-
What Is an RMAN Full Backup?
-
Method 1. Basic RMAN Full Backup Script Oracle 19c
-
Method 2. Automated RMAN Full Backup Script Oracle 19c
-
How to Back Up Oracle Database 19c Using Vinchin?
-
RMAN Full Backup Script Oracle 19c FAQs
-
Conclusion
Protecting your Oracle 19c database is not just a best practice—it’s a necessity. A reliable backup strategy ensures you can recover from hardware failures, data corruption, or accidental deletions. Oracle’s Recovery Manager (RMAN) is the built-in tool for this job. But how do you create a robust, repeatable RMAN full backup script for Oracle 19c? Let’s break it down step by step.
A solid backup plan does more than just copy data; it forms the backbone of your disaster recovery strategy. In most environments, a full (level 0) backup works alongside incremental backups and archive log management to provide comprehensive protection. Understanding how these pieces fit together will help you design scripts that meet both compliance needs and business expectations.
What Is an RMAN Full Backup?
An RMAN full backup is a complete copy of all data blocks in your Oracle database at a specific point in time. In Oracle terms, this “full backup” is often implemented as an “incremental level 0” backup using RMAN commands. This type of backup serves as the foundation for all future incremental backups and is essential if you want to restore your database quickly after failure.
It’s important to note that a full backup alone does not guarantee point-in-time recovery unless archived redo logs are included or managed properly. Including archived redo logs allows you to roll forward changes made after the last full backup so you can restore your database to any consistent state required by business or regulatory needs.
For most production systems, running regular full backups—often weekly—is recommended while using incremental backups daily for efficiency and speed. This layered approach balances storage use with recovery objectives.
Method 1. Basic RMAN Full Backup Script Oracle 19c
Before running any backups with RMAN on Oracle 19c, there are several critical checks every administrator should perform to avoid common pitfalls.
Pre-requisites and Verification
A successful RMAN full backup depends on proper preparation:
Check ARCHIVELOG Mode: Your database must be in ARCHIVELOG mode so that online backups capture all changes.
Verify Disk Space: Ensure enough free space exists at your chosen destination; running out mid-backup can cause failures.
Review DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST_SIZE: If using Fast Recovery Area (FRA), confirm its size supports both new backups and archive logs.
Validate Permissions: Confirm that the OS user running RMAN has write access to target directories.
Test Connectivity: Make sure you can connect as SYSDBA via SQL*Plus or RMAN before starting scripted jobs.
You can check ARCHIVELOG mode by connecting with SQL*Plus:
sqlplus / as sysdba ARCHIVE LOG LIST
Step-by-Step: Manual Full Backup Using RMAN
This method suits ad-hoc or manual scenarios where direct control is preferred.
1. Start RMAN and Connect:
rman target /
2. Run the Backup Command:
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;
AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSETreduces storage requirements.PLUS ARCHIVELOGensures all necessary redo logs are included for complete recovery coverage.
3. Specify Backup Location (Optional):
To direct output files:
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE FORMAT '/u01/backup/%d_%U.bkp' PLUS ARCHIVELOG FORMAT '/u01/backup/%d_%U.arc';
Here %d inserts your database name; %U generates unique file identifiers.
4. Use Advanced Formatting:
For better organization:
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG DELETE INPUT FORMAT '/u01/backup/%d_FULL_%T_%U';
%Tadds date information.DELETE INPUTremoves archived logs already backed up—helpful when disk space is tight but use with caution!
5. Include Control File Explicitly:
While PLUS ARCHIVELOG includes control files by default,
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG INCLUDE CURRENT CONTROLFILE;
6. Validate Your Backup:
Always verify integrity after completion:
VALIDATE DATABASE;
Or validate specific sets by handle/tag if desired:
VALIDATE BACKUPSET <handle>;
7. Check Results:
Review output messages carefully or run:
LIST BACKUP SUMMARY;
This approach gives granular control over each step—a good fit when testing new configurations or troubleshooting issues directly on production systems.
Method 2. Automated RMAN Full Backup Script Oracle 19c
Automating regular backups minimizes risk from human error while ensuring consistent protection across busy schedules—even when no one’s watching at midnight! Most administrators rely on shell scripts combined with system schedulers like cron (Linux) or Task Scheduler (Windows).
Building a Resilient Automation Script
Let’s walk through building an effective automated solution:
1. Create Your Shell Script
Save as rman_full_backup.sh. Adjust variables as needed:
#!/bin/bash
export ORACLE_SID=ORCL
export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1
export PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH
BACKUP_DIR="/u01/backup"
LOGFILE="$BACKUP_DIR/log/rman_full_$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M).log"
# Source environment if available
if [ -f /usr/local/bin/oraenv ]; then . /usr/local/bin/oraenv <<< "$ORACLE_SID"; fi
exec > $LOGFILE 2>&1
rman target / <<EOF
RUN {
ALLOCATE CHANNEL c1 DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '$BACKUP_DIR/%d_%U.bkp';
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 DATABASE TAG='FULL_${ORACLE_SID}_$(date +%Y%m%d)' PLUS ARCHIVELOG DELETE INPUT;
BACKUP CURRENT CONTROLFILE TAG='CTRL_${ORACLE_SID}_$(date +%Y%m%d)';
RELEASE CHANNEL c1;
}
EOF
# Check exit code & alert if failed
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then echo "Backup failed!" | mail -s "RMAN Backup Failure" admin@example.com; fiThis script covers several best practices:
Uses environment variables instead of hard-coded values where possible.
Logs output per run into timestamped files inside
/u01/backup/log.Allocates channels explicitly—helpful when tuning performance across multiple disks.
Applies tags so each set stands out during audits or restores.
Sends email alerts if something goes wrong (requires local mail setup).
2. Make It Executable
chmod 750 rman_full_backup.sh
3. Schedule Regular Runs With Cron
Edit crontab (crontab -e) to schedule weekly runs at Sunday 2 AM:
0 2 * * 0 /path/to/rman_full_backup.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
Adjust timing based on maintenance windows or low-load periods unique to your business cycle.
4. Configure Retention Policy Separately
Set retention policy once within RMAN CLI—not inside every script—for clarity:
CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY TO RECOVERY WINDOW OF 7 DAYS;
Then let cleanup happen automatically via scheduled jobs using:
DELETE NOPROMPT OBSOLETE;
5. Monitor Backups Proactively
Don’t just trust automation blindly! Review log files regularly—or automate parsing them—and periodically test restores from recent sets onto development databases.
6. Validate Backups Automatically
Add validation steps either within main scripts or separate scheduled jobs:
rman target / <<EOF VALIDATE DATABASE; EOF
Advanced Automation Tips
For larger deployments:
Use parallel channels (
ALLOCATE CHANNEL c2...) across multiple disks/LUNs for faster throughput.Integrate monitoring tools that parse logfiles looking specifically for errors like
ORA-,RMAN-, etc., sending alerts instantly upon detection.Store copies offsite—or sync them securely—to protect against site-wide disasters such as fire or ransomware attacks.
Document every change made in scripts; version-control them alongside other infrastructure-as-code assets!
Isn’t peace of mind worth spending some extra minutes upfront? Automating well means sleeping soundly even during unexpected outages!
How to Back Up Oracle Database 19c Using Vinchin?
While manual scripting offers flexibility, many organizations seek streamlined solutions for enterprise-scale protection of their databases—including Oracle environments like yours. Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers professional-grade support for today’s leading platforms such as Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with special emphasis here on robust Oracle integration.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery empowers users with features including advanced source-side compression, incremental backup capabilities tailored for Oracle workloads, batch database operations, flexible retention policies including GFS options, and seamless cloud/tape archiving—all designed to maximize efficiency while minimizing risk and administrative effort across large infrastructures.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your Oracle data straightforward:
Step 1—Select the Oracle database to back up;
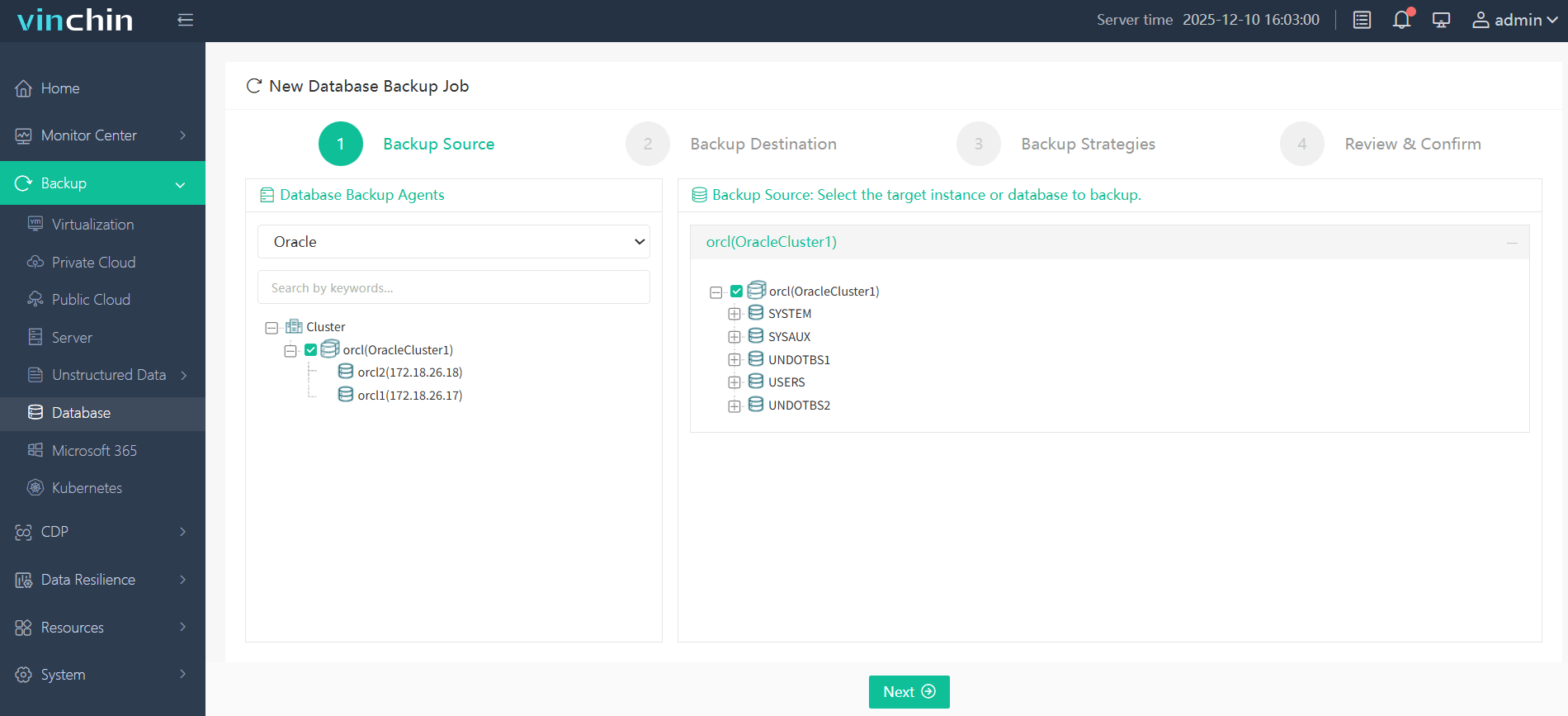
Step 2—Choose the appropriate storage location;
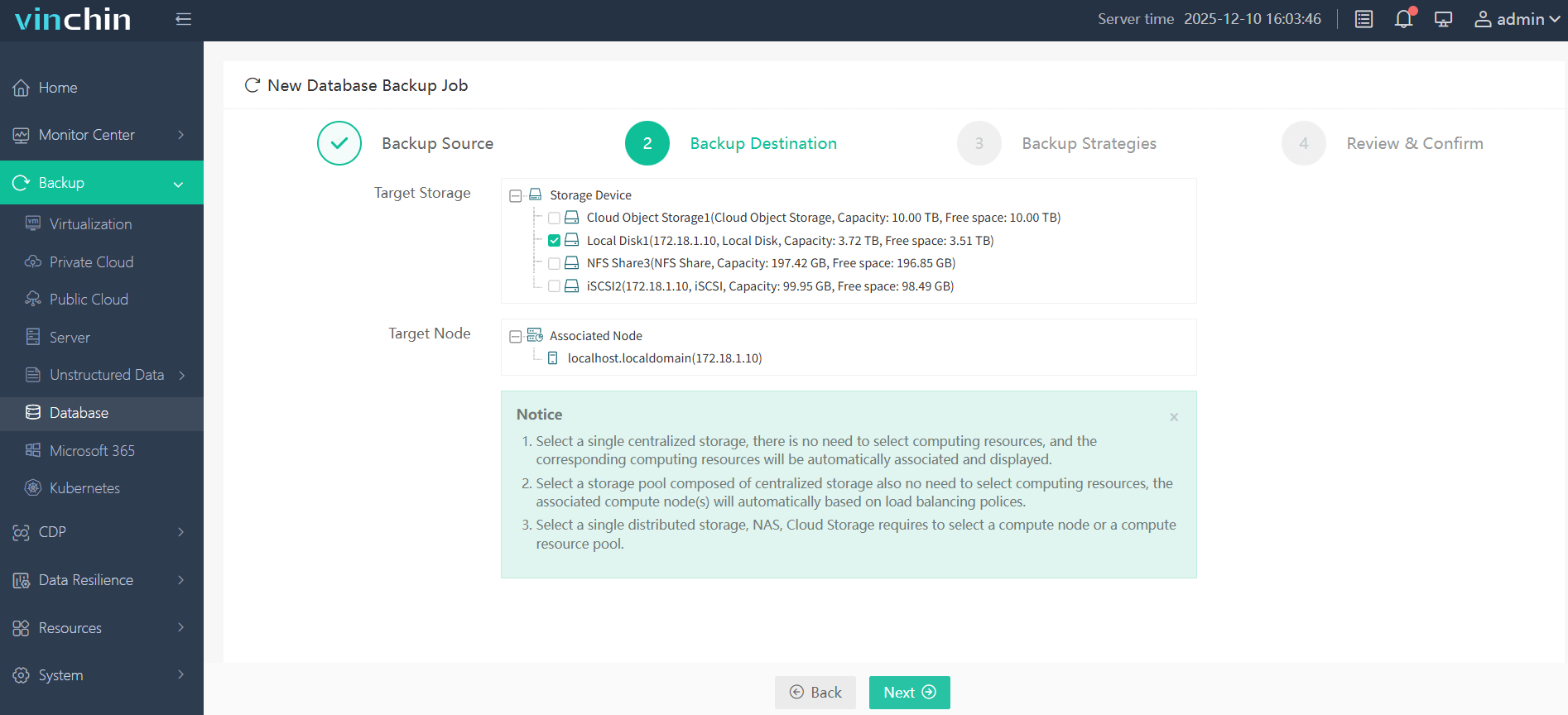
Step 3—Define detailed strategies around scheduling and retention;
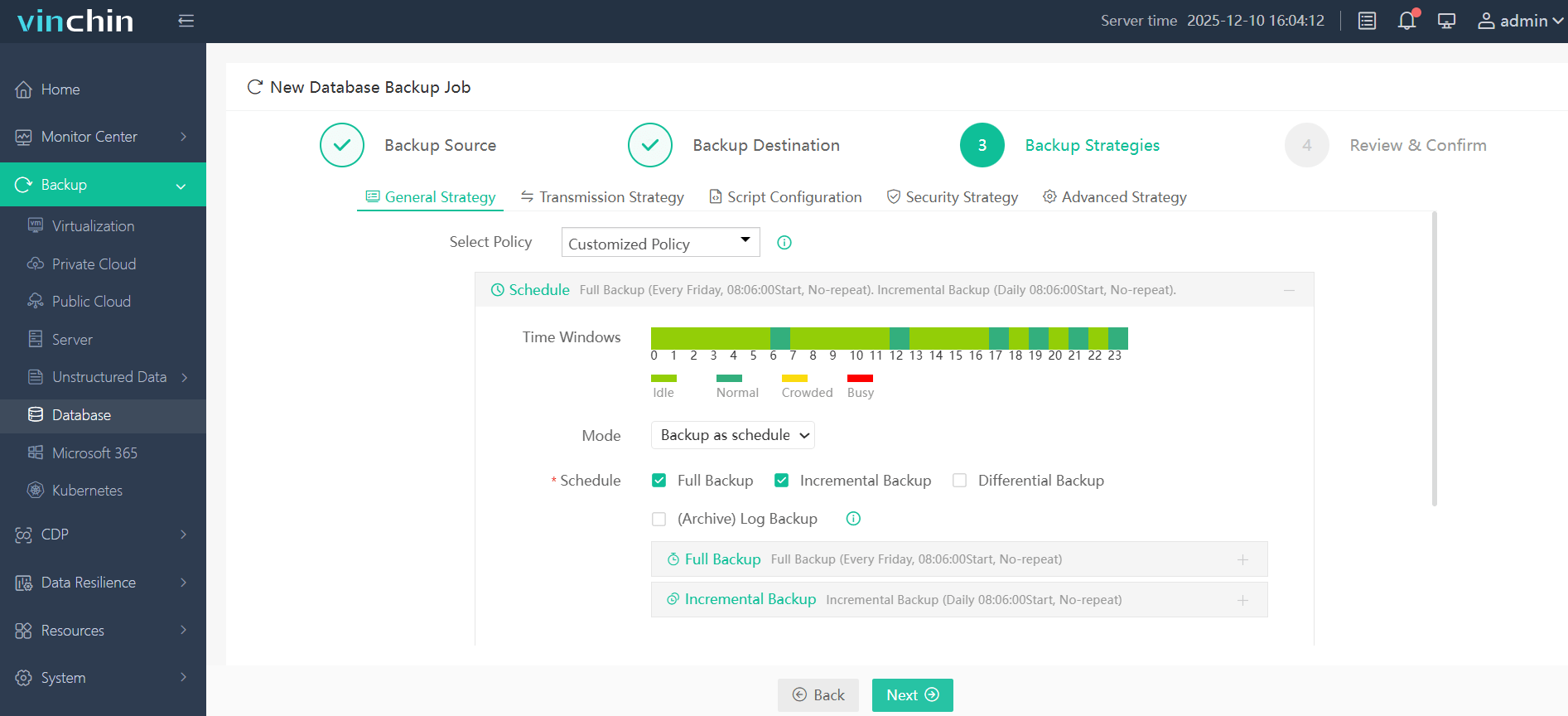
Step 4—Submit the job with confidence in just minutes.
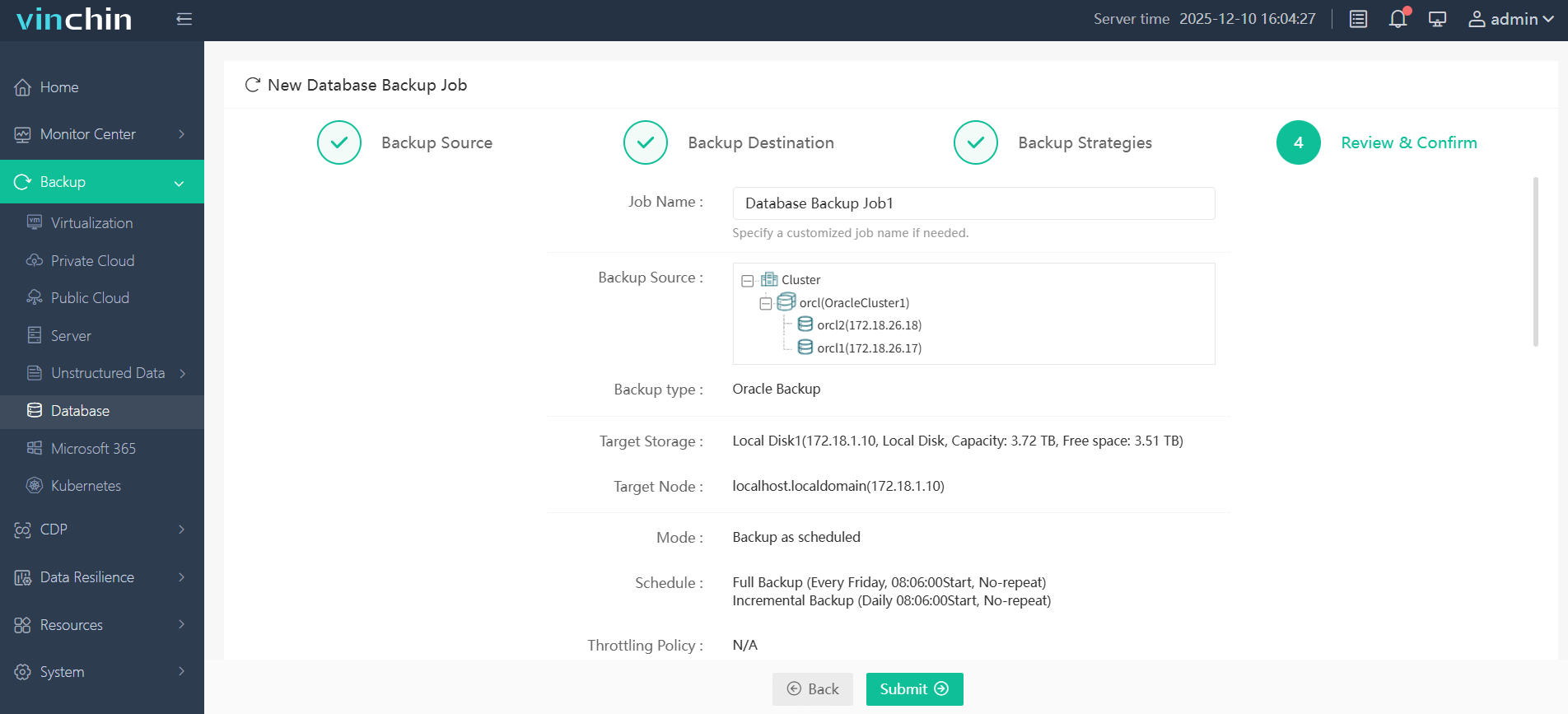
Recognized globally among enterprise IT teams—with thousands of satisfied customers—Vinchin Backup & Recovery consistently earns top marks for reliability and usability. Try it risk-free now with a fully featured 60-day trial by clicking below!
RMAN Full Backup Script Oracle 19c FAQs
Q1: How do I schedule an automatic weekly RMAN full backup in Linux?
A1: Write a shell script calling your RMAN commands then add it to cron with crontab -e.
Q2: What should I do if my automated RMAN job fails due to insufficient disk space?
A2: Free up space immediately then review retention policies; consider moving old backups offsite before rerunning jobs.
Q3: How can I confirm my latest automated full backup completed successfully?
A3: Check both the generated log file contents for errors like "RMAN-" codes and run LIST BACKUP SUMMARY; in RMAN CLI afterward.
Conclusion
Creating an effective rman full backup script oracle 19c protects business-critical data against loss—from accidental deletes to catastrophic failures—and ensures fast recovery when needed most. Testing restore procedures regularly matters as much as taking frequent backups. Vinchin offers streamlined solutions if you'd rather focus less on scripting details yourself!
Share on:








