-
What Is OCI RMAN Backup?
-
Why Use Object Storage for Backups?
-
How to Use RMAN with OCI Object Storage?
-
How to Configure Oracle Database Backup Module for OCI Object Storage?
-
Restoring from OCI Object Storage
-
Introducing Vinchin Backup & Recovery for Enterprise-Level Database Protection
-
OCI RMAN Backup to Object Storage FAQs
-
Conclusion
Are you searching for a secure way to back up your Oracle database to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage using RMAN? Many operations administrators want cloud backups for durability, scalability, and cost savings. In this guide, you’ll learn what OCI RMAN backup is, why object storage is ideal for backups, how to configure everything step by step—including both initial setup and ongoing management—and how to restore data if disaster strikes. We’ll also show how Vinchin can simplify Oracle database protection in OCI environments.
What Is OCI RMAN Backup?
OCI RMAN backup means using Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) to send Oracle database backups directly into OCI Object Storage. RMAN is Oracle’s built-in tool for managing backup and recovery tasks. By connecting it with OCI Object Storage, you move your critical data offsite—protecting it from local failures like hardware crashes or site disasters.
This integration lets you automate retention policies and leverage cloud features such as encryption at rest or in transit. It’s fully supported by Oracle, so you can trust its reliability in production environments.
Why Use Object Storage for Backups?
Object storage in OCI offers high durability—your data is stored redundantly across multiple devices within a region. Each backup goes into a bucket—a logical container that makes organizing easy. You can set retention rules so old backups are deleted automatically when no longer needed.
Encryption protects your data both during transfer and while stored in the cloud. You choose between Standard (hot) storage for quick access or Archive (cold) storage for long-term retention at lower cost. With features like immutability settings, accidental deletion becomes much less likely—a key benefit for compliance-driven industries.
For disaster recovery planning or regulatory needs, object storage provides an offsite location that’s always available when you need it most.
How to Use RMAN with OCI Object Storage?
Backing up an Oracle database to OCI Object Storage with RMAN involves several steps—from preparing your environment through running regular automated jobs. Let’s walk through each stage so you can build confidence at every level.
Before diving into commands, remember: all backups sent to object storage must be encrypted per Oracle policy.
Step 1: Prepare Your Environment
First-time setup requires some groundwork:
Make sure you have an active OCI account.
Create a dedicated bucket in Object Storage where all backups will go.
Collect these details from the Identity section of the OCI Console:
Tenancy OCID
User OCID
Compartment OCID
Generate an API key pair (private/public) for authentication.
Note down the fingerprint of your public key after uploading it under your user profile.
You’ll use these credentials during module installation and configuration.
Step 2: Download and Install the Oracle Database Cloud Backup Module
The next step is installing the plugin that lets RMAN talk directly with OCI Object Storage:
1. Download oci_install.jar from Oracle Technology Network.
2. Place this file on your database server.
3. Unzip if necessary.
4. Run this command—replace placeholders with real values:
java -jar oci_install.jar \ -host https://objectstorage.<region>.oraclecloud.com \ -pvtKeyFile /path/to/oci_private_key.pem \ -pubFingerPrint <public_key_fingerprint> \ -uOCID <user_ocid> \ -tOCID <tenancy_ocid> \ -walletDir /path/to/wallet_directory \ -libDir /path/to/library_directory \ -bucket <bucket_name> \ -configFile /path/to/oci_config.ora
This extracts libopc.so, creates a wallet holding credentials securely, and generates a config file (oci_config.ora) used by RMAN later on.
If you need more control over parameters—such as specifying metadata buckets—you can edit oci_config.ora after installation.
Step 3: Configure RMAN Channels and Encryption
Now open RMAN on your server:
Set up channels so that all SBT (tape-like) operations point at the new library:
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE sbt PARMS='SBT_LIBRARY=/path/to/libopc.so,SBT_PARMS=(OPC_PFILE=/path/to/oci_config.ora)'; CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'MEDIUM'; CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE sbt BACKUP TYPE TO COMPRESSED BACKUPSET;
All cloud backups must be encrypted before leaving your server:
If Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) is enabled:
SET ENCRYPTION ON;
For password-based encryption:
SET ENCRYPTION ON IDENTIFIED BY 'your_password';
Choose whichever method fits your security policy best—but never skip encryption!
Step 4: Run Your First Backup
With everything configured, start backing up right away:
BACKUP CURRENT CONTROLFILE; BACKUP DATABASE;
After completion, check that files appear inside your chosen bucket via the OCI Console under Object Storage > Buckets > Your Bucket Name > Objects tab.
To verify within RMAN itself:
LIST BACKUP;
This shows all completed backup sets—including those now residing safely in object storage.
Step 5: Automate Regular Backups Using Scripts
Manual runs are fine at first but automation saves time—and reduces risk of missed jobs:
1. Write shell scripts calling rman target / @backup_script.rman.
2. Schedule them using cron jobs on Linux or Task Scheduler on Windows.
3. Monitor logs regularly by checking output files or querying V$RMAN_OUTPUT.
Advanced users may increase parallelism:
CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE sbt PARALLELISM 4;
This speeds up large database transfers by opening multiple channels simultaneously—as long as network bandwidth allows.
How to Configure Oracle Database Backup Module for OCI Object Storage?
The Database Backup Module acts as a bridge between RMAN and cloud object storage—it handles authentication securely behind-the-scenes while streaming data efficiently over HTTPS connections.
Setting it up follows these steps:
1. Generate API signing keys using OpenSSL or similar tools.
2. Upload public key via Identity > Users > Your User > API Keys, then copy its fingerprint.
3. Download oci_install.jar onto your server if not already done.
4. Run installer as shown above—making sure paths match actual locations on disk.
5. Edit generated config file (oci_config.ora) if extra options are needed—for example setting temporary buckets or adjusting retry logic.
6. Instruct RMAN which library/config file combo should handle SBT device type operations:
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE sbt PARMS='SBT_LIBRARY=/path/to/libopc.so,SBT_PARMS=(OPC_PFILE=/path/to/oci_config.ora)';
7.Ensure encryption settings match organizational requirements before launching any production job.
Restoring from OCI Object Storage
Restoration is just as important as backup—after all, what good is a backup if you cannot recover?
Here's how restoration works at different skill levels:
Beginner Level:
Make sure the Database Cloud Backup Module is installed again—even if restoring onto new hardware after disaster strikes! Use same config file format pointing at correct bucket/location info.
Intermediate Level:
Open RMAN prompt; configure channel exactly like during backup phase:
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE sbt PARMS='SBT_LIBRARY=/path/to/libopc.so,SBT_PARMS=(OPC_PFILE=/path/to/oci_config.ora)';
If password-encrypted backups were used originally:
SET DECRYPTION IDENTIFIED BY 'your_password';
Then run standard restore commands such as:
RESTORE CONTROLFILE FROM AUTOBACKUP; ALTER DATABASE MOUNT; RESTORE DATABASE; RECOVER DATABASE; ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS;
Introducing Vinchin Backup & Recovery for Enterprise-Level Database Protection
For organizations seeking streamlined protection of their Oracle databases in OCI environments, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers robust enterprise-level solutions tailored to modern needs—including full support for platforms like Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with special emphasis here on comprehensive Oracle coverage relevant to this article's focus keyword set (“OCI,” “RMAN,” “backup”). Key features include batch database backup management; flexible data retention policies; seamless cloud backup integration; restore-to-new-server capability; and integrity checks—all designed to automate processes, ensure compliance readiness, enable rapid disaster recovery scenarios across hybrid clouds or new servers, and maintain reliable recoverability of mission-critical workloads.
The intuitive web console makes protecting an Oracle environment remarkably simple:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
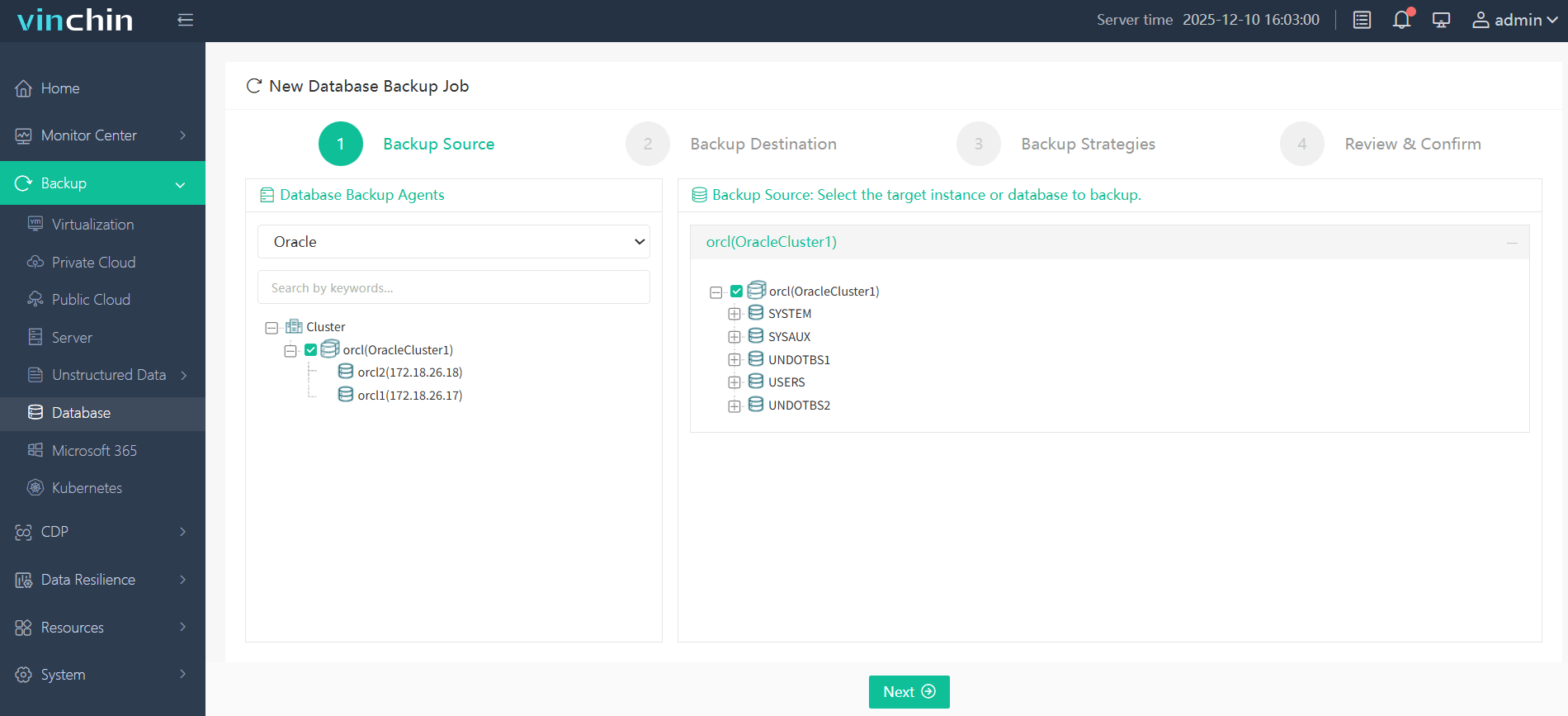
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
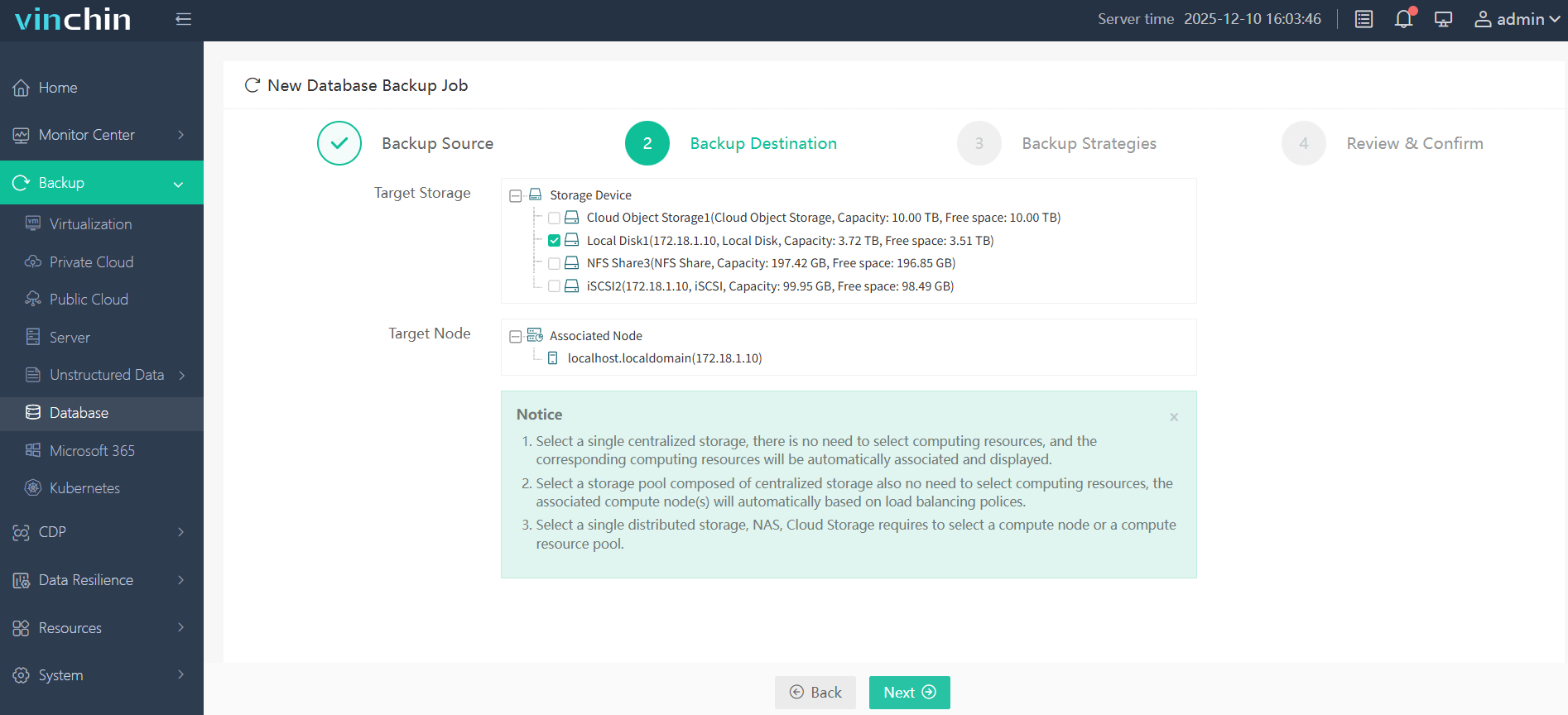
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
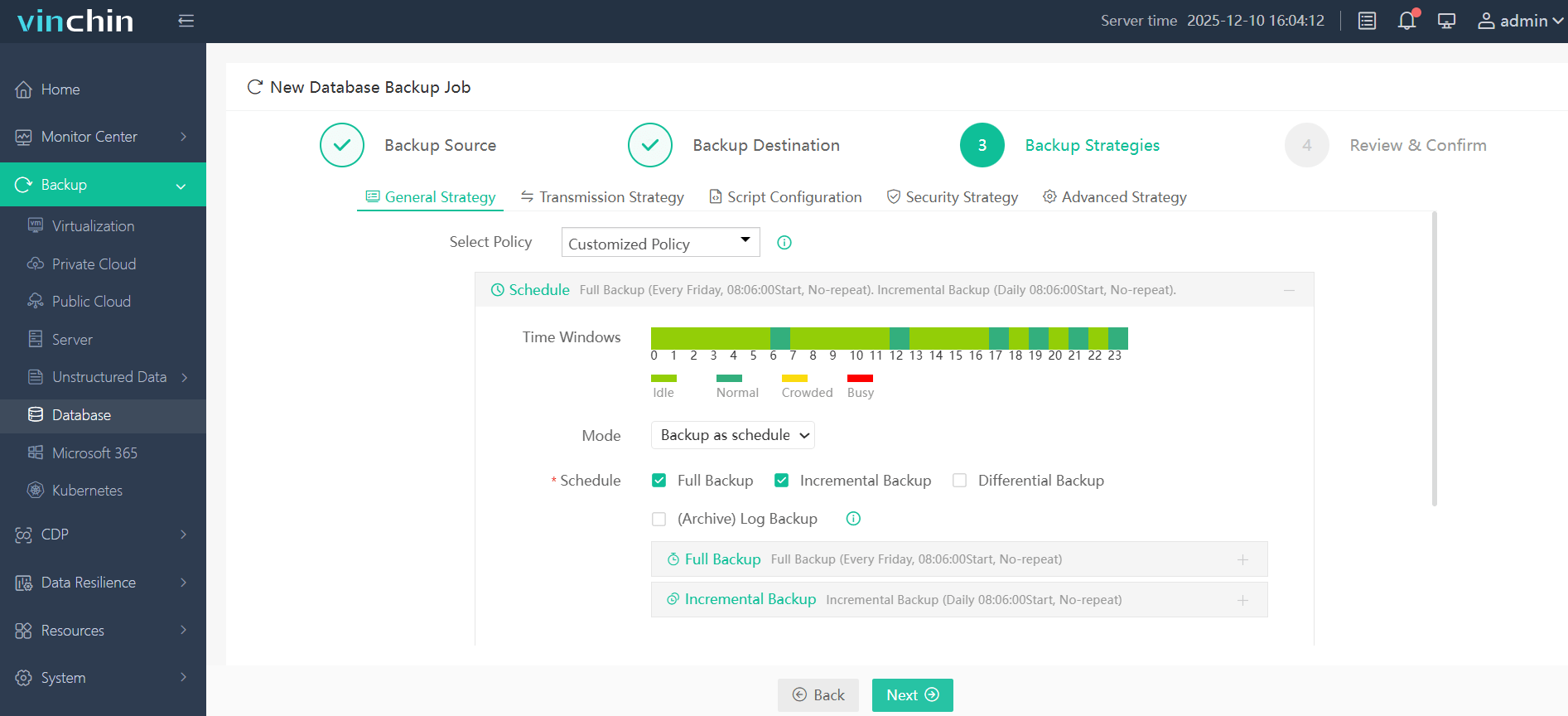
Step 4. Submit the job
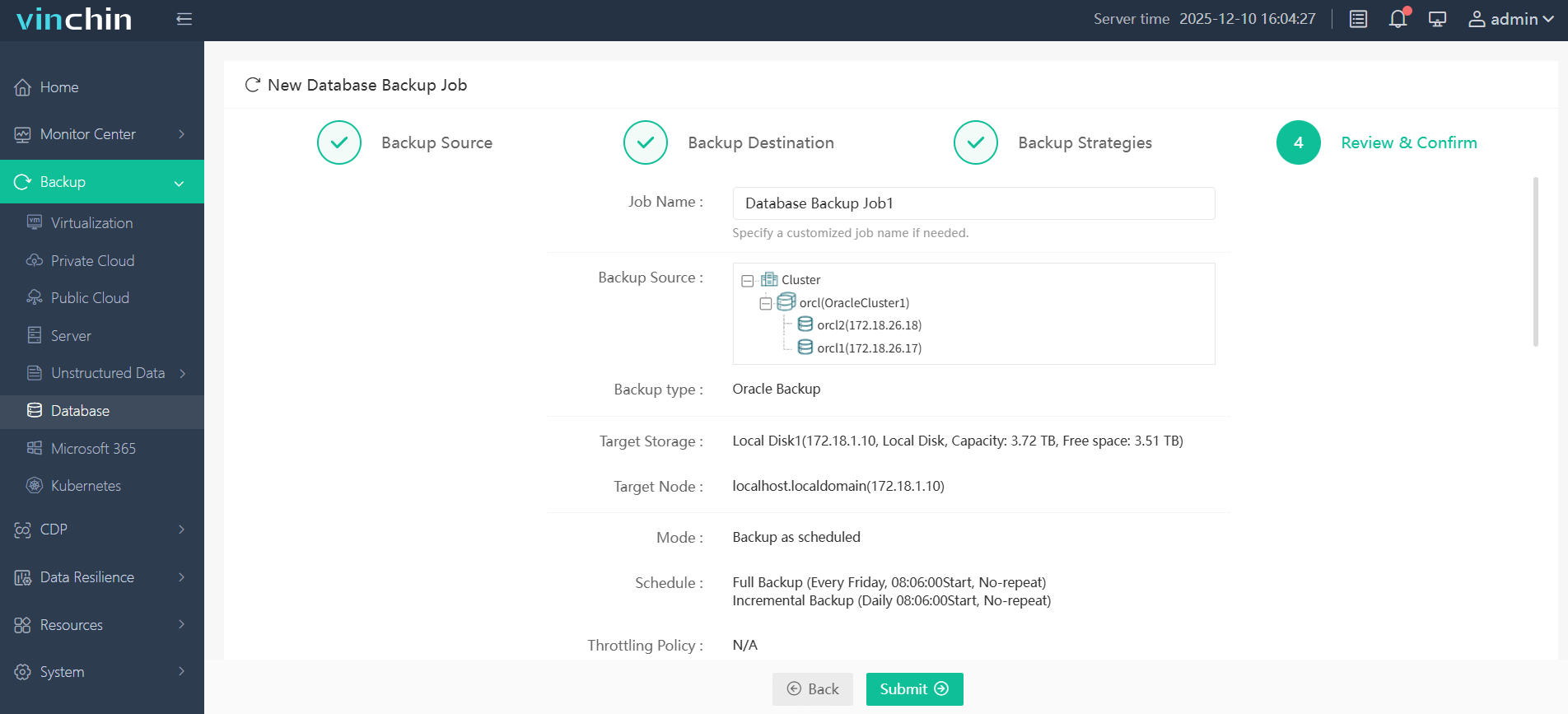
Vinchin Backup & Recovery enjoys global recognition among enterprises for reliability and ease-of-use—try its fully featured 60-day free trial today by clicking below!
OCI RMAN Backup to Object Storage FAQs
Q1: Can I back up my on-premises Oracle database directly into OCI Object Storage?
Yes—with proper network access outwards over HTTPS plus installation of Database Cloud Backup Module configured against correct credentials/bucket info.
Q2: What do I do if my scheduled nightly job fails due to network timeout?
Check internet connectivity between source host & target region endpoint; consider increasing retry count in oci_config . ora ; review firewall/proxy settings blocking outbound traffic .
Q3: How do I monitor ongoing cloud-based backups?
Review logs produced by each scheduled script ; query V$RMAN_OUTPUT view ; inspect uploaded objects via Objects tab inside relevant Bucket within Console .
Conclusion
Backing up databases with “OCI RMAN backup to object storage” gives strong security plus flexibility whether handling daily operations or disaster recovery events.Following best practices ensures safe restores whenever needed.Vinchin makes protecting critical workloads even easier —try it today!
Share on:







