-
What Is Oracle 11g RMAN Duplicate Database?
-
Why Duplicate Database From Backup in Oracle 11g?
-
Method 1 Using RMAN Duplicate Database From Backup
-
Method 2 Using Active Database Duplication in RMAN
-
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Protection for Oracle Databases
-
Oracle 11g RMAN Duplicate Database From Backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Duplicating an Oracle 11g database with RMAN is a vital skill for operations administrators. Whether you need to build a test environment, migrate data, or set up disaster recovery, the DUPLICATE command in RMAN is your go-to tool. But what does it take to duplicate an Oracle 11g database from backup? Let’s walk through the process step by step and explore some advanced scenarios.
What Is Oracle 11g RMAN Duplicate Database?
The DUPLICATE command in RMAN creates a full copy of your source database. This new instance, often called a "clone," has its own unique DBID and operates independently. You can use this clone for testing, reporting, or as part of your standby setup. There are two main ways to duplicate: using existing backups or copying directly from the active database over the network. Both methods automate restore and recovery tasks, making cloning safer and faster than manual approaches.
Why Duplicate Database From Backup in Oracle 11g?
Why choose duplication from backup instead of always using active duplication? Several reasons make this approach attractive:
Reduced Source Load: By working with backups, you avoid putting extra strain on your production system.
Network Flexibility: Backups can be moved to any destination host—even if there’s no direct connection between source and target.
Point-in-Time Cloning: You can restore the database to a specific time or SCN (System Change Number), which is useful for testing changes or recovering lost data.
Disaster Recovery: If your original system fails, you can quickly create a replacement instance from backup.
Have you ever needed to test an upgrade without risking live data? Duplication from backup makes that possible with minimal risk.
Method 1 Using RMAN Duplicate Database From Backup
Duplicating from backup is reliable and flexible. Here’s how you do it according to best practices.
First, ensure you have a valid RMAN backup of your source database—including all datafiles, archived logs, and at least one control file backup. Copy these files so they’re accessible by the destination (auxiliary) server.
Before starting the duplication process itself, let’s look at each stage more closely:
1. Prepare the Auxiliary Instance:
Begin by creating a password file for the new database using orapwd—this ensures secure authentication for administrative users like SYS. Next, create a minimal parameter file (PFILE, usually named init<SID>.ora). At minimum, include parameters such as DB_NAME (matching the source), DB_UNIQUE_NAME (must differ from source), and set CONTROL_FILES to point where control files will reside on the auxiliary host. It’s also wise to specify memory settings like MEMORY_TARGET or SGA_TARGET based on available resources on your destination server. Create all necessary directories for datafiles, control files, redo logs, and archive logs before proceeding.
2. Copy Backups:
Use tools like scp or another secure method to transfer all relevant RMAN backup pieces—including archived logs and control file backups—to storage accessible by the auxiliary server.
3. Start the Auxiliary Database:
Set your environment variable (ORACLE_SID) to match your new database name on the auxiliary host. Start up the instance in NOMOUNT mode using your PFILE:
sqlplus / as sysdba STARTUP NOMOUNT PFILE='/path/to/init<SID>.ora'
4. Connect to RMAN:
On your destination server, connect as follows:
rman AUXILIARY /
If you're restoring via Recovery Catalog rather than just control file autobackup—and especially if you've changed DBIDs—you may need:
SET DBID <source_dbid>
5. Run the DUPLICATE Command:
If your backup files are stored in different locations than those used by your source system—or if directory structures differ—use clauses like BACKUP LOCATION, DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT, or even explicit SET NEWNAME commands within a RUN block (see advanced mapping below). For simple cases where paths match exactly:
DUPLICATE DATABASE TO <new_db_name> BACKUP LOCATION '/path/to/backup' NOFILENAMECHECK;
The option
NOFILENAMECHECKis required when both databases share identical directory structures; otherwise use conversion parameters.To perform point-in-time recovery during duplication:
DUPLICATE DATABASE TO <new_db_name>
BACKUP LOCATION '/path/to/backup'
UNTIL TIME "TO_DATE('2023-10-27 15:00:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS')"
NOFILENAMECHECK;Make sure all necessary archived logs up until that time are present in your backup location.
Method 2 Using Active Database Duplication in RMAN
Active duplication lets you clone directly over network connections without needing pre-existing backups on disk at destination—a great choice when both servers are online together with reliable connectivity.
Here’s how it works:
1. Prepare Both Servers:
Ensure both systems have matching password files for SYS user authentication (orapwd). Update TNS configuration (tnsnames.ora, listener.ora) so each host can reach both databases over TCP/IP networks without firewall blocks.
2. Start Auxiliary Instance:
On target machine create minimal PFILE including unique identifiers (DB_UNIQUE_NAME) plus memory/control file locations as above; start instance in NOMOUNT mode.
3. Connect via RMAN:
Connect simultaneously to both databases:
rman TARGET sys/password@SOURCE_DB AUXILIARY sys/password@DEST_DB
4. Run DUPLICATE Command Over Network:
Use FROM ACTIVE DATABASE clause:
DUPLICATE DATABASE TO <new_db_name> FROM ACTIVE DATABASE NOFILENAMECHECK;
For improved performance during large transfers add SECTION SIZE parameter (e.g., SECTION SIZE 8G) so multiple channels work concurrently.
To reduce bandwidth usage enable compression inline:
DUPLICATE DATABASE TO <new_db_name> FROM ACTIVE DATABASE USING COMPRESSED BACKUPSET NOFILENAMECHECK;
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Protection for Oracle Databases
For organizations seeking streamlined protection beyond native tools like RMAN, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers professional enterprise-grade solutions tailored for modern environments—including comprehensive support for Oracle databases alongside MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB systems. With features such as advanced source-side compression (exclusive for Oracle), incremental backup capabilities tailored specifically for Oracle workloads, batch database management functions, robust GFS retention policies ensuring compliance-ready archiving cycles, and automated integrity checks validating recoverability—all designed to maximize efficiency while minimizing operational risk across critical business applications.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding Oracle databases straightforward:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
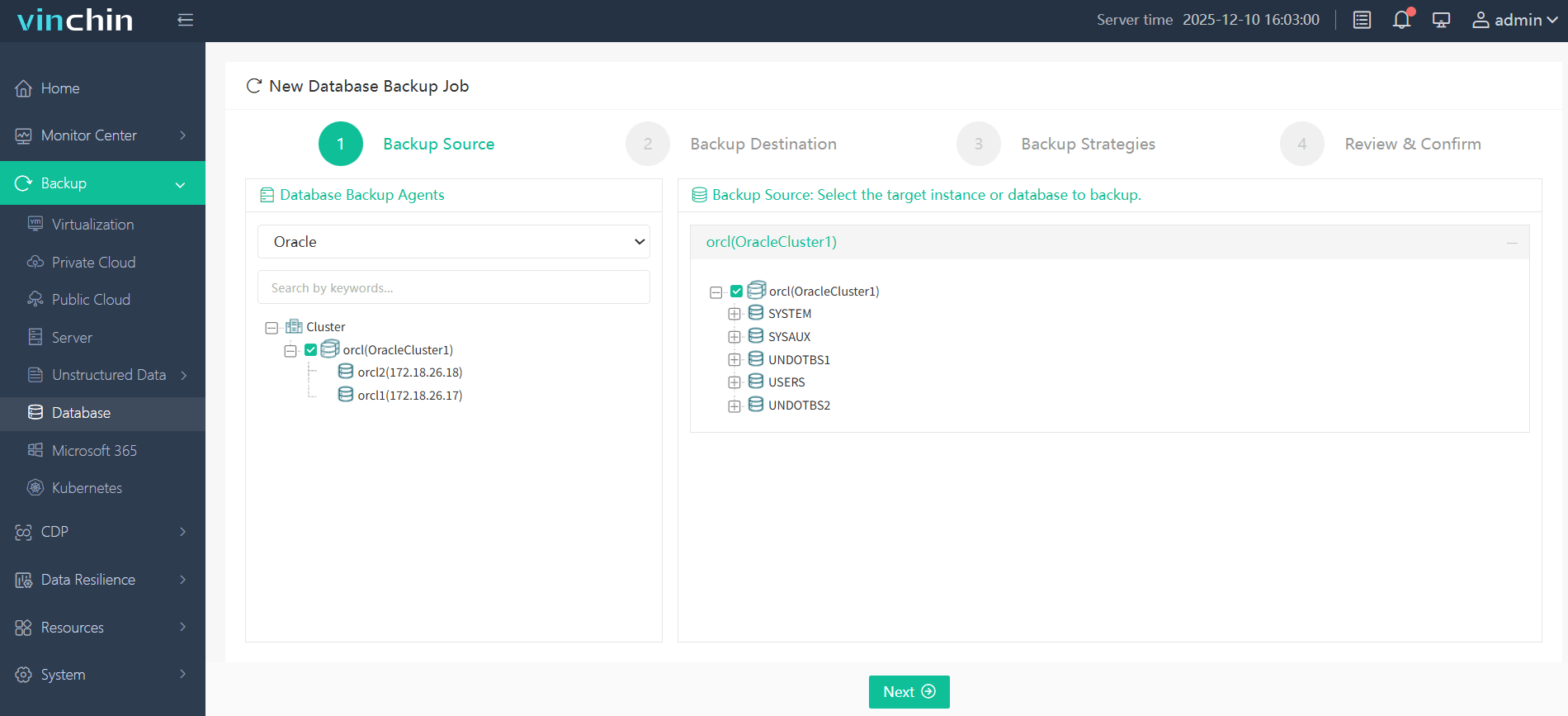
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
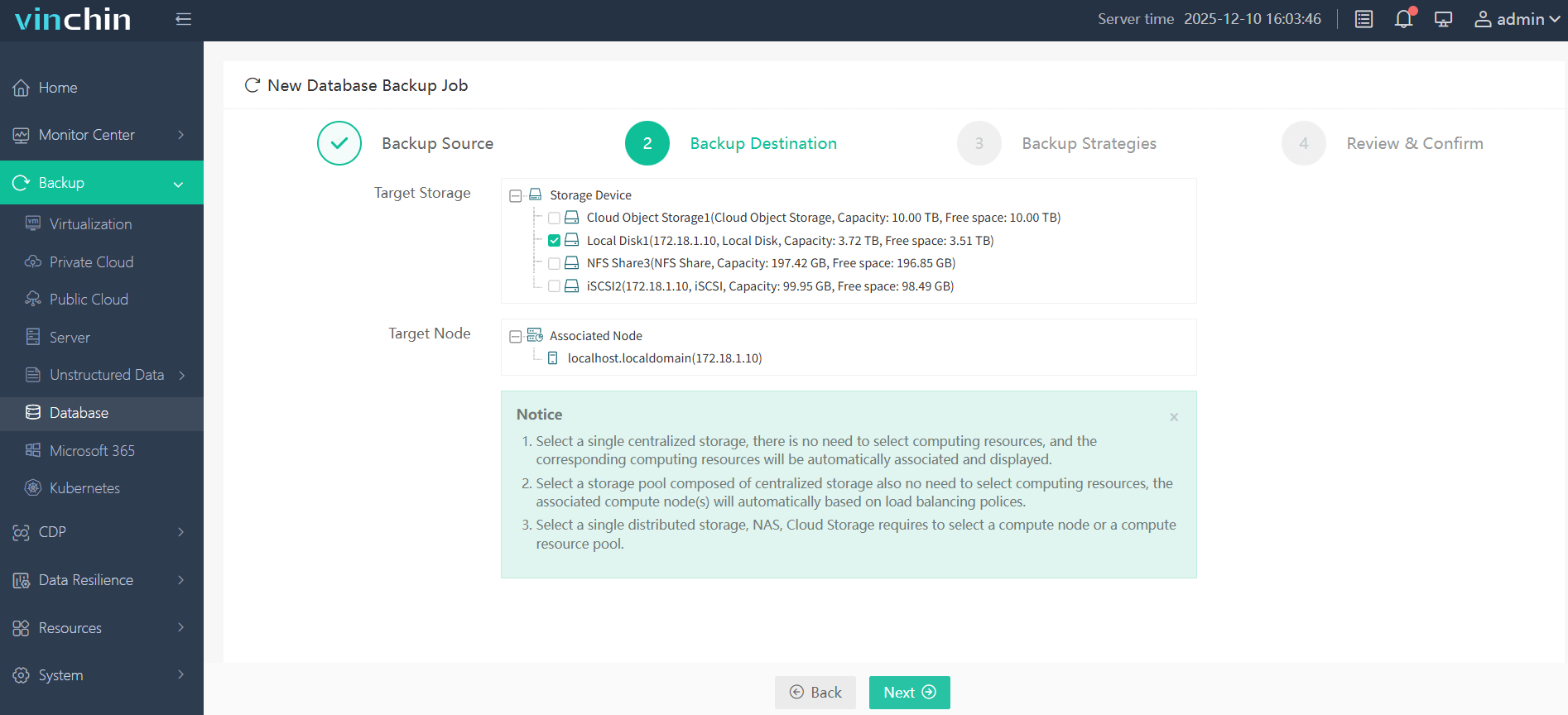
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
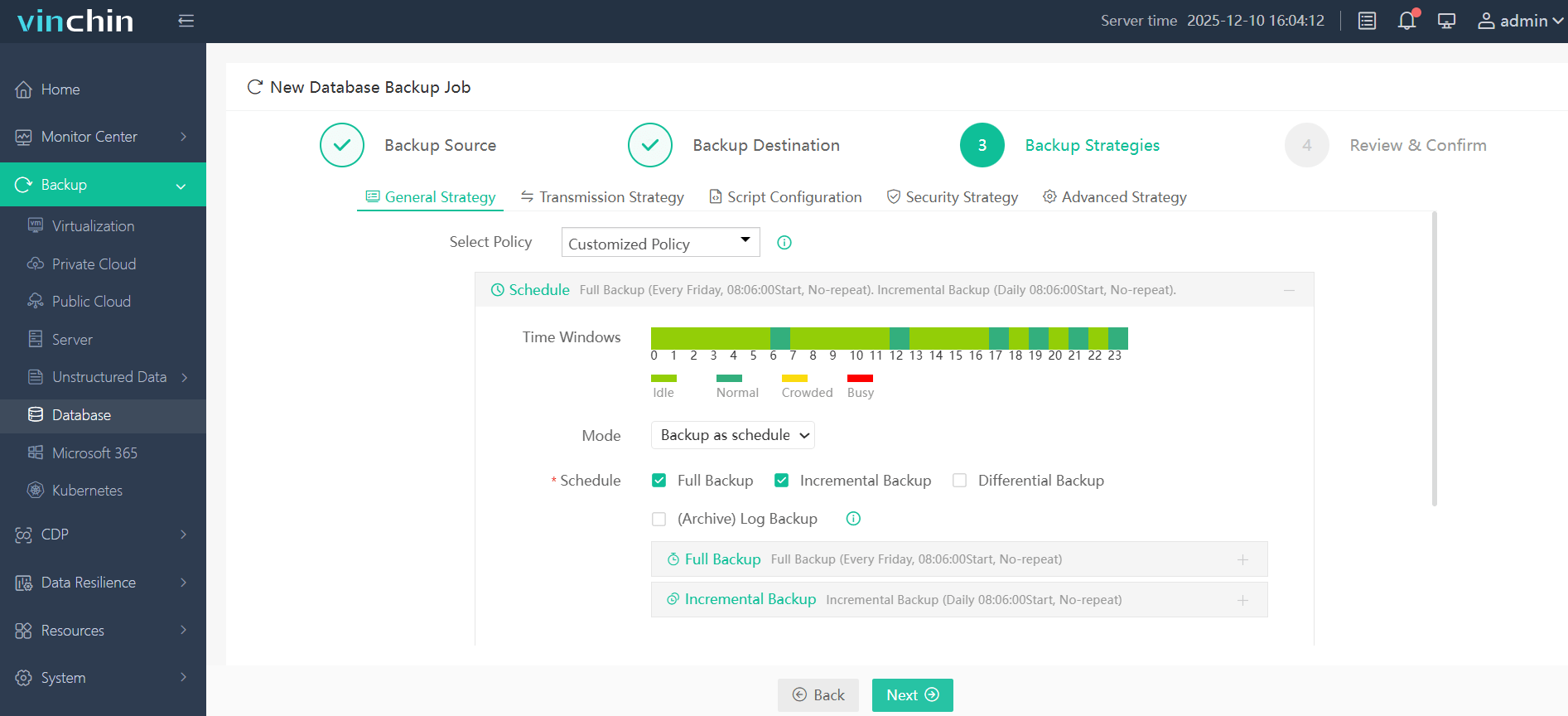
Step 4. Submit the job
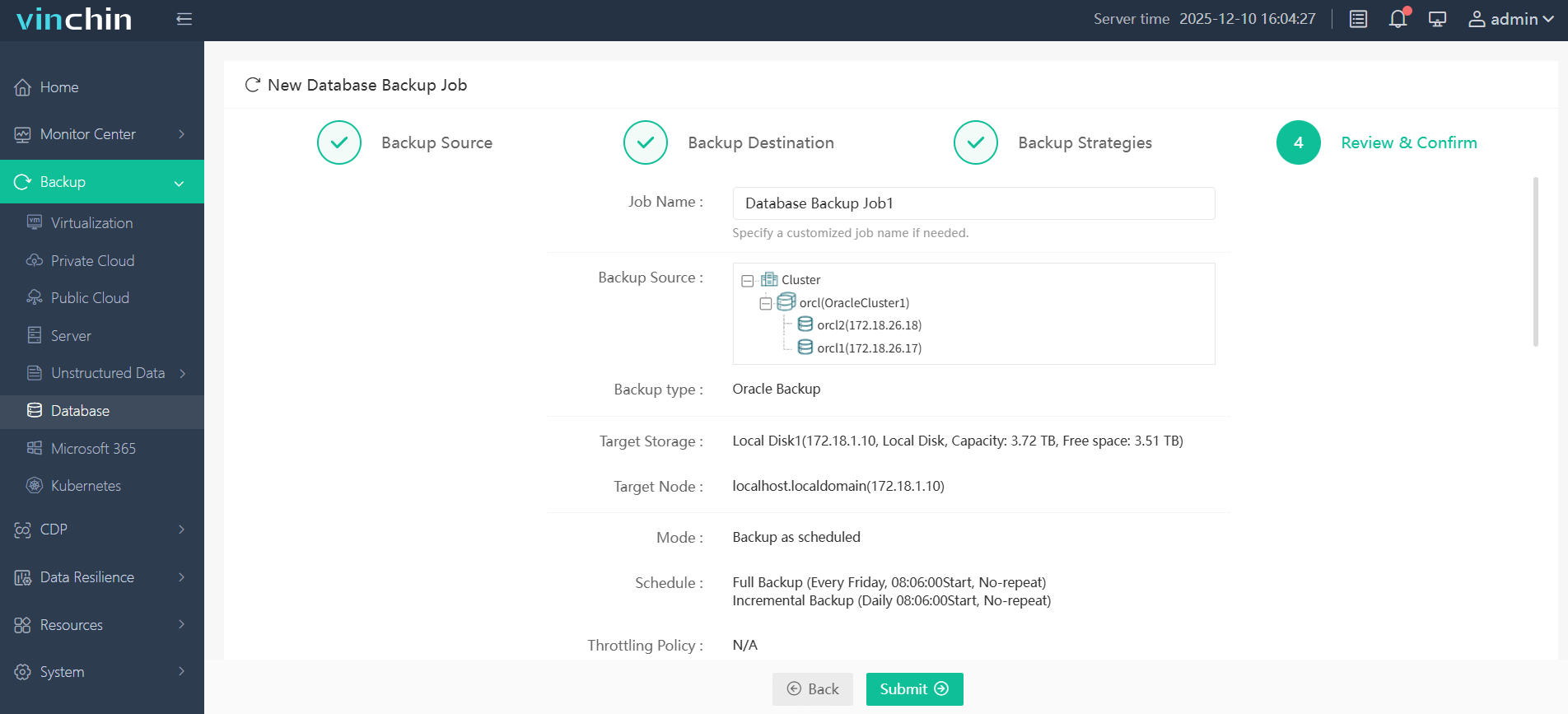
Vinchin Backup & Recovery enjoys global recognition among enterprises thanks to its reliability and top-rated customer support—explore every feature free with their fully functional 60-day trial by clicking download now!
Oracle 11g RMAN Duplicate Database From Backup FAQs
Q1: Can I duplicate an Oracle 11g database if my destination uses different folder names than my source?
A1: Yes; use DB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT or LOG_FILE_NAME_CONVERT parameters—or SET NEWNAME commands—to map old paths to new ones during duplication.
Q2: Can I duplicate only certain tablespaces instead of cloning everything?
A2: Yes; add TABLESPACE or SKIP TABLESPACE clauses within DUPLICATE command syntax as needed.
Q3: What should I do if some archived redo logs are missing during duplication?
A3: Either copy missing logs into place before starting—or limit restoration scope using UNTIL TIME/SCN clauses so only available archives are required.
Q4: What causes most common failures during an RMAN duplicate operation? How do I troubleshoot them?
A4: Check auxiliary instance parameter settings first; verify permissions on directories/backups; confirm all required archives exist; review alert/RMAN output logs immediately after errors appear.
Conclusion
Duplicating an Oracle 11g database from backup with RMAN gives administrators safe options for building test labs or disaster recovery sites while minimizing risk on production systems—all backed by clear automation steps documented here today! For even greater simplicity across mixed environments try Vinchin's robust solution free today—it could transform how easily you protect critical business information!
Share on:






