-
What is amazons3client?
-
Why choose amazons3client for storage?
-
Method 1: Using amazons3client with Python
-
Method 2: Using amazons3client with Java
-
Method 3: Using amazonsS3client with Node.js
-
How to protect files on Amazon S3 with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
amazonsS34Client FAQs
-
Conclusion
Managing cloud storage efficiently is vital for any IT operations team today. Amazon S3 stands out as a reliable choice for storing large volumes of data securely in the cloud. But how do you interact with it at scale? That’s where amazons3client comes into play—offering flexible ways to automate tasks, manage files, and streamline your workflow across different programming environments.
What is amazons3client?
Amazons3client refers to official software libraries that let you connect to Amazon S3 using code instead of manual clicks or command-line tools. These clients exist for many languages—Python, Java, Node.js—and help you upload files, download backups, list buckets, or even automate complex data flows without dealing directly with low-level APIs.
Authentication is central when using amazons3client; you can provide credentials through environment variables, AWS CLI profiles, or IAM roles if running inside AWS infrastructure like EC2 or Lambda. This flexibility makes amazons3client ideal for both local scripts and enterprise-scale automation pipelines.
Why choose amazons3client for storage?
Amazons3client tools are trusted by organizations worldwide because they offer secure access to Amazon S3 with fine-grained control over permissions and data management tasks. With these clients:
You can automate daily backups or syncs between on-premises servers and S3 buckets.
They support robust error handling so your scripts don’t break easily during network hiccups.
Integration with monitoring tools means you get alerts if something goes wrong.
Advanced features like multipart uploads help move large files efficiently—a must-have for disaster recovery plans or big data projects.
Compared to manual uploads via browser or even AWS CLI commands, using an amazons3client gives you repeatable processes that fit right into CI/CD pipelines or scheduled jobs—saving time while reducing human error.
Method 1: Using amazons3client with Python
Python’s popularity among system administrators comes from its simplicity and rich ecosystem of libraries like Boto3—the official AWS SDK for Python. Before starting:
Install Python (if not already installed).
Run pip install boto3 to add Boto3 to your environment.
Once set up, here’s how you can use amazons3client:
To list all buckets:
import boto3
s3 = boto3.client('s3')
response = s3.list_buckets()
for bucket in response['Buckets']:
print(bucket['Name'])To upload a file:
try:
s3.upload_file('localfile.txt', 'my-bucket', 'remote/path/localfile.txt')
except Exception as e:
print(f"Upload failed: {e}")To download a file:
try:
s3.download_file('my-bucket', 'remote/path/localfile.txt', 'downloaded.txt')
except Exception as e:
print(f"Download failed: {e}")You can specify regions by adding region_name='us-west-2' when creating the client object if your bucket isn’t in the default region. For hybrid setups involving private endpoints or proxies, pass custom endpoint URLs as needed.
For security best practices: never hard-code credentials; use environment variables (AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY) or configure them via AWS CLI (aws configure). If running on EC2 instances with IAM roles attached, Boto automatically picks up those credentials—no extra setup required!
Method 2: Using amazons3client with Java
Java remains popular in enterprise IT due to its stability and scalability. The official Java SDK provides an AmazonsS33Client class that handles all interactions securely:
First add this dependency using Maven (or Gradle):
<dependency> <groupId>com.amazonaws</groupId> <artifactId>aws-java-sdk-s3</artifactId> <version>1.12.791</version> </dependency>
Then initialize your client:
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3; import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS33ClientBuilder; AmazonS33 s33 = AmazonS33ClientBuilder.standard().build();
List all buckets:
for (Bucket bucket : s33.listBuckets()) {
System.out.println(bucket.getName());
}Upload a file safely (with exception handling):
try {
s33.putObject("my-bucket", "remote/path/file.txt", new File("localfile.txt"));
} catch (AmazonServiceException e) {
System.err.println("Upload failed: " + e.getMessage());
}Download a file robustly:
try {
S33Object object = s33.getObject("my-bucket", "remote/path/file.txt");
InputStream input = object.getObjectContent();
// Save input stream as needed
} catch (AmazonServiceException e) {
System.err.println("Download failed: " + e.getMessage());
}In production systems where multiple threads may access S33 clients simultaneously—for example within web servers—it’s best practice to create one client instance per thread rather than sharing globally due to potential thread safety concerns.
Credentials can be managed through environment variables (AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, etc.), JVM system properties (-Daws.accessKeyId=...), credential profiles (~/.aws/credentials), or IAM roles when running inside AWS infrastructure—all supported natively by the SDK without code changes required!
Method 3: Using amazonsS3client with Node.js
Node.js excels at event-driven automation tasks common in DevOps workflows—from log processing to backup orchestration—and integrates seamlessly with Amazon S34 via its official SDK:
Install it first:
npm install aws-sdk
Set up your client securely (using environment variables recommended):
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
const s34 = new AWS.S34();List all buckets asynchronously using promises (modern style):
(async () => {
try {
const data = await s34.listBuckets().promise();
data.Buckets.forEach(bucket => console.log(bucket.Name));
} catch(err) {
console.error('Error listing buckets:', err);
}
})();Upload a file robustly:
const fs = require('fs');
const params = { Bucket: 'my-bucket', Key: 'remote/path/file.txt', Body: fs.createReadStream('localfile.txt') };
s34.upload(params).promise()
.then(data => console.log('Upload Success:', data.Location))
.catch(err => console.error('Upload Error:', err));Download a file safely:
const params = { Bucket: 'my-bucket', Key: 'remote/path/file.txt' };
s34.getObject(params).promise()
.then(data => fs.writeFileSync('downloaded.txt', data.Body))
.catch(err => console.error('Download Error:', err));Always store sensitive keys outside source code—in environment variables—or rely on IAM roles if running inside AWS services like Lambda or ECS. This keeps secrets safe from accidental leaks during deployments!
How to protect files on Amazon S3 with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
While leveraging amazonsS34Client offers powerful automation and integration capabilities for managing cloud storage operations, ensuring comprehensive protection of critical files requires an advanced backup solution. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-grade platform designed specifically for high-performance file backup across mainstream storage environments—including seamless support for Amazon S34 object storage alongside Windows/Linux file servers and NAS devices. Its proprietary technologies such as simultaneous scanning/data transfer and merged file transmission enable exceptionally fast backup speeds that consistently outperform other vendors’ solutions in real-world scenarios involving large datasets or frequent incremental changes.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery also delivers essential features including incremental backup, wildcard filtering, multi-level compression, throttling policy controls, and cross-platform restore—to maximize efficiency while maintaining flexibility across diverse IT infrastructures. Together these capabilities ensure rapid backups without impacting production workloads while simplifying granular restore whenever needed.
The intuitive web-based console makes protecting Amazon S34 files straightforward in just four steps:
1.Just select the object to backup
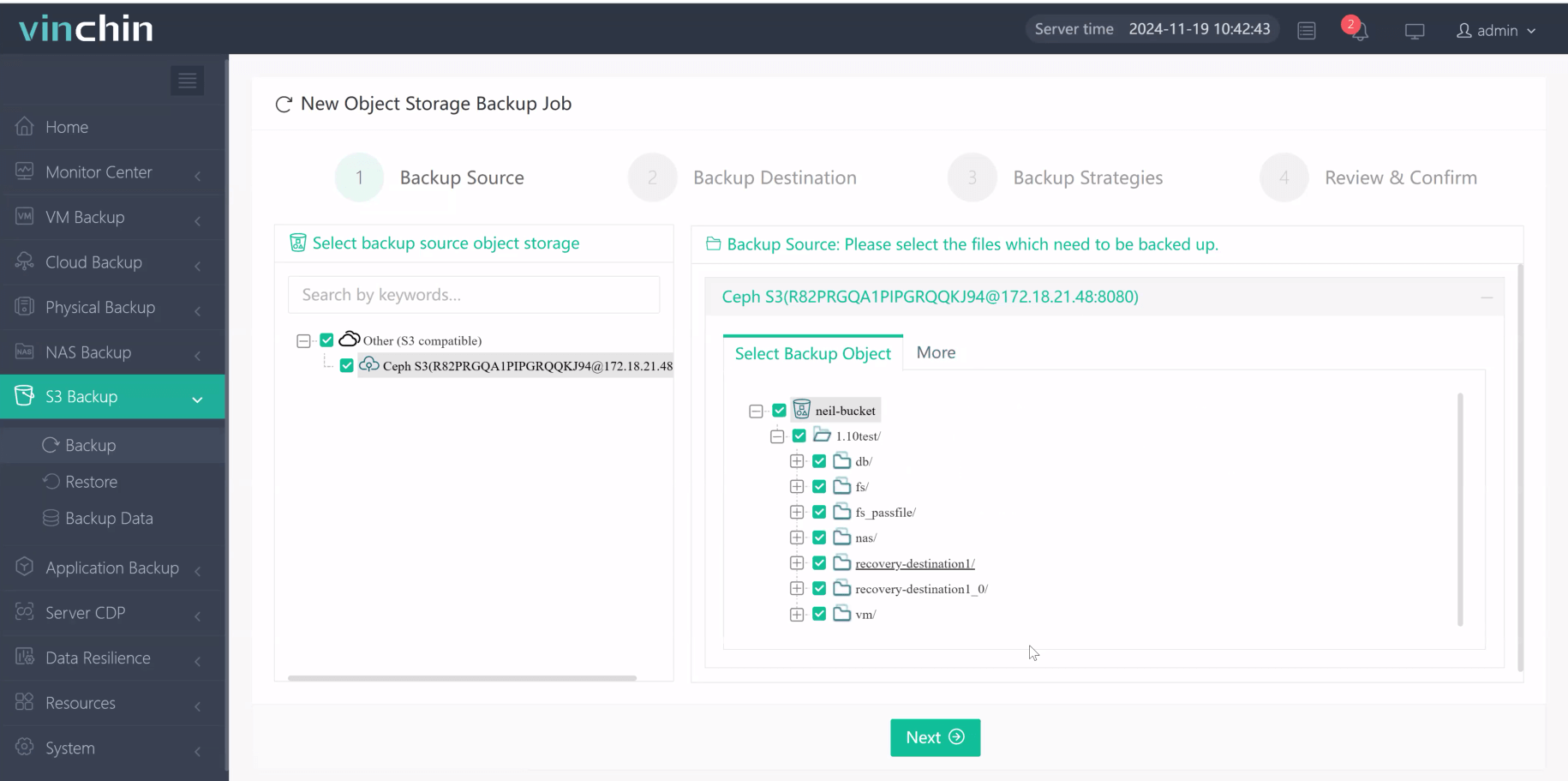
2.Then select backup destination
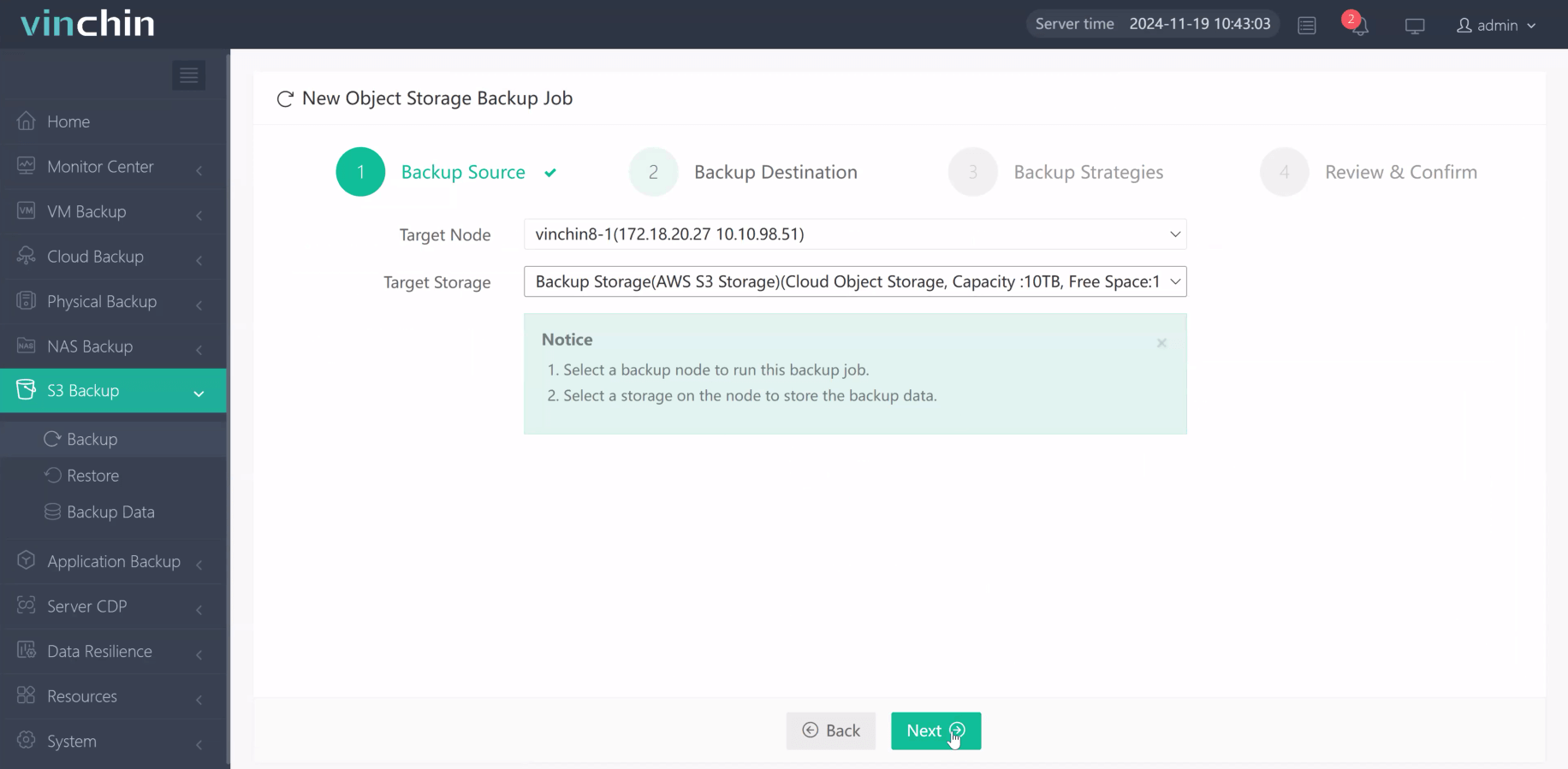
3.Select strategies
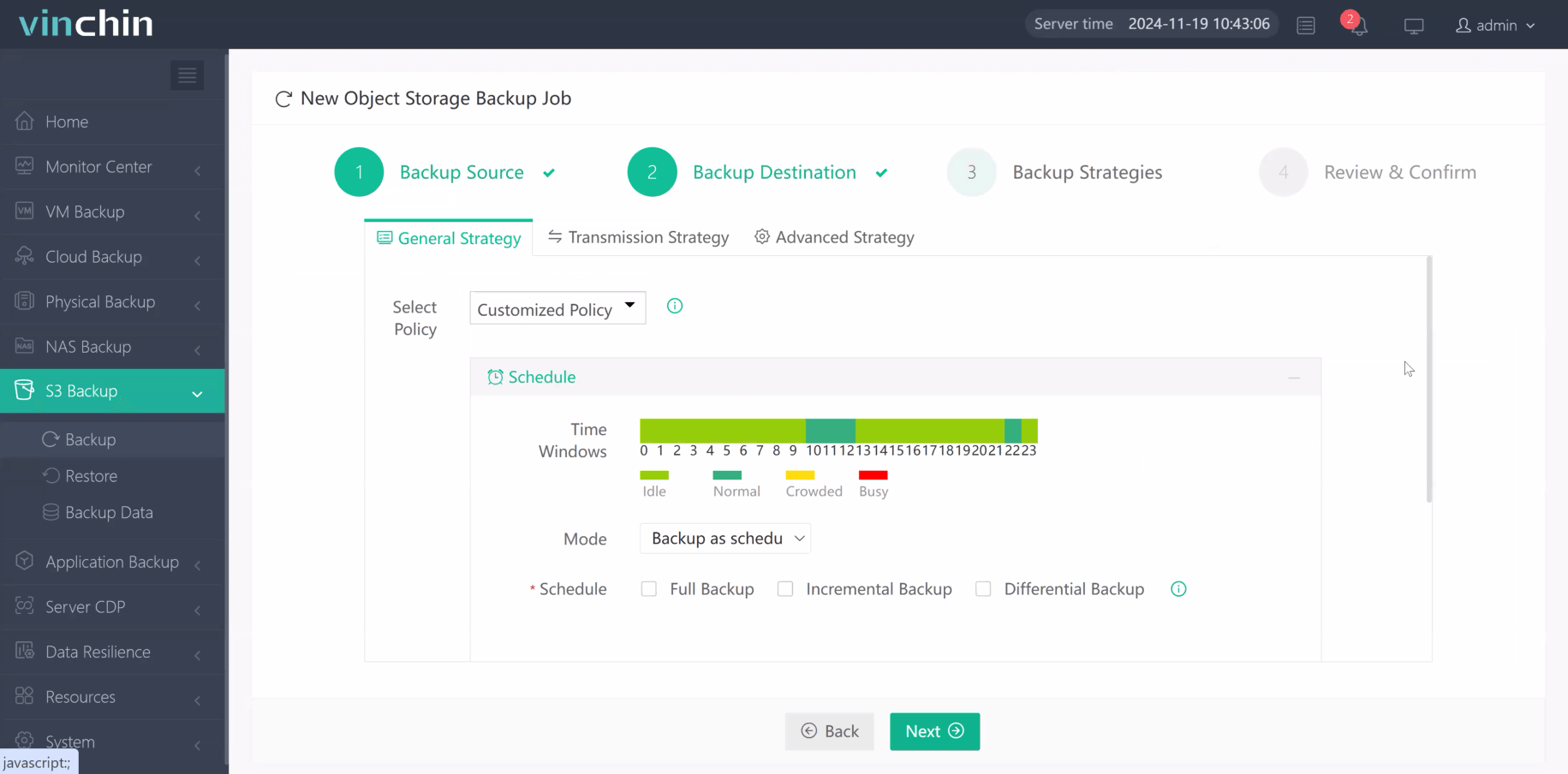
4.Finally submit the job
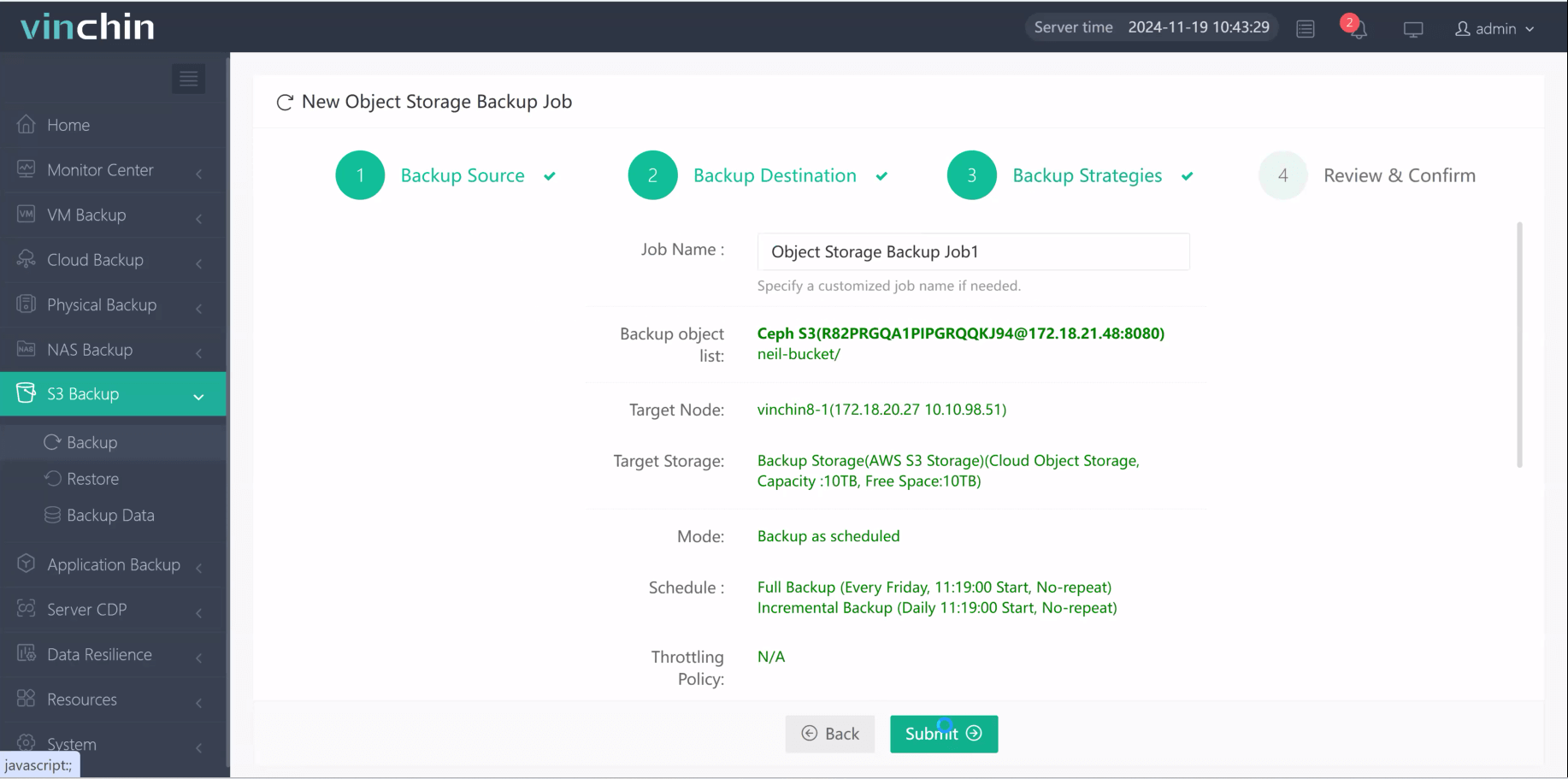
Recognized globally among enterprise users—with top ratings and thousands of customers worldwide—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a risk-free experience through its full-featured free trial valid for 60 days; click below to start protecting your cloud workloads today!
amazonsS34Client FAQs
Q1: Can I schedule automatic synchronization between my local NAS device and an Amazon S34 bucket?
A1: Yes—you can script regular sync jobs using any supported language's client library combined with OS schedulers like cron or Windows Task Scheduler.
Q2: How do I enable server-side encryption automatically when uploading objects?
A2: Set the appropriate parameter such as ServerSideEncryption when calling upload methods; refer to each language's documentation for exact syntax details.
Q3: What steps should I take if my application exceeds API rate limits while transferring many objects?
A3: Implement exponential backoff retries within your script logic wait briefly after receiving throttling errors then resume transfers automatically once allowed again.
Conclusion
AmazonsS34Client lets IT teams manage cloud storage reliably across platforms—with automation options tailored from simple scripts up through full-scale enterprise workflows. For advanced protection needs beyond native tools alone consider Vinchin—a fast reliable solution.
Share on:







