-
What Is a Database in MySQL
-
Prerequisites for Creating a Database
-
Method 1: Using Command Line to Create Database in MySQL
-
Method 2: Using phpMyAdmin to Create Database in MySQL
-
Method 3: Using MySQL Workbench to Create Database in MySQL
-
Troubleshooting Database Creation Issues
-
Protecting Your New Database: Introducing Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
How to Create Database in MySQL FAQs
-
Conclusion
Creating a database is often the first task when building any application that needs to store data. For IT operations professionals working with MySQL—one of the world’s most popular open-source relational database management systems—this is a routine but critical job. Knowing how to create databases efficiently helps you support everything from small websites to large enterprise platforms. In this guide, you’ll learn how to create a database in MySQL using different methods: command line, phpMyAdmin, and MySQL Workbench. We’ll also cover common issues you might face during setup and explain how to protect your valuable data assets.
What Is a Database in MySQL
A database in MySQL is an organized collection of structured information stored as tables. Each table holds rows and columns of related data. Databases can also include views, indexes, stored procedures, and other objects that help manage or retrieve information quickly. With MySQL’s flexibility and performance, databases power many business-critical applications worldwide. Understanding how databases work—and how they are created—is essential for any IT administrator or developer who wants reliable data storage.
Prerequisites for Creating a Database
Before you start creating databases in MySQL, make sure your environment is ready. First, confirm that MySQL Server is installed on your system and running properly. On Linux systems, check its status by running systemctl status mysql or systemctl status mysqld. On Windows machines, open Services from the Control Panel (services.msc) and look for MySQL in the list.
Next, ensure you have access credentials—a username and password—with at least the CREATE privilege on your target server. If you plan to use graphical tools like phpMyAdmin or MySQL Workbench instead of command line tools, verify these applications are installed and configured correctly so they can connect to your server instance.
Finally, keep your login details handy before proceeding further.
Method 1: Using Command Line to Create Database in MySQL
Many administrators prefer using the command line because it offers speed and precise control over every step.
Start by opening your terminal (Linux/macOS) or command prompt (Windows). To connect locally as root user:
mysql -u root -p
If you need to connect remotely—for example from another server—add host information:
mysql -h [hostname_or_IP] -u [username] -p
After entering your password at the prompt, you’ll see mysql> indicating successful login.
It’s good practice to review existing databases before creating new ones:
SHOW DATABASES;
To create a new database named your_database_name, run:
CREATE DATABASE your_database_name;
If there’s a chance this name already exists—or if scripts may run multiple times—use this safer version:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS your_database_name;
Setting Default Character Set and Collation (Optional)
Choosing an appropriate character set ensures proper storage of text data across languages or special symbols. By default, recent versions of MySQL use utf8mb4, which supports full Unicode—including emojis—while older utf8 does not handle all characters correctly. You can specify both character set and collation like this:
CREATE DATABASE your_database_name CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
This setting helps prevent future problems with internationalization or special characters.
After creation completes successfully (no error message), confirm by listing all databases again:
SHOW DATABASES;
To start working inside your new database immediately:
USE your_database_name;
From here you can begin creating tables or importing data as needed.
For persistent configuration changes—such as always using certain charsets—you may edit global settings in my.cnf (Linux) or my.ini (Windows), but be careful since these affect all future databases unless overridden per-database.
Method 2: Using phpMyAdmin to Create Database in MySQL
phpMyAdmin provides a web-based interface ideal for those who prefer visual tools over typing commands directly into terminals. It’s commonly bundled with shared hosting environments but can also be installed separately on servers.
Begin by logging into phpMyAdmin through your browser using valid credentials provided by your hosting provider or system administrator.
Once logged in successfully:
Click on Databases at the top navigation bar.
Find Create database, enter a unique name for your new database.
Optionally select collation from its drop-down menu if specific sorting rules are required; otherwise leave default values.
Click Create button when ready.
phpMyAdmin will display confirmation once creation succeeds; look for it listed along the left sidebar panel under available databases.
To begin managing tables within this new space:
Click on its name from sidebar list.
Use tabs such as Structure, Insert, or Export according to what tasks come next.
If user management is needed right away:
Go back up top menu bar,
Select User accounts
Click Add user account
Fill out requested fields including username/password
To streamline setup check box labeled Create database with same name and grant all privileges
Complete process following prompts shown onscreen
This approach makes initial setup easy even if you’re not comfortable with SQL syntax yet—but remember advanced features may still require direct queries later on!
Method 3: Using MySQL Workbench to Create Database in MySQL
MySQL Workbench is an official desktop client tool available across Windows/Linux/macOS platforms. It offers powerful visual modeling features alongside basic administrative tasks like schema creation—which makes it popular among developers handling complex projects locally or remotely.
Open MySQL Workbench application then connect using saved credentials under section labeled MySQL Connections; double-click desired connection profile then enter password if prompted until dashboard loads fully.
Look near top toolbar area for icon resembling cylinder plus sign (Create a new schema in connected server) then click it—or right-click anywhere inside left-hand panel called Schemas choosing option labeled Create Schema
A dialog window appears where:
Enter desired schema/database name into field marked Name
Optionally pick preferred character set/collation matching application requirements
Click Apply
You’ll see preview window showing generated SQL statement; review briefly then click Apply again followed by final confirmation via clicking Finish
Your newly created schema now appears within left-side Schemas panel; right-click its entry selecting option called Set as Default Schema so subsequent actions apply here automatically without extra steps each time
From here onward proceed building tables/views/functions according project needs—all visually managed through intuitive GUI elements rather than raw SQL code alone!
Troubleshooting Database Creation Issues
Even experienced admins sometimes encounter problems when trying to create new databases—especially after fresh installations or migrations between servers/environments.
Connection and Authentication Errors
Connection failures are common stumbling blocks during initial setup:
If you see “Can’t connect to MySQL server on 'localhost' (10061)” check whether service actually runs (
systemctl status mysql/ restart if necessary).For “Access denied for user 'user'@'host'” errors verify correct username/password combination was entered AND that account has permission connecting from current client IP address—not just localhost! You can inspect permissions assigned via query:
SHOW GRANTS FOR 'your_username'@'your_host';
If unsure about allowed hosts revisit user definitions inside built-in mysql.user table adjusting accordingly via admin tools or direct queries as needed.
Other Common Problems During Creation
Sometimes names conflict with existing objects—or violate naming conventions enforced by server settings:
If error says "database exists," add clause
IF NOT EXISTSwhen issuing CREATE statement.Stick only with letters/numbers/underscores avoiding reserved keywords per naming rules.
GUI users may find buttons grayed out/unresponsive if their session lost connectivity mid-task; try refreshing page/restarting app after confirming backend service remains healthy.
In rare cases disk space limits prevent successful creation; monitor free space regularly especially before bulk imports/migrations.
Lastly some cloud-hosted environments restrict certain privileges—even root logins—to enforce security best practices so consult documentation/support channels provided by vendor whenever unexpected denials occur!
Protecting Your New Database: Introducing Vinchin Backup & Recovery
After successfully creating a new MySQL database, safeguarding it against potential threats becomes crucial for long-term reliability and compliance needs across organizations of any size.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-level backup solution supporting today’s mainstream platforms—including Oracle, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, TiDB—and especially robust support for MySQL environments.
Key features relevant for protecting newly created databases include:
Incremental backup capabilities tailored for efficient storage usage
Batch backup management across multiple instances
Multi-level compression options
Flexible retention policies
Automated recovery verification via SQL scripts
Together these functions streamline backup operations while ensuring recoverability even after accidental deletions or ransomware attacks.
Step 1: Select the MySQL database to backup
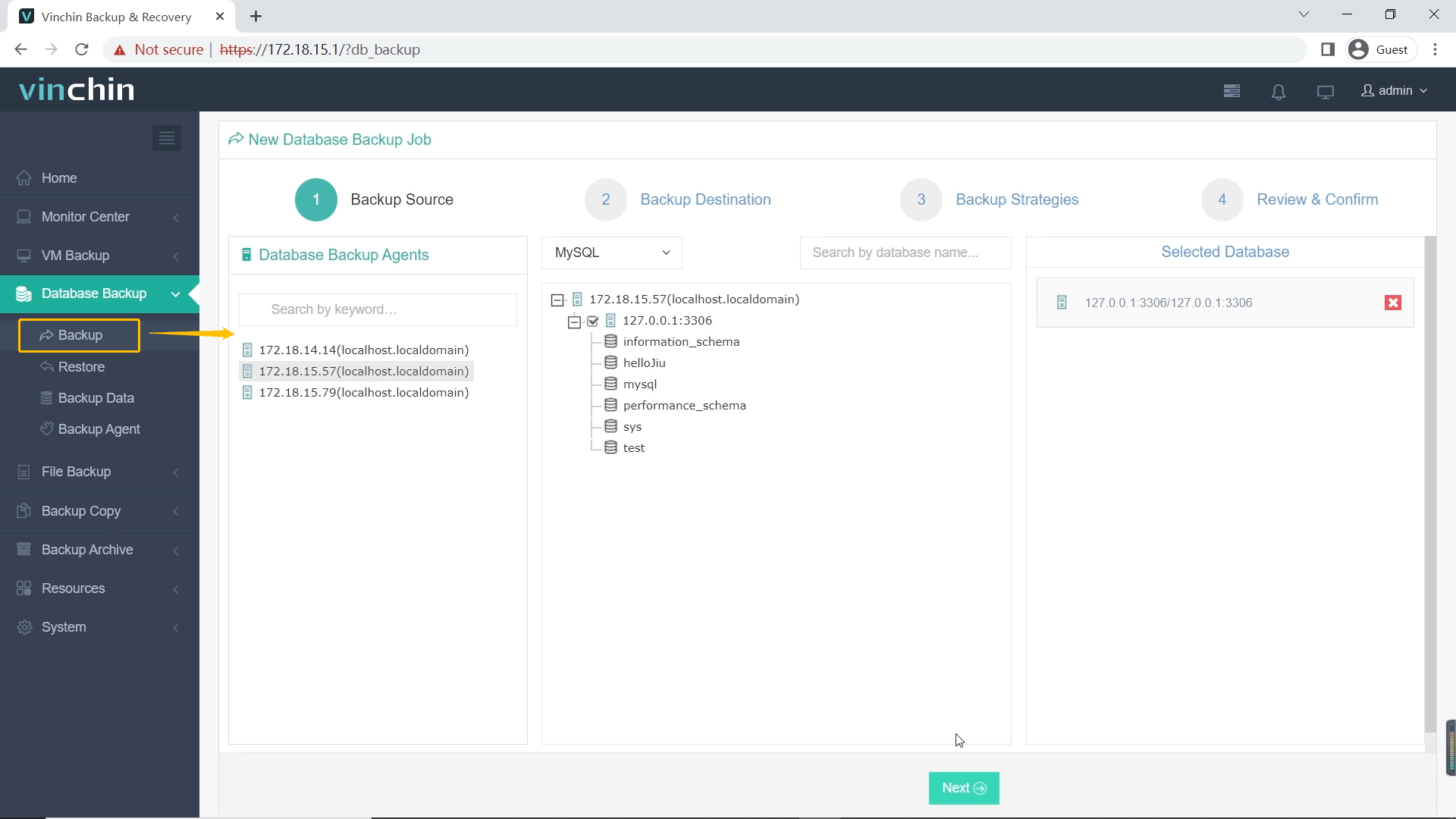
Step 2: Choose backup storage
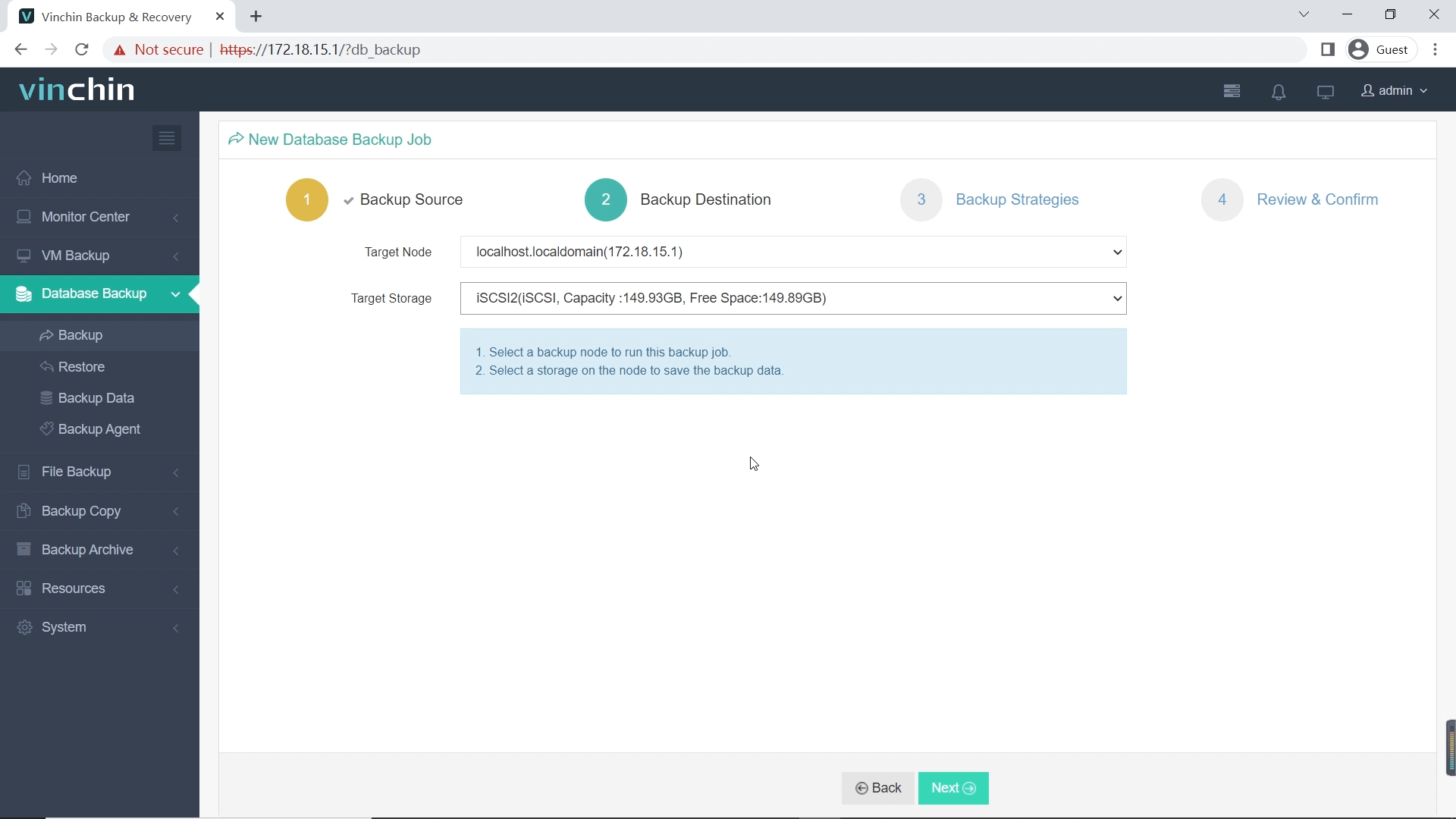
Step 3: Define backup strategy

Step 4: Submit the job

With thousands of satisfied customers worldwide and consistently high ratings among enterprise users, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers trusted data protection. Try every feature free for 60 days—click below to download now!
How to Create Database in MySQL FAQs
Q1: Can I create a new database on my production server without downtime?
A1: Yes—as long as resources allow—you can safely add new databases while other services remain online since creation itself does not interrupt running workloads.
Q2: What should I do if my GUI tool cannot connect but CLI works?
A2: Check network firewalls/client IP whitelists/server bind-address settings ensuring GUI traffic reaches correct port/IP used by CLI.
Q3: Which character set should I choose when supporting multiple languages?
A3: Select utf8mb4 plus utf8mb4_unicode_ci collation—it covers nearly all modern scripts including emojis ensuring broad compatibility.
Conclusion
Creating databases in MySQL is straightforward whether using command line tools or graphical interfaces like phpMyAdmin/MySQL Workbench—just follow best practices around permissions/naming/settings each time. Regular backups matter too. Vinchin delivers reliable protection trusted globally. Try their free trial today
Share on:







