-
What Is Hadoop Backup?
-
Why Hadoop Backup Matters?
-
Method 1: Using DistCp for Hadoop Backup
-
Method 2: Using HDFS Snapshots for Hadoop Backup
-
How to Protect Hadoop HDFS Files with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Hadoop Backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Hadoop is at the heart of many modern data platforms. It stores vast amounts of business-critical information across distributed clusters. But what happens if something goes wrong? Data loss can be catastrophic. That’s why hadoop backup is essential—not just as a precaution but as a core part of any IT strategy. In this guide, we’ll walk through what hadoop backup means, why it’s vital, and how you can implement reliable protection using proven methods.
What Is Hadoop Backup?
Hadoop backup involves making secure copies of data stored in Hadoop clusters so you can restore it after an incident. Unlike traditional databases that keep everything in one place, Hadoop uses the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) to spread files across many servers or nodes. This design boosts performance and resilience against hardware failures.
However, built-in replication alone does not equal true backup. Replication keeps several live copies within the same cluster—but if someone deletes a file or malware corrupts your data, all replicas are affected at once. A proper hadoop backup creates independent copies—often in another location or cluster—that you can use to recover lost information even after major disasters.
Key Concepts in Hadoop Backup
Understanding some basic terms helps clarify how backups work in Hadoop:
Replication: HDFS automatically makes multiple copies of each file block across different nodes for fault tolerance.
Backup: An extra copy stored separately from production data; used to restore files after accidental deletion or corruption.
Disaster Recovery: The process of restoring systems and data after catastrophic events like hardware failure or ransomware attacks.
A good hadoop backup plan combines these elements so you’re ready for anything—from minor mistakes to major outages.
Why Hadoop Backup Matters?
Many teams assume that HDFS replication is enough protection because it guards against disk failures or node crashes. But is that really true? Let’s look closer.
Replication works well when hardware fails because other nodes still hold healthy copies of your files. But if someone accidentally deletes important folders—or if software bugs overwrite critical datasets—all replicas vanish together since they’re synchronized instantly across the cluster.
Backups solve this problem by creating point-in-time snapshots outside normal operations. If disaster strikes—whether from human error, cyberattack, or silent corruption—you have a safe version to restore from quickly.
Real-World Disaster Recovery Scenarios
Consider these examples:
1. A developer runs a faulty script that wipes out key directories by mistake; all replicas disappear instantly.
2. Ransomware encrypts every file on your cluster; replication only spreads the damage faster.
3. Silent bit rot corrupts important blocks over time; without backups from earlier states, recovery becomes impossible.
Industry reports confirm these risks. Without solid hadoop backup strategies, organizations face long downtimes—and sometimes permanent data loss—that could have been avoided with regular backups.
Method 1: Using DistCp for Hadoop Backup
DistCp (Distributed Copy) is a native tool designed specifically for copying large volumes of data between HDFS clusters or compatible storage systems like cloud buckets or NFS shares. It leverages MapReduce jobs to parallelize transfers efficiently—even when moving petabytes at scale.
Before starting with DistCp, make sure both source and target clusters are reachable over the network and have enough free space available for incoming files.
DistCp shines when you need offsite backups—for example, replicating production data into a separate disaster recovery site—or migrating between environments during upgrades.
How to Use DistCp for Basic Backups?
To perform a full directory copy between two clusters:
hadoop distcp hdfs://source-namenode:8020/source/path hdfs://target-namenode:8020/target/path
This command launches parallel tasks that transfer all files from /source/path on your source cluster to /target/path on the destination cluster.
For incremental backups—copying only new or changed files since last time—add the -update flag:
hadoop distcp -update hdfs://source-namenode:8020/source/path hdfs://target-namenode:8020/target/path
The -update option checks file size and modification timestamps so only updated items move over the network—a big time-saver when dealing with massive datasets.
If your environment supports snapshot diffs (available in newer Hadoop releases), you can further optimize bandwidth by transferring only differences between two snapshots:
hadoop distcp -diff s1 s2 hdfs://source-namenode:8020/source/path hdfs://target-namenode:8020/target/path
Here s1 and s2 are snapshot names representing two points in time; only changed blocks are copied out—a huge win for efficiency during frequent backups.
Always verify successful completion by comparing file counts at both ends—or run checksum validation jobs as needed before deleting old versions!
Method 2: Using HDFS Snapshots for Hadoop Backup
HDFS Snapshots offer another powerful way to protect critical directories inside your cluster itself—they create read-only point-in-time images that capture current contents instantly without interrupting users’ workflows.
Snapshots consume little extra space unless underlying files change significantly afterward (thanks to efficient block-level tracking). They’re ideal when you need quick rollback options after accidental deletions—or want short-term safety nets while testing risky updates.
How To Create And Manage Snapshots?
First step is enabling snapshots on chosen directories:
hdfs dfsadmin -allowSnapshot /data/important
Once allowed, create named snapshots anytime:
hdfs dfs -createSnapshot /data/important daily_backup_2024_06_01
List available snapshots within a directory:
hdfs dfs -ls /data/important/.snapshot
Restore individual files easily by copying them back out:
hdfs dfs -cp /data/important/.snapshot/daily_backup_2024_06_01/myfile.txt /data/important/myfile.txt
When no longer needed—or after exporting elsewhere—delete old snapshots safely:
hdfs dfs -deleteSnapshot /data/important daily_backup_2024_06_01
Snapshot Management And Cleanup
While snapshots are lightweight compared to full clones elsewhere—they still consume namespace memory proportional to number created per directory! Too many retained indefinitely may degrade NameNode performance over time.
Best practice suggests setting retention policies:
1. Limit total number kept per folder based on business needs (e.g., daily x7 + weekly x4).
2. Automate cleanup via scheduled scripts calling deleteSnapshot regularly after verifying exports complete successfully elsewhere.
Remember also that all snapshots reside within same physical cluster as live data! For true disaster recovery—including site-wide outages—you must combine snapshotting with external exports via tools like DistCp described above.
How to Protect Hadoop HDFS Files with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
While robust storage architectures like Hadoop HDFS provide inherent resilience, comprehensive backup remains essential for true data protection. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-grade solution purpose-built for safeguarding mainstream file storage—including Hadoop HDFS environments—as well as Windows/Linux file servers, NAS devices, and S3-compatible object storage. Specifically optimized for large-scale platforms like Hadoop HDFS, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers exceptionally fast backup speeds that surpass competing products thanks to advanced technologies such as simultaneous scanning/data transfer and merged file transmission.
Among its extensive capabilities, five stand out as particularly valuable for protecting critical big-data assets: incremental backup (capturing only changed files), wildcard filtering (targeting specific datasets), multi-level compression (reducing space usage), cross-platform restore (recovering backups onto any supported target including other file servers/NAS/Hadoop/object storage), and integrity check (verifying backups remain unchanged). Together these features ensure efficient operations while maximizing security and flexibility across diverse infrastructures.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers an intuitive web console designed for simplicity. To back up your Hadoop HDFS files:
Step 1. Select the Hadoop HDFS files you wish to back up
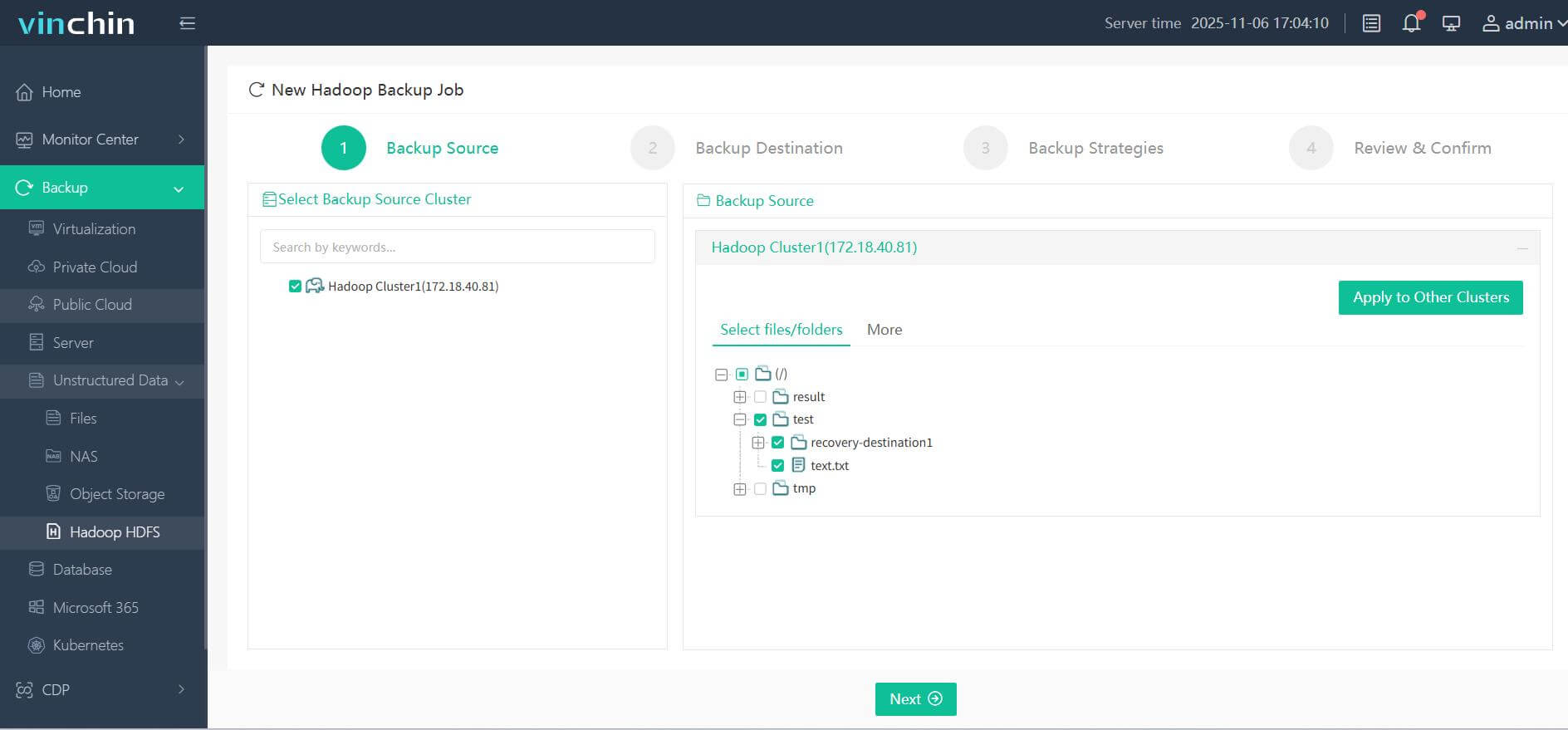
Step 2. Choose your desired backup destination
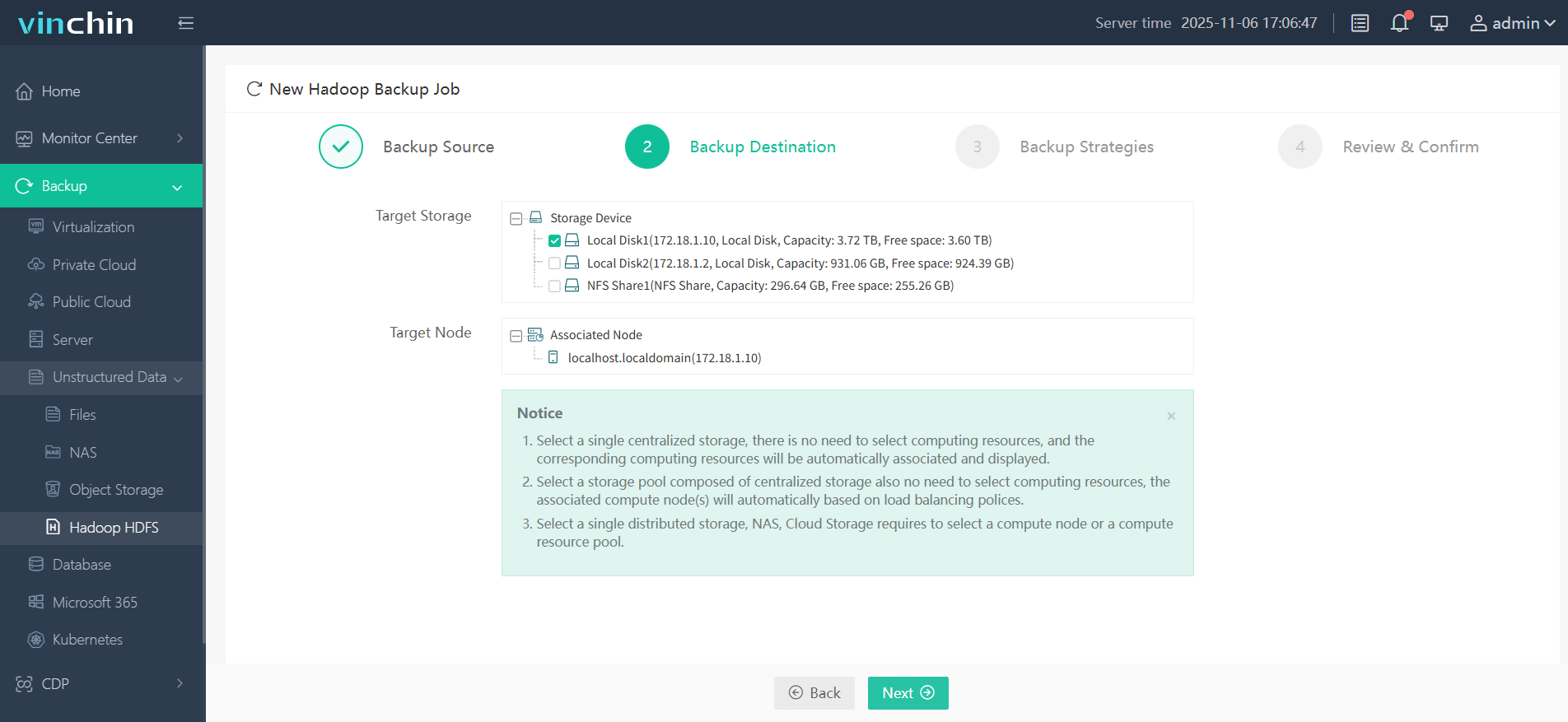
Step 3. Define backup strategies tailored for your needs
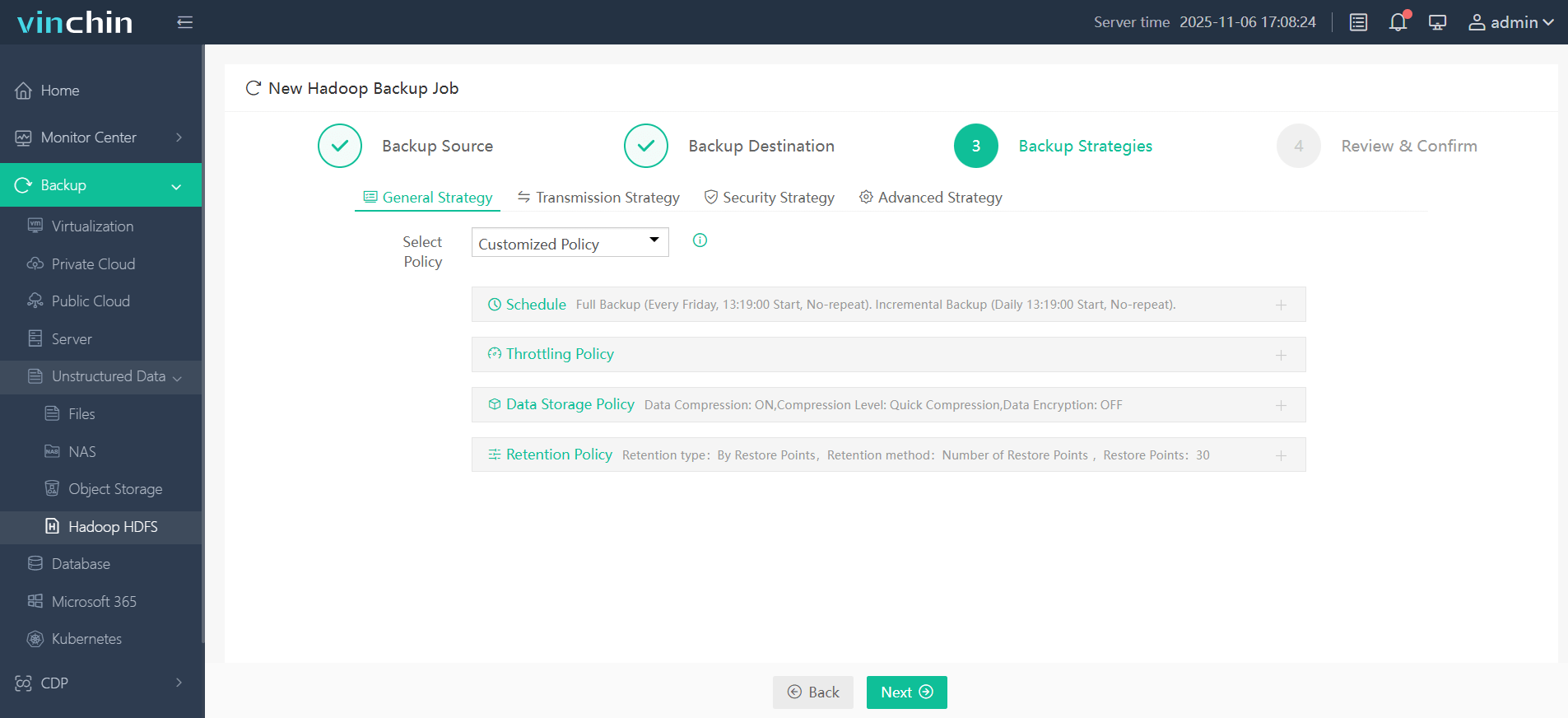
Step 4. Submit the job
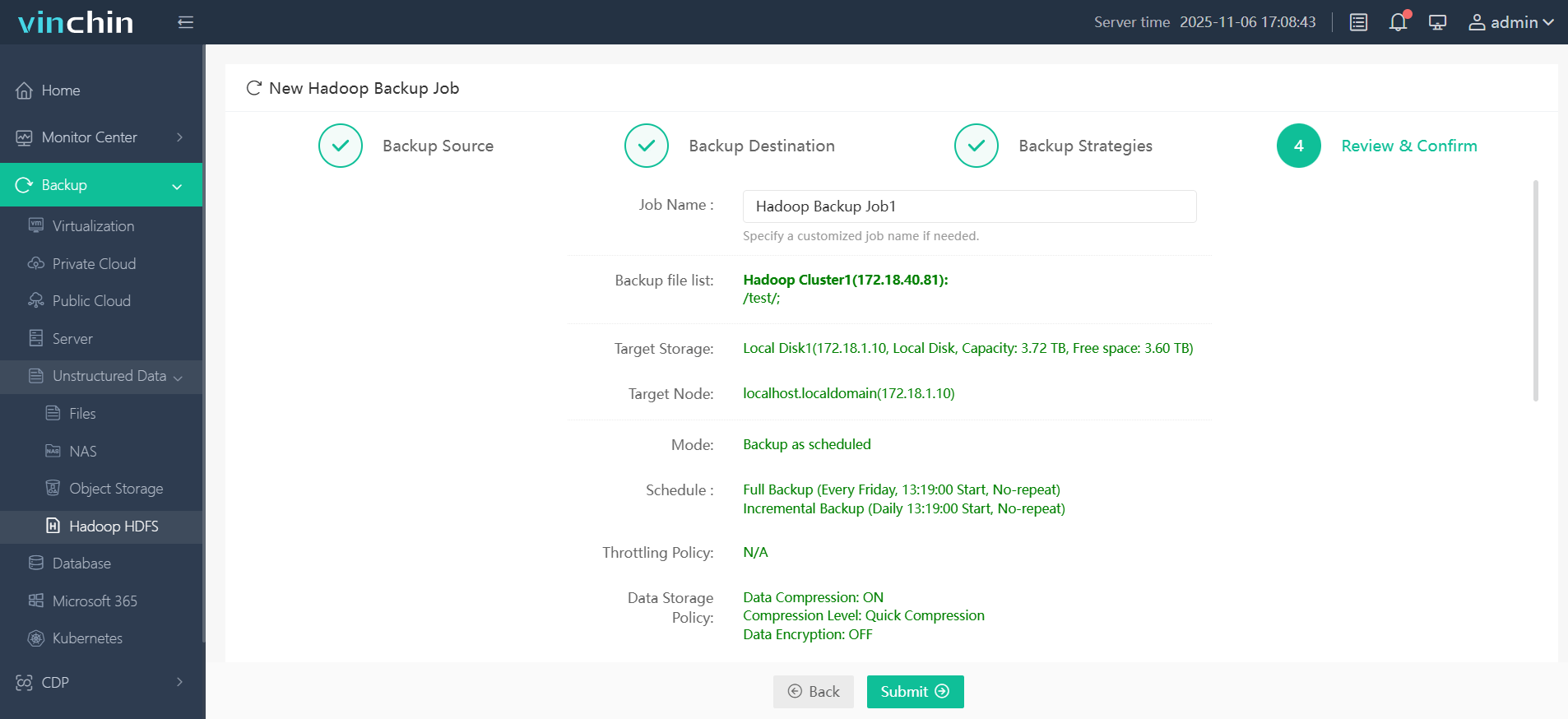
Join thousands of global enterprises who trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery—renowned worldwide with top ratings—for reliable data protection. Try all features free with a 60-day trial; click below to get started!
Hadoop Backup FAQs
Q1: How do I schedule automated nightly backups without manual effort?
A1: Use Linux CRON jobs triggering shell scripts wrapping distcp commands—or configure policy-based schedules directly inside Vinchin’s web console interface.
Q2: What’s safest way backing up only changed files since last run?
A2: Run hadoop distcp -update ... for incremental syncs—or leverage snapshot diff mode if supported by your distribution/version combination!
Q3: Can I recover deleted folders even weeks later?
A3: Yes—if regular snapshots exist covering desired period; simply copy missing items back out using hdfs dfs -cp ... syntax shown above!
Q4: How do I minimize impact on running workloads during large-scale backups?
A4: Schedule heavy jobs during low activity windows; throttle resource usage via rate-limiting flags; use Vinchin's built-in controls where available.
Conclusion
Backing up your big data isn’t optional—it’s mission-critical insurance against accidents big and small alike! Native tools like DistCp plus HDFS Snapshots provide strong foundations—but enterprise demands often require more automation and security than DIY scripts alone deliver reliably long term.Vinchin offers advanced yet easy-to-use solutions tailored specifically toward modern hybrid environments.Try it free today—and sleep better knowing every byte stays protected!
Share on:






