-
What Is RMAN Catalog?
-
Why Use RMAN Catalog?
-
Setting Up rman catalog start with Command
-
How to Protect Oracle Database Workloads With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
rman catalog start with FAQs
-
Conclusion
Managing Oracle database backups is a critical task for any operations administrator. When you move or restore backup files, you need a way to make Oracle RMAN aware of these files again. That’s where the rman catalog start with command comes in handy. This article explains what the RMAN catalog is, why you should use it, and how to register backup files using the catalog start with command—step by step.
What Is RMAN Catalog?
The RMAN catalog is a schema stored in a separate Oracle database that keeps metadata about your backups, archived logs, and database structure details. While RMAN can use your target database’s control file to store this information by default, using a recovery catalog gives you a central place to manage backup data across many databases.
This central repository tracks backup history for multiple databases at once and retains records longer than your control file’s retention period allows. According to the Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User’s Guide, an external recovery catalog is essential for advanced backup management—especially if you run large or multi-database environments.
The recovery catalog also stores scripts for common tasks and supports detailed reporting features that help administrators audit their backup strategies over time.
Why Use RMAN Catalog?
Using an RMAN catalog offers several important advantages over relying only on control files:
First, it protects your backup metadata even if your target database’s control file gets lost or corrupted—a risk during hardware failures or disasters.
Second, it lets you manage backups from many databases in one place instead of juggling separate records for each system.
Third, it enables much longer retention of backup history than what’s possible with just control files alone; this helps meet compliance requirements or internal policies about data protection.
Finally, the recovery catalog supports features like stored scripts (for automating repetitive tasks) and detailed reporting (for audits), making overall backup management more efficient and reliable.
If you operate complex systems or have strict business continuity needs, setting up an RMAN recovery catalog is considered best practice by most experts.
Setting Up rman catalog start with Command
When you move Oracle backup files between servers or restore them from another location (such as after disaster recovery), RMAN does not automatically know about these new locations. The rman catalog start with command registers all valid Oracle backup sets, datafile copies, control file copies, and archived redo logs found under a specified directory path prefix.
This process ensures that every eligible file becomes visible to RMAN—even if they were created elsewhere or restored from tape/NAS storage—and can be used for future restores or recoveries without manual intervention.
Let’s walk through how this works step by step:
1. Connect to RMAN and the Target Database
Before registering any files with catalog start with, connect both to your target Oracle database instance (the one whose backups you want to manage) and—if using one—to your external recovery catalog:
rman target / catalog rman_user@catdb
Replace rman_user@catdb with your actual connection string for the recovery catalog database user account. If not using an external recovery catalog yet (just relying on local control files), omit everything after target /.
2. Identify Directory Path Prefix
Decide which directory contains—or starts—the set of backup files needing registration. For example: /disk1/backups/. Be careful here: On Unix/Linux systems especially,
A trailing slash (
/disk1/backups/) tells RMAN to scan only that specific directory.Omitting the slash (
/disk1/backups) causes RMAN to include all subdirectories starting with that prefix—including/disk1/backups-year2023,/disk1/backups-old, etc.—which may result in unwanted extra files being scanned.On Windows systems use backslashes:
C:\oracle\backups\.
Always double-check which directories are included before running commands on production systems!
3. Run CATALOG START WITH Command
At the RMAN prompt type:
CATALOG START WITH '/disk1/backups/';
RMAN scans all accessible files matching this path prefix that are not already known in its repository (either local control file or external recovery catalog). It lists each discovered file before asking whether you wish to proceed.
4. Confirm Cataloging
After scanning completes,
RMAN displays something like:
Do you really want to catalog the above files (enter YES or NO)?
Type YES at this prompt if everything looks correct; otherwise type NO if unexpected paths appeared due to incorrect prefixes—you can then adjust accordingly before retrying.
Once confirmed,
RMAN catalogs every listed file into its metadata repository so they become available for future restore/recovery operations immediately.
5. Verify Cataloged Files
To confirm successful registration,
run:
LIST BACKUP;
This shows all known backups—including newly registered ones—so you can verify nothing was missed during scanning/cataloging steps above.
For further validation,
you might run SQL queries against views like RC_BACKUP_SET within your external recovery catalog schema:
SELECT HANDLE FROM RC_BACKUP_SET WHERE HANDLE LIKE '/disk1/backups/%';
This helps ensure every expected file now appears within official records managed by Oracle itself—not just OS-level listings!
6. Use NOPROMPT For Automation
If automating via scripts—or simply want hands-off operation—you may skip manual confirmation prompts entirely by adding NOPROMPT keyword:
CATALOG START WITH '/disk1/backups/' NOPROMPT;
This approach suits scheduled jobs run via cron/Scheduler where human interaction isn’t practical but always review logs afterward since mistakes could go unnoticed otherwise!
Here’s how such automation might look inside a shell script scheduled nightly:
#!/bin/bash rman target / catalog rman_user@catdb <<EOF CATALOG START WITH '/backups/' NOPROMPT; EXIT; EOF
Remember: Always test automated scripts thoroughly on non-production datasets first!
How to Protect Oracle Database Workloads With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Beyond native tools like RMAN for managing Oracle backups—including advanced options such as mass-registration via CATALOG START WITH—it is valuable to consider modern enterprise solutions built specifically for today’s diverse IT landscapes. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional-grade platform supporting mainstream databases including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—all natively integrated out-of-the-box.
For organizations protecting critical workloads such as Oracle databases, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers key capabilities including incremental backups support, advanced source-side compression tailored for high-performance environments, flexible batch database backup scheduling across multiple instances at once, granular data retention policies including GFS retention strategies for compliance needs, and robust storage protection mechanisms against ransomware threats—all designed to streamline administration while maximizing security and efficiency throughout the lifecycle of enterprise data protection operations.
With its intuitive web console interface simplifying daily tasks into four clear steps
Step 1: Select the Oracle database to back up
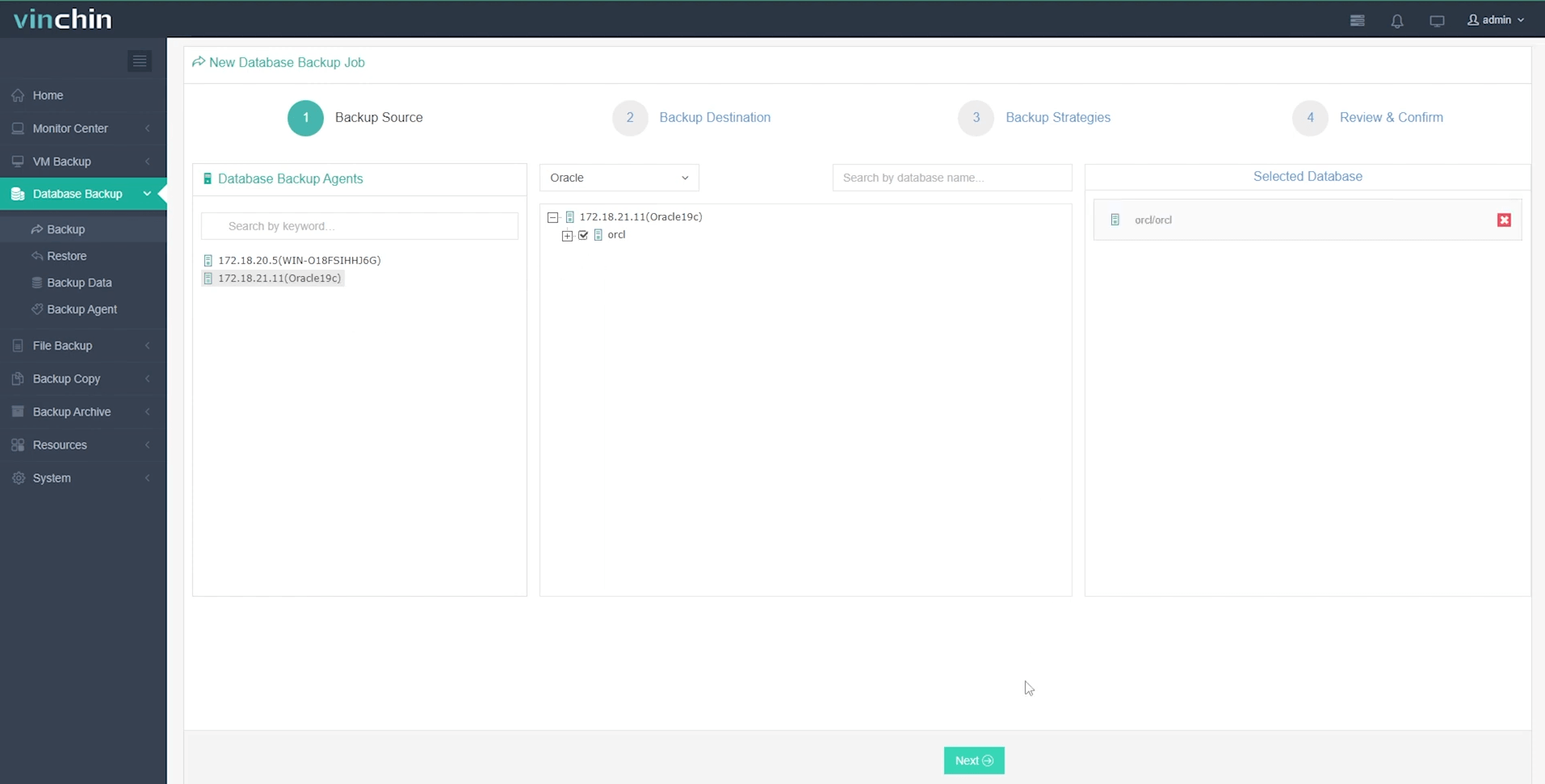
Step 2: Choose your preferred backup storage
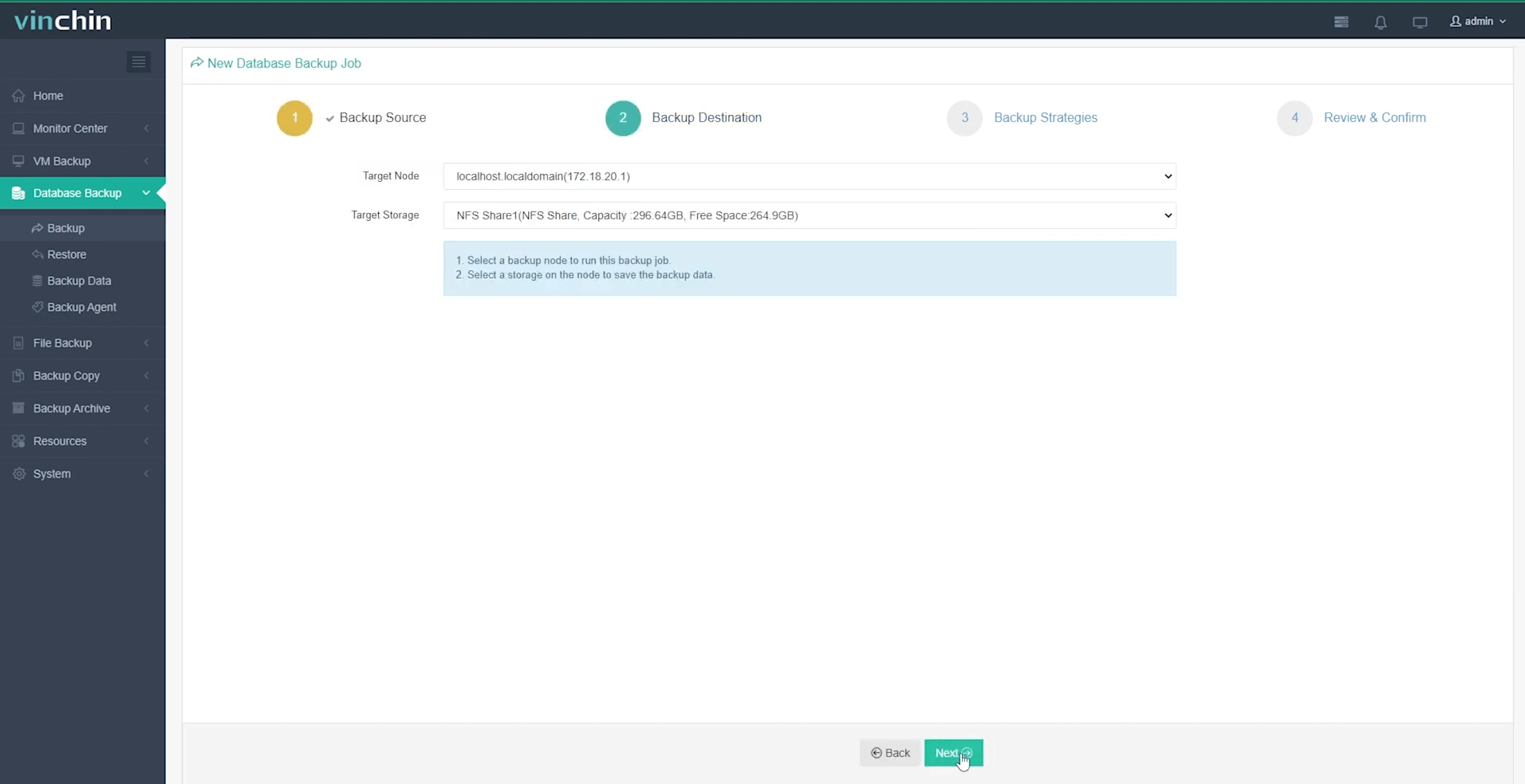
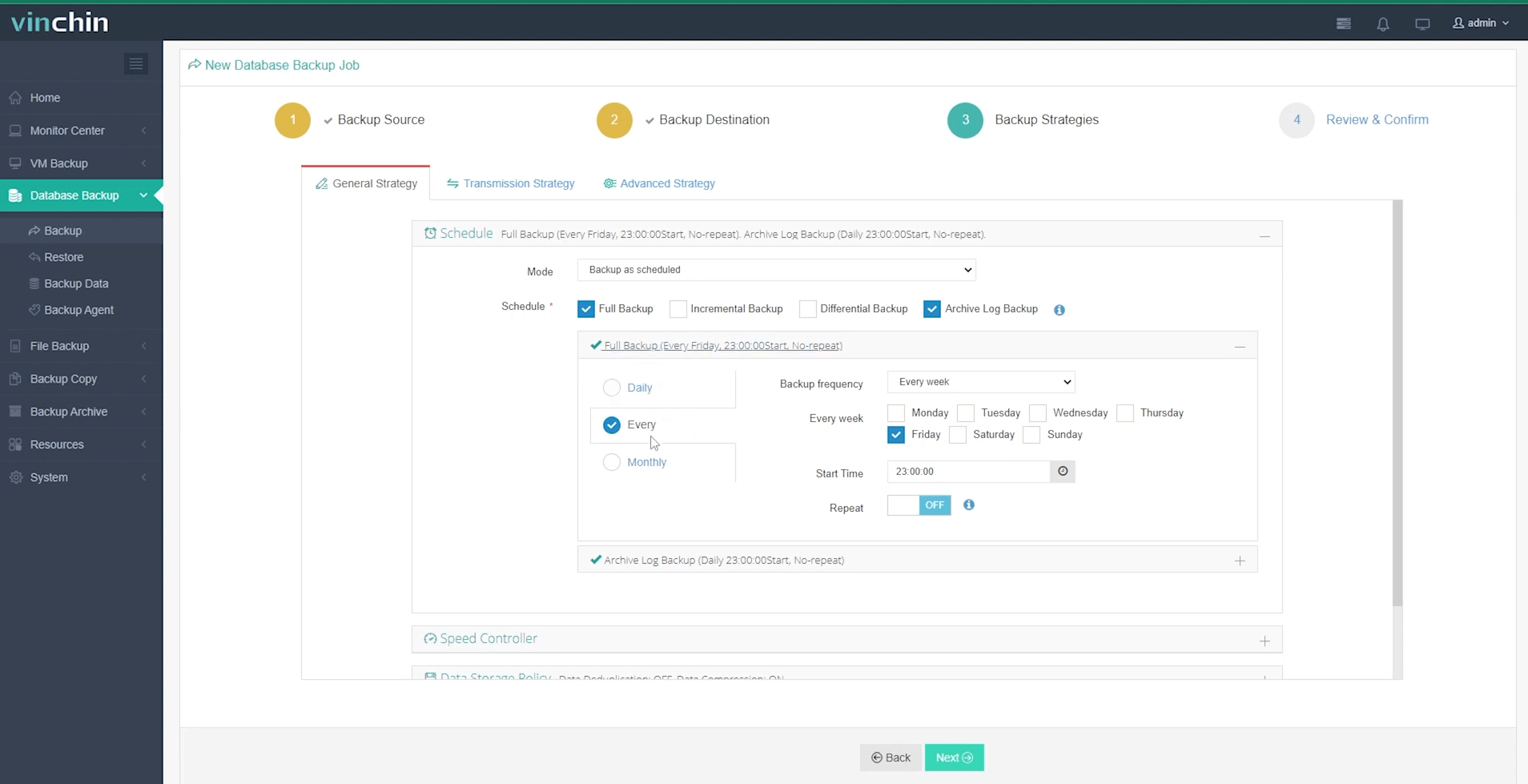
Step 3: Define a tailored backup strategy
Step 4: Submit the job
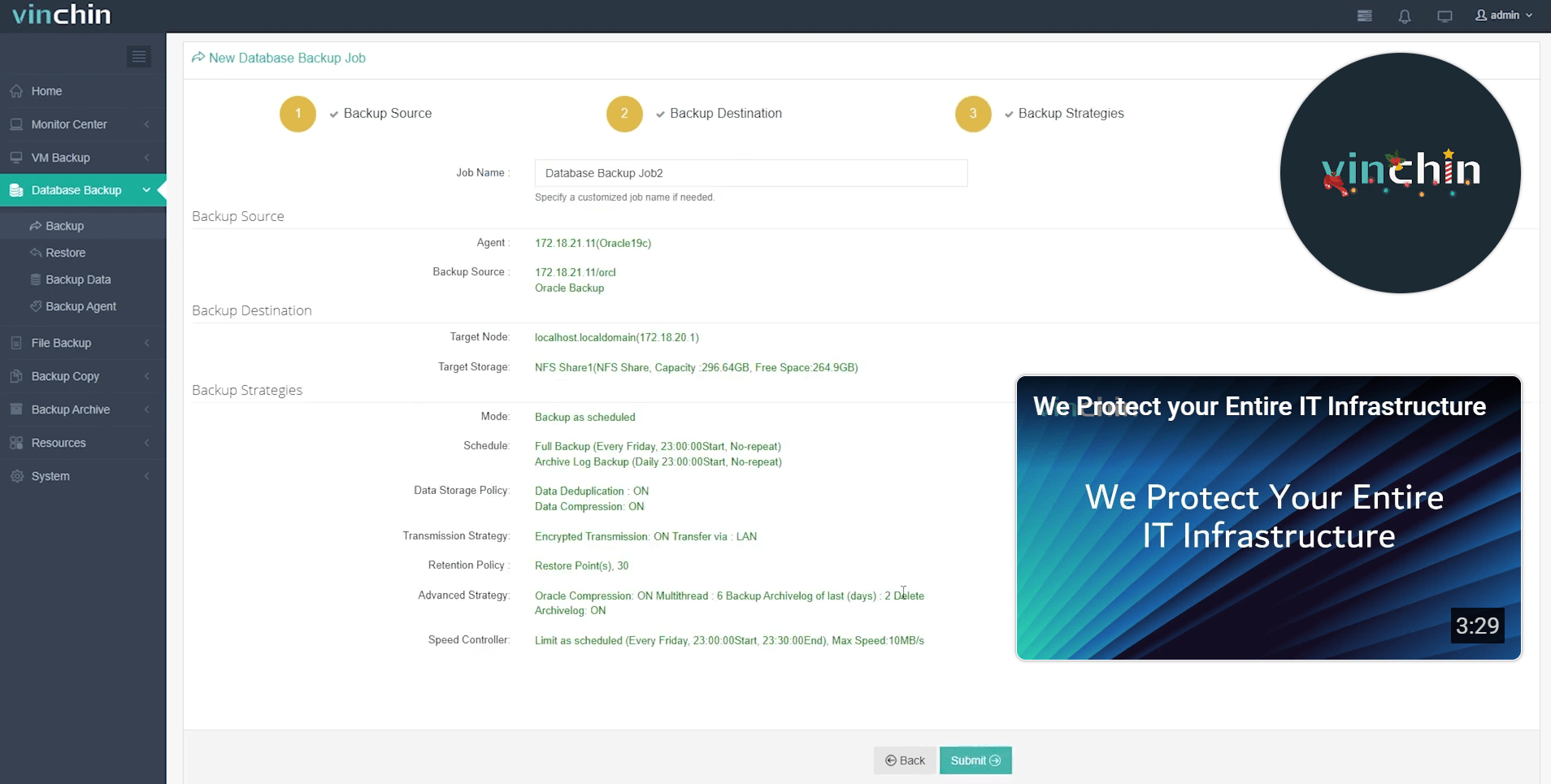
Recognized globally among enterprise users—with top ratings and thousands of satisfied customers worldwide—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured 60-day free trial so you can experience powerful protection firsthand. Click below now to get started risk-free!
rman catalog start with FAQs
Q1: Can I use catalog start with after restoring old NAS snapshots?
Yes—you can point at any mounted directory containing valid Oracle-format backups regardless of original creation method/location.
Q2: What does "RMAN–06004" mean during registration?
It signals an invalid/corrupt header was encountered; try verifying affected file(s) using DBVERIFY tool before retrying registration attempt(s).
Q3: How do I automate periodic re-cataloging across multiple folders?
Write a shell script looping through desired paths | call CATALOG START WITH 'path' NOPROMPT | schedule script via CRON/Scheduler utility.
Conclusion
The rman catalog start with command makes registering moved or restored Oracle backup files simple—even across complex environments—with options suited for manual checks OR full automation alike! For complete protection plus streamlined management across diverse workloads consider trying Vinchin free today—it could transform your daily operations fast!
Share on:







