-
What Are Oracle Agents?
-
What Are the Types of Oracle Agents?
-
Why Use Oracle Agents in Databases?
-
How to Install an Oracle Agent?
-
How to Protect Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
Oracle Agents FAQs
-
Conclusion
Oracle agents are transforming how IT teams automate tasks across cloud databases. These intelligent software components use artificial intelligence to handle routine jobs, monitor systems, and optimize business processes. For operations administrators managing complex Oracle environments, understanding these agents is now essential. But what are Oracle agents? How do they work behind the scenes? Let’s explore step by step.
What Are Oracle Agents?
Oracle agents are advanced software programs built to perform specific tasks within Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) or on-premises Oracle setups. Unlike simple scripts or static automation tools, these agents leverage technologies like large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). This means they can understand context from data sources, plan actions intelligently, adapt to changes in real time, and even interact with users through natural language.
At their core, Oracle agents act as digital assistants embedded within cloud applications or infrastructure services. They can automate workflows—such as running health checks or generating reports—answer user queries about system status or policies, and make decisions based on live data feeds. By integrating deeply into OCI’s ecosystem via APIs and secure connections, they help organizations streamline operations while maintaining control over sensitive resources.
What Are the Types of Oracle Agents?
Oracle offers several types of agents designed for different roles:
First are conversational agents. These interact directly with users using natural language processing. You might ask them about database performance or request a summary report—they respond instantly by pulling information from connected systems.
Next come functional agents. These focus on automating specific business functions such as HR onboarding workflows or finance reconciliations. For example, a functional agent might process payroll data every week without manual intervention.
Supervisory agents oversee other agents’ activities. They coordinate multiple tasks across departments or ensure that all automated jobs finish correctly before triggering downstream processes.
Finally, utility agents handle specialized technical jobs like executing SQL queries against databases, retrieving documents from storage buckets, or scheduling recurring maintenance windows.
Each type fits seamlessly into Oracle’s cloud environment by using secure authentication methods and following organizational policies set by administrators.
Why Use Oracle Agents in Databases?
Why have so many organizations adopted Oracle agents for database management? The answer lies in efficiency gains—and much more.
First off: automation reduces human error. When you let an agent handle routine backups or patch deployments using consistent procedures every time, mistakes drop dramatically compared to manual work.
Agents also boost productivity by running 24/7 without breaks—no need to wait until morning if something goes wrong at midnight! They provide real-time monitoring too: if a tablespace fills up quickly or CPU usage spikes unexpectedly during off-hours, an agent can alert you before problems escalate into outages.
Security is another key benefit. Because each agent operates under strict identity access management (IAM) controls within OCI—and logs every action—it’s easier to enforce compliance rules around sensitive data handling than when relying solely on human operators.
Let’s look at some practical examples:
1. An agent monitors backup job completion rates nightly; if any fail due to network issues it triggers an immediate retry—and sends an alert so you’re never caught off guard.
2. Another agent checks audit logs daily for suspicious login attempts; if it finds anomalies it escalates them straight away rather than waiting for weekly reviews.
3. A third automates quarterly patch rollouts across dozens of databases simultaneously—saving hours of manual effort per cycle while reducing risk of missed updates.
By freeing up skilled staff from repetitive chores like these—orchestrated reliably by software—you enable your team to focus on higher-value projects such as performance tuning or strategic planning instead of firefighting day-to-day issues.
How to Install an Oracle Agent?
Installing an Oracle agent is straightforward but requires careful preparation for security and reliability reasons. Here’s how you do it:
Before starting:
Make sure you have administrator credentials for your Oracle Cloud Console account.
Confirm that your tenancy has enough service limits available—for example compute instances if deploying new virtual machines.
Ensure network connectivity between the target database(s) and the region where you’ll deploy the agent; configure firewall rules as needed so traffic flows securely between endpoints.
Prepare necessary IAM policies: create a Dynamic Group representing your agent instance(s), then assign least privilege permissions via custom IAM Policies so the agent can access only required resources (like Object Storage buckets or Autonomous Databases).
Gather credentials with appropriate privileges for any databases/tools your agent must connect to during operation; store them securely according to best practices recommended by your security team.
Now follow these steps:
1. Sign in to Oracle Cloud Console using admin credentials
2. In the navigation bar select your desired region
3. Open the navigation menu, choose Analytics & AI
4. Under AI Services, select Generative AI Agents
5. Click Create Agent to launch setup wizard
6. Enter a unique name plus description so others know its purpose
7. Choose which tools this agent should use—for example select RAG Tool if document retrieval is needed; pick SQL Tool if querying databases directly
8. Configure permissions/access controls carefully: assign previously created dynamic group/IAM policy combo here
9. Review all settings one last time then click Create
After deployment finishes:
10. Go back into the main dashboard under Agents
11. Monitor status/logs regularly—look out especially for connection errors during initial runs
12 If configuration changes are needed later just select desired agent then click Edit
13 Always test new/updated configurations first in non-production environments before rolling out widely!
How to Protect Databases with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
Once you've deployed Oracle agents and streamlined operational workflows, securing your database environment becomes paramount—especially given today's complex threat landscape and compliance demands. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional enterprise-level solution supporting most mainstream databases including Oracle (as well as MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB). For robust protection of critical data in Oracle environments specifically, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers features such as incremental backup support (for efficient change capture), batch database backup capabilities (for large-scale operations), multi-level data compression options (to save space), flexible retention/GFS policies (to meet regulatory needs), along with scheduled backups—all designed for reliability and operational ease while minimizing storage costs and maximizing recovery agility.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your Oracle database straightforward:
Step 1: Select the Oracle database to back up
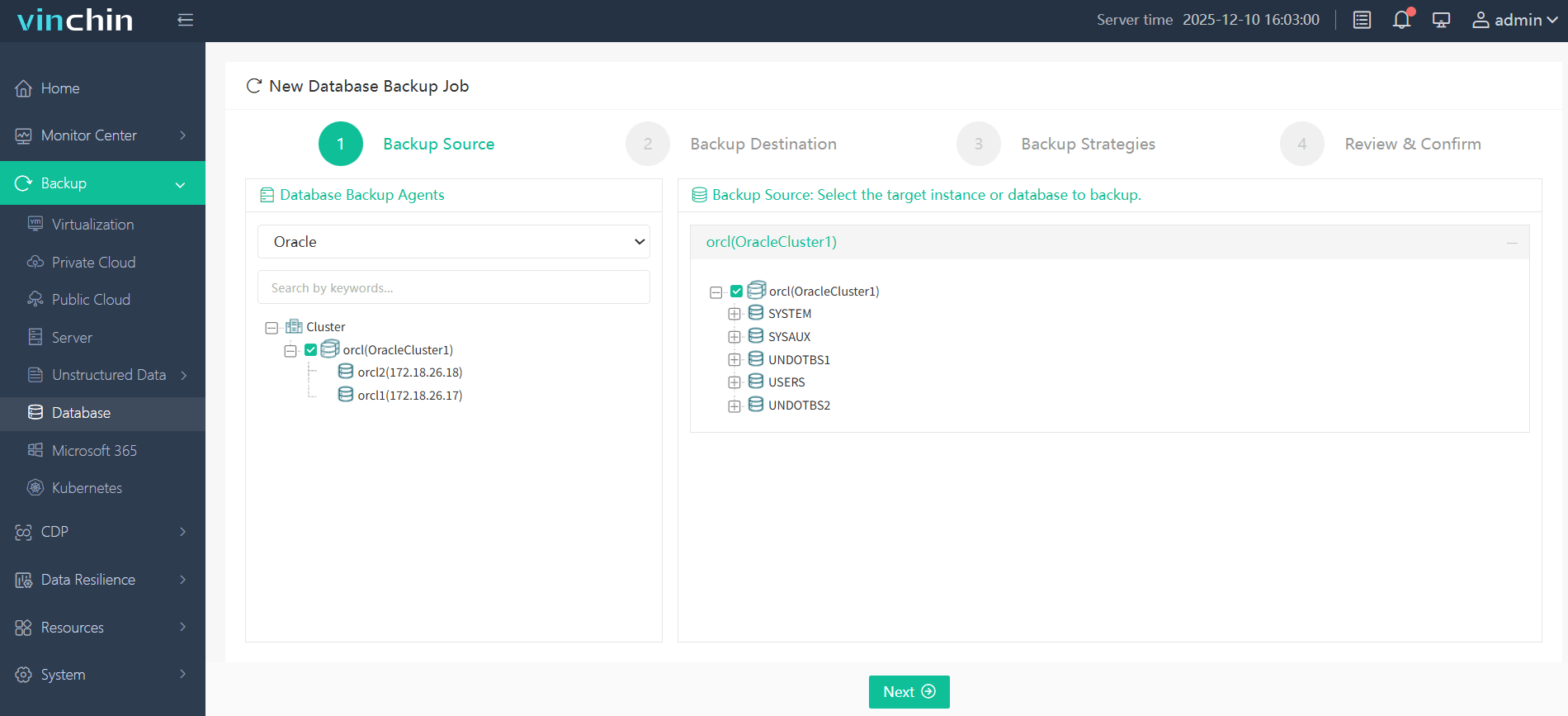
Step 2: Choose the backup storage
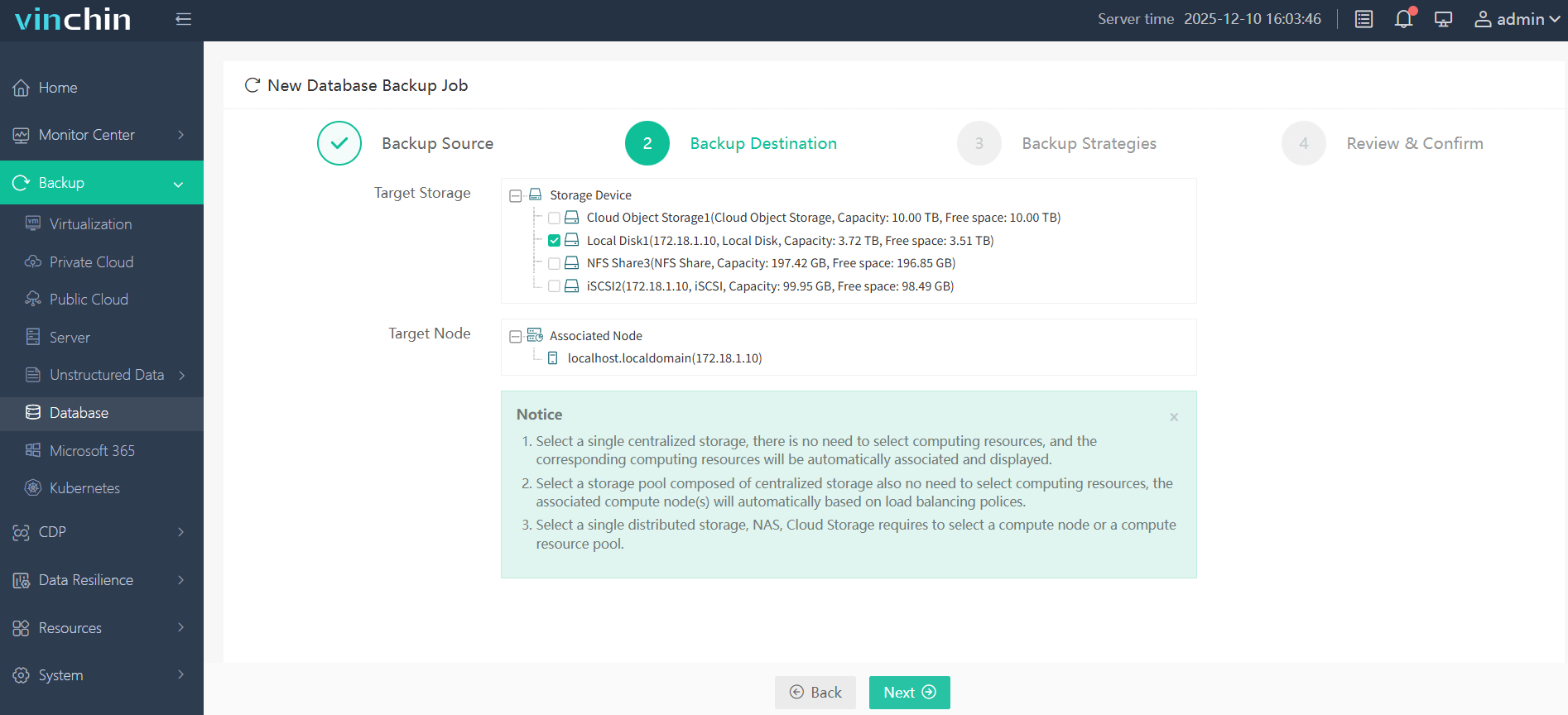
Step 3: Define the backup strategy
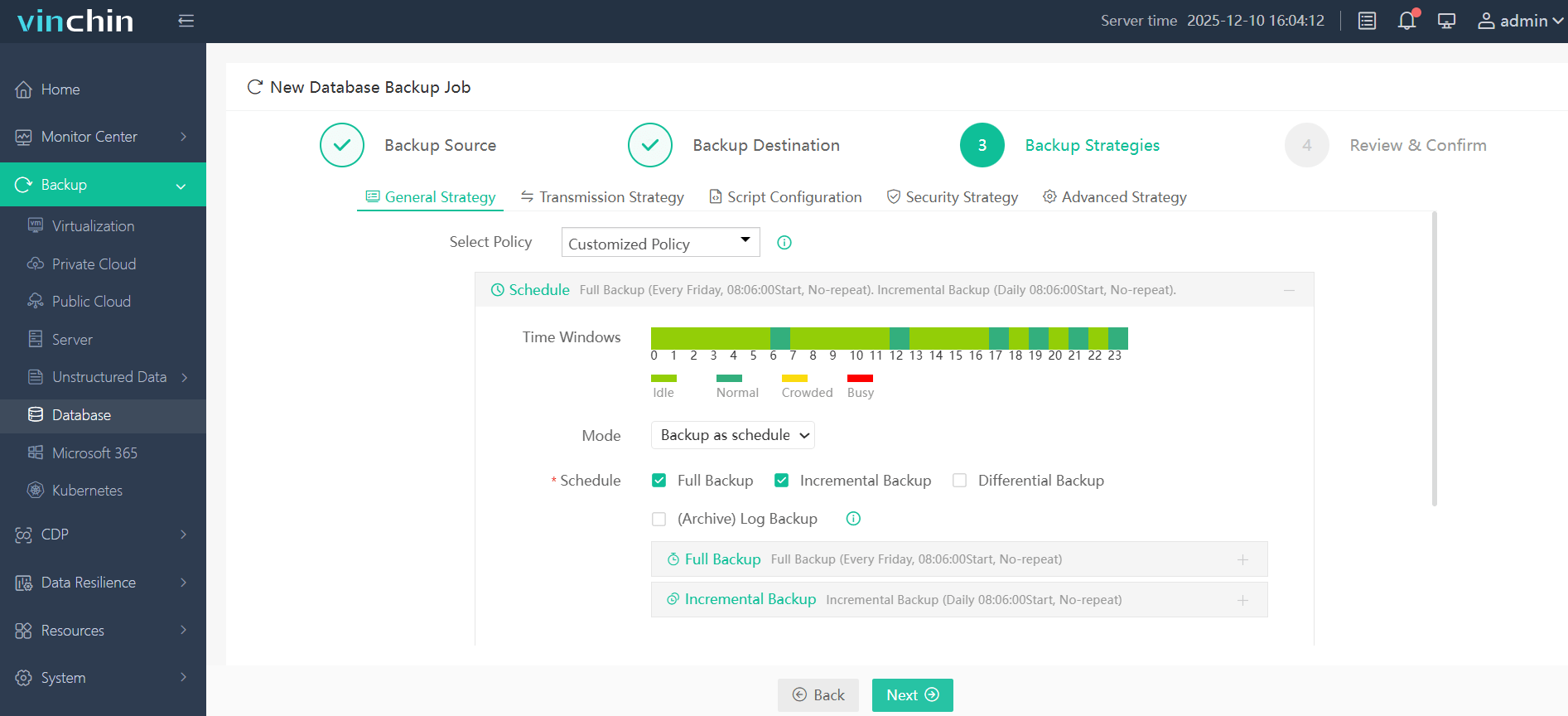
Step 4: Submit the job
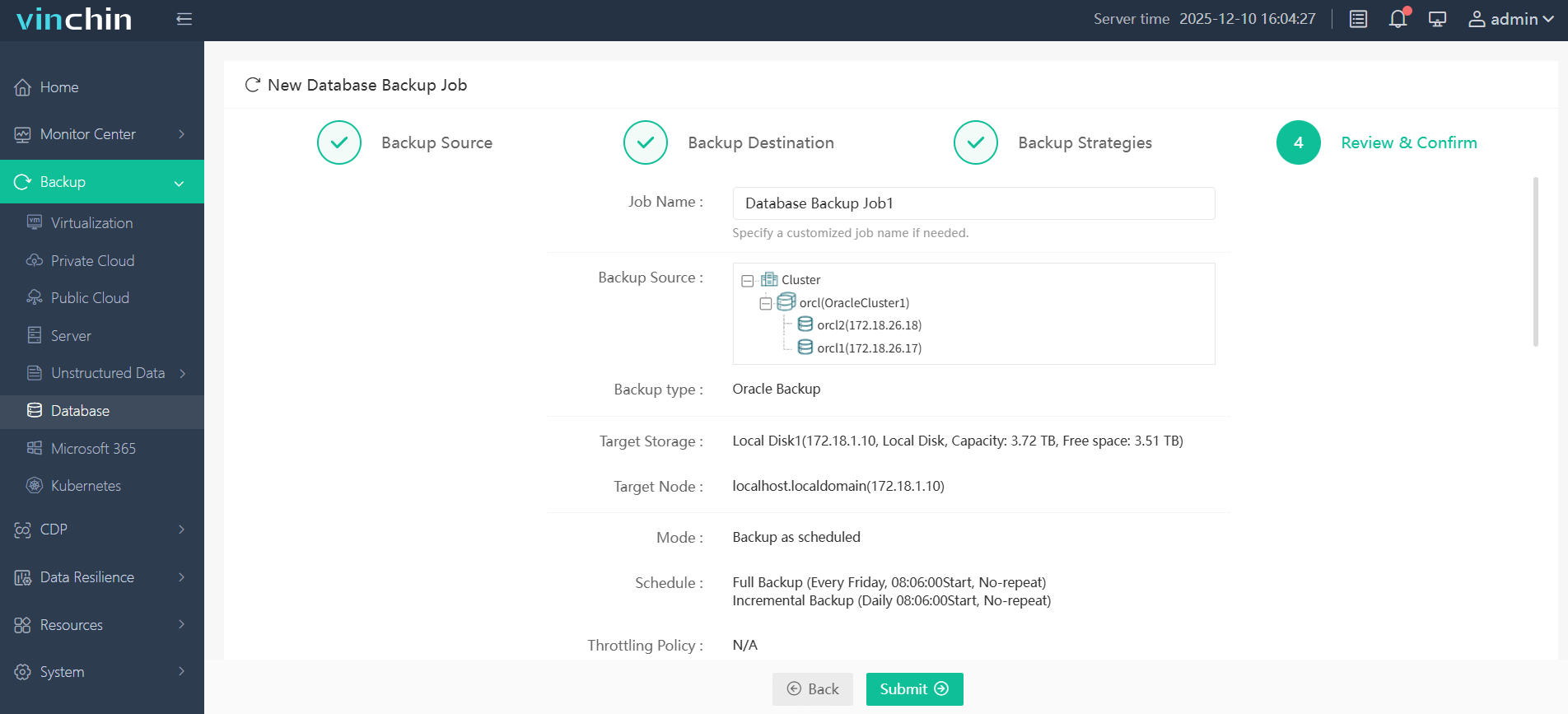
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is trusted worldwide for enterprise-grade data protection—with thousands of customers giving top ratings globally—and offers a full-featured free trial for 60 days; click below to get started today!
Oracle Agents FAQs
Q1: Can I integrate an Oracle agent with my company’s internal ticketing system?
Yes—you can configure most conversational/functional agents with webhook URLs that send alerts/results directly into ticket queues automatically after task completion events fire off inside OCI workflows!
Q2: What network setup do I need if my target database sits behind a corporate firewall?
You must establish secure connectivity such as VPN Connect/FastConnect between OCI subnet hosting your agent instance(s) AND private IP space housing backend DB servers—with proper routing/firewall rules allowing bidirectional traffic ONLY over approved ports/protocols required per application documentation guidelines published officially online today...
Q3: How do I audit what actions my deployed oracleagents performed last month?
Review activity records stored centrally under associated resource group(s) within native OCI Logging interface—or export raw event streams externally toward SIEM platform already standardized internally organization-wide currently.
Conclusion
Oracle agents bring smart automation right into daily IT operations—making complex tasks simpler while boosting reliability across cloud environments. For robust protection, Vinchin delivers powerful yet easy-to-use backups trusted worldwide. Try it free today!
Share on:







