-
What Are Oracle Database Tools?
-
Why Use Oracle Database Tools?
-
Method 1: Using Oracle Enterprise Manager for Database Management
-
Method 2: Using Oracle SQL Developer for Development Tasks
-
Method 3: Using RMAN for Backup and Recovery
-
How to Protect Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
FAQs About Oracle Database Tools
-
Conclusion
Oracle databases are at the heart of many enterprise IT systems worldwide. Choosing the right oracle database tools is crucial for smooth operations, data protection, and compliance with business requirements. With so many options available—from native utilities to specialized third-party solutions—it can be hard to know where to start or how to get the most from your toolkit. In this guide, we’ll walk through essential Oracle database tools for management, development, backup, and recovery. Whether you’re new to Oracle or an experienced administrator looking to deepen your expertise, you’ll find actionable advice here.
What Are Oracle Database Tools?
Oracle database tools are software applications designed specifically for managing all aspects of Oracle databases. These range from graphical interfaces that simplify administration tasks to command-line utilities built for speed and automation. Some focus on monitoring performance; others help with coding or disaster recovery planning. By using these tools together, you can streamline daily work while ensuring your databases stay secure and efficient.
Why Use Oracle Database Tools?
Relying on proper oracle database tools saves time and reduces mistakes during routine operations like user management or backups. They also help enforce security policies and optimize performance without manual guesswork. For developers, these tools offer features such as code editors and schema designers that make building robust applications easier than ever before.
Method 1: Using Oracle Enterprise Manager for Database Management
Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) is a comprehensive web-based platform made for centralized administration of Oracle environments.
Getting Started with OEM
To begin using OEM, log in through your browser using administrator credentials at your designated Enterprise Manager Console URL. Once inside, you’ll see a dashboard summarizing health metrics like CPU usage and storage allocation across all managed databases.
User Management and Security
Managing users is one of the most common tasks in OEM. Click on Targets, then Databases, select your desired instance by name, then go to the Administration tab where you’ll find options such as Users, Roles, and Profiles listed clearly on screen.
Here you can create new users by clicking Create User, assign roles like DBA or read-only access via Roles, or set password policies under Profiles for added security control.
For auditing activities—such as tracking who accessed sensitive tables—navigate to Security then choose Audit Settings where you can enable detailed logging of user actions.
Performance Diagnostics
Monitoring performance helps prevent slowdowns before they impact business processes. Under the main menu’s Performance tab within any selected database instance, view real-time graphs showing wait events or top SQL statements consuming resources.
Advanced users can generate Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) reports directly from OEM by selecting Performance Hub then choosing AWR Reports from available options—a powerful way to analyze trends over time rather than just snapshots.
If bottlenecks appear frequently during peak hours, use Real-Time SQL Monitoring found under the same tab; it highlights problematic queries so you can tune them quickly using provided recommendations.
Backup Management in OEM
Backing up data regularly is vital for disaster recovery readiness. From any database page in OEM’s console:
Go to the Availability section
Select Backup & Recovery
Launch the guided process via the bolded option labeled Backup Wizard
This wizard walks you through selecting backup types (full or incremental), scheduling jobs automatically using built-in calendars under Job Activity settings—and even validating completed backups with one click under Backup Reports.
Automating Routine Tasks
OEM allows administrators to automate repetitive jobs such as statistics gathering or index rebuilding:
Open the main menu
Choose Job Activity
Click on “Create Job” button
You can schedule scripts daily/weekly/monthly depending on maintenance windows without manual intervention each time.
Method 2: Using Oracle SQL Developer for Development Tasks
Oracle SQL Developer is an integrated development environment (IDE) tailored specifically for working with Oracle databases.
Connecting Your Database
After installing SQL Developer on Windows/macOS/Linux:
Launch application
Click bolded button labeled “New Connection”
Enter connection details (username/password/service name)
Once connected successfully after pressing “Connect,” all objects appear organized in left navigation pane.
Query Execution & Code Editing
Writing queries becomes straightforward inside SQL Developer:
Right-click active connection
Select “Open SQL Worksheet”
Type any valid SQL/PLSQL code here; execute statements by clicking green arrow icon labeled “Run Statement.” Results display below worksheet immediately.
For more complex scripts involving multiple steps—or debugging stored procedures—you may set breakpoints directly within editor window then launch Debugger mode from top toolbar.
Use Explain Plan feature found above worksheet area before running heavy queries; it provides visual breakdowns of execution paths so tuning becomes easier even if you’re not an expert yet.
Managing Database Objects
Beyond query writing,
SQL Developer lets admins modify tables/indexes/views graphically:
Expand object tree left side
Right-click table/view/procedure name
Choose actions like “Edit,” “Drop,” or “Rename” from context menu—all changes reflected instantly upon confirmation.
Schema comparison tools allow reviewing differences between test/dev/prod environments quickly—a must-have when deploying updates safely across teams!
Method 3: Using RMAN for Backup and Recovery
Recovery Manager (RMAN) is Oracle’s dedicated command-line utility focused solely on reliable backup/recovery operations at scale.
Starting RMAN Sessions
Open terminal/command prompt locally where client installed;
Type rman then press Enter key,
Connect securely as SYSDBA role required:
CONNECT TARGET / AS SYSDBA;
Or specify remote service explicitly if needed:
CONNECT TARGET sys@your_database AS SYSDBA;
Replace placeholders accordingly based on deployment specifics!
Backup Strategies Explained
RMAN supports several backup types suited for different needs:
1) Full Backups – capture entire database state including system files/control files/logs (BACKUP DATABASE;)
2) Incremental Backups – store only changed blocks since last run (BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 DATABASE;)
3) Archival Backups – preserve redo logs separately (BACKUP ARCHIVELOG ALL;)
Each type has pros/cons regarding speed/storage usage—choose mix matching organizational RTO/RPO goals best!
Validate existing backups anytime using command below:
VALIDATE BACKUPSET;
This ensures no corruption exists prior restoration attempts later down line…
Recovery Process Overview
When disaster strikes,
Restore full/incremental sets easily via commands such as:
RESTORE DATABASE; RECOVER DATABASE;
Point-in-time recoveries possible too—for example after accidental data deletion—with syntax similar but specifying SCN/time markers explicitly (RECOVER DATABASE UNTIL TIME 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS';)
Always check status/history first using reporting commands like LIST BACKUP or REPORT OBSOLETE which identify outdated/unneeded files safe-to-delete freeing up disk space proactively!
How to Protect Oracle Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
In addition to native utilities, organizations seeking advanced protection should consider purpose-built enterprise solutions. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional-grade platform supporting today’s mainstream databases—including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL/PostgresPro, and MongoDB—with robust capabilities tailored especially for complex environments like Oracle.
Key features include incremental backup support (for Oracle), batch database backup management, flexible data retention policies including GFS retention policy options, cloud backup/tape archiving integration, and ransomware protection—all designed to ensure high availability while minimizing administrative overhead across large-scale deployments.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your Oracle environment simple:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up;
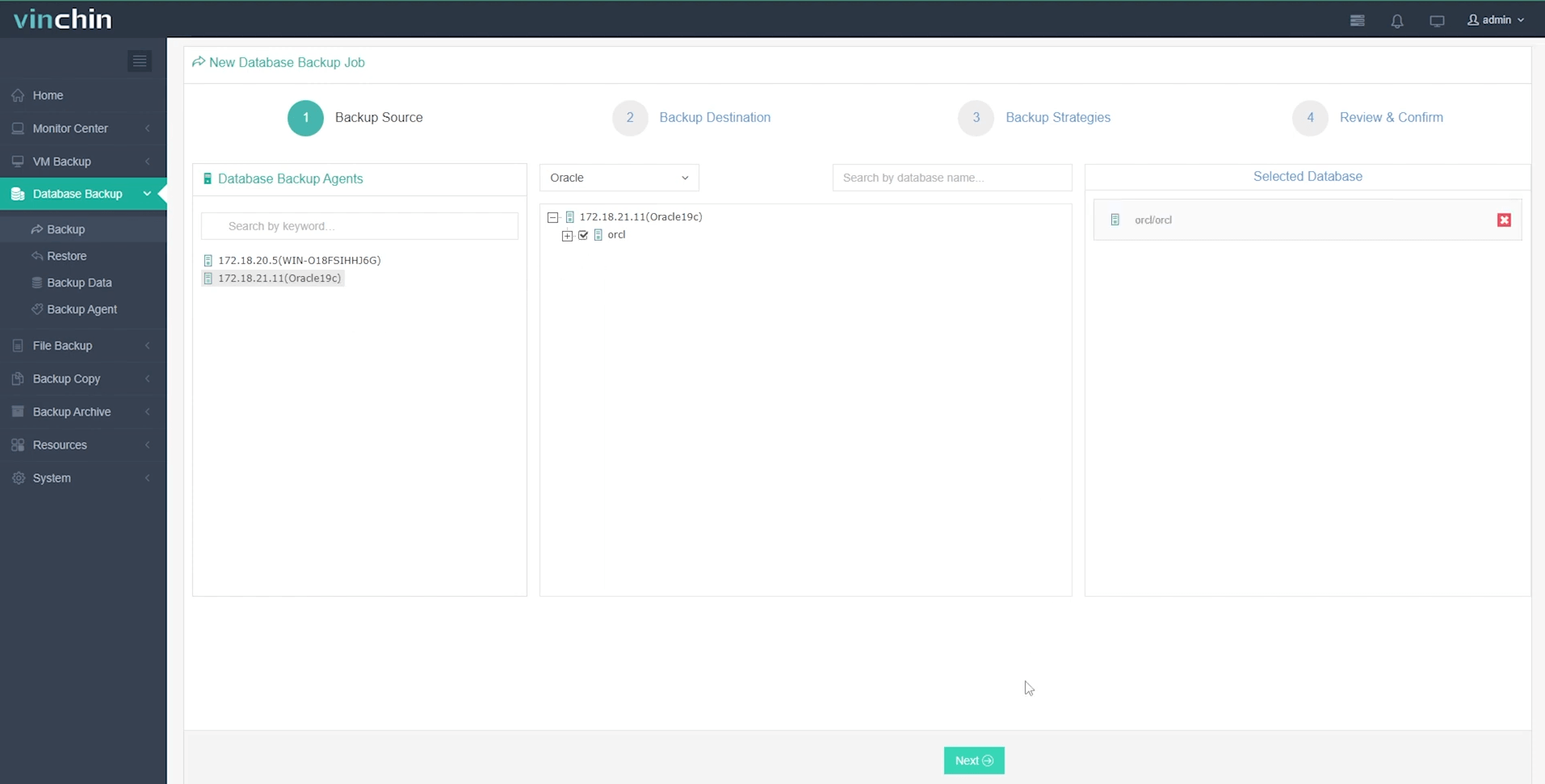
Step 2. Choose backup storage;
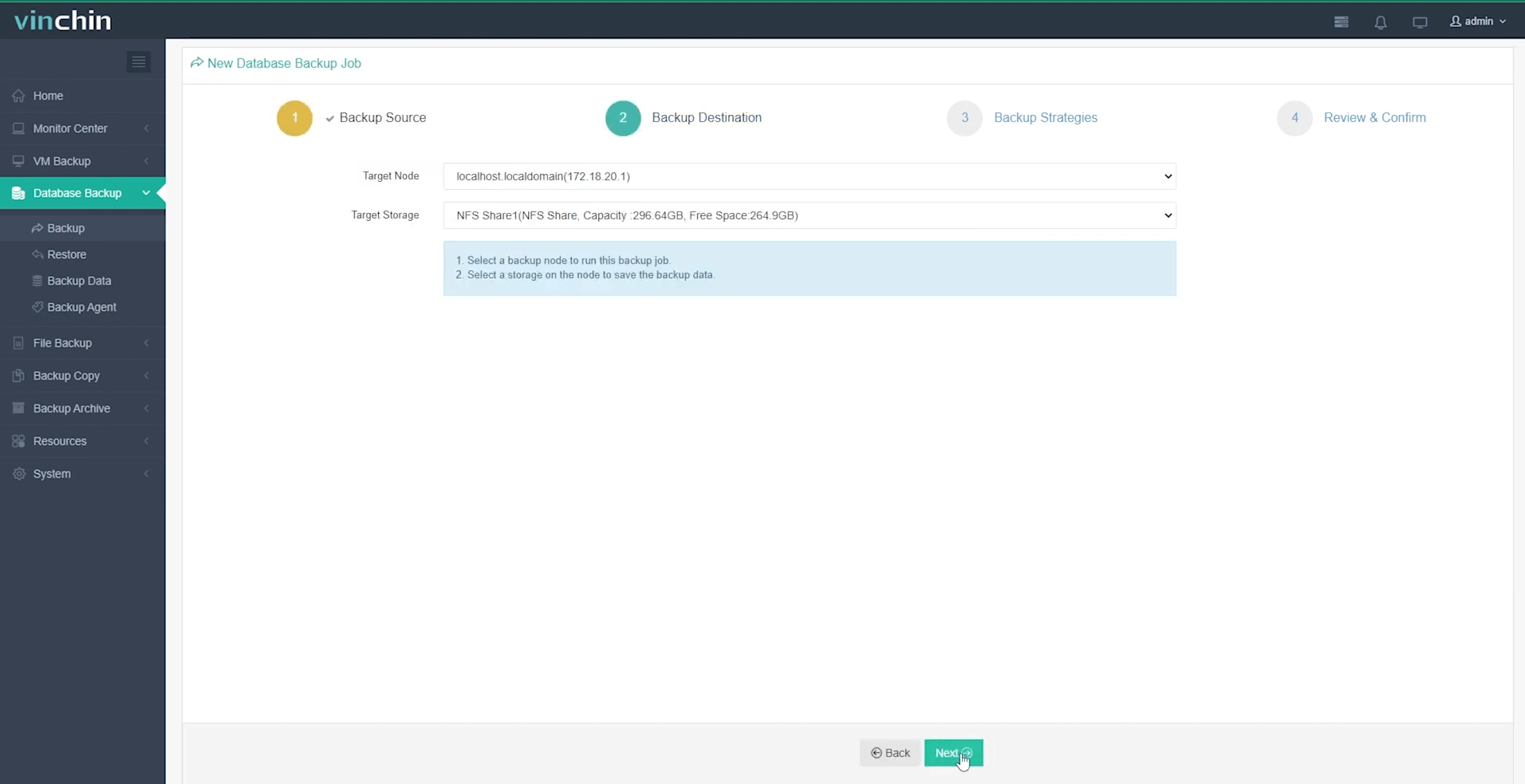
Step 3. Define a suitable backup strategy;
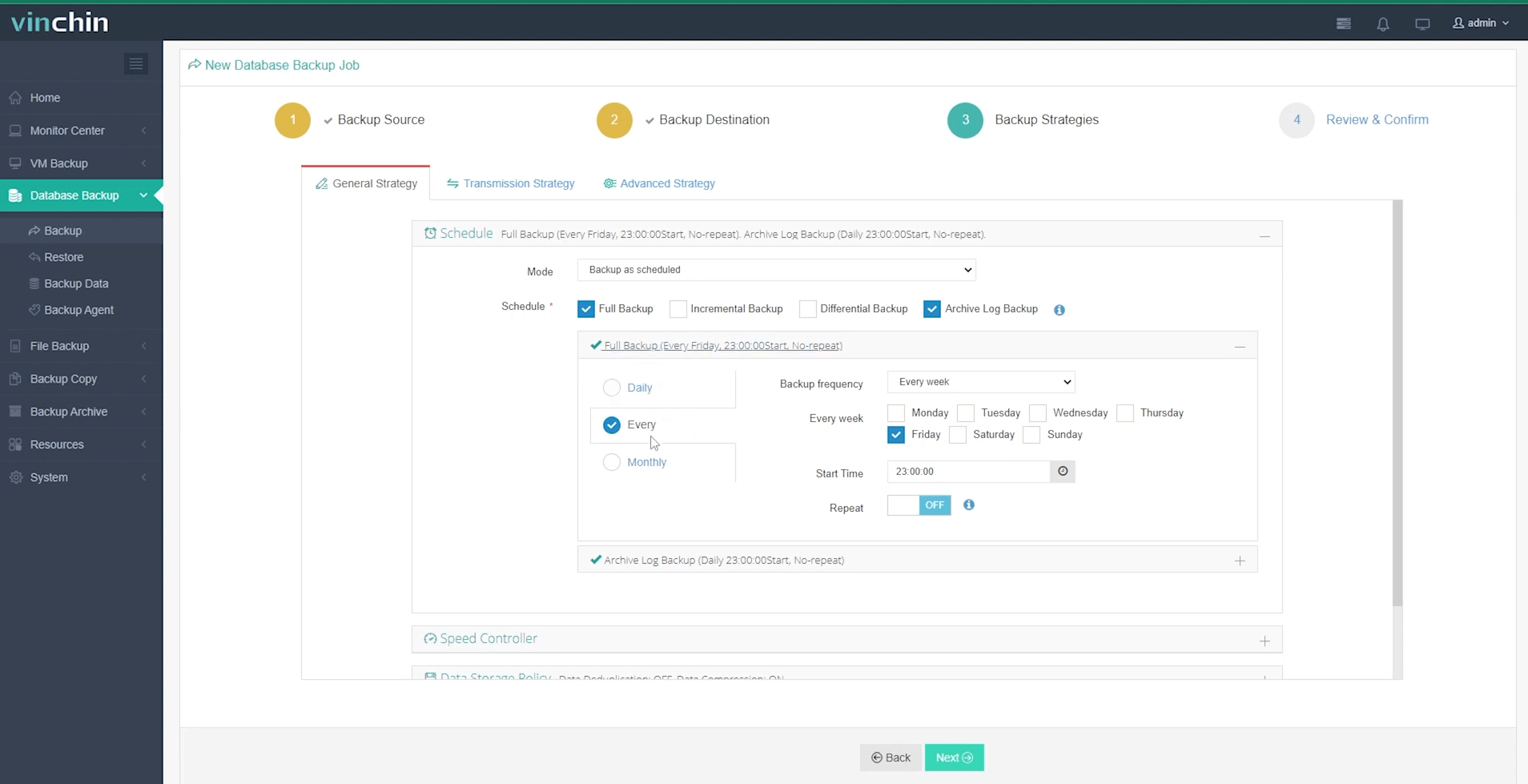
Step 4. Submit the job.
Trusted globally by thousands of enterprises with top ratings in industry reviews—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured 60-day free trial so you can experience its benefits firsthand—click below to download now!
FAQs About Oracle Database Tools
Q1: Can I monitor multiple remote databases simultaneously within one OEM dashboard?
Yes—you simply register additional targets inside Enterprise Manager Console allowing unified oversight regardless physical location/network segment involved!
Q2: How do I resolve failed RMAN backups due to insufficient disk space?
Free up space by deleting obsolete backups (REPORT OBSOLETE) then rerun job—or adjust retention policy downward temporarily until capacity expanded again later!
Q3: Is there a way to compare two schemas visually without exporting/importing objects manually?
Yes—in SQL Developer use Schema Comparison feature found under Tools > Database Diff—it highlights differences graphically making synchronization much simpler/faster than scripting everything yourself!
Conclusion
Mastering oracle database tools empowers administrators at every level—from basic monitoring through advanced disaster recovery planning—to deliver secure high-performance services reliably day after day! For organizations seeking extra peace-of-mind around data protection specifically consider adding Vinchin’s purpose-built solution into existing workflows today.
Share on:






