-
What Is RMAN Backup?
-
What Is ASM Diskgroup?
-
Why Use ASM Diskgroup for RMAN Backup?
-
Method 1: RMAN Backup to ASM Diskgroup Using Command Line
-
Method 2: RMAN Backup to ASM Diskgroup Using Oracle Enterprise Manager
-
Professional Solution for Oracle Database Backup
-
RMAN Backup to ASM Diskgroup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Backing up Oracle databases is a core task for every operations administrator. When your storage uses Oracle ASM diskgroups instead of traditional file systems or raw devices, your backup process changes in important ways. This article explains what RMAN backup is, what ASM diskgroups are, why combining them is best practice—and how to do it right. We’ll walk through two proven methods: using the command line and Oracle Enterprise Manager. Along the way, you’ll learn practical tips that help make your backups safer and more efficient.
What Is RMAN Backup?
RMAN stands for Recovery Manager—it’s Oracle’s built-in tool for database backup and recovery tasks. With RMAN you can create full or incremental backups of your database files as well as archived redo logs. Unlike manual file copies or OS-level tools, RMAN tracks detailed metadata about each backup set it creates—making restores faster and less error-prone.
RMAN supports storing backups on local disks, tape libraries (with extra setup), network shares—and most importantly for this guide—ASM diskgroups. It automates many complex tasks such as validating backup integrity or restoring only changed blocks during recovery.
What Is ASM Diskgroup?
ASM stands for Automatic Storage Management. It’s Oracle’s integrated storage virtualization layer designed specifically for databases.
An ASM diskgroup is a logical pool of physical disks managed by ASM software inside Oracle Database itself—not by your operating system or hardware RAID controller. Data stored in an ASM diskgroup gets automatically striped across all disks in that group; this balances input/output load (I/O) while providing redundancy if configured with mirroring options.
Why does this matter? You don’t have to manage file locations manually anymore—ASM handles placement behind the scenes based on available space and performance needs.
Beginners benefit from simplified storage management.
Intermediate admins appreciate improved performance without tuning OS-level filesystems.
Advanced users rely on built-in redundancy features that protect against single-disk failures—even across clustered RAC environments where shared storage is essential.
Why Use ASM Diskgroup for RMAN Backup?
Storing RMAN backups inside an ASM diskgroup brings several advantages over using regular filesystem paths:
Performance: Automatic striping spreads read/write activity across multiple disks.
Resilience: Mirroring protects against single-disk failures; no need to worry about losing one drive.
Centralized Management: All datafiles—including tablespaces, logs, control files—and now even your backups live under one roof.
Disaster Recovery: During restore operations after a failure event (hardware crash or corruption), having everything managed by ASM simplifies recovery steps since file locations are abstracted away.
Operational Simplicity: No more juggling mount points or OS permissions; just specify the diskgroup name (like +DATA) when backing up or restoring data.
Compared to backing up onto local filesystems—which requires careful path planning—using an ASM diskgroup eliminates OS-level complexity while integrating seamlessly into high availability frameworks like Oracle RAC clusters.
Method 1: RMAN Backup to ASM Diskgroup Using Command Line
The command line gives you direct control over every aspect of an Oracle database backup into an ASM diskgroup using RMAN utility commands available on every installation.
Before starting any backup job—especially large ones—it’s wise to check free space in your target diskgroup so you don’t run out mid-process:
Pre-backup validation
First connect to SQL*Plus (or use SQLcl) as a user with access to V$ views:
SELECT name AS "DiskGroup", total_mb AS "Total MB", free_mb AS "Free MB" FROM v$asm_diskgroup;
This shows how much room remains in each configured diskgroup so you can plan accordingly.
Next connect to your target database using RMAN:
rman target /
Once connected:
1. To back up the entire database into an ASM diskgroup named +DATA:
BACKUP DATABASE FORMAT '+DATA';
Here “+DATA” refers to your chosen diskgroup name; replace it if needed.
2. Want compression? Add AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET before DATABASE:
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE FORMAT '+DATA';
3. To include archived redo logs along with datafiles:
BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG FORMAT '+DATA';
4. Need only specific datafiles? Specify them by number (from DBA_DATA_FILES view):
BACKUP DATAFILE 1,2,3 FORMAT '+DATA';
5. Tagging helps organize multiple backups—for example weekly fulls vs daily incrementals:
BACKUP DATABASE TAG 'FULL_DB_WEEKLY' FORMAT '+DATA';
For larger environments—or when balancing load—you may want to configure channels explicitly so different streams write simultaneously into one or more diskgroups:
CONFIGURE CHANNEL DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT '+FRA'; BACKUP DATABASE;
Replace ‘+FRA’ with another valid diskgroup if desired; this improves throughput during big jobs but requires careful planning around available bandwidth and free space per group.
Validating Backups
You should always validate both source datafiles and destination writeability before relying on any new backup routine:
BACKUP VALIDATE DATABASE ARCHIVELOG ALL;
This command checks whether all source files are readable—but note it doesn’t actually write anything into the target location nor confirm there’s enough space left! Always combine validation runs with manual checks of free_mb values above before launching production jobs.
After completion list all existing backups tracked by RMAN metadata catalog:
LIST BACKUP;
This displays details including creation time, type (full/incremental), associated tags—and crucially—the exact location inside each specified diskgroup (+DATA/+FRA etc).
Method 2: RMAN Backup to ASM Diskgroup Using Oracle Enterprise Manager
Oracle Enterprise Manager provides a graphical interface that makes managing complex tasks like backing up databases much easier—even if you’re not comfortable at the command line yet.
Depending on which version you use (Enterprise Manager Cloud Control vs EM Express), menu names may vary slightly—but core workflow remains similar:
Start by logging into Oracle Enterprise Manager as a user with DBA privileges then navigate to your target database home page:
1. Click Availability from main navigation bar
2. Select Backup & Recovery, then choose Schedule Backup
3. In wizard dialog select type of backup required (Full Database, individual tablespace(s), specific datafile(s))
4. When prompted where to store results pick Disk, then enter desired destination such as +DATA under Destination field
5. Configure optional settings like compression level (“Compress”), custom tags (“Tag”), parallelism (“Degree of Parallelism”) depending on workload size
6. Review summary screen carefully then click Submit job request
OEM generates underlying RMAN commands automatically based on GUI selections—you don’t need deep scripting knowledge upfront! However experienced users can review generated scripts after submission via Job Details page under History tab; this bridges visual workflows back toward CLI mastery over time—a great learning tool!
During execution monitor progress directly within OEM dashboard; alerts flag issues instantly while logs provide granular feedback about success/failure status per step completed.
Professional Solution for Oracle Database Backup
Beyond native tools, organizations seeking streamlined management often turn to specialized solutions designed for enterprise environments. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional-grade platform supporting today’s mainstream databases—including Oracle first and foremost—as well as MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB. For those working specifically with Oracle databases, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers robust capabilities such as incremental backup support, batch database backup operations, flexible data retention policy management including GFS retention strategy, restore-to-new-server functionality, and advanced source-side compression—all engineered for efficiency and reliability at scale. These features collectively ensure optimized storage utilization, automated protection cycles aligned with business requirements, rapid disaster recovery readiness, and minimal administrative overhead even in demanding multi-database environments.
The web console provided by Vinchin Backup & Recovery is exceptionally intuitive—enabling administrators at any skill level to complete comprehensive protection workflows quickly:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
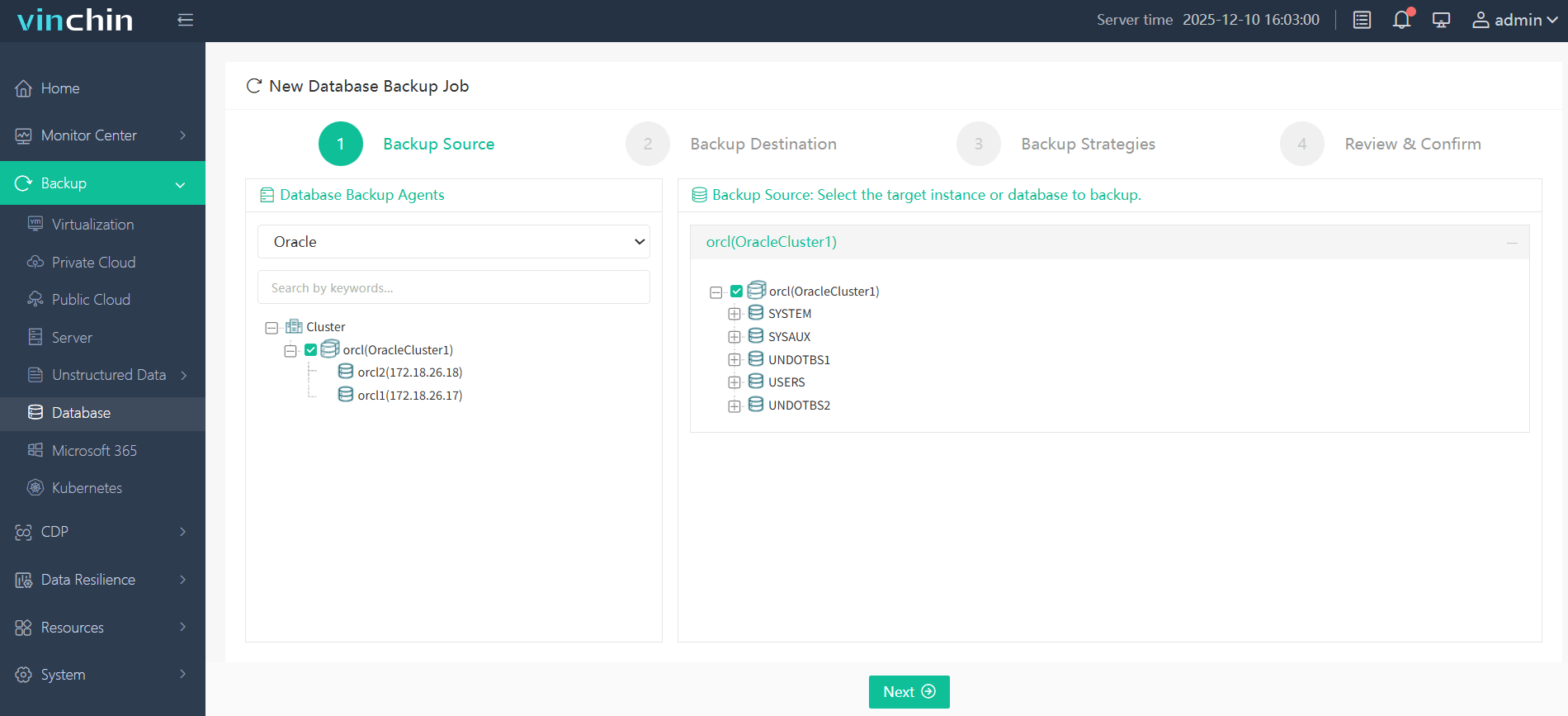
Step 2. Choose the backup storage
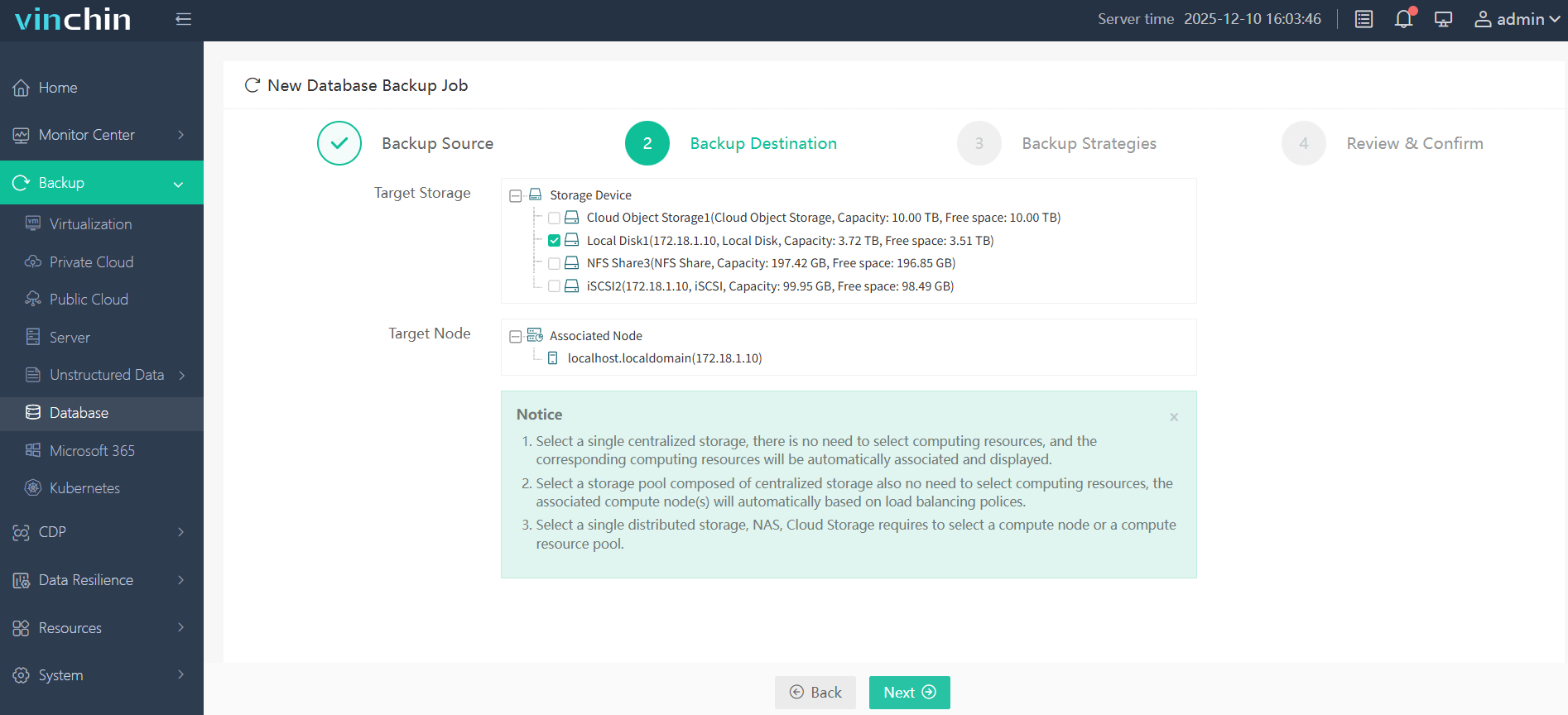
Step 3. Define the backup strategy
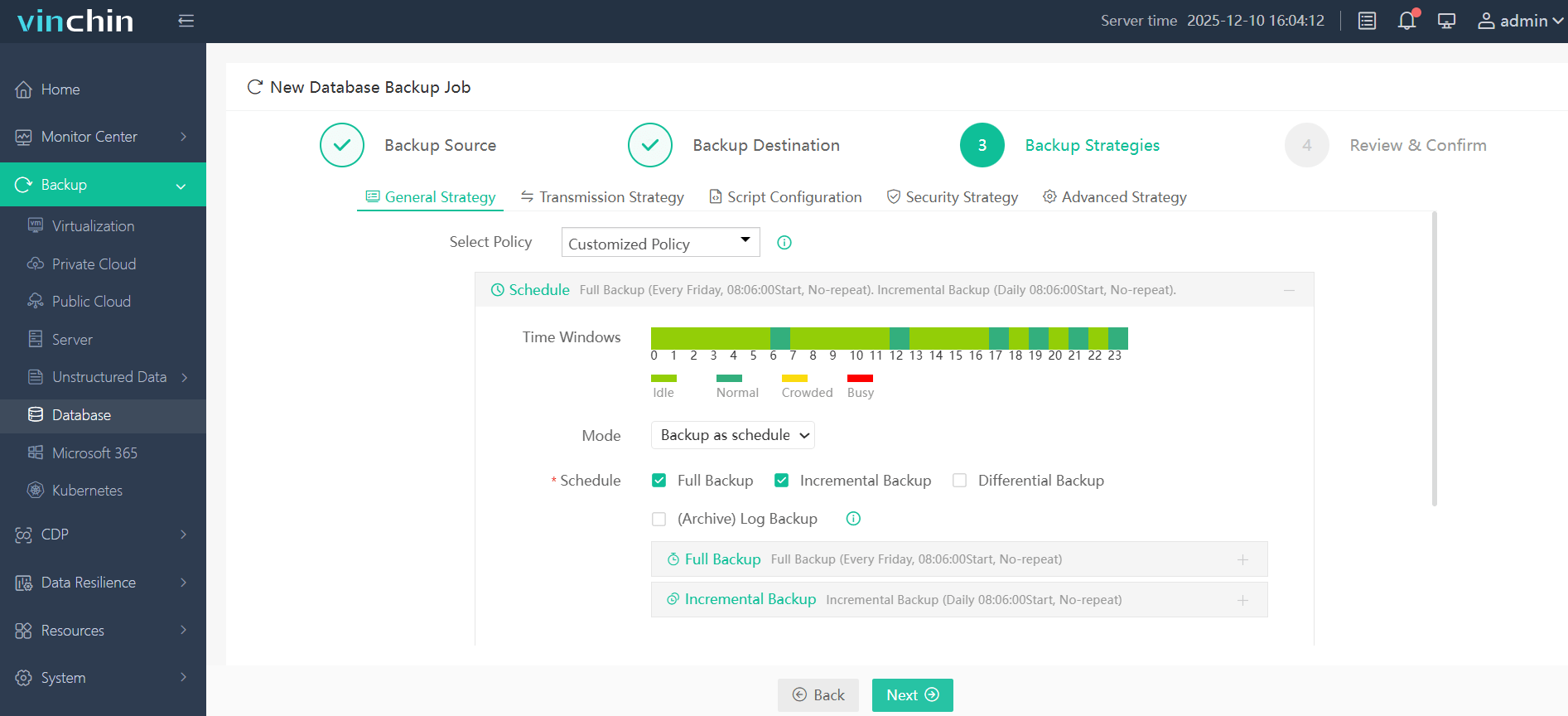
Step 4. Submit the job
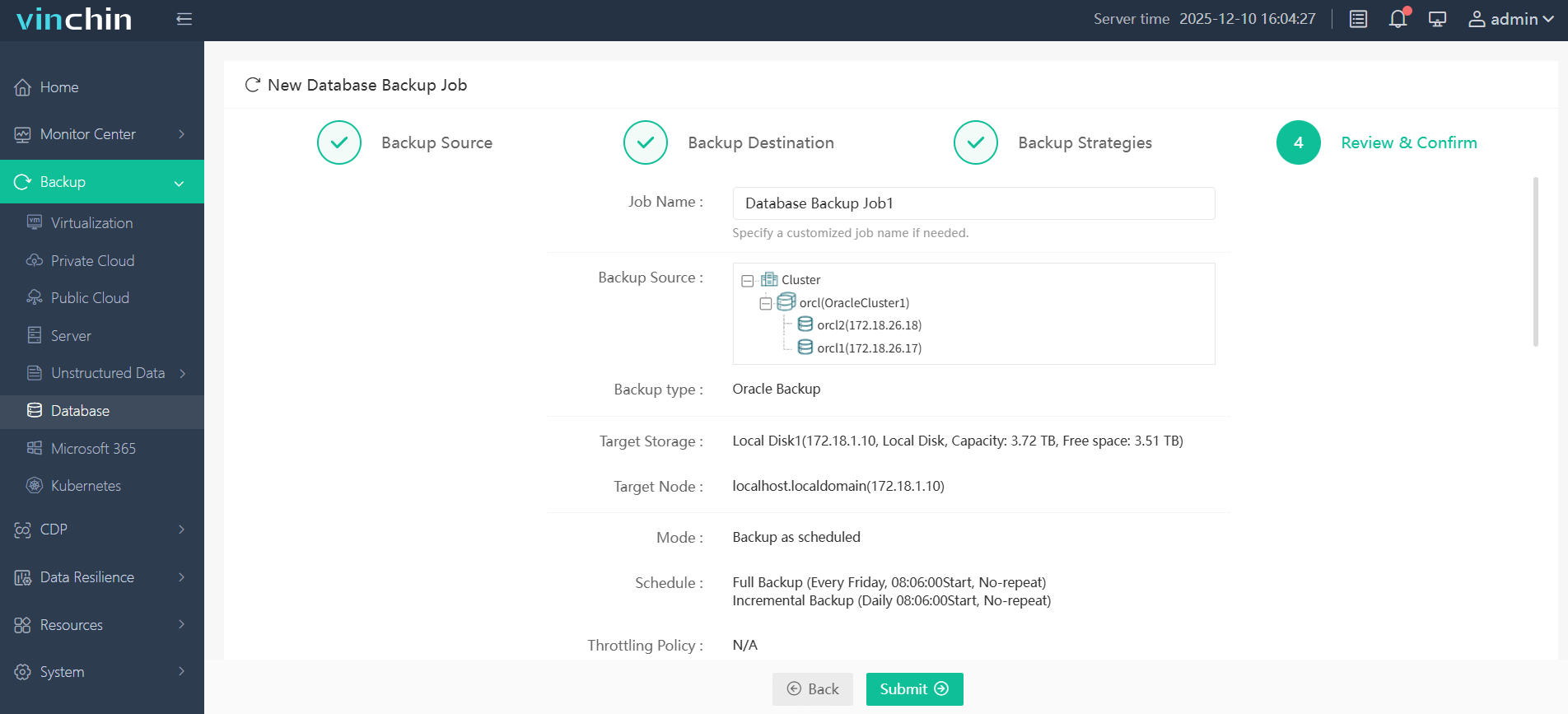
Trusted globally by enterprises large and small—with top ratings from industry analysts—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured 60-day free trial so you can experience its power firsthand before making any commitment; click below to get started today.
RMAN Backup to ASM Diskgroup FAQs
Q1: Can I encrypt my RMAN backups stored in an ASM diskgroup?
Yes; enable encryption at session level using SET ENCRYPTION ON before running your BACKUP command so all pieces written into +DISKGROUP remain protected end-to-end.
Q2: How do I monitor ongoing space usage trends inside my primary backup-targeted disk group?
Query V$ASM_DISKGROUP periodically—or schedule automated reports—to track FREE_MB versus TOTAL_MB metrics over time ensuring proactive expansion before hitting limits.
Q3: If my scheduled nightly job fails midway due network hiccup how do I resume safely?
Use LIST FAILURE followed by ADVISE FAILURE then rerun incomplete portions via RESTORE/RECOVER commands targeting affected objects only—not whole DB unless necessary.
Conclusion
Backing up Oracle databases directly into an ASM diskgroup using RMAN delivers speed plus resilience whether managed from CLI or visually through OEM dashboards alike—all without extra OS-level complexity getting in way! Vinchin further streamlines these workflows thanks its intuitive interface plus robust automation capabilities—try their free trial today!
Share on:







