-
What Is SQL Server Database Rename?
-
Why Rename a SQL Server Database?
-
How to Rename a SQL Server Database Using T-SQL?
-
How to Rename a SQL Server Database Using SSMS?
-
Protecting Your Renamed SQL Server Database With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
SQL Server Database Rename FAQs
-
Conclusion
Renaming a SQL Server database is a routine task for many operations administrators. You might need to fix a typo, follow new naming rules, or update names after a business change. But this process can disrupt users and applications if not done carefully. In this guide, you’ll learn what a SQL Server database rename involves, why it matters, and how to do it safely using both T-SQL commands and SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). We’ll also cover risks, troubleshooting tips, automation ideas, and best practices so you can handle renames with confidence.
What Is SQL Server Database Rename?
A SQL Server database rename means changing the name of an existing user-defined database. This operation does not touch your data or tables—only the name changes. All objects inside stay exactly as they were before. System databases like master, model, or msdb cannot be renamed. Only user databases are eligible.
Renaming does not affect permissions inside the database or its internal structure. However, any scripts or connections that use the old name will break until you update them.
Why Rename a SQL Server Database?
There are many reasons to perform a sql server database rename. Sometimes the original name no longer fits because your project changed direction or merged with another team’s work. You might need to fix spelling mistakes or make names more descriptive for easier management. New company policies could require standard naming conventions across all environments.
Another common case is restoring a backup under a temporary name—later you want to give it a proper one. Sometimes you inherit servers from others and want consistent names across production and test systems.
No matter the reason, renaming helps keep your environment organized and reduces confusion for everyone who works with your databases.
How to Rename a SQL Server Database Using T-SQL?
Using T-SQL gives you precise control over the renaming process. This method is fast and scriptable but requires exclusive access—no other users can be connected during the operation.
First, connect to the master database. Set your target database to single-user mode so only one connection (yours) is allowed. This disconnects everyone else and rolls back any open transactions. After renaming, return the database to multi-user mode so normal access resumes.
Here’s how you do it step by step:
1. Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to your server.
2. Open a new query window and select the master database.
3. Run these commands—replace OldDatabaseName and NewDatabaseName with your actual names:
USE master; GO ALTER DATABASE OldDatabaseName SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE; GO ALTER DATABASE OldDatabaseName MODIFY NAME = NewDatabaseName; GO ALTER DATABASE NewDatabaseName SET MULTI_USER; GO
This sequence ensures no one else interferes during the rename. The ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE option forces all other connections out right away—even if they have open transactions—so plan ahead and warn users before running this in production.
Adding Error Handling in T-SQL
For more robust scripts in production environments, consider wrapping your code in a TRY...CATCH block:
BEGIN TRY USE master; ALTER DATABASE OldDatabaseName SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE; ALTER DATABASE OldDatabaseName MODIFY NAME = NewDatabaseName; ALTER DATABASE NewDatabaseName SET MULTI_USER; END TRY BEGIN CATCH PRINT 'Error occurred: ' + ERROR_MESSAGE(); END CATCH;
This helps catch errors such as permission issues or active connections that refuse to close.
How to Rename a SQL Server Database Using SSMS?
If you prefer working in a graphical interface, SSMS makes renaming straightforward. Still, you must ensure no active connections exist before starting.
Here's how you do it:
1. Open Object Explorer in SSMS and connect to your SQL Server instance.
2. Expand Databases to see your list of databases.
3. Right-click the target database and select Properties.
4. Go to the Options page, find Restrict Access, set it to Single, then click OK.
5. Right-click the same database again and choose Rename.
6. Type your new name and press Enter.
7. Return to Properties > Options, set Restrict Access back to Multi, then click OK again.
You may need to refresh Object Explorer (right-click on Databases > Refresh) before seeing changes take effect. If other users are connected when you try this, SSMS will display an error message—so always schedule renames during maintenance windows when possible.
For large or busy environments, SSMS might not handle renames smoothly due to background connections or open transactions; in those cases, T-SQL is more reliable.
Protecting Your Renamed SQL Server Database With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Once you've completed critical operations such as renaming your SQL Server databases, strengthening backup protection becomes essential to maintain data safety and compliance across modern IT environments. Vinchin Backup & Recovery provides a unified, professional solution that supports major database platforms—including Oracle, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL/PostgresPro, MongoDB, and Microsoft SQL Server—all out-of-the-box and without the complexity of legacy tools still common in many organizations today.
Enterprise-Grade Features for SQL Server Protection
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers advanced capabilities tailored for SQL Server workloads, including:
Incremental backup and source-side compression for optimized performance
Batch scheduling across multiple instances
Flexible retention policies with GFS support
Built-in ransomware protection to secure every restore point automatically
All operations are managed via an intuitive web console in just four steps:
1. Select source SQL Server database(s),
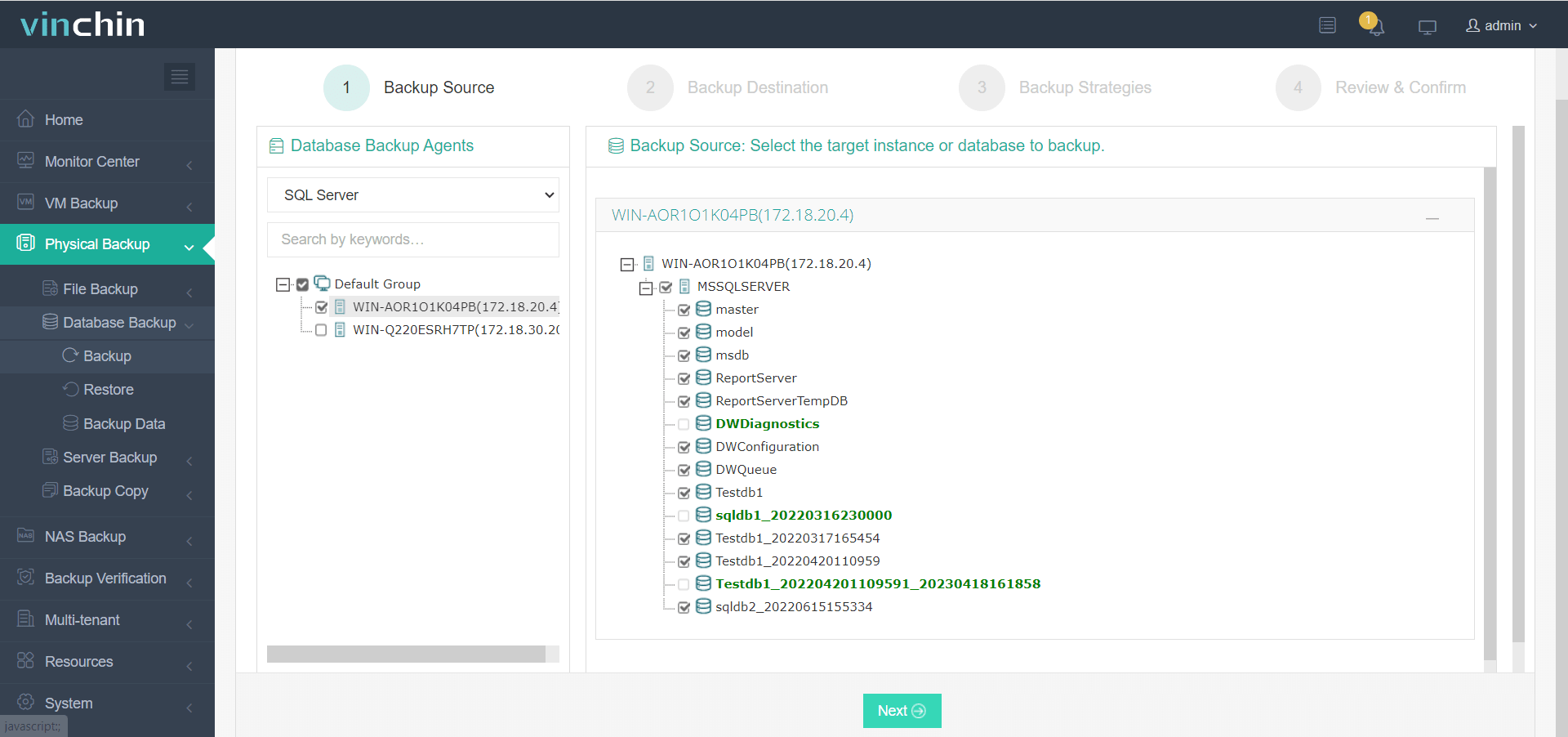
2. Choose target storage location(s),
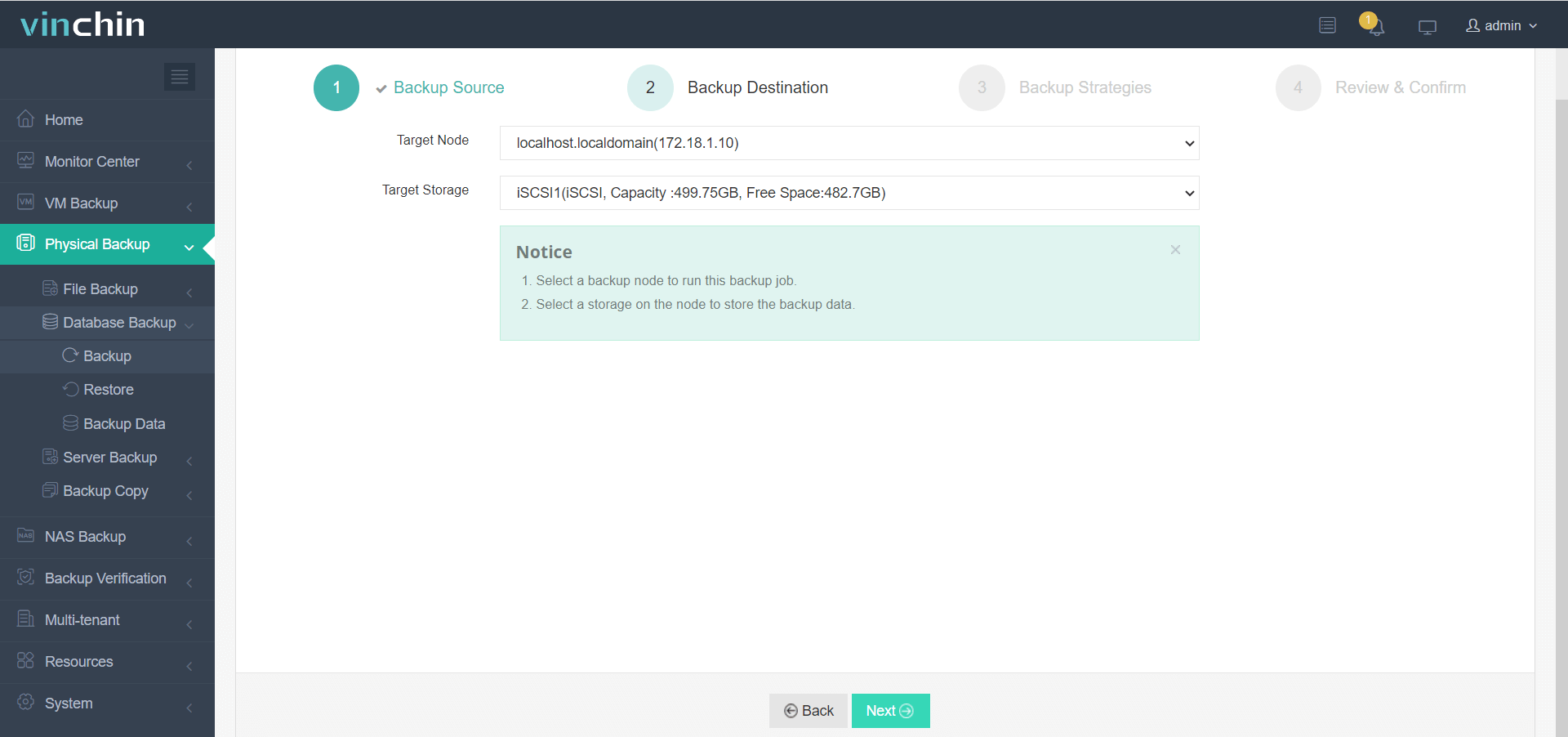
3. Configure backup strategies,

4. Submit the job.
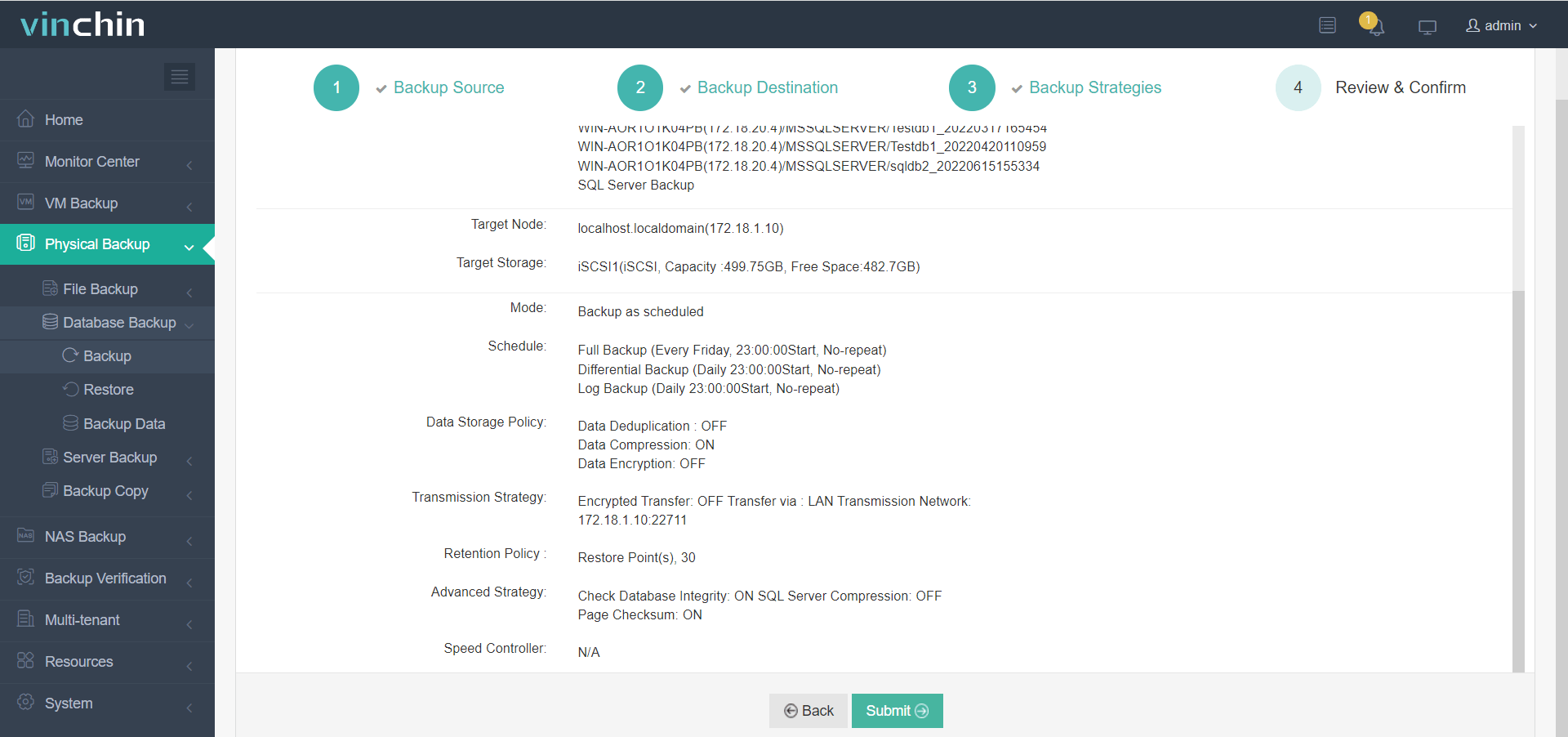
Trusted by thousands of enterprises worldwide and highly rated by industry analysts, Vinchin Backup & Recovery simplifies complex backup management while ensuring continuous data availability across hybrid clouds and traditional datacenters alike.
Experience all features free for 60 days—try it today!
SQL Server Database Rename FAQs
Q1: Can I rename a database that's part of an Always On Availability Group?
A1: No—you must remove it from the group first, perform the rename operation, then add it back.
Q2: Will renaming my SQL Server database affect replication settings?
A2: Yes—replication references will break; you must reconfigure replication after renaming.
Q3: How do I find out which applications connect using the old name?
A3: Check application logs or use Extended Events in SQL Server to trace connection attempts by name.
Conclusion
Renaming a SQL Server database is simple but requires careful planning and communication with stakeholders. Always test changes first, update references everywhere they appear, validate backups before starting—and consider Vinchin for reliable backup protection as part of any major change process.
Share on:








