-
What Is a Backup Repository?
-
Why Use a Backup Repository?
-
Types of Backup Repositories
-
How to Set Up a Backup Repository?
-
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
-
Backup Repository FAQs
-
Conclusion
Every IT environment needs a safe place to store backups. That’s where a backup repository comes in. Whether you manage a small business or a large enterprise, understanding backup repositories is key to protecting your data and ensuring business continuity.
A backup repository is more than just extra storage space—it’s the backbone of your disaster recovery plan. If you’re responsible for keeping systems running smoothly, knowing how to set up and protect these repositories can make all the difference when things go wrong.
What Is a Backup Repository?
A backup repository is a dedicated storage location for backup files and related metadata. Think of it as a secure vault where your backup solution saves copies of your critical data.
The repository can be a folder on a local disk, a network share, or even cloud object storage. It holds not just the raw backup data but also indexes and metadata needed for fast restores. Most modern backup systems manage repositories through specialized services called data movers or agents—these handle all read/write operations to prevent corruption or loss.
When you back up workloads—whether virtual machines, databases, or files—the system writes those backups into this controlled area rather than scattering them across random drives or shares.
Why Use a Backup Repository?
Why not just copy files to another drive? A proper backup repository offers much more control and safety.
First, it centralizes your backup data so you can manage everything from one place—no hunting through different folders when disaster strikes. With repositories you can enforce retention policies that automatically delete old backups after their expiration date.
Repositories also support deduplication (removing duplicate blocks) and compression (shrinking file sizes), saving valuable space while improving efficiency. Many solutions offer immutability settings that lock backups against deletion or tampering until their retention period ends—a crucial defense against ransomware attacks.
Finally, because repositories organize both data and metadata together, they speed up recovery times by making restores quick and reliable.
Types of Backup Repositories
Backup repositories come in many forms to fit different needs—from simple setups to complex enterprise environments.
On-Premises vs. Cloud Repositories
Let’s start with the basics: on-premises versus cloud-based options.
On-premises repositories live within your own infrastructure—usually as folders on internal disks (DAS), direct-attached storage arrays (SAN), or shared network locations using protocols like SMB/CIFS or NFS. These provide high-speed access but may lack offsite protection if disaster strikes your facility.
Cloud repositories use remote object storage services such as Amazon S3-compatible platforms or other public/private clouds. These offer scalability—you pay only for what you use—and built-in geographic redundancy for disaster recovery scenarios.
Some organizations combine both approaches: keeping recent backups onsite for fast restores while sending older archives offsite to the cloud for long-term retention.
Advanced Repository Types
As environments grow more complex, so do their requirements:
Deduplicating Appliances: Specialized hardware devices that remove duplicate blocks before storing backups—saving space without sacrificing performance.
Immutable Repositories: Storage configured so that once written, no one—not even administrators—can modify or delete backups until their retention period expires (“write once read many,” often called WORM).
Scale-Out Repositories: Logical pools combining multiple physical locations into one seamless resource; this allows easy expansion as your needs grow without reconfiguring jobs.
Object Storage Integration: Modern solutions increasingly support native integration with object stores (on-premises or cloud). This enables features like versioning and geo-redundancy out-of-the-box.
Choosing the right type depends on factors like speed requirements, regulatory compliance needs (such as GDPR), budget constraints, and risk tolerance for disasters like fire or ransomware attacks.
How to Set Up a Backup Repository?
Setting up a robust backup repository is essential—but don’t worry if it sounds daunting at first! Here’s how most admins get started on Linux servers using industry best practices:
Begin by installing any required agent/data mover software provided by your chosen platform onto the target machine hosting the repository directory. This service manages secure transfers between production workloads and storage targets—and helps avoid permission issues later on!
Next:
1. Create a dedicated directory for storing backups—for example:
cd /opt/ sudo mkdir my_backup_repository
2. Assign ownership so only authorized service accounts have access:
sudo chown -R bhsvc:bhsvc my_backup_repository
Replace bhsvc with the correct user/group used by your platform’s agent process.
3. Set permissions carefully:
sudo chmod 0770 my_backup_repository
Using 0770 restricts access further than 0775, allowing only owner/group members full rights—a good practice unless broader access is needed.
4. Confirm settings:
ls -ld my_backup_repository
If using NAS devices via NFS/CIFS shares:
Ensure correct export/share permissions at both OS level and NAS management interface.
Map service account credentials properly so agents can write/read without errors (
sudo chown -R u_bhsvc:g_bhsvc ...).
Security Hardening Tips:
Restrict SSH access to trusted IPs only; disable password logins in favor of SSH keys; configure firewall rules so only necessary ports are open between production hosts and repository server(s). Always keep OS patches current!
Troubleshooting Permissions:
If jobs fail due to “permission denied,” double-check directory ownership matches what your agent expects—and verify SELinux/AppArmor profiles aren’t blocking access behind-the-scenes!
Once ready:
Open your solution’s web console,
Go to Settings > Repositories,
Click Add New Repository,
Enter name/path (/opt/my_backup_repository) plus assign transporter/data mover,
Enable options like compression/deduplication,
For ransomware defense: turn on immutability during job creation by enabling its setting under advanced options,
Save configuration,
Your new repository now appears under available storage locations! Click its name anytime in Repositories view to check status/free space/configuration details—or hover/click three dots menu for actions like verify/self-heal if supported.
Never manually delete files inside these directories outside official tools—it risks corrupting indexes beyond repair!
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional solution designed to provide data protection and disaster recovery for virtualized environments. It supports various virtual platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, Proxmox, XCP-ng, etc., and database, NAS, file server, Linux & Windows Server, etc. Tailored for virtual environments, Vinchin offers automated backups, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free options, offsite copying, instant recovery, data deduplication, and cloud archiving. With data encryption and ransomware protection.
With agentless backup feature, it enables quick integration of VMs into the backup system. It offers disaster recovery features such as Instant Restore to reboot VMs from backups in seconds, offsite copy for remote backup storage, and automatic backup verification for integrity checks. Additionally, it facilitates VM migration across different hypervisors for seamless virtual environment transitions.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your virtual machine with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the backup object.
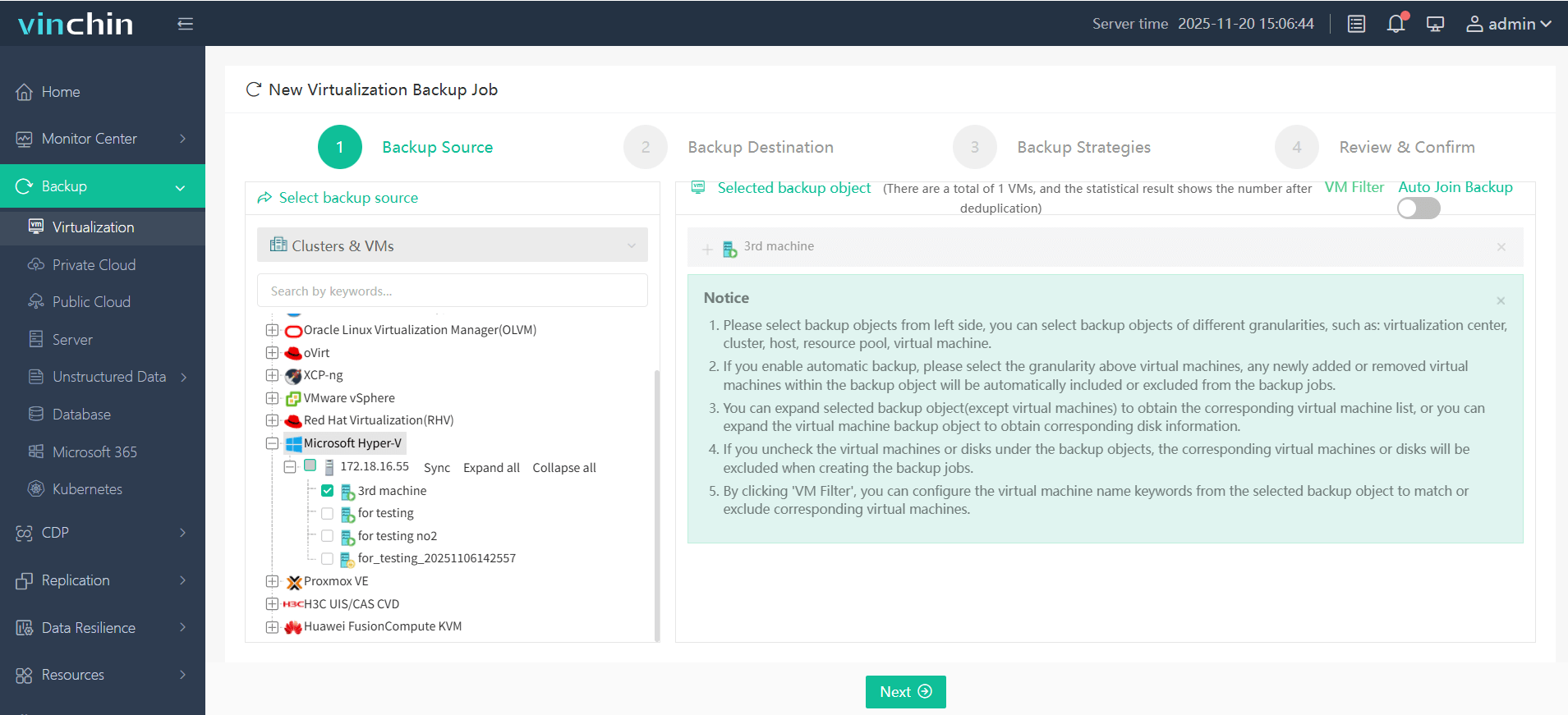
2.Select backup destination.
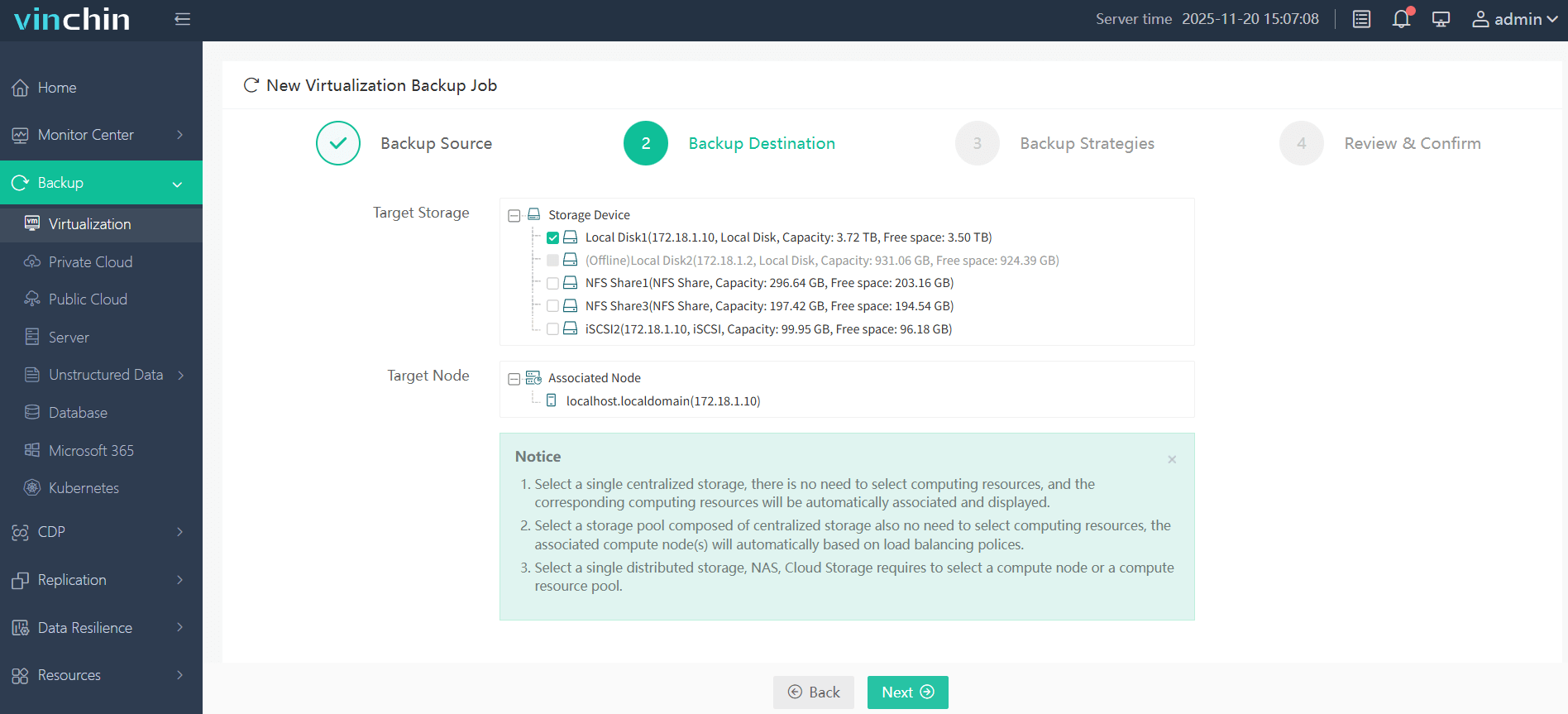
3.Configure backup strategies.
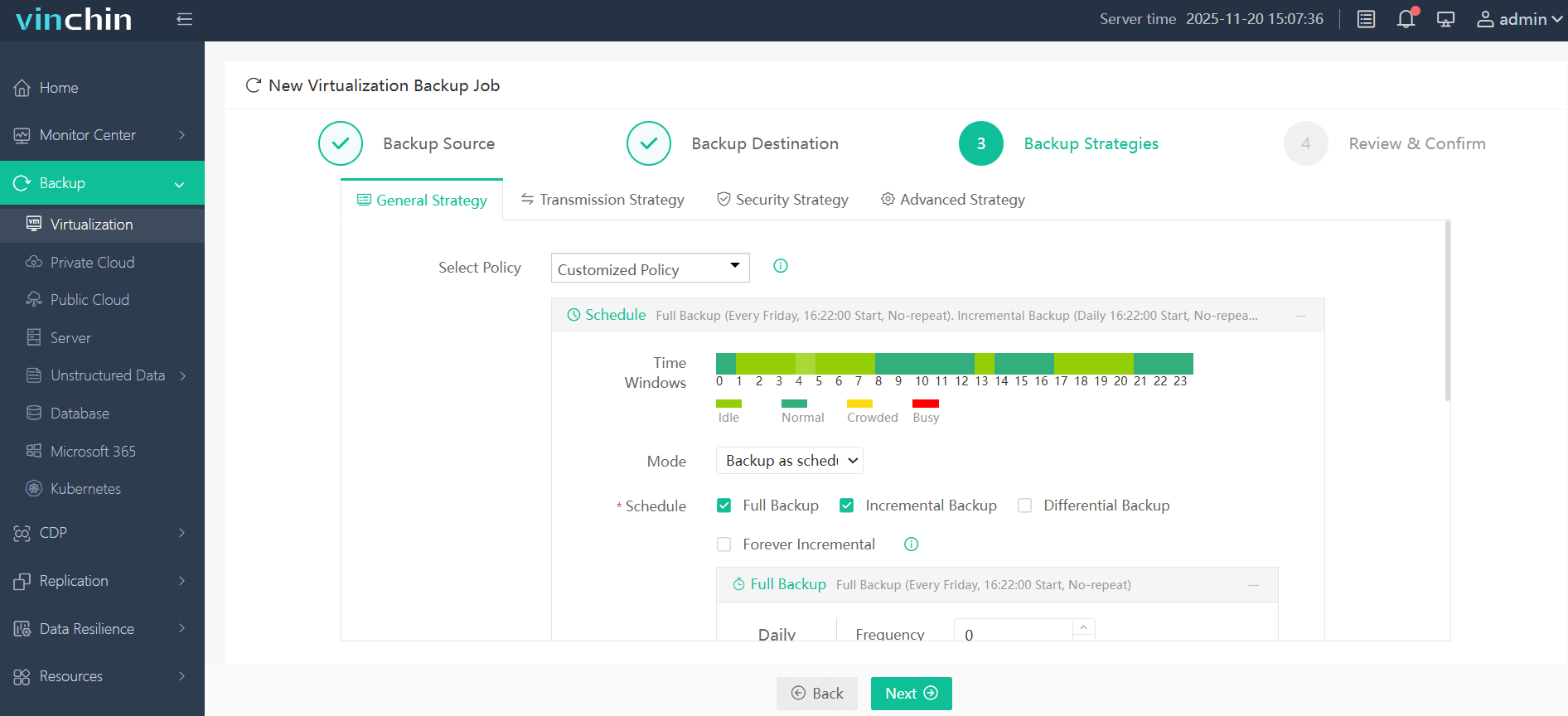
4.Review and submit the job.
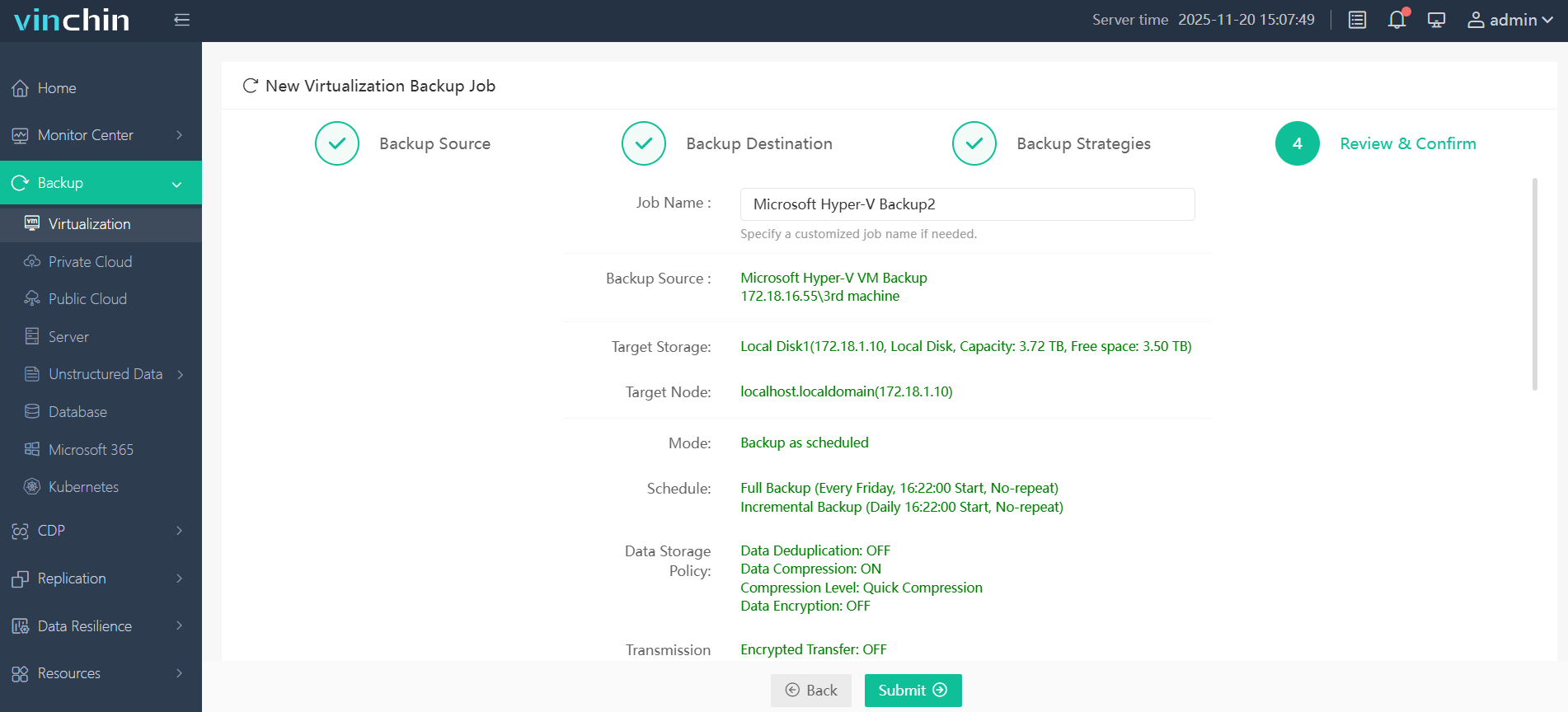
Discover the power of this comprehensive system firsthand with a free 60-day trial! Leave your specific needs, and you will get a customized solution that fits your IT environment perfectly.
Backup Repository FAQs
Q1: How can I improve my backup repository's throughput?
A1: Use high-speed disks/NICs; enable multithreading/concurrent streams in software settings; avoid sharing bandwidth-heavy apps on same server; regularly defragment file-based repositories if supported by OS/tools used.
Q2: How do I set up alerts when my backup repository runs low on space?
A2: In most platforms go to SETTINGS > REPOSITORIES > select desired repo > enable threshold alerting/email notifications when free space drops below defined percentage value.
Q3: What's the fastest way to troubleshoot "permission denied" errors during job runs?
A3: Check directory/file ownership matches agent user > confirm group membership > review SELinux/AppArmor logs > test manual write/delete using same credentials as agent process.
Conclusion
A well-designed backup repository forms the core of any reliable IT protection plan—from daily operations through worst-case recoveries! By learning setup/security best practices now you'll save headaches later—and with Vinchin's advanced features safeguarding every byte has never been easier! Try our free trial today!
Share on:









