-
What is MinIO in Kubernetes?
-
Why Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes
-
Method 1: How to Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes with Helm?
-
Method 2: How to Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes Manually?
-
Method 3:How to Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes Using the MinIO Operator?
-
Enterprise Backup & Recovery for Your MinIO Kubernetes Workloads
-
MiniO Kubernetes FAQs
-
Conclusion
Object storage is a core part of modern cloud-native infrastructure. MinIO is a high-performance object storage solution that speaks Amazon S3’s language. When you run MinIO on Kubernetes, you get scalable storage built for containers and microservices. But how do you deploy MinIO on Kubernetes? And how can you keep your data safe? Let’s walk through everything from basics to advanced protection.
What is MinIO in Kubernetes?
MinIO is an open-source object storage server compatible with Amazon S3 APIs. In Kubernetes environments, it acts as a cloud-native backend for storing unstructured data like backups, logs, images, or AI/ML datasets. By running inside your cluster, MinIO delivers fast access and integrates smoothly with containerized workloads.
Why Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes
Pairing MinIO with Kubernetes brings several advantages. First, Kubernetes automates deployment and scaling so your storage grows as your needs change. Second, because MinIO supports the S3 API, you can use familiar tools and workflows without rewriting code. Third, running “minio kubernetes” gives you high availability across nodes plus redundancy for safety—whether on-premises or in any public cloud. This makes it ideal for modern apps that demand flexibility.
Many organizations use this combination to store application backups or logs directly within their clusters. Others rely on it to serve large datasets to AI/ML pipelines or provide persistent volumes for stateful workloads needing reliable object storage.
Method 1: How to Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes with Helm?
Helm is the package manager for Kubernetes—it simplifies deploying complex applications like MinIO by using charts.
Prerequisites and Configuration Tips
Before starting:
Make sure Helm (v3+) and kubectl are installed.
Your user must have permissions to create namespaces and resources.
For production deployments or distributed setups, review MinIO Helm Chart documentation about setting
mode: distributedinstead ofstandalone.
You should also avoid using default credentials in production; set strong values via secrets if possible.
Step-by-Step Deployment
First add the official repository:
helm repo add minio https://charts.min.io/ helm repo update
Next create a configuration file called minio-values.yaml:
mode: standalone # Use 'distributed' for multi-node setups persistence: size: 10Gi resources: requests: memory: 1Gi accessKey: "minioadmin" # Change these! secretKey: "minioadmin" service: type: ClusterIP
Tip: For better security in real-world scenarios, store credentials as a secret using existingSecret.
Now install:
helm install minio minio/minio -f minio-values.yaml -n minio-system --create-namespace
To access locally:
kubectl port-forward svc/minio 9000:9000 -n minio-system
Open your browser at http://localhost:9000 and log in with your keys.
Method 2: How to Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes Manually?
Manual deployment gives full control over every resource definition—ideal if you want custom settings or need to understand what happens behind the scenes.
Prerequisites
You’ll need kubectl configured against your cluster and permissions to create PVCs (PersistentVolumeClaims), Deployments (or StatefulSets), and Services.
Step-by-Step Deployment
Start by defining persistent storage:
apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: minio-pvc spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi
Apply it:
kubectl apply -f minio-pvc.yaml
Next define the deployment (for simple cases):
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment # For more resilient setups consider StatefulSet below! metadata: name: minio spec: selector: matchLabels: app: minio strategy: type: Recreate # Causes downtime during updates; see note below. template: metadata: labels: app: minio spec: containers: - name: minio image: minio/minio:latest # Always check Docker Hub for latest tags. args: - server - /data env: - name: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: my-miniosecrets key: accesskey - name: MINIO_SECRET_KEY valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: my-miniosecrets key: secretkey ports: - containerPort: 9000 volumeMounts: - name: data mountPath: /data volumes: - name : data persistentVolumeClaim : claimName : minio-pvc
Note: For stateful workloads like distributed clusters—or when uptime matters—use a StatefulSet instead of Deployment.
Expose via Service:
apiVersion : v1 kind : Service metadata : name : minio spec : type : ClusterIP ports : – port : 9000 targetPort : 9000 selector : app : minio
Apply service:
kubectl apply -f minio-service.yaml
Access console locally:
kubectl port-forward svc/minio 9000 :9000
Then visit http://localhost :9000 in your browser.
Method 3:How to Deploy MinIO on Kubernetes Using the MinIO Operator?
The Operator automates advanced management tasks such as scaling clusters up/down or handling upgrades safely—all through Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs).
Prerequisites
Ensure kubectl is installed; cluster-admin privileges are required since CRDs will be created system-wide. Also verify which StorageClass names exist (local-path may not be present everywhere).
Step-by-Step Deployment
Install Operator via Kustomize:
kubectl apply –k "github.com/min io/operator?ref=v7 .0 .1"
Create namespace:
kubectl create namespace min io
Define Tenant manifest (deployment.yaml) :
apiVersion:min io.min . io/v2 kind :Tenant metadata : name:min io namespace:min io spec : requestAutoCert:true image:min io/min io :latest # Always confirm latest stable tag! mountPath:/export pools : –name :pool–0 servers :3 volumesPerServer :3 volumeClaimTemplate : spec : accessModes : –ReadWriteOnce resources : requests : storage :100Gi storageClassName:<your-storage-class> # Adjust based on environment!
Apply tenant manifest :
kubectl apply –f deployment . yaml
To expose outside cluster , define LoadBalancer service :
apiVersion:v1 kind:Sercive metadata : name:min io–loadbalancer namespace:min io spec : type:L oadBalancer selector : v1.min . io/tenant:min io ports : –name:a pi protocol:T CP port :9000 targetPort :9000 –name:c ons ole protocol:T CP port :9443 targetPort :9443
Apply service :
kubectl apply –f loadbalancer . yaml
Get external IP address :
kubectl get svc –n mini o mini o–loadbalancer
Access console at https://<EXTERNAL-IP>:9443 using credentials stored in secrets (kubectl get secrets –n mini o). The Operator makes scaling up servers easy—just edit Tenant YAML then reapply!
Enterprise Backup & Recovery for Your MinIO Kubernetes Workloads
After successfully deploying your “minio kubernetes” environment, ensuring robust backup protection becomes essential. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-level solution purpose-built for comprehensive Kubernetes backup needs. It offers full/incremental/fine-grained backup & restore by cluster, namespace, application, PVC, policy-based automation including one-off jobs, encrypted transmission/storage options (with WORM support), cross-cluster/cross-version recovery—even across heterogeneous environments—and intelligent multithreading/concurrent transfer acceleration for rapid PVC throughput. These features combine powerful flexibility with secure automation so organizations can confidently protect critical workloads at scale while meeting compliance requirements.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery features an intuitive web console that streamlines backup operations into four straightforward steps tailored specifically for Kubernetes environments:
Step 1. Select the backup source

Step 2. Choose the backup storage destination
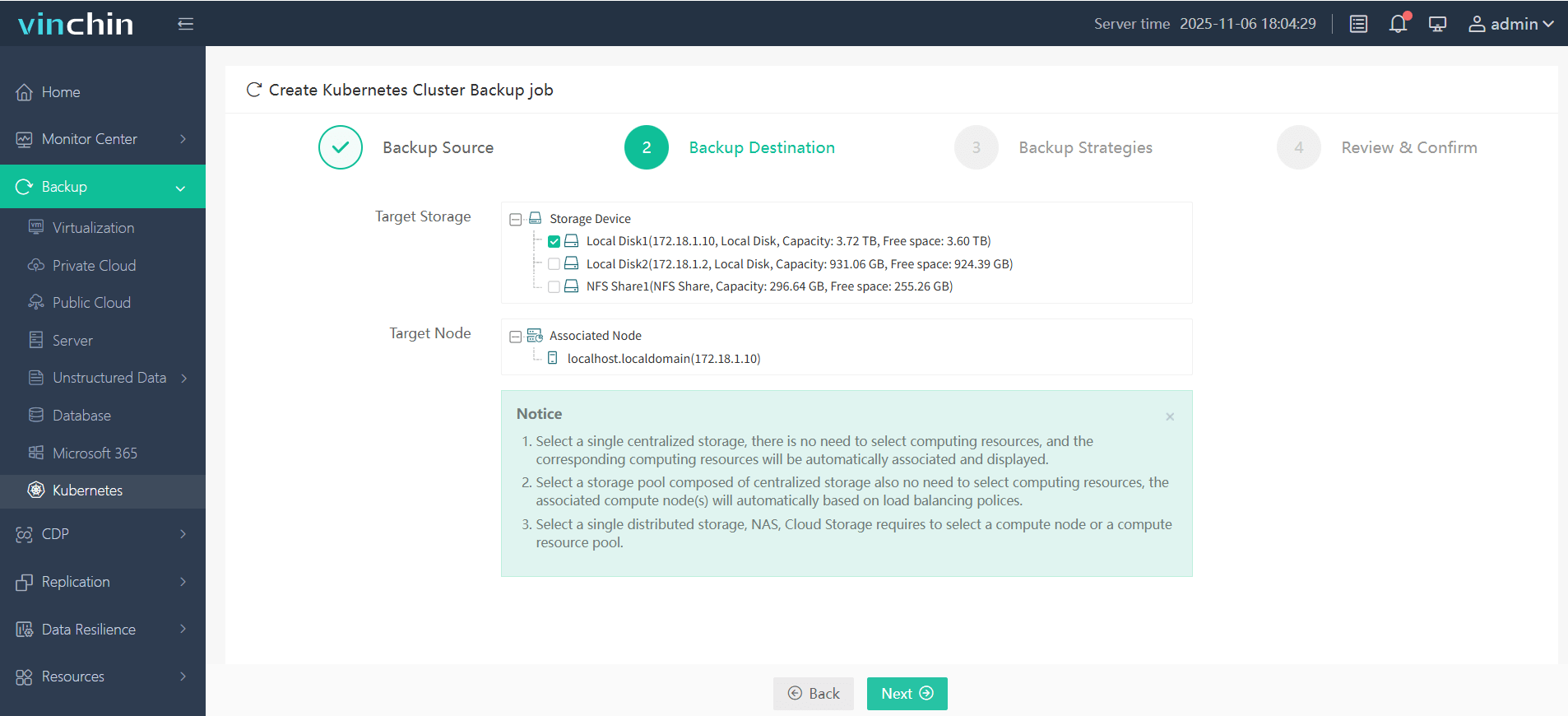
Step 3. Define the desired backup strategy
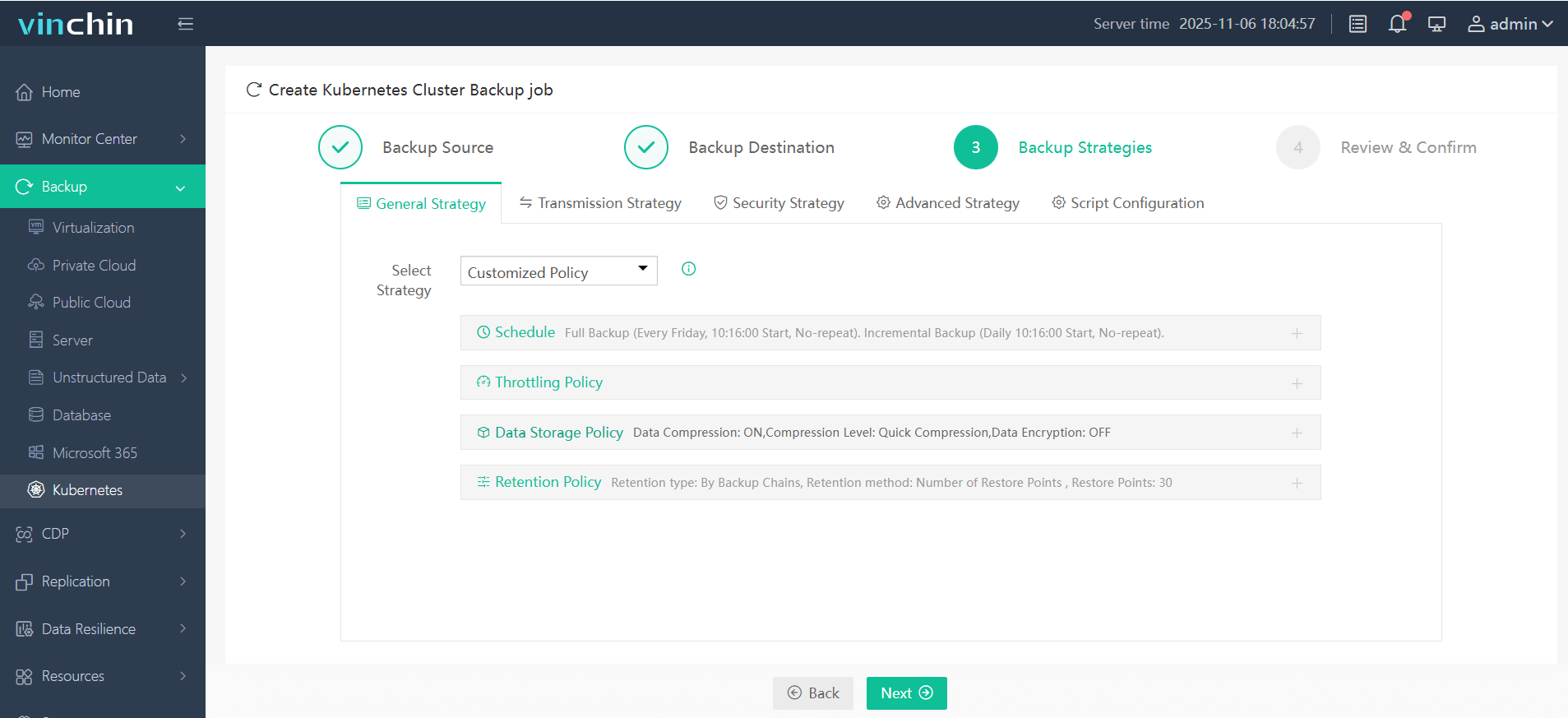
Step 4. Submit the job
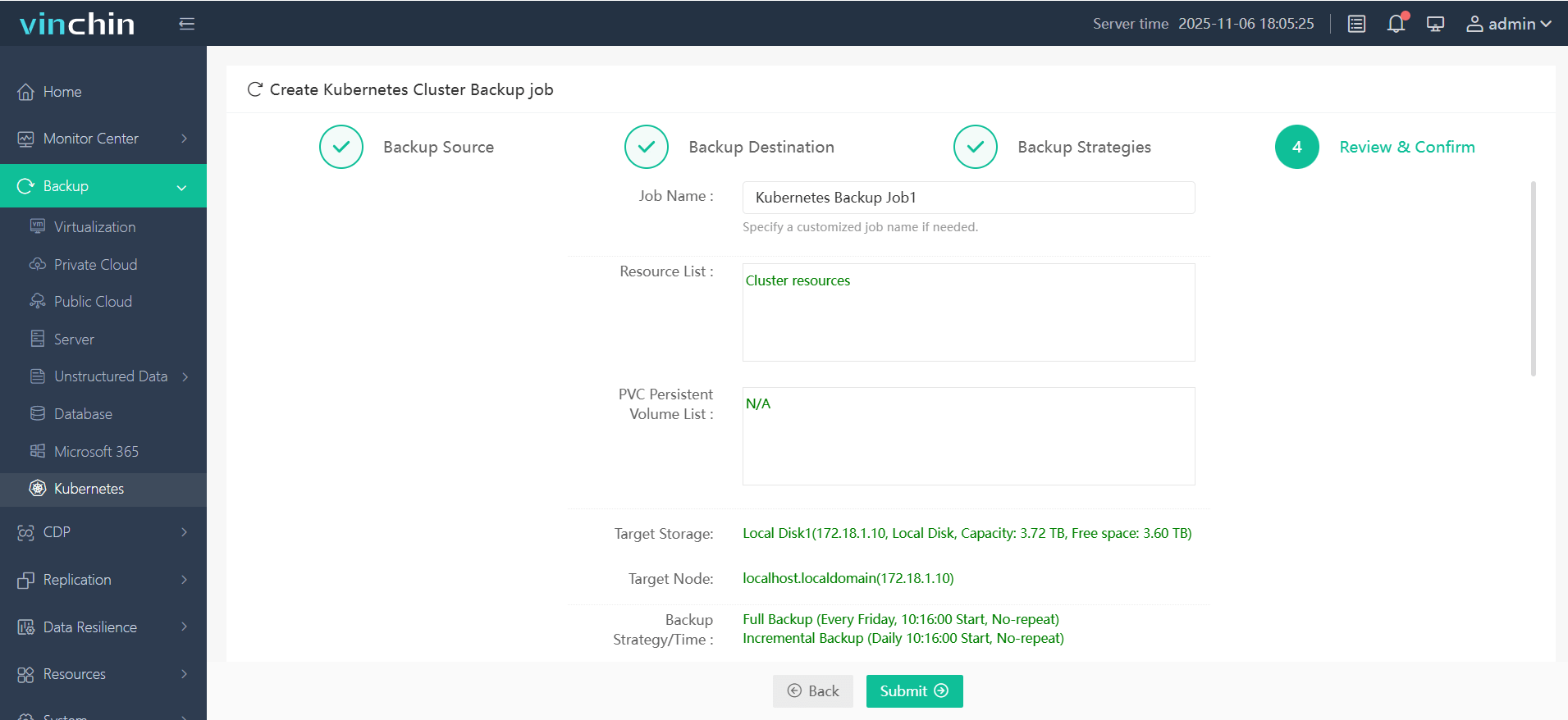
Recognized globally by thousands of enterprises—with top industry ratings—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured free trial valid for up to 60 days; click below to experience leading-edge data protection firsthand.
MiniO Kubernetes FAQs
Q1. How do I scale a MiniO Tenant deployed with the Operator?
A1. Edit Tenant CRD, increase servers/volumes, then reapply YAML.
Q2. Can I enable TLS for MiniO in Kubernetes?
A2. Yes; provide certificates as secrets, reference them in deployment/Tenant spec.
Q3. What if my PVC stays Pending after applying manifests?
A3. Check available PVs ( kubectl get pv,pvc), confirm correct StorageClass, adjust YAML if needed.
Conclusion
Running MiniO on Kubernetes gives scalable S3-compatible storage ready for any workload. With robust backup from Vinchin Backup & Recovery, your data remains protected no matter what happens — try Vinchin’s free trial today!
Share on:









