-
What Is Oracle RMAN Backup Database?
-
Why Use RMAN for Database Backups?
-
Method 1. Performing Full Database Backup with RMAN
-
Method 2. Incremental Backups Using RMAN
-
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Protection for Oracle Databases
-
Oracle RMAN Backup Database FAQs
-
Conclusion
Backing up your Oracle database is essential for business continuity. Data loss can happen due to hardware failure or human error at any time. Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is the built-in tool designed to protect your data efficiently. This guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough of key RMAN backup procedures so you can keep your data safe and your business running smoothly.
What Is Oracle RMAN Backup Database?
Oracle RMAN (Recovery Manager) is a command-line utility that automates backup and recovery tasks for Oracle databases. It allows you to create full or incremental backups, manage archived redo logs, restore lost data files, and recover from failures quickly. Because it works closely with the Oracle database engine, RMAN ensures that all backups are consistent—even if users are connected while backups run.
You can use RMAN to back up an entire database or select specific tablespaces or data files based on your needs. Backups can be stored on disk or tape devices according to your storage strategy. Advanced features include compression for saving space, encryption for security compliance, and flexible retention policies that help automate backup lifecycle management. With these capabilities, RMAN makes it easier to meet both regulatory requirements and internal service-level agreements.
Why Use RMAN for Database Backups?
RMAN stands out because it is tightly integrated with the Oracle database engine itself—it understands internal structures better than generic tools ever could. This integration means you get reliable backups even when the database remains open during production hours—a major advantage in busy environments where downtime is costly.
RMAN automates many routine tasks: managing backup files across different storage media; tracking which backups exist; deleting obsolete copies based on defined policies; handling archived redo logs; supporting both full and incremental strategies; even verifying backup integrity automatically after jobs complete.
Incremental backups save only changed blocks since previous runs—saving time and storage space without sacrificing reliability. With these features combined, you minimize risk while keeping recovery times short in case disaster strikes.
Method 1. Performing Full Database Backup with RMAN
A full database backup captures every data file along with control files—and optionally archived redo logs—to provide a complete snapshot of your system at one point in time. This forms the foundation of any robust backup plan because it enables full restoration if needed later.
You can perform a full backup while the database is open (hot backup) if ARCHIVELOG mode is enabled—or closed (cold backup) if not.
Before starting your first backup job, it's wise to configure some essential persistence settings:
Configuring Essential RMAN Persistence Settings
Setting up key parameters before running backups helps prevent mistakes down the line:
Configure default device type:
At the RMAN prompt:
CONFIGURE DEFAULT DEVICE TYPE TO DISK;
Set parallelism:
For faster performance:
CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK PARALLELISM 2;
Enable control file autobackup:
Protects critical metadata:
CONFIGURE CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP ON;
Define retention policy:
Automate cleanup of old backups:
CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY TO REDUNDANCY 2;
These settings ensure that future jobs run smoothly without manual intervention each time.
Steps for Full Database Backup
To perform a full Oracle rman backup database operation:
1. Start RMAN with proper privileges
Open a terminal window then connect using SYSDBA or SYSBACKUP privilege:
rman target "sys/password@yourdb as sysbackup"
If running locally as OS user with DBA rights:
rman target /
2. (Optional) Review current configuration
At the prompt:
SHOW ALL;
3. Run full backup command
To back up everything:
BACKUP DATABASE;
4. Include archived redo logs for point-in-time recovery
For more comprehensive protection:
BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;
Want to save disk space? Add
DELETE INPUTso completed archive logs are removed after being backed up:
BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG DELETE INPUT;
5. (Optional) Specify custom location/format
Direct output where you want:
BACKUP DATABASE FORMAT '/backup/path/%d_%t_%s.rman';
6. (Optional) Tag this job
Make identification easy later:
BACKUP DATABASE TAG = 'WEEKLY_FULL';
7. Verify completion status
Check what’s been created:
LIST BACKUP;
If your environment uses ARCHIVELOG mode—which most production systems do—you may run these commands while users remain connected without interruption.
If NOARCHIVELOG mode is active instead (common in test/dev), shut down then mount—not open—the instance before backing up.
Method 2. Incremental Backups Using RMAN
Incremental strategies allow you to back up only those blocks that have changed since prior runs—saving both time during busy windows and precious storage capacity over weeks or months.
Here’s how incremental approaches work step by step:
1. Create level 0 base image copy
Start by establishing a baseline similar in scope to a full backup:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 DATABASE;
2. Perform level 1 differential incremental
Capture only changes since last level 0 OR previous level 1 differential:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 DATABASE;
3. (Optional) Run cumulative incremental
Collect all changes since last level 0 regardless of intervening level 1s—a bit larger but simplifies restores later:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 CUMULATIVE DATABASE;
4. Schedule regular cycles
Many admins schedule weekly level 0s plus daily level 1s—balancing speed versus redundancy so no single day’s worth of changes gets lost between jobs.
5. Enable block change tracking
Dramatically speeds up scans by recording changed blocks in advance—enable this feature like so:
Default location uses
DB_CREATE_FILE_DEST, but specify custom path if needed:
ALTER DATABASE ENABLE BLOCK CHANGE TRACKING USING FILE '/u01/oradata/yourdb/bct.trc';
6. Check history regularly
Confirm what’s available using
LIST BACKUP OF DATABASE;
Differential incrementals are smaller/faster but require applying multiple sets during restore; cumulative incrementals take longer per run but simplify recovery steps afterward.
These incremental strategies form the core of an efficient oracle rman backup database plan for active environments where minimizing impact matters most.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Protection for Oracle Databases
For organizations seeking streamlined automation beyond native tools, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers professional enterprise-grade protection tailored for today’s mainstream databases—including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with special emphasis on robust support for Oracle environments like yours. Key features such as advanced source-side compression, incremental backup capabilities, batch database processing, flexible retention policies including GFS options, and cloud/tape archiving empower IT teams to optimize storage usage while ensuring rapid recoverability under any scenario—all managed through one intuitive platform.
The web console makes safeguarding your Oracle databases remarkably simple:
Step 1—Select the Oracle database to back up;
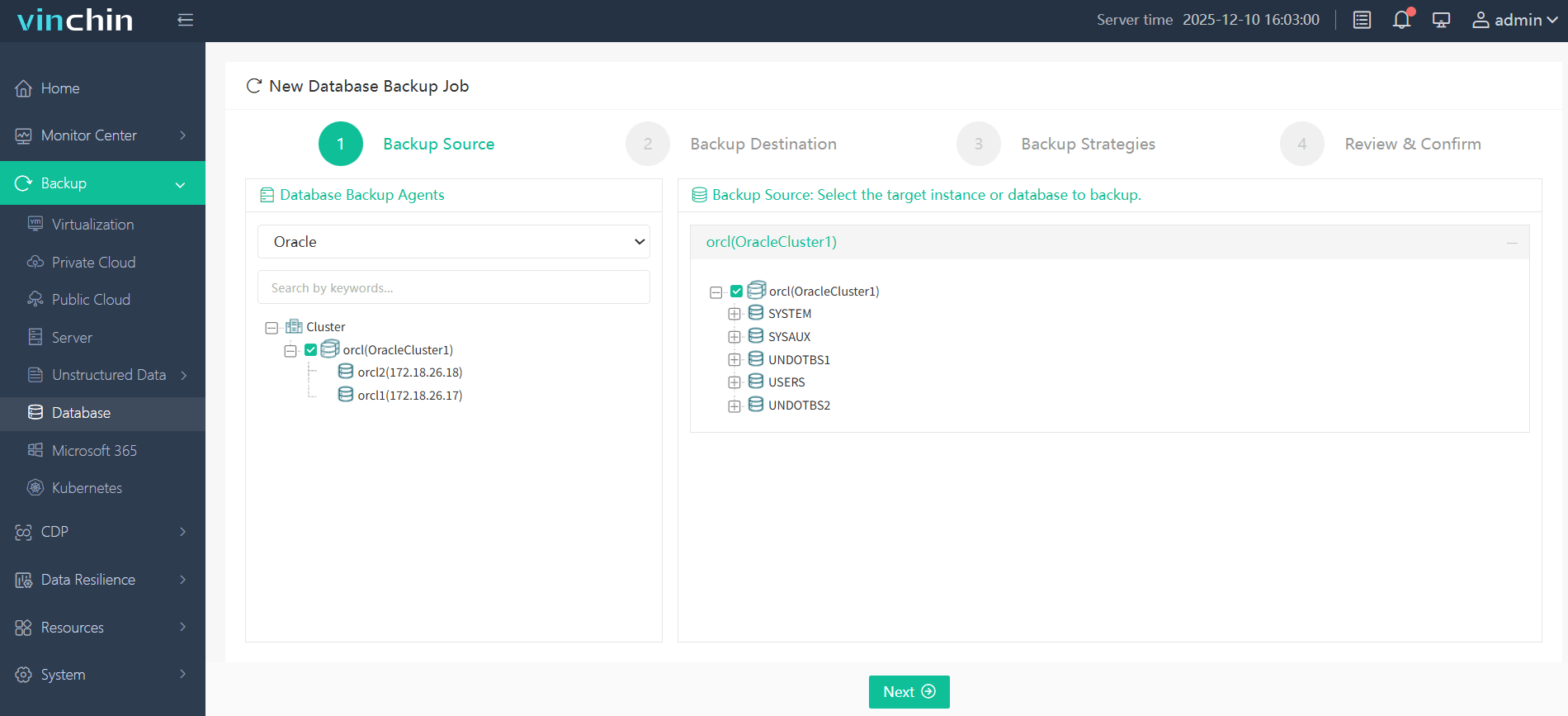
Step 2—Choose your preferred storage destination;
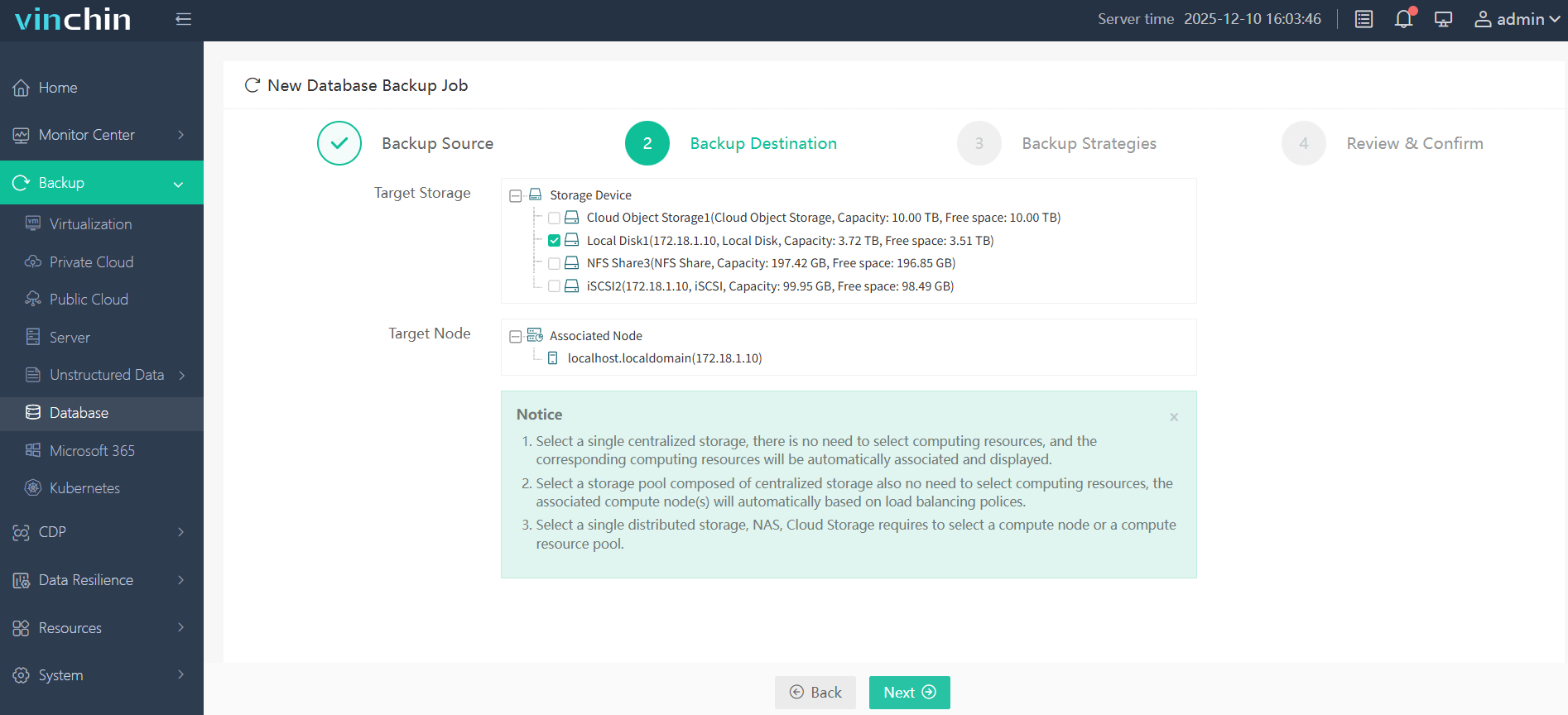
Step 3—Define detailed scheduling and retention strategies;
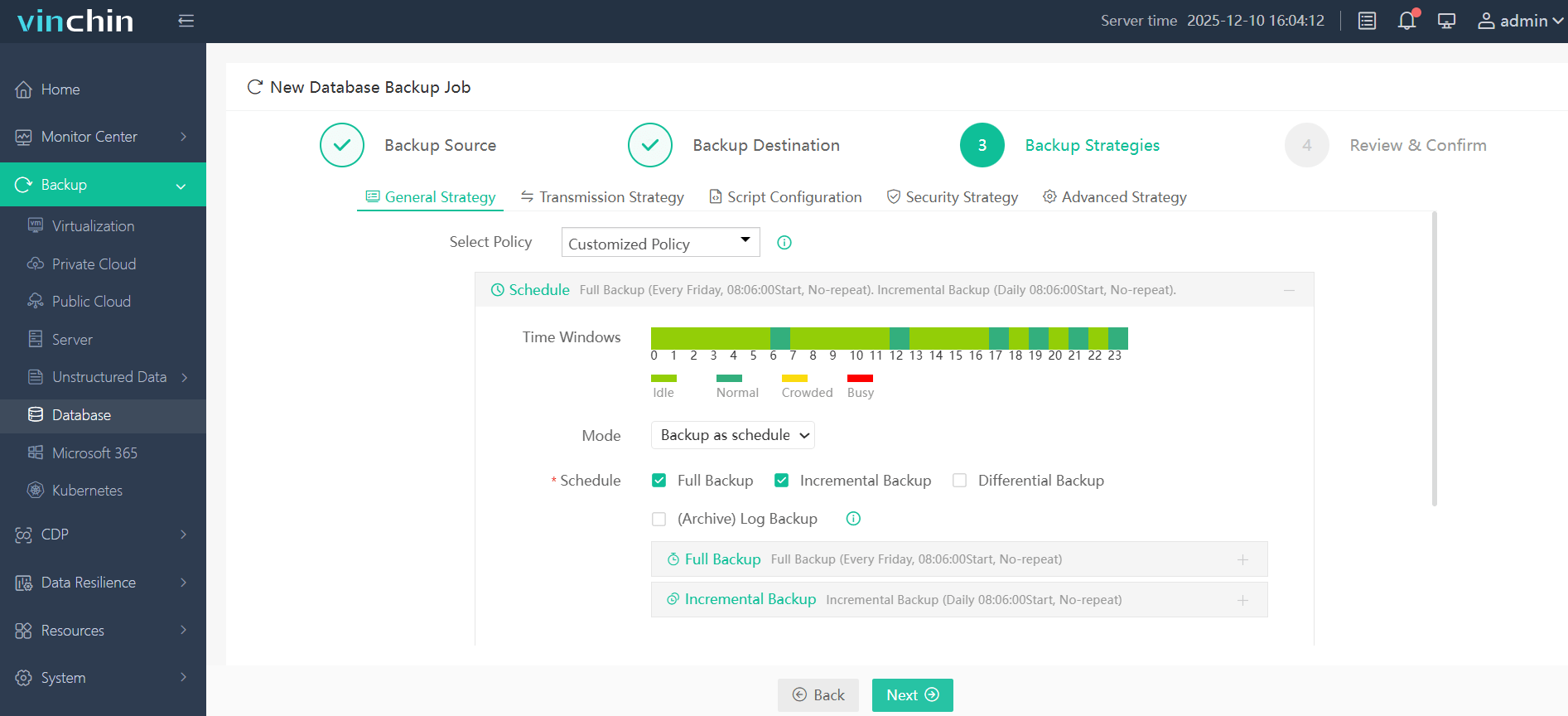
Step 4—Submit the job with just a few clicks.
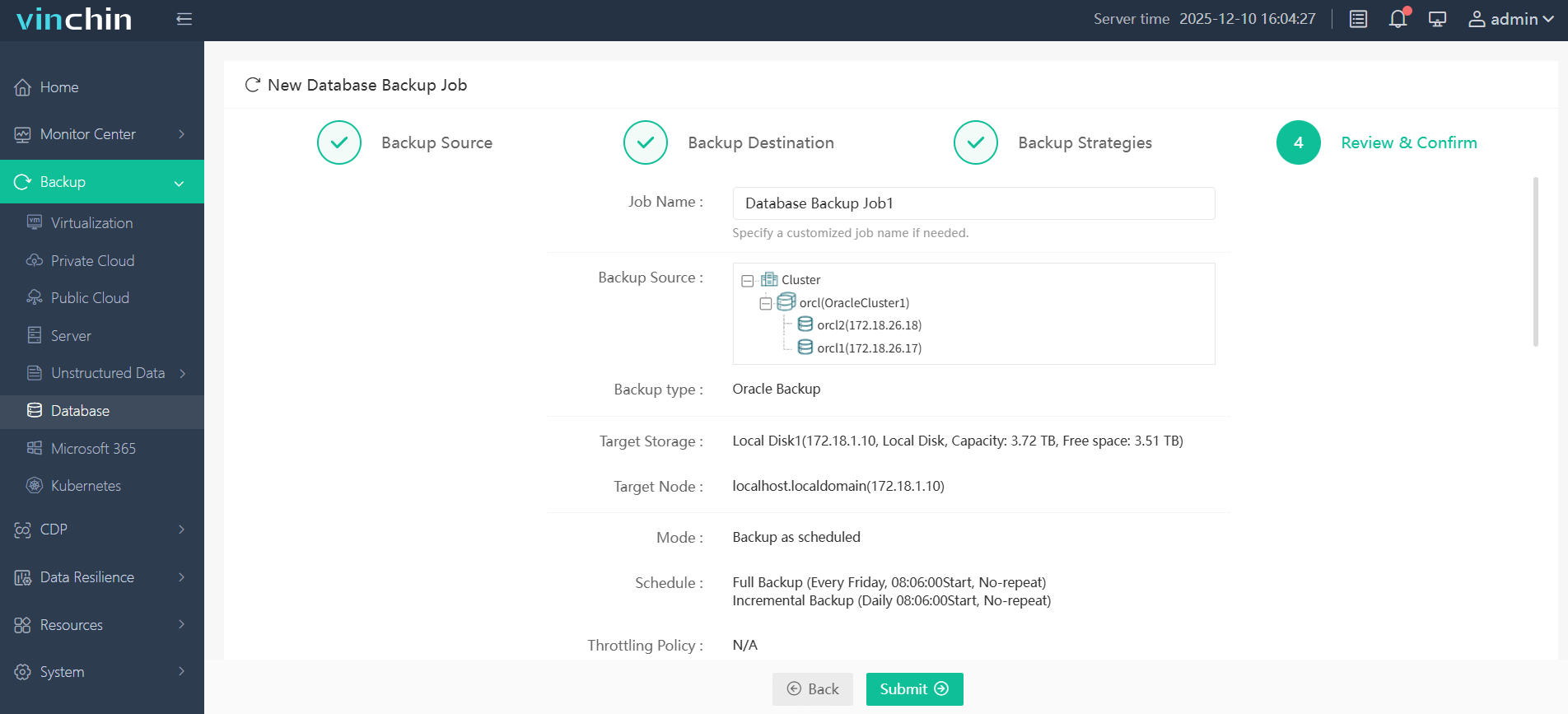
Vinchin Backup & Recovery enjoys global recognition among enterprise customers thanks to its reliability and ease-of-use—explore every feature free for sixty days by clicking download below!
Oracle RMAN Backup Database FAQs
Q1: Can I compress my oracle rman backup database files?
A1: Yes; add AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET in your BACKUP command to reduce file size.
Q2: How do I set automatic deletion rules for old backups?
A2: Use CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY TO REDUNDANCY n then run DELETE OBSOLETE.
Q3: How can I monitor an active rman job's progress?
A3: Query V$SESSION_LONGOPS or check V$RMAN_STATUS from another session during execution.
Conclusion
Oracle Recovery Manager gives you powerful tools—from basic full images through advanced incremental strategies—to safeguard critical databases efficiently at scale. For streamlined automation, Vinchin delivers robust enterprise-grade protection. Try their sixty-day free trial today!
Share on:








