-
What Is the Hadoop Database Platform?
-
How Is a Hadoop Database Different From Traditional Databases?
-
Why Choose a Hadoop Database Over Traditional Solutions?
-
Protecting Your Data With DistCp: Copying Across Clusters
-
Using HDFS Snapshots for Fast Recovery
-
How to Protect Hadoop HDFS Files with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
FAQs About Managing Your Hadoop Database Environment
-
Conclusion
Many people search for "hadoop database" when they want to understand how Hadoop manages data or how it compares with traditional databases. If you are an operations administrator, you need clear answers—and practical ways to protect your data in a Hadoop environment. Let’s walk through what matters most for your daily work.
What Is the Hadoop Database Platform?
Hadoop is not a database in the classic sense—it’s an open-source framework designed for storing and processing huge datasets across clusters of computers. Its core modules include:
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): Stores data by splitting files into blocks distributed across many nodes.
MapReduce: Processes large-scale data jobs in parallel.
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): Manages resources and schedules tasks.
Hadoop Common: Provides shared utilities that tie everything together.
Within HDFS, the architecture relies on two key components: the NameNode, which manages metadata like file names and permissions; and multiple DataNodes, which store actual data blocks on disk drives across servers. This design lets organizations scale out storage easily while keeping costs low.
Hadoop handles both structured and unstructured data—logs, images, sensor feeds—and can process petabytes efficiently thanks to its distributed nature.
How Is a Hadoop Database Different From Traditional Databases?
It’s easy to confuse Hadoop with databases because both manage data—but their purposes differ greatly.
Traditional relational databases store structured information in tables with fixed schemas; they excel at fast queries and transactions but struggle when handling massive or unstructured datasets. In contrast, a hadoop database platform stores raw or semi-structured content without rigid schemas—think clickstreams or IoT sensor logs—and scales horizontally by adding commodity servers instead of expensive hardware upgrades.
While relational systems focus on real-time transactions with strict consistency rules, Hadoop shines at batch analytics over vast amounts of diverse data types—often used for building big data lakes or running machine learning jobs.
You might hear about tools like Hive or HBase that run atop Hadoop—they provide SQL-like access or NoSQL tables—but these are add-ons rather than core features of the hadoop database platform itself.
Why Choose a Hadoop Database Over Traditional Solutions?
Why do so many enterprises turn to hadoop database technology? The answer comes down to scale, flexibility, cost savings—and resilience against failure:
You can grow your cluster from just a few nodes up to thousands as your needs expand.
Because it runs on standard hardware and open-source software, you avoid costly licensing fees.
Store any kind of information—from structured records to free-form documents—with no need for complex schema migrations.
Data gets replicated automatically across several DataNodes; if one server fails, another holds a copy so nothing is lost.
A rich ecosystem supports analytics tools ranging from Spark jobs to AI frameworks—all integrated into your big-data workflow.
If your business must analyze terabytes of logs every day—or combine video files with transaction records—a hadoop database setup often makes more sense than trying to stretch legacy systems beyond their limits.
Protecting Your Data With DistCp: Copying Across Clusters
Backing up critical information stored in your hadoop database should be part of every admin’s routine. One popular tool is DistCp (Distributed Copy), built right into Apache Hadoop for moving large volumes between clusters or directories inside HDFS.
DistCp launches MapReduce jobs that copy files in parallel—making it much faster than manual scripts when dealing with millions of objects or multi-terabyte workloads. Here’s how you use it:
First make sure both source and destination paths exist within accessible clusters; then run:
hdfs distcp -update -delete hdfs://source/path hdfs://destination/path
The -update flag copies only changed files since last sync; -delete removes obsolete items at the destination so both sides match exactly—a common requirement during disaster recovery drills or scheduled backups.
Monitor progress using the YARN ResourceManager web interface under “Applications” tab—or check job status via command line:
yarn application -status <application_id>
Once complete, verify all expected files appear at the destination path using:
hdfs dfs -ls hdfs://destination/path
If network hiccups occur mid-transfer—or if permissions block certain directories—the job may fail partway through. Always review error logs under /logs/userlogs on each node involved; retry failed transfers after fixing issues such as firewall rules or quota limits.
Using HDFS Snapshots for Fast Recovery
Another way admins safeguard their hadoop database contents is through HDFS snapshots—a feature that creates read-only copies of entire directories at specific points in time. Snapshots let you roll back accidental deletions quickly without restoring full backups from tape archives or cloud storage providers.
To use this feature:
1. Enable snapshots first by running:
hdfs dfsadmin -allowSnapshot /data/important
2. Create a new snapshot whenever needed:
hdfs dfs -createSnapshot /data/important snap_202406
3. List all available snapshots:
hdfs dfs -ls /data/important/.snapshot
4. Restore deleted files by copying them back from .snapshot/snap_202406 directory using standard hdfs dfs -cp commands.
5. Remove old snapshots when space runs low:
hdfs dfs -deleteSnapshot /data/important snap_202406
Snapshots consume little extra space because only changes made after creation get stored separately—a technique called copy-on-write.
For best results: schedule regular snapshot creation via cron jobs; monitor disk usage under /data/.snapshot; prune outdated versions monthly so storage does not fill up unexpectedly.
How to Protect Hadoop HDFS Files with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
While robust storage architectures like Hadoop HDFS provide inherent resilience, comprehensive backup remains essential for true data protection. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-grade solution purpose-built for safeguarding mainstream file storage—including Hadoop HDFS environments—as well as Windows/Linux file servers, NAS devices, and S3-compatible object storage. Specifically optimized for large-scale platforms like Hadoop HDFS, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers exceptionally fast backup speeds that surpass competing products thanks to advanced technologies such as simultaneous scanning/data transfer and merged file transmission.
Among its extensive capabilities, five stand out as particularly valuable for protecting critical big-data assets: incremental backup (capturing only changed files), wildcard filtering (targeting specific datasets), multi-level compression (reducing space usage), cross-platform restore (recovering backups onto any supported target including other file servers/NAS/Hadoop/object storage), and integrity check (verifying backups remain unchanged). Together these features ensure efficient operations while maximizing security and flexibility across diverse infrastructures.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers an intuitive web console designed for simplicity. To back up your Hadoop HDFS files:
Step 1. Select the Hadoop HDFS files you wish to back up
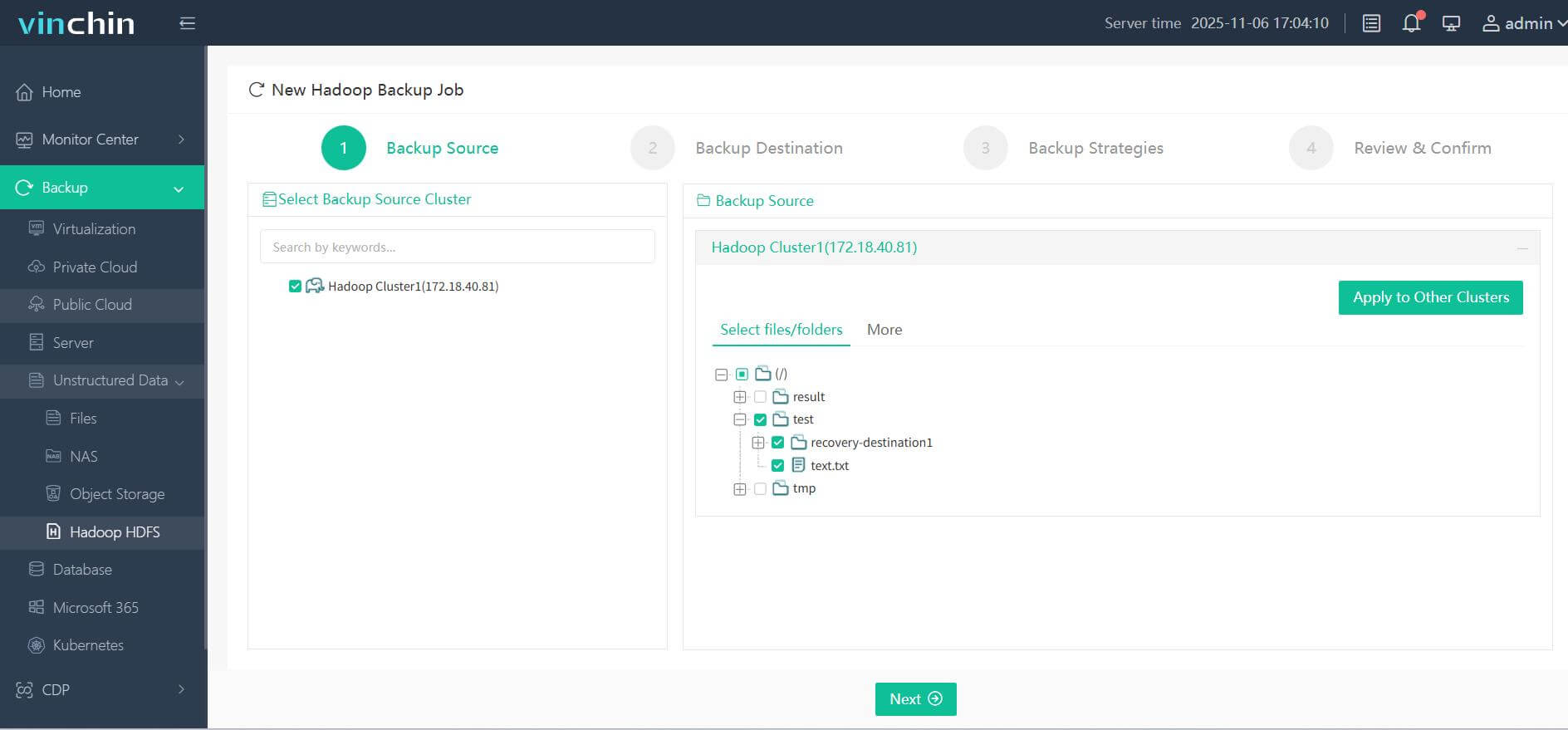
Step 2. Choose your desired backup destination
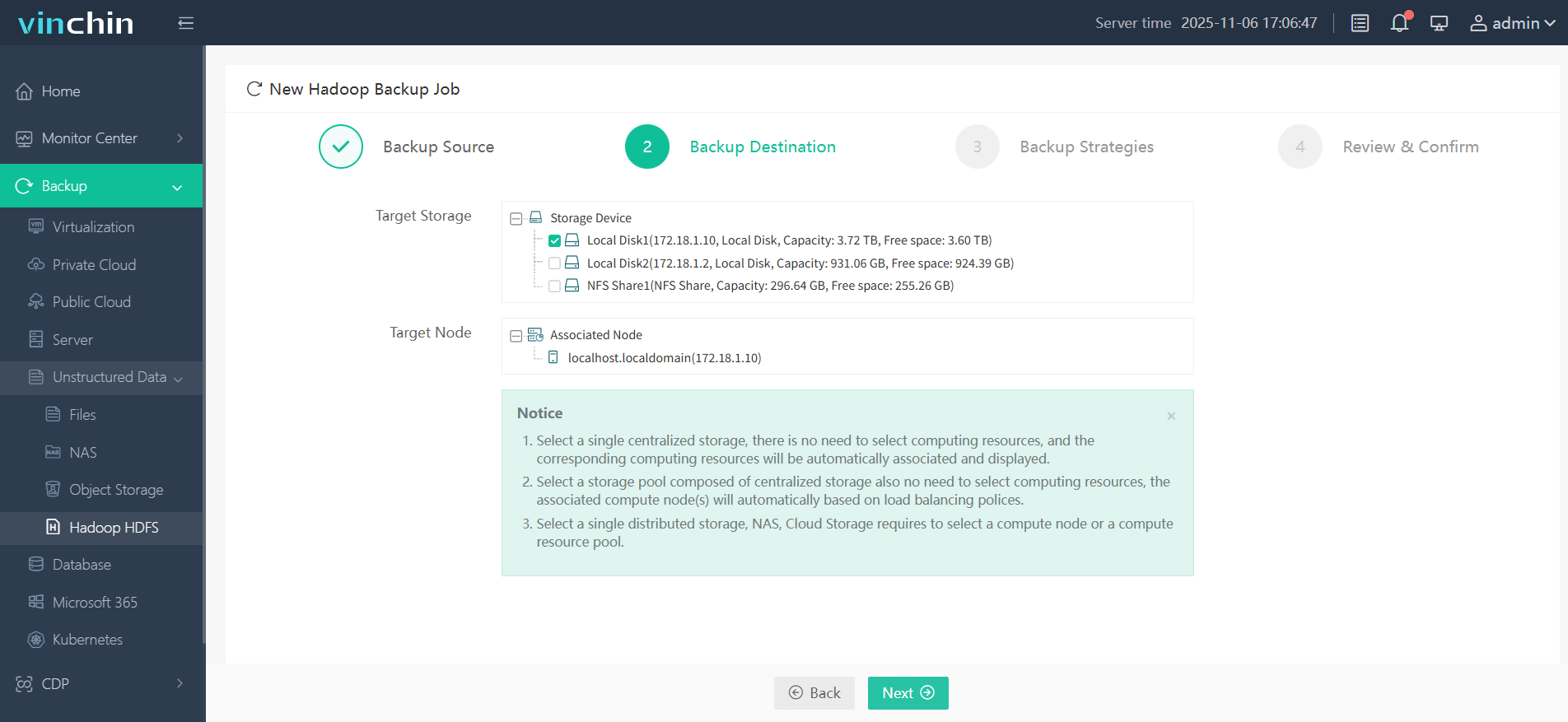
Step 3. Define backup strategies tailored for your needs
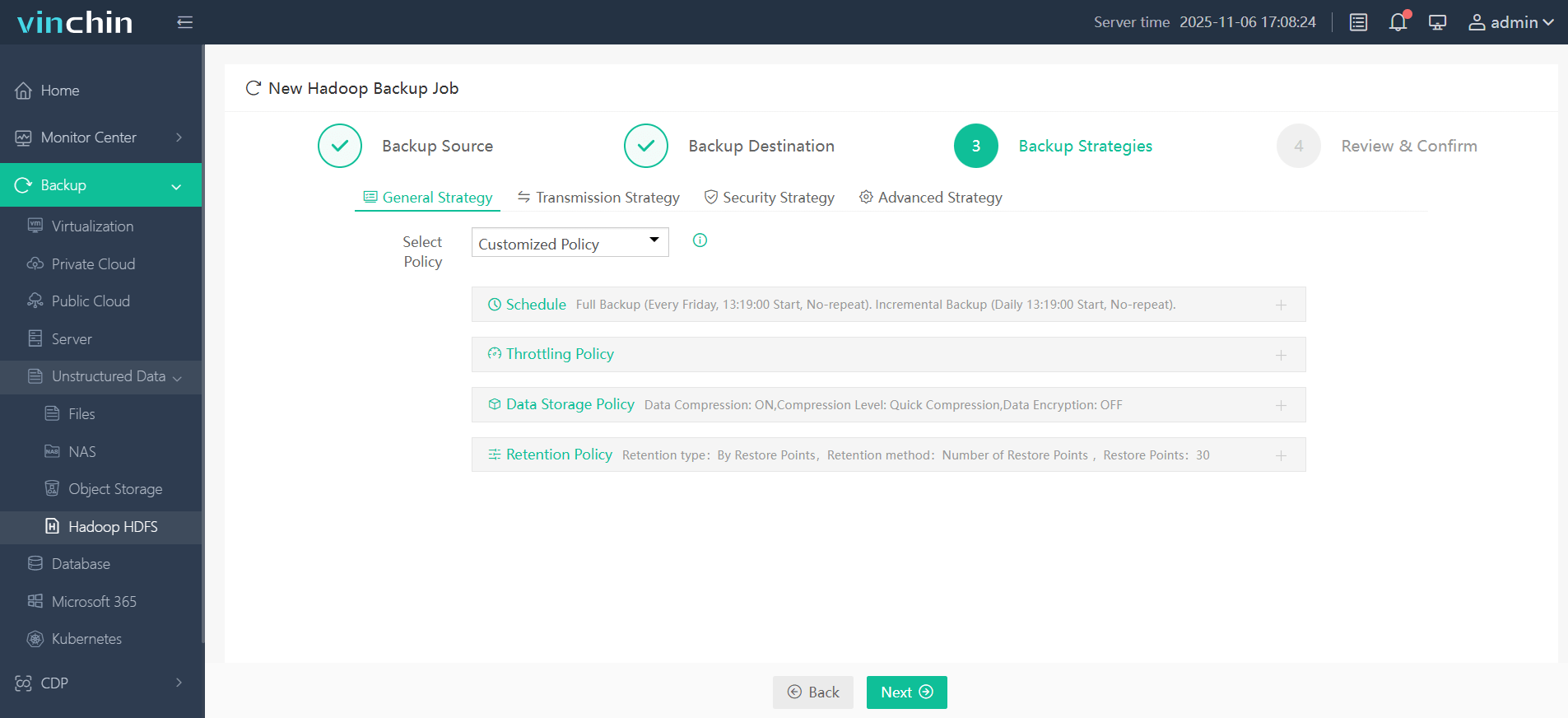
Step 4. Submit the job
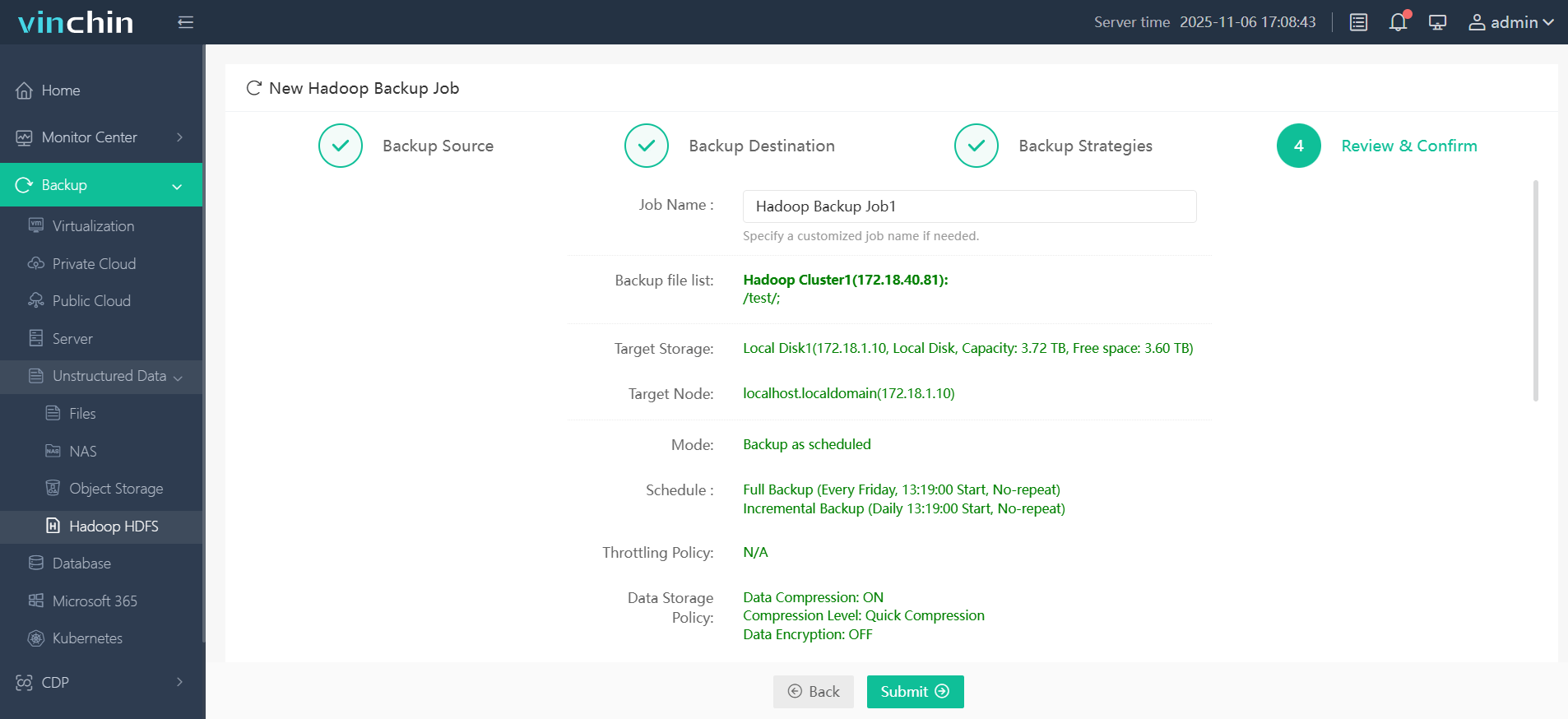
Join thousands of global enterprises who trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery—renowned worldwide with top ratings—for reliable data protection. Try all features free with a 60-day trial; click below to get started!
FAQs About Managing Your Hadoop Database Environment
Q1: How often should I back up my production-level hadoop database?
A1: Set schedules based on business RPO goals—for example hourly incremental plus daily full backups—to minimize potential loss during outages while balancing resource usage.
Q2: What should I do if my DistCp transfer fails due to network errors?
A2: Check error logs via ResourceManager UI/logs directory; resolve connectivity issues then rerun distcp command with same parameters until success.
Q3: Can I automate snapshot creation/removal without manual intervention?
A3: Yes—use OS-level schedulers like cron combined with scripted calls (hdfs dfsadmin, hdfs dfs) targeting desired folders/times.
Conclusion
Although not technically a traditional database system, the hadoop database platform delivers unmatched scalability and flexibility for today’s big-data challenges—and protecting its contents requires careful planning at every stage. Whether you rely on native tools or advanced solutions like Vinchin's enterprise-grade backup suite depends on your needs—but robust protection should never be optional.
Share on:









