-
What Is an Oracle RMAN Script?
-
Why Use Oracle RMAN Scripts?
-
Method 1: How to Create a Basic Backup Script Using Oracle RMAN?
-
Method 2: How to Automate Backups with Shell Scripts for Oracle RMAN?
-
Method 3: How to Manage Oracle RMAN Scripts Using Oracle Enterprise Manager?
-
Protecting Your Database with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Oracle RMAN Script FAQs
-
Conclusion
Backing up your Oracle database is not just a best practice—it is essential. Over time, backup strategies have evolved from manual exports to sophisticated automation. Today’s enterprises rely on tools that combine reliability with flexibility. Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) stands out as the built-in solution for this job. But how do you make it truly efficient? The answer often lies in using an oracle rman script. These scripts bridge the gap between RMAN’s power and operational reliability. In this article, we break down what these scripts are, why you need them, and how to create, automate, optimize, and manage them step by step.
What Is an Oracle RMAN Script?
An oracle rman script is a set of commands written for Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) to automate backup, restore, and maintenance tasks. Instead of typing commands one by one during each session—which can be tedious—you store them in a file or within the recovery catalog for repeated use.
There are two main types of RMAN scripts: file-based scripts and stored scripts. File-based scripts are simple text files saved on your server or workstation; they are portable but managed outside of Oracle infrastructure. Stored scripts reside inside the recovery catalog database; they offer centralized management but depend on catalog availability (Oracle Help Center, 2024). Choosing between these depends on your environment’s needs—portability versus central control.
Scripts can be run from the command line using RMAN itself or scheduled through operating system tools like cron or Task Scheduler. You can also manage them through graphical interfaces such as Enterprise Manager.
Why Use Oracle RMAN Scripts?
Using RMAN scripts brings several advantages that go beyond convenience. First, they save time by automating routine tasks—no more repetitive typing or missed steps during late-night maintenance windows! Second, they reduce mistakes since you’re not entering commands manually every time.
Third—and especially important for operations administrators—scripts help enforce corporate backup policies across all environments: development, testing, production. This means retention periods stay consistent; destinations don’t change unexpectedly; compression levels remain uniform where required by compliance rules.
Finally, scripting supports auditing requirements because you keep a clear record of what was run and when—a must-have for regulated industries or organizations facing regular IT audits. Would you want to trust your backups to memory alone?
Method 1: How to Create a Basic Backup Script Using Oracle RMAN?
Creating a basic oracle rman script is straightforward yet powerful when done right. By writing your commands into a text file and executing them with RMAN directly from the command line or batch process manager, you ensure repeatable results every time.
To get started with a full database backup script:
First ensure your environment variables are set correctly (like ORACLE_HOME and ORACLE_SID), and verify that you have sufficient permissions for both OS-level access and database authentication.
Next:
1. Open any plain text editor (such as vi or Notepad) and create a file named rman_backup_full.rmn.
2. Add these lines to perform a full database backup including archived logs:
run {
backup incremental level 0 database plus archivelog delete all input;
}3. Save this file in your chosen directory—for example /u01/app/scripts/rman/.
4. To execute it from terminal:
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/rman target sys/YourPassword nocatalog @/u01/app/scripts/rman/rman_backup_full.rmn
This command connects directly to your target database instance without using a recovery catalog (nocatalog)—a common approach for smaller setups or test environments.
You can adapt similar scripts for incremental backups by changing level 0 to level 1, or add validation tasks within the same block (Oracle Help Center).
Method 2: How to Automate Backups with Shell Scripts for Oracle RMAN?
Manual backups may work once—but daily operations demand automation so nothing gets missed due to human error or forgetfulness! Wrapping your oracle rman script inside an operating system shell script lets you schedule jobs reliably using cron (Linux) or Task Scheduler (Windows).
Here’s how you can automate daily full backups on Linux:
Start by creating a shell script called rmanctl.sh in your preferred directory:
#!/bin/bash export ORACLE_SID=oradb export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/19.3.0/dbhome_1 export PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH sRmanDir="/u01/app/scripts/rman" sRmanLogs="/u01/app/scripts/logs" sRScript="$sRmanDir/rman_backup_full.rmn" sRLog="$sRmanLogs/rman_backup_full.log" $ORACLE_HOME/bin/rman target / nocatalog log=$sRLog @$sRScript
Make sure it’s executable:
chmod 744 rmanctl.sh
Then schedule it via cron so it runs every day at 2 AM:
0 2 * * * /u01/app/scripts/rmanctl.sh
This setup ensures timely execution while keeping logs available for later review—a must if something goes wrong overnight!
Method 3: How to Manage Oracle RMAN Scripts Using Oracle Enterprise Manager?
Some administrators prefer graphical interfaces over editing files directly—and that’s where Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) shines! OEM allows centralized management of oracle rman script tasks through its web console without touching command lines at all.
To manage scripts within OEM:
1. Log in as an authorized user with necessary privileges.
2. Navigate through Targets, then select Databases, picking yours from the list.
3. Under Availability, choose Backup & Recovery options.
4. Click Schedule Backup which opens up an intuitive wizard interface.
5. Select desired type of backup—full/incremental/custom—as prompted.
6. On reaching the customization step (Customize RMAN Script) edit generated code freely—or paste pre-tested versions developed offline!
7. Review everything carefully before setting schedules/timeslots appropriate for business needs; click Submit once satisfied!
OEM stores these jobs centrally within its own repository/recovery catalog making reuse easy across teams/departments—even allowing versioning/history tracking per job definition over time!
From an operations perspective: While OEM offers excellent visibility into job status/history plus integrated alerting/reporting features—it does introduce dependency on OEM infrastructure itself which must remain healthy/up-to-date alongside core databases being protected! For highly customized workflows involving complex logic/scripting some admins still prefer direct file/script management outside GUI tools entirely due greater flexibility/control offered there instead.
Protecting Your Database with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
For organizations seeking streamlined protection beyond native scripting methods, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers comprehensive enterprise-level support—including robust coverage for Oracle databases alongside MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB environments commonly found today’s infrastructures.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery combines advanced features such as incremental backup capabilities tailored specifically for Oracle workloads; batch database backup; flexible data retention policies including GFS retention policy; cloud backup/tape archiving options; plus storage protection against ransomware threats—all designed to maximize efficiency while minimizing risk across diverse deployment scenarios.
With its intuitive web console interface managing backups becomes remarkably simple:
Step 1: Select the Oracle database to back up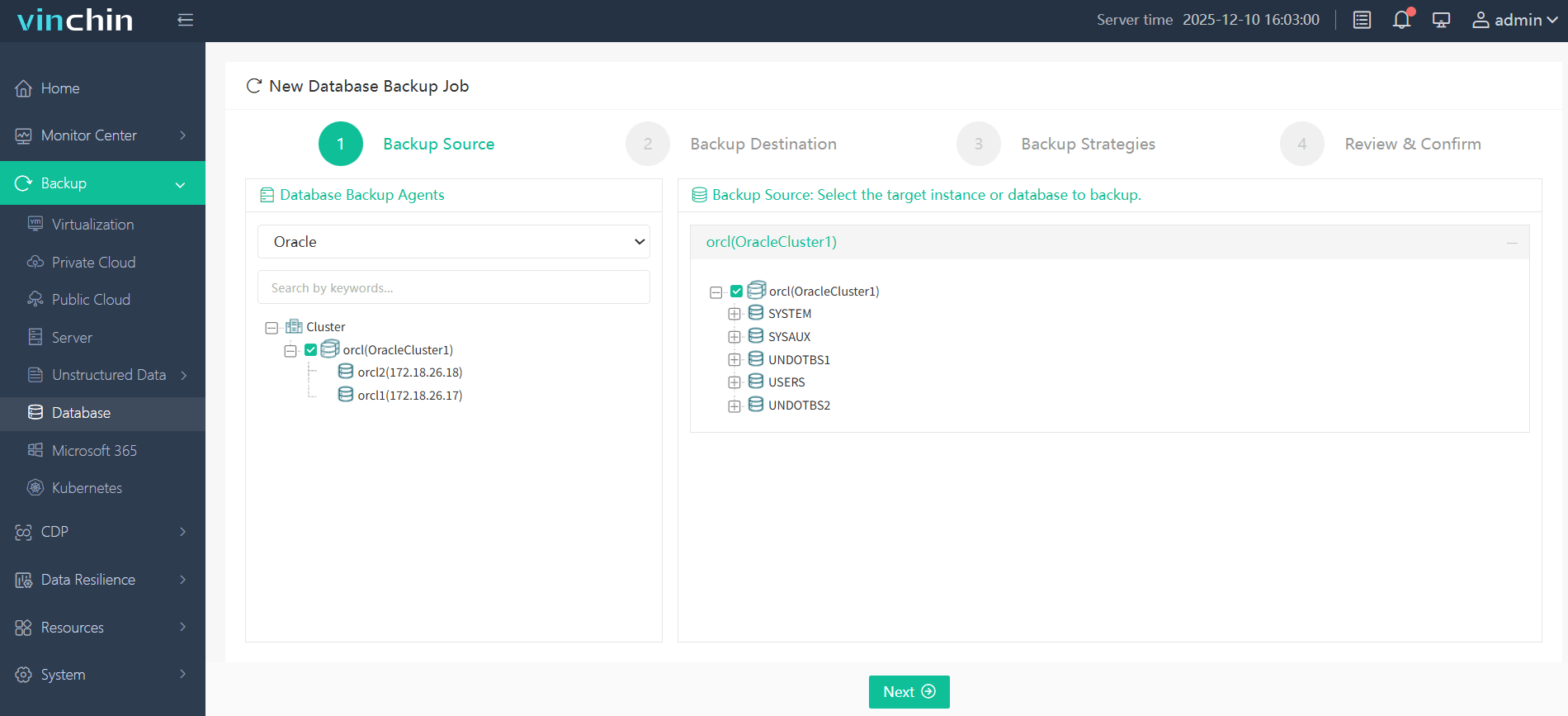
Step 2: Choose the backup storage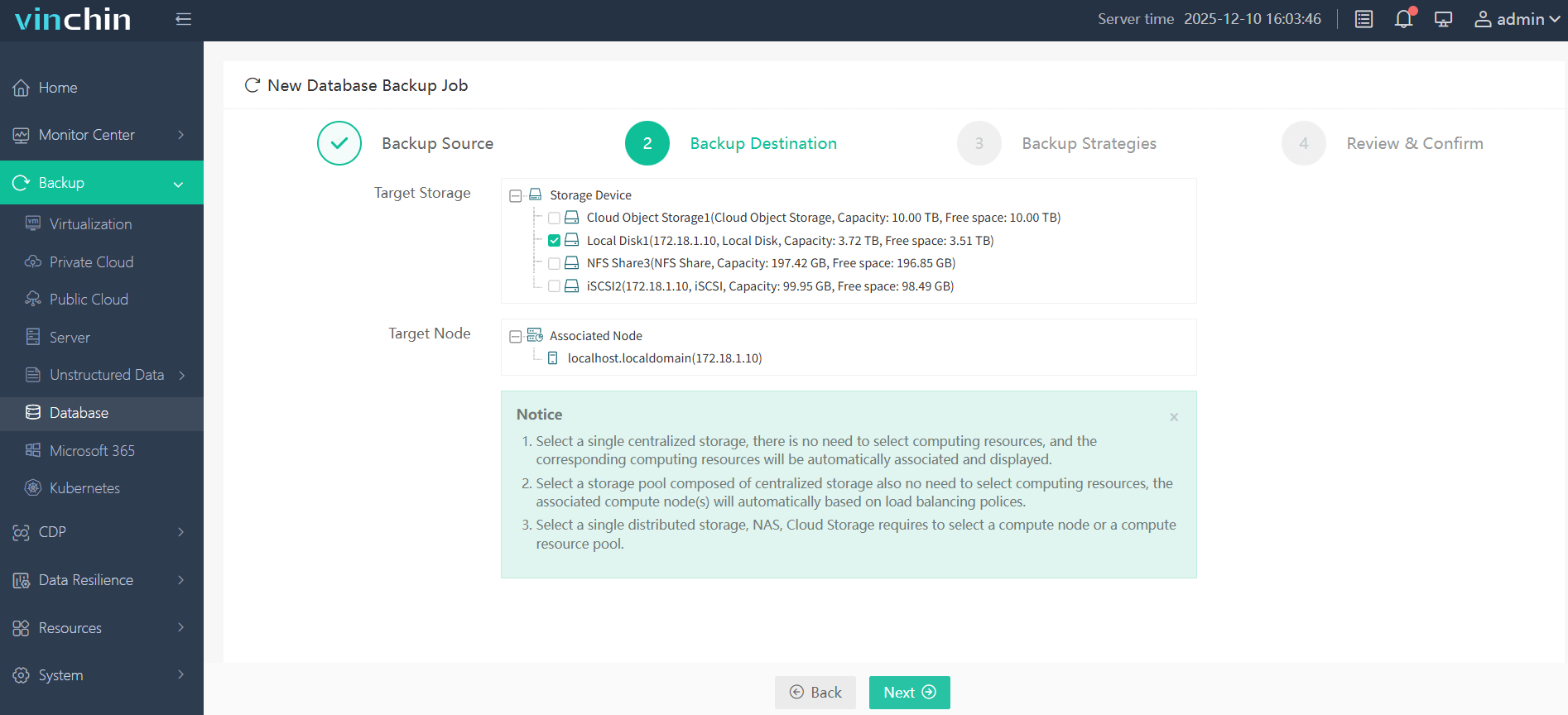
Step 3: Define the backup strategy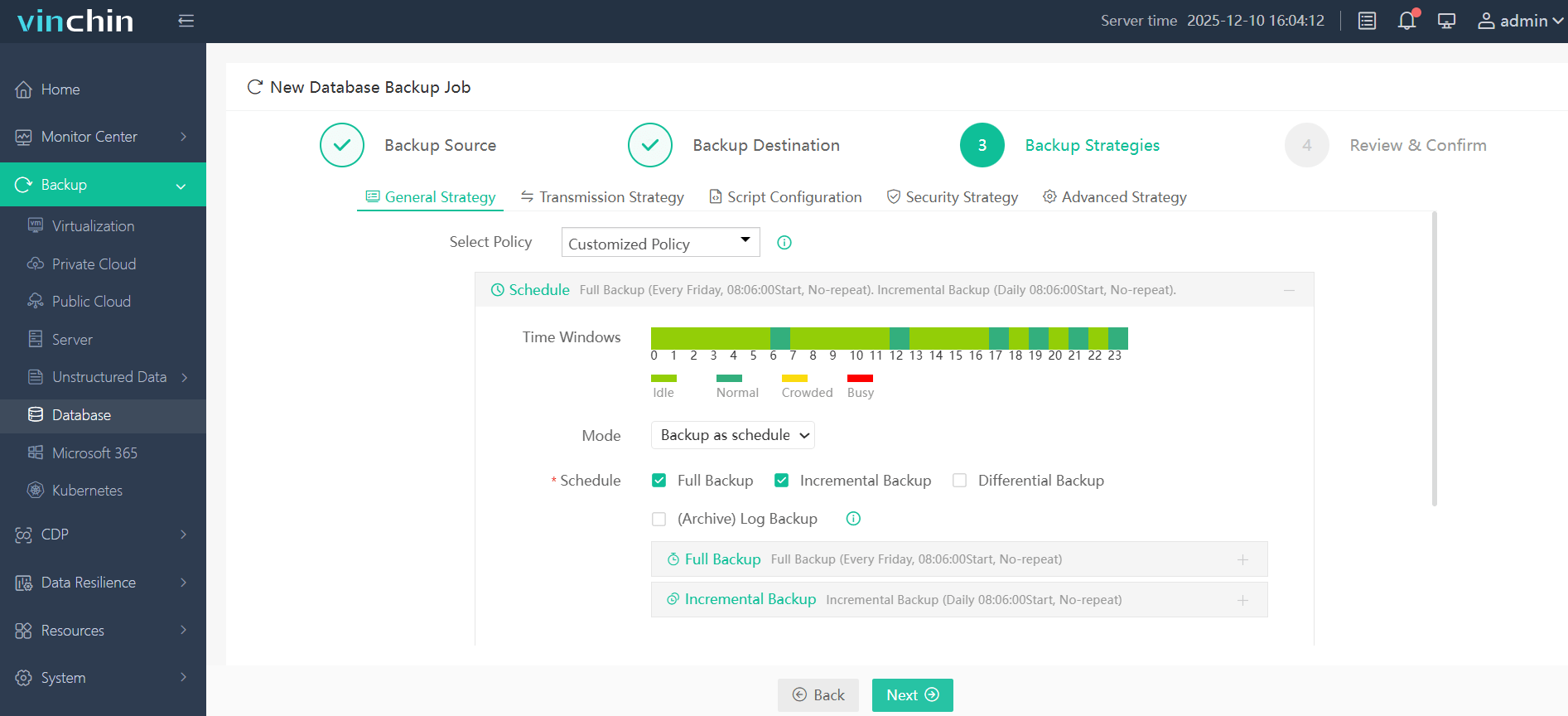
Step 4: Submit the job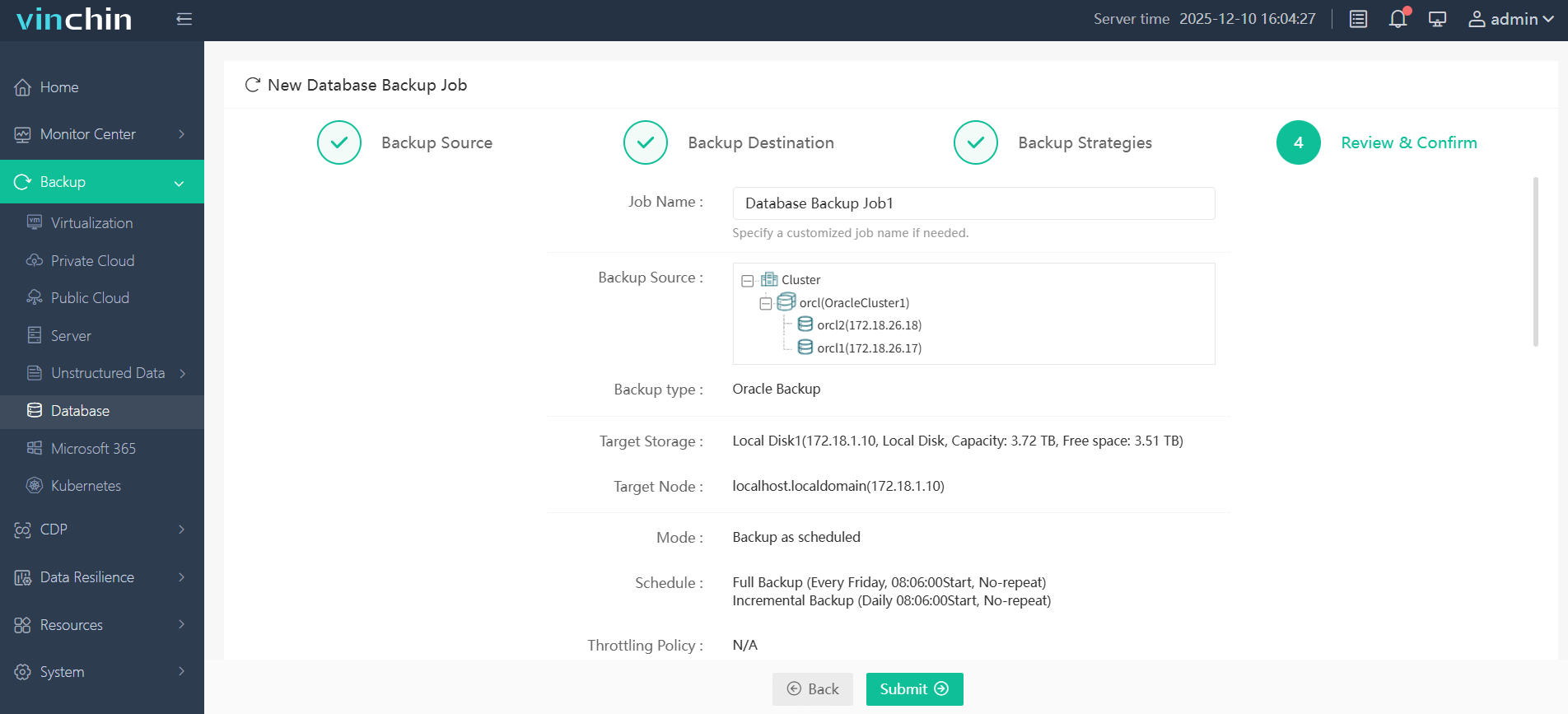
Recognized globally among leading enterprise data-protection solutions—with thousands of customers worldwide—Vinchin Backup & Recovery consistently earns top ratings for reliability and ease-of-use. Try all features free for 60 days—click download below to get started.
Oracle RMAN Script FAQs
Q1: Can I use an oracle rman script to back up only specific tablespaces?
Yes; specify tablespaces using the BACKUP TABLESPACE command in your script.
Q2: How do I check if my RMAN backup script ran successfully?
Review output logs created during execution or check job status within Enterprise Manager dashboards.
Q3: Can I restore my database to a specific point in time using an RMAN script?
Yes; include either SET UNTIL TIME or SET UNTIL SCN before issuing restore commands inside your script block.
Q4: How do I pass dynamic values like dates into my oracle rman script?
Use substitution variables inside .rmn files then call them from shell wrappers passing arguments accordingly (USING clause) at runtime.
Q5: My oracle rman script fails with "ORA-19554 error allocating device." What should I check?
Verify destination paths exist/have enough space/configured channels match available devices/access rights.
Conclusion
Using an oracle rman script automates critical tasks while enforcing standards across environments—from simple text files through robust automation pipelines right up centralized GUI tools like OEM. Scripts make processes safer, reliable, and auditable. For ultimate simplicity, Vinchin delivers advanced protection atop native capabilities—all through one easy-to-use platform!
Share on:








