-
What Is OpenStack?
-
Why Restart OpenStack Services?
-
How to Manually Restart OpenStack Components?
-
How to Restart OpenStack Using Ansible?
-
How to Back Up OpenStack Virtual Machines with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
Restart OpenStack FAQs
-
Conclusion
OpenStack powers many private and public clouds around the world. Sometimes you need to restart OpenStack services—maybe after changing configurations or fixing issues. Doing this right keeps your cloud stable and your users happy. In this guide, you’ll learn how to restart OpenStack step by step: from basic commands to automation tools like Ansible.
What Is OpenStack?
OpenStack is an open-source cloud platform that helps you manage compute, storage, and networking resources through modular services. Each service runs as its own process—often on different nodes—to provide flexibility and scalability. Many organizations use OpenStack to build private clouds or support large workloads across multiple data centers.
Why Restart OpenStack Services?
Restarting OpenStack services is common for operations administrators. You may need to do it after updating configuration files, applying patches or upgrades, troubleshooting problems, or recovering from failures. A quick restart can bring back a hung service but may also disrupt running workloads if done carelessly. That’s why following best practices—and verifying each service after restarting—is so important for smooth cloud operations.
How to Manually Restart OpenStack Components?
Manual restarts give you direct control over each OpenStack service using command-line tools on your Linux servers.
Basic Commands for Single-Node Environments
If you’re just starting out or managing a small deployment, most OpenStack services run as Linux system services controlled by either service or systemctl commands (depending on your distribution). For example:
To restart the Nova compute service:
sudo systemctl restart nova-compute
or
sudo service nova-compute restart
You can check if a service is running with:
sudo systemctl status nova-compute
or
sudo service nova-compute status
Other key services include Glance (image), Cinder (block storage), Neutron (networking), Keystone (identity), Horizon (dashboard), Heat (orchestration), Swift (object storage), among others. Here are some common examples:
To restart Glance image services:
sudo systemctl restart glance-api sudo systemctl restart glance-registry
To restart Cinder block storage components:
sudo systemctl restart cinder-api sudo systemctl restart cinder-scheduler sudo systemctl restart cinder-volume sudo systemctl restart cinder-backup
For Neutron networking agents:
sudo systemctl restart neutron-server sudo systemctl restart neutron-dhcp-agent sudo systemctl restart neutron-l3-agent sudo systemctl restart neutron-metadata-agent sudo systemctl restart neutron-linuxbridge-agent
On controller nodes running Nova API components:
sudo systemctl restart nova-api sudo systemctl restart nova-conductor sudo systemctl restart nova-consoleauth sudo systemctl restart nova-novncproxy sudo systemctl restart nova-scheduler
On compute nodes:
sudo systemctl restart nova-compute
Always prefix commands with sudo if you are not logged in as root.
Restart Order Dependencies
Restarting all services at once can cause problems because some depend on others being available first. Always follow an order that respects these dependencies:
Start with Keystone since it provides authentication for other components; then move on to core infrastructure like Glance (images) and Cinder (block storage). Next come Nova (compute) followed by Neutron (networking). Finally handle dashboard-related processes such as Horizon.
A typical safe sequence looks like this:
1. Keystone
2. Glance
3. Cinder
4. Nova
5. Neutron
6. Horizon
This order helps prevent race conditions during startup where one component waits indefinitely for another that isn’t ready yet.
Cluster Considerations for HA Setups
In high-availability clusters—where controllers are spread across several nodes—you must take extra care when restarting OpenStack components.
First: never stop all controllers at once! Instead,
Restart one node at a time.
After each node restarts its set of services,
check their health before moving forward.
Use cluster management tools like Pacemaker when available.
For clustered resources managed by Pacemaker,
use commands such as:
sudo pcs resource disable openstack-cinder-volume-clone sudo pcs resource enable openstack-cinder-volume-clone
Resource names may differ depending on your deployment tool; always verify them using pcs status.
After restarting any critical component in HA mode,
validate functionality beyond just checking process status.
For example:
Check Nova compute services:
openstack compute service list
Check Neutron agents:
openstack network agent list
If something fails to start properly,
use logs for troubleshooting—for example,
run journalctl -u <service> -n 100 for recent log entries.
This gives real-time insight into what went wrong so you can fix it fast.
How to Restart OpenStack Using Ansible?
Automation makes life easier—especially when managing many nodes at scale.
Ansible is an open-source tool that lets you automate IT tasks including restarting OpenStack services across multiple servers at once using simple playbooks written in YAML format.
Getting Started With Ansible Playbooks
Beginner administrators can create basic playbooks targeting groups of hosts defined in their inventory file.
Suppose you want to quickly reboot all Nova compute workers:
Create a file called restart-nova-compute.yml containing:
--- - hosts: compute_nodes become: yes tasks: - name: Restart nova-compute service on all computes service: name: nova-compute state: restarted
Run it using the command line:
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini restart-nova-compute.yml
This approach saves time compared to logging into each server individually.
Handling Service Dependencies in Playbooks
Intermediate users should consider dependencies between components even when automating restarts.
You can define tasks sequentially within your playbook—for example,
restarting Keystone before Nova API:
--- - hosts: controller_nodes become: yes tasks: - name: Restart keystone via Apache2 web server service: name=apache2 state=restarted - name: Restart glance-api next service: name=glance-api state=restarted - name: Restart cinder-api after glance starts up successfully service: name=cinder-api state=restarted # Continue adding other dependent services here...
For rolling restarts across clusters without downtime,
use Ansible’s serial keyword so only one host restarts at a time:
--- - hosts: controller_nodes serial: 1 # Only one host at a time! become: yes tasks: - name: Rolling keystone API restarts across controllers service: name=apache2 state=restarted
Idempotency And Error Handling In Automation
Advanced users know idempotency means repeating playbooks won’t break anything—they only make changes if needed.
Always use state: restarted instead of separate stop/start actions so reruns are safe.
Add error handling logic so failures don’t go unnoticed:
--- - hosts: compute_nodes become: yes tasks: - name: Try restarting nova-compute safely service: name=nova-compute state=restarted ignore_errors: yes register: result - name : Fail loudly if unrecoverable fail : msg : "Critical failure detected!" when : "'inactive' in result.msg"
With these techniques,
you ensure reliability even during complex maintenance windows.
How to Back Up OpenStack Virtual Machines with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
Before performing major changes such as restarting critical cloud environments, robust VM backup is essential for business continuity and data safety. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-level virtual machine backup solution supporting more than fifteen mainstream virtualization platforms—including comprehensive integration with OpenStack, VMware vSphere/ESXi/vCenter Server, Hyper-V/Windows Server, Proxmox VE, oVirt/RHV/OLVM, XCP-ng/XenServer, ZStack, and more—making it suitable for diverse hybrid infrastructures.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers advanced features highly relevant for protecting OpenStack VMs such as forever-incremental backup technology, granular restore capabilities, cross-platform V2V migration between supported hypervisors, scheduled backup jobs with flexible retention policies including GFS strategy, and built-in data deduplication plus compression—all designed to maximize efficiency while minimizing risk and storage usage.
Using the intuitive web console of Vinchin Backup & Recovery makes backing up an OpenStack VM straightforward in four steps:
Step 1. Select the OpenStack VM(s) requiring protection;
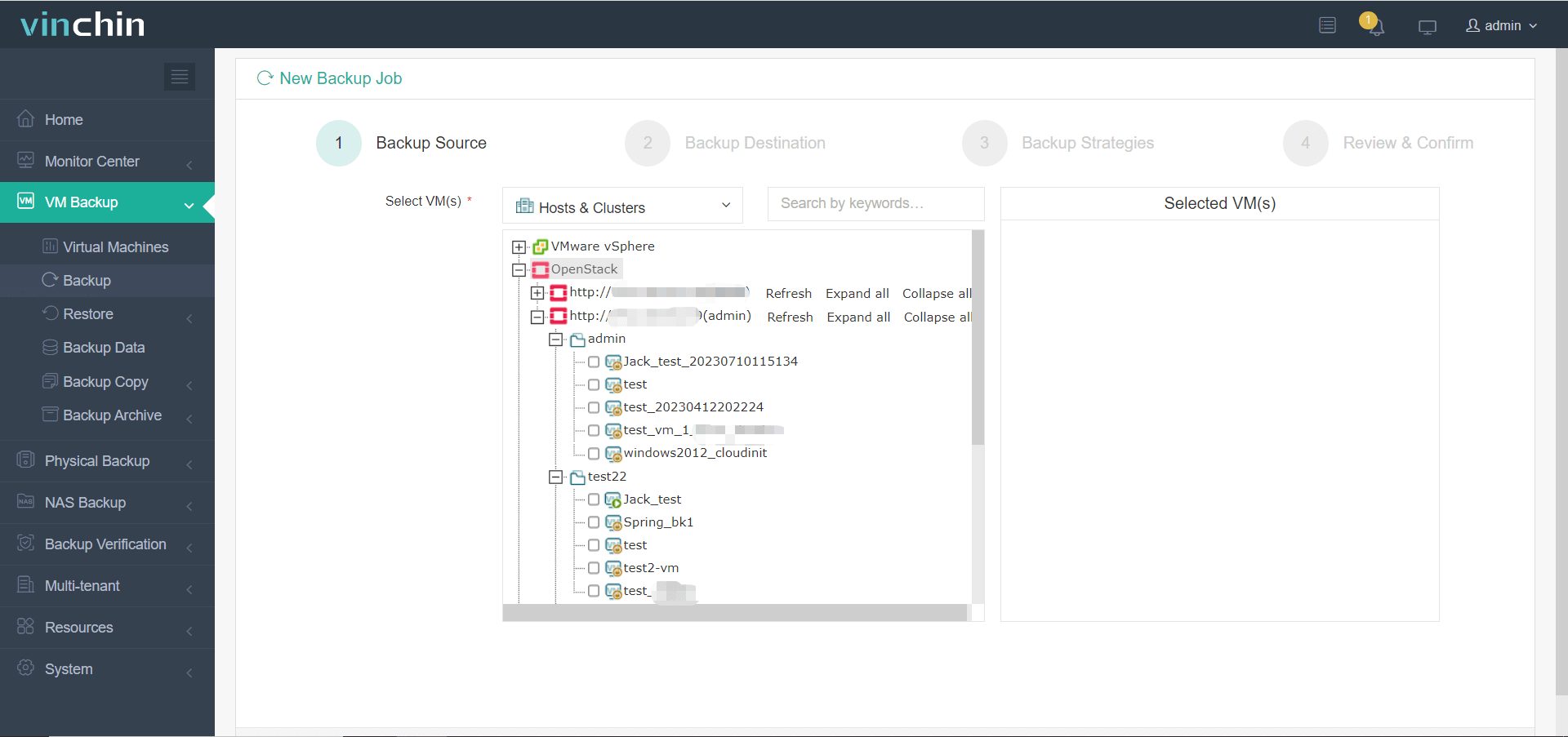
Step 2. Choose the desired backup storage location;
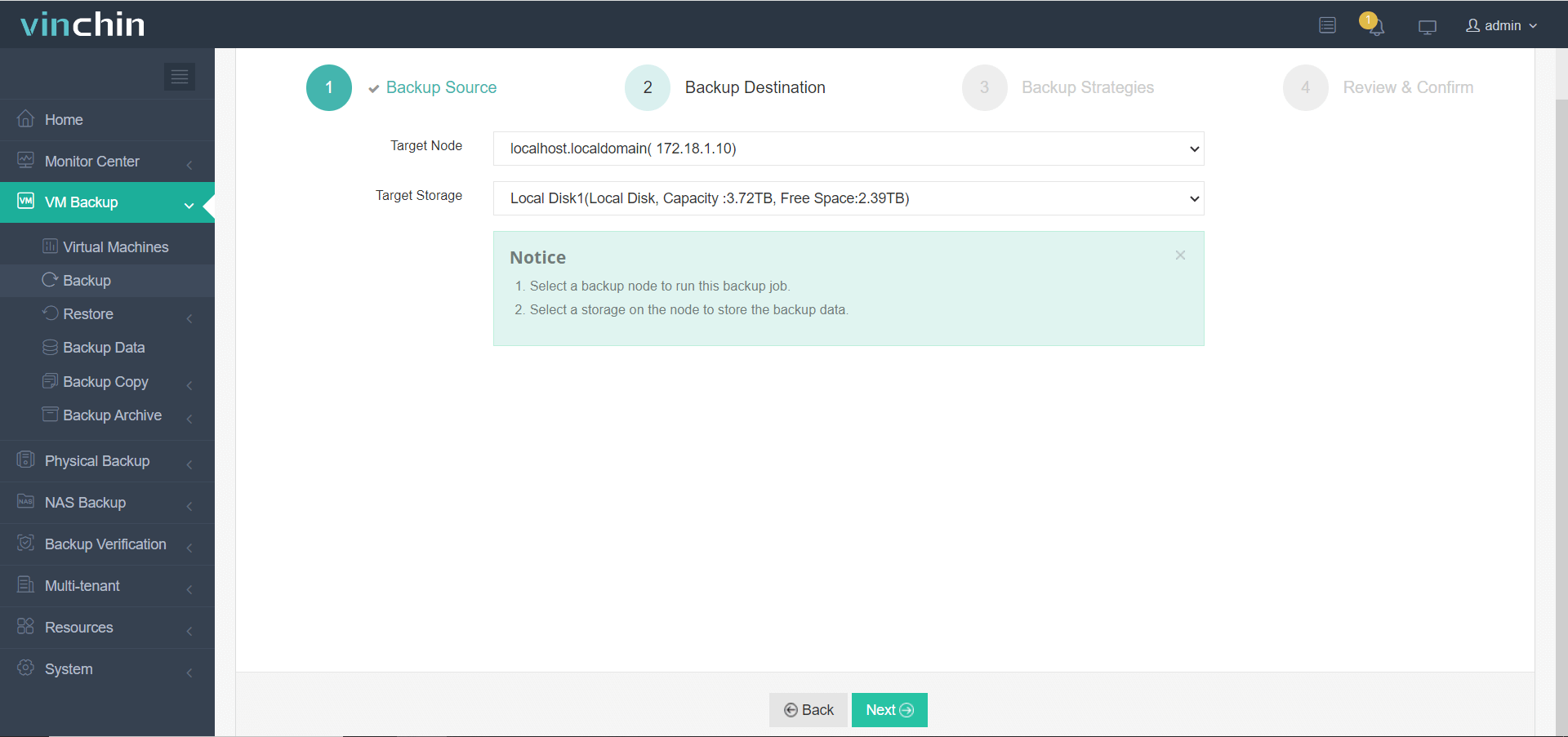
Step 3. Configure backup strategies;
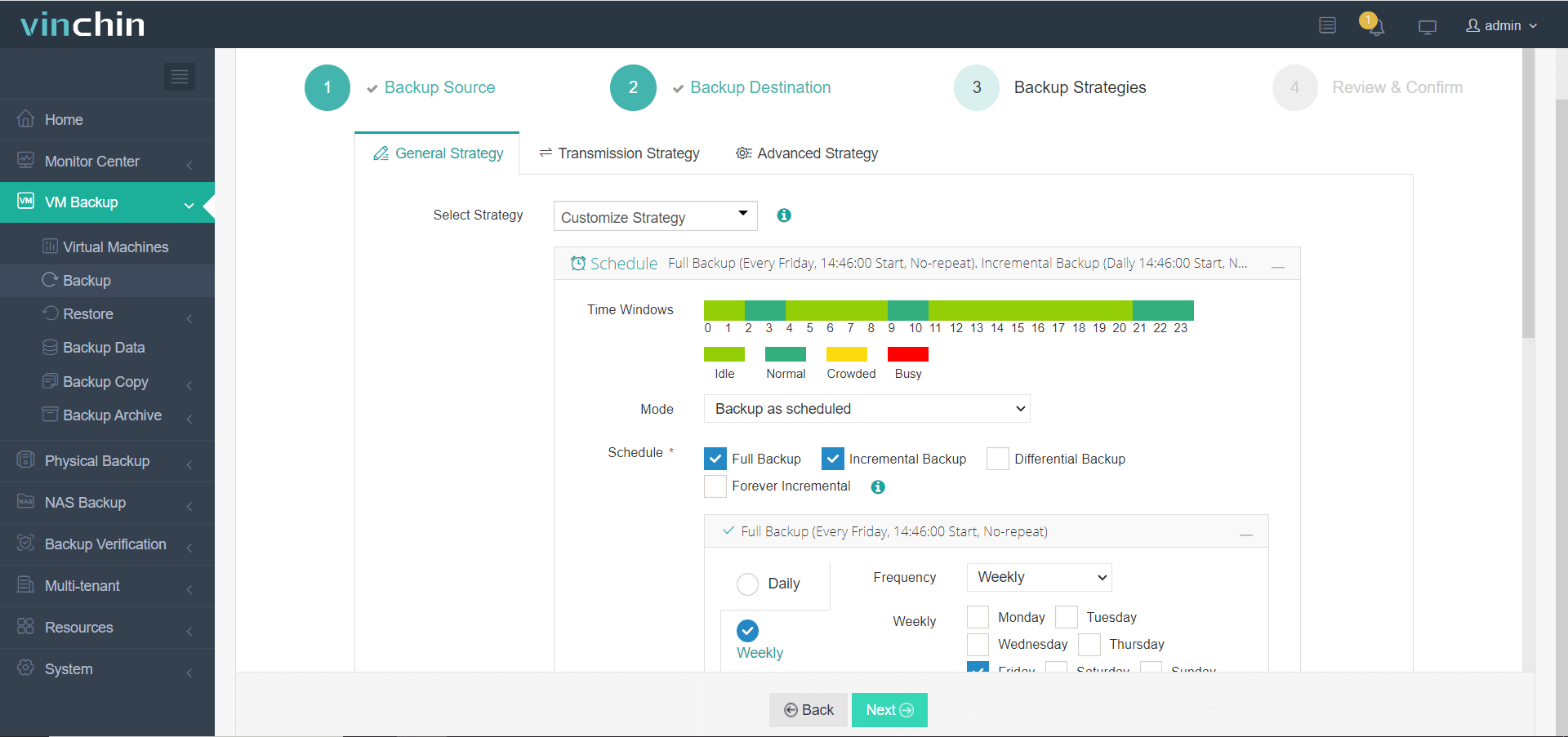
Step 4. Submit the job for execution.
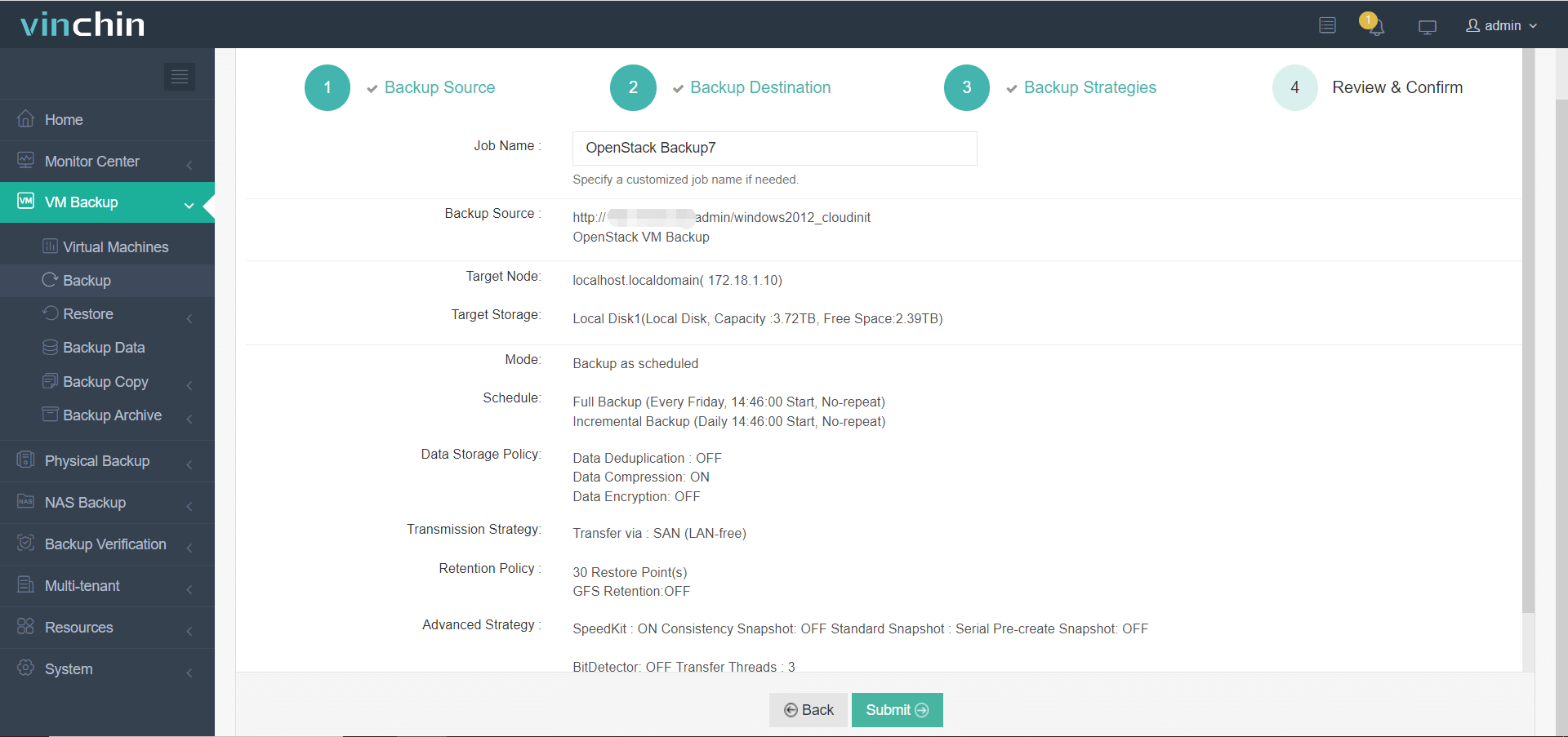
Trusted worldwide by thousands of enterprises—with top ratings and strong customer satisfaction—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a full-featured free trial valid for sixty days; click below to get started today!
Restart OpenStack FAQs
Q1. Can I safely reboot just one instance without affecting others?
A1. Yes! Use openstack server reboot <instance_id> from CLI—it targets only that specific VM without impacting neighbors.
Q2. What should I do if an essential control-plane process refuses to start?
A2. Check logs under /var/log/<service> directory plus output from systemctl status <service>; fix config errors/missing dependencies before retrying another manual start attempt!
Q3. How do I minimize downtime while performing rolling cluster-wide restarts?
A3. Use Ansible's serial execution (serial: keyword); drain live migrations off target node first (openstack compute service set --disable <host> nova-compute) then proceed once workloads have moved away automatically.
Conclusion
Knowing how—and when—to restart openstack ensures healthy cloud operations with minimal disruption or risk of downtime. For reliable VM backups before any major change, Vinchin delivers proven results trusted worldwide. Back up early; back up often—it pays off every time!
Share on:








