE/admin/<SID>/adump), etc.Make sure there’s enough free disk space on the target system for all datafiles plus growth margin.
Confirm that SIDs are unique across both systems to avoid conflicts.
Password File Handling
On your source server:
1. If not already present in $ORACLE_HOME/dbs, create a password file using:
orapwd file=$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/orapw<SID> password=<sys_password>
2. On your target server:
Create a new password file using
orapwdwith exactly the same SYS password as used on the source.Do not simply copy password files between different operating systems due to possible compatibility issues.
Parameter File Preparation
From your source instance:
1. Generate a parameter file (PFILE):
SQL> CREATE PFILE='$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/init<aux_sid>.ora' FROM SPFILE;
2. Transfer this PFILE securely to your target server.
3. Edit it on the target:
Change
DB_NAMEto match your auxiliary SID.Adjust directory paths if needed so they point only at valid locations on your target system.
Set parameters like
CONTROL_FILES,DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT,LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERTif directory structures differ.
Network Configuration
Set up Oracle Net connectivity:
Add TNS entries for both databases in each server's
tnsnames.ora.On your target machine's
listener.ora, configure a static entry for the auxiliary instance SID.Start listeners using lsnrctl start after confirming configuration changes.
Step-by-Step Execution and Validation
Once setup is complete:
1. Start auxiliary instance in NOMOUNT mode using edited PFILE:
sqlplus / as sysdba SQL> startup nomount pfile='$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/init<aux_sid>.ora'; SQL> exit;
2. Connect via RMAN from any host with network access:
rman TARGET sys@<source_tns> AUXILIARY sys@<aux_tns>
Tip: Avoid putting passwords directly in scripts; enter them interactively when prompted or use secure wallet authentication where possible.
3. Run duplication command:
RMAN> DUPLICATE TARGET DATABASE TO <aux_sid> FROM ACTIVE DATABASE NOFILENAMECHECK;
4. Monitor progress within RMAN output window; errors such as "ORA-12514" indicate listener misconfiguration while "ORA-19809" points toward filename conflicts—double-check all path settings if these arise.
5. After completion:
Log into SQL*Plus on auxiliary host,
sqlplus / as sysdba SQL> SELECT name FROM v$database; SQL> SELECT open_mode FROM v$database; SQL> EXIT;
Check physical file locations match expectations by querying v$datafile.
6. Clean up temporary files if needed; update scripts/documentation based on lessons learned during execution.
Method 2: Duplicating With Scripts
For larger environments—or when regular cloning jobs are needed—automation becomes essential.
Automation Techniques & Advanced Options
Automated scripts help standardize processes while reducing manual error risk:
1. Prepare environment just like Method 1: ensure correct password file creation (using orapwd) on target; edit PFILE carefully; confirm robust network connectivity between hosts.
2. Start auxiliary instance in NOMOUNT mode as before.
3. Write an RMAN script (duplicate_db.rman) tailored for complex requirements—for example relocating datafiles/logs:
connect TARGET sys@<source_tns>
connect AUXILIARY sys@<aux_tns>
run {
# Redirect datafiles/logs if directory structures differ
duplicate target database to <aux_sid>
from active database
db_file_name_convert='/source/path/','/target/path/'
log_file_name_convert='/source/path/','/target/path/'
nofilenamecheck;
}Note: Paths must match actual OS-level directories—including trailing slashes—to prevent mapping errors!
4. Execute script non-interactively while logging output for review later:
rman cmdfile=duplicate_db.rman log=duplicate_db.log
5. Monitor progress by tailing log output (tail -f duplicate_db.log). For deeper insight into ongoing operations—including estimated completion times—you can query Oracle views like v$session_longops.
6. Validate results post-clone just as described above: check open status via SQL*Plus queries; inspect physical layout against intended design.
Customizing Clones With Additional Parameters
Advanced users often tweak additional settings inside their scripts:
Use SET commands within RUN blocks to override initialization parameters temporarily during duplication—for example,
set db_unique_name='NEWCLONE' set control_files='/new/location/control01.dbf'
These adjustments allow fine-grained control over resulting environments without manual intervention after cloning completes.
How to Back Up Oracle Databases With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
After completing an Oracle database clone or migration, implementing robust protection through automated backups becomes essential for business continuity and compliance requirements alike. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional enterprise-level solution supporting today’s mainstream databases—including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with comprehensive features designed specifically for demanding production environments like yours.
For Oracle users especially, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers incremental backup capabilities alongside batch database backup management, flexible data retention policies including GFS support, cloud backup integration with tape archiving options, and any-point-in-time recovery functionality—all working together to streamline administration while maximizing resilience against threats such as ransomware or accidental loss.
The intuitive web console makes protecting your Oracle environment straightforward:
Step 1: Select the Oracle database to back up
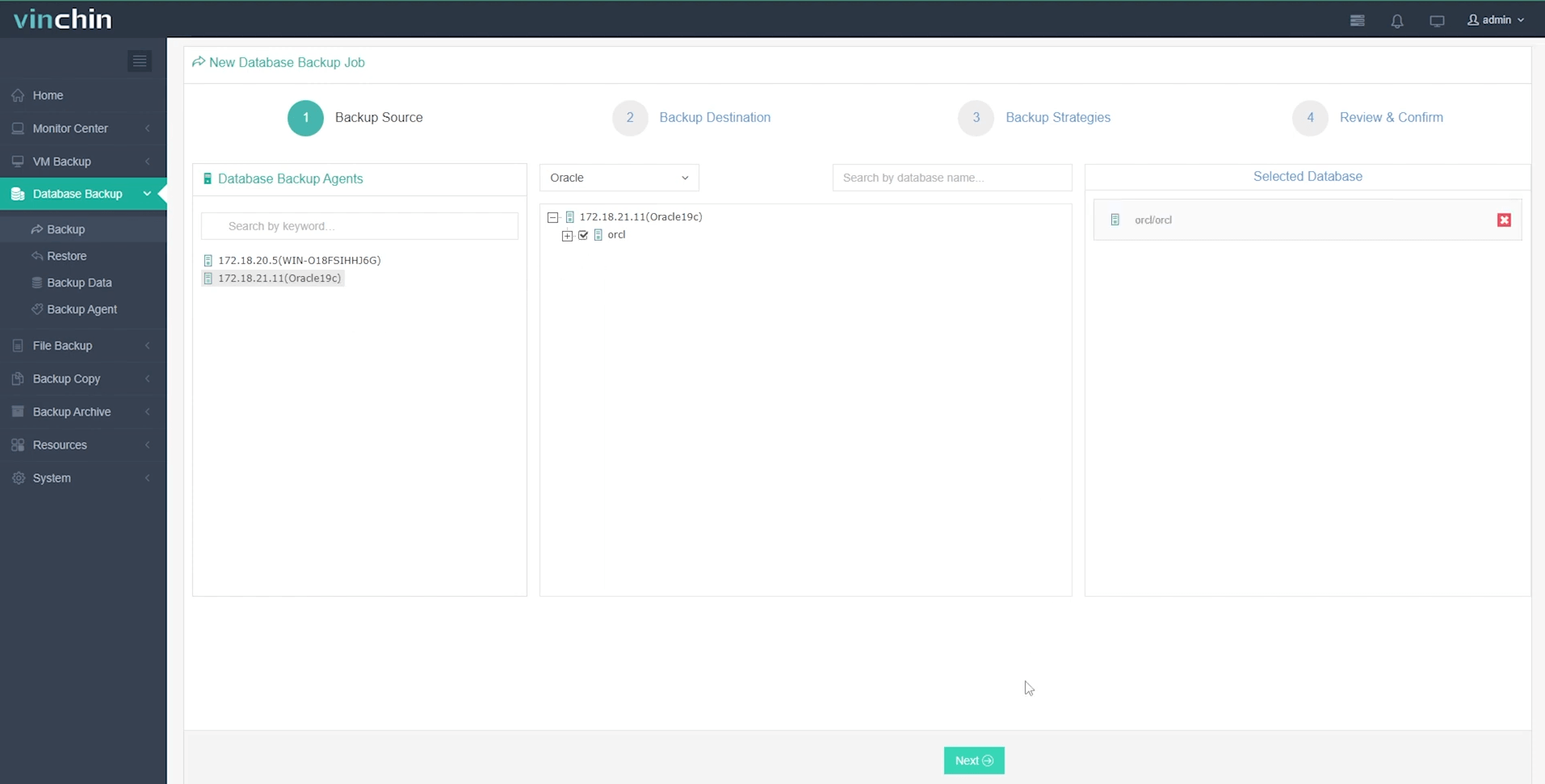
Step 2: Choose your preferred backup storage
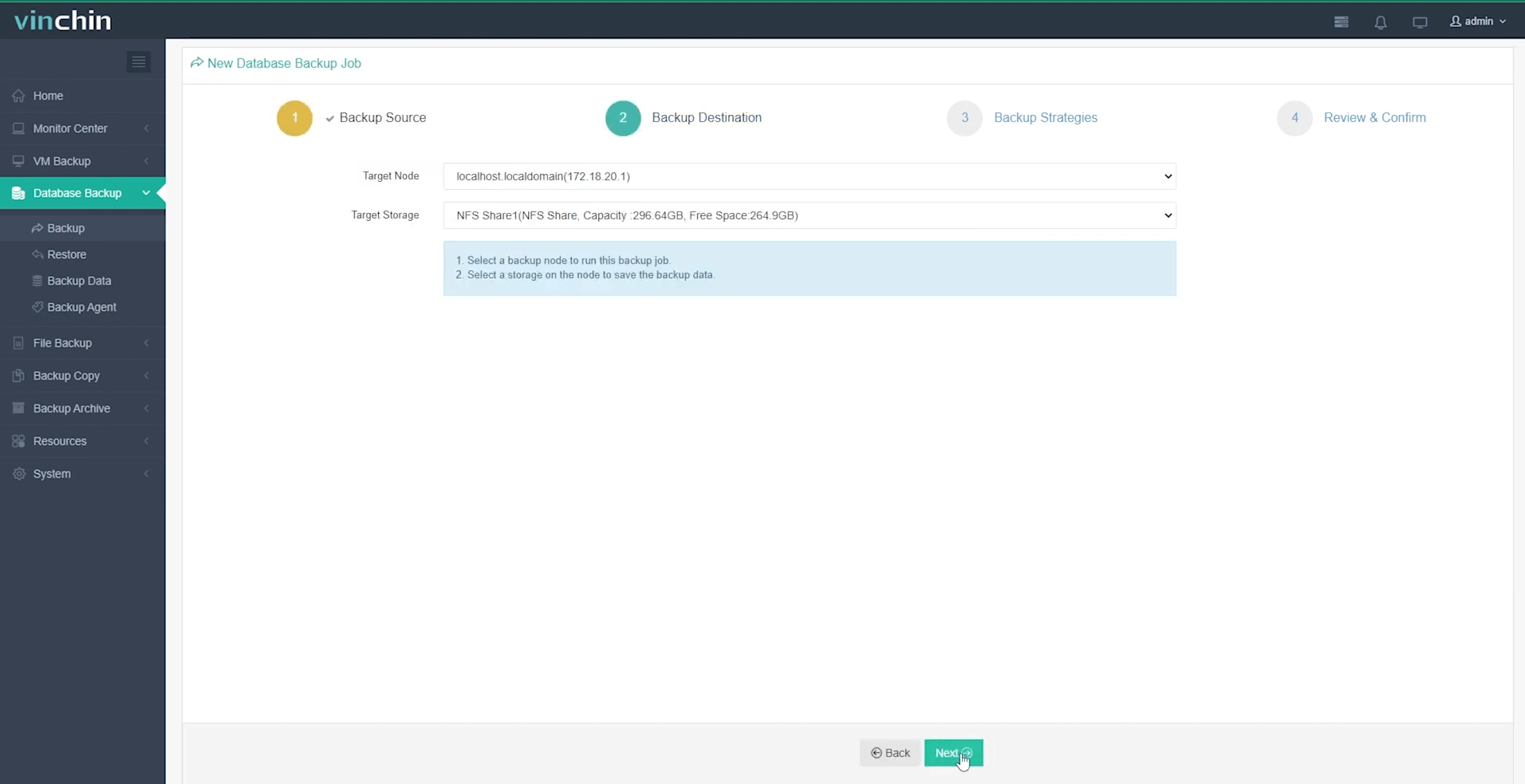
Step 3: Define a tailored backup strategy
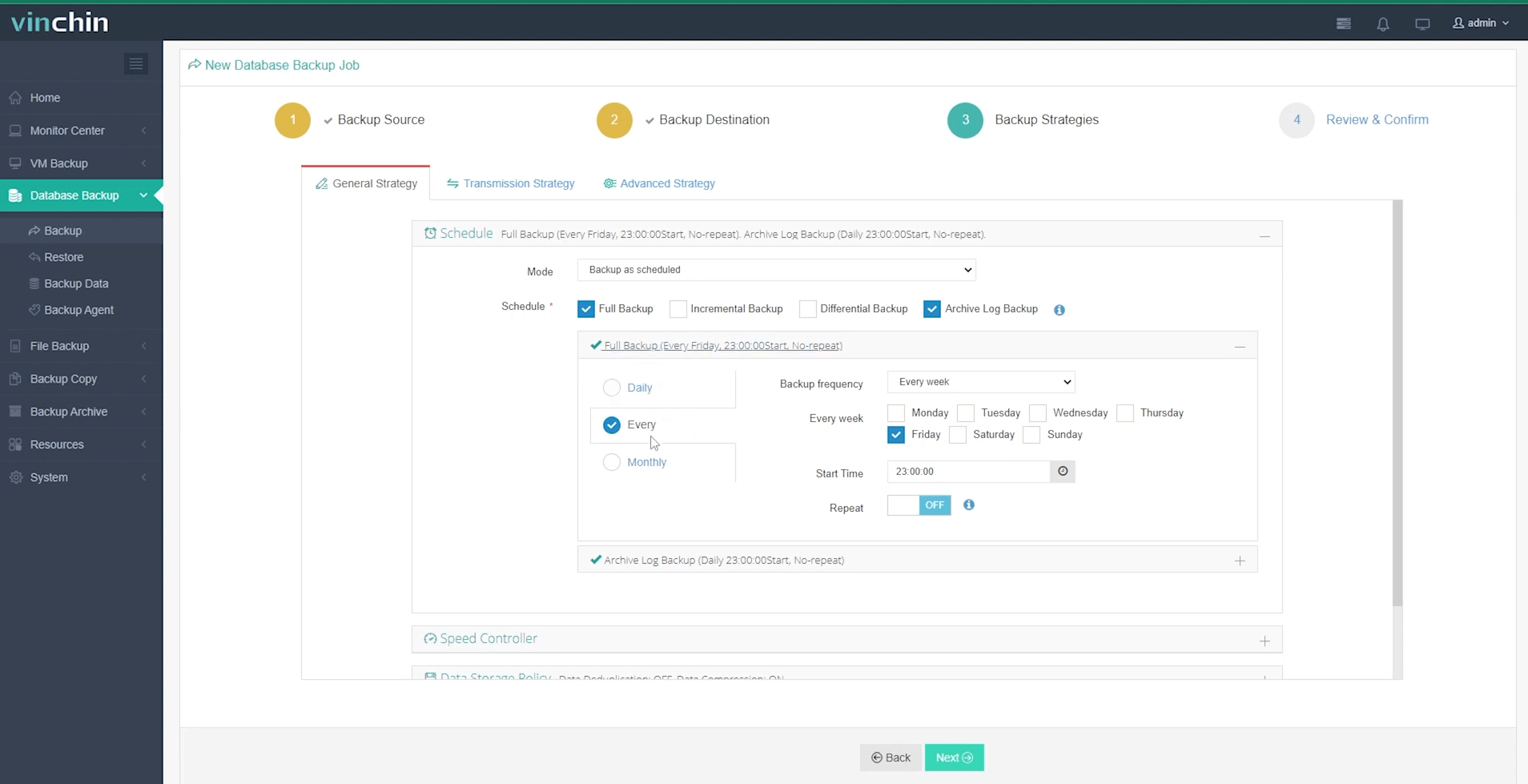
Step 4: Submit the job
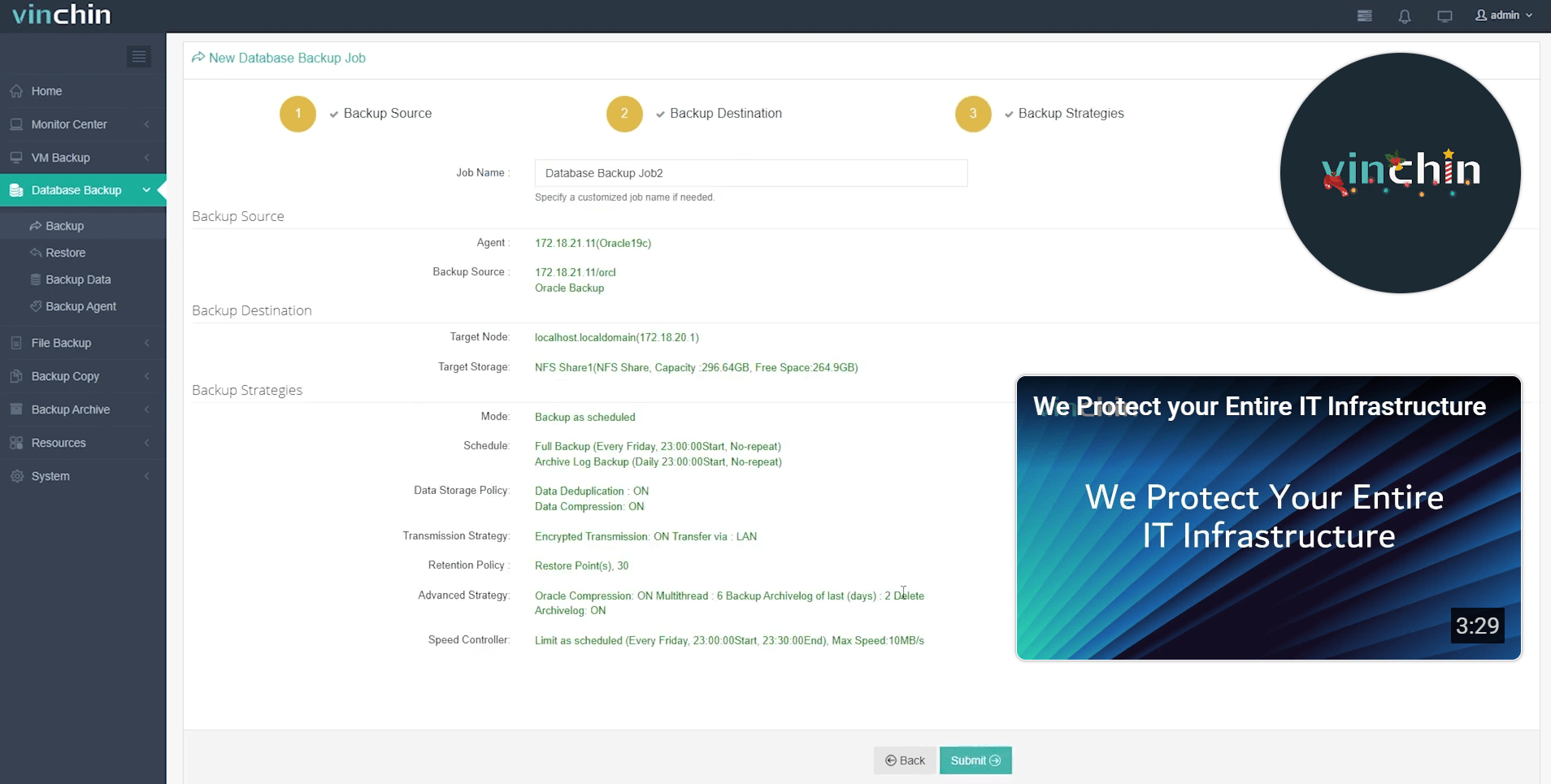
Recognized globally by enterprises of all sizes—and consistently top-rated by customers—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured 60-day free trial so you can experience its power firsthand before making any commitment.
RMAN Duplicate From Active Database FAQs
Q1: Can I perform an active duplicate if my production system has heavy load?
Yes—but expect some performance impact since live reads occur during duplication; schedule clones during low usage periods when possible.
Q2: How do I monitor progress of an ongoing active duplication?
Query v$session_longops view in SQL*Plus or watch real-time messages in your RMAN session window/log file output.
Q3: What should I do if my archive logs are deleted before clone completes?
Adjust archive log retention policy beforehand—or specify UNTIL TIME clause in DUPLICATE command—to ensure required logs remain available throughout operation.
Conclusion
RMAN Duplicate From Active Database gives administrators rapid cloning power without downtime headaches—a true asset for modern IT teams managing mission-critical workloads.For ongoing protection,Vinchin delivers robust yet easy-to-use enterprise-grade backups.Try Vinchin’s free trial today—and safeguard every copy of your valuable business data!
Share on:






