-
What Is Oracle RMAN?
-
Why User Privileges Matter in RMAN?
-
What Are Oracle RMAN User Privileges?
-
Method 1. Granting SYSDBA Role for RMAN Access
-
Method 2. Granting Specific Privileges Required by RMAN
-
How to Protect Oracle Database with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Oracle RMAN User Privileges FAQs
-
Conclusion
Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is essential for database backup and recovery. But before you run your first backup job, you need to set up user privileges correctly. Why does this matter? Because only users with proper privileges can protect your data—and mistakes here can lead to failed backups or security risks. In this guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about Oracle RMAN user privileges—from basic concepts to advanced enterprise setups.
What Is Oracle RMAN?
Oracle RMAN is Oracle's built-in tool for backing up, restoring, and recovering databases. It automates complex tasks like ffull, incremental backups, restores, and even disaster recovery testing. Since it comes bundled with every Oracle Database installation, there's no extra software needed—just configure it right out of the box.
RMAN works closely with the database engine itself. This tight integration means it can perform actions that other tools cannot—such as block-level recovery or validating backups without restoring them first.
Why User Privileges Matter in RMAN?
User privileges are more than just a checkbox—they’re central to both security and daily operations. Only users granted specific administrative rights can run backup or restore jobs using RMAN commands. This restriction helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data or accidental changes during maintenance windows.
If you grant too many privileges (for example by giving everyone SYSDBA), you increase risk: someone could make unintended changes or bypass audit controls. On the other hand, if you grant too few privileges, critical backup jobs might fail at midnight when nobody is watching! Striking a balance between least privilege and operational reliability is key.
Correct privilege assignment also supports automation—think scheduled scripts running overnight—and ensures smooth disaster recovery drills when time is critical.
What Are Oracle RMAN User Privileges?
To use RMAN for backup or restore tasks, a user must have special system-level administrative rights within Oracle Database:
SYSDBA: The classic all-powerful privilege; allows any operation on the database.
SYSBACKUP: Introduced in Oracle 12c; designed specifically for backup/recovery duties only.
Both are system privileges—not roles—and can be granted directly to users as needed. While SYSDBA gives total control over everything (including startup/shutdown), SYSBACKUP limits access strictly to what’s required for protecting data through backups. For most organizations today, granting SYSBACKUP instead of SYSDBA follows best practices around separation of duties—a core principle in IT governance frameworks like ISO 27001.
Without one of these two privileges assigned properly (either directly or via an OS group), any attempt to connect with RMAN will result in an “insufficient privileges” error message.
Method 1. Granting SYSDBA Role for RMAN Access
Granting SYSDBA is the most direct way to enable full access for backup administrators—but it comes with broad power over your entire database environment.
First connect as a privileged account (usually already holding SYSDBA):
-- Connect as a privileged user CONNECT / AS SYSDBA; GRANT SYSDBA TO username;
After this step completes successfully:
To connect from command line using password authentication:
rman target 'username/password@db_service as sysdba'
Or if using operating system authentication (where your OS account belongs to the correct DBA group):
rman target /
Be aware: SYSDBA bypasses all object-level permissions—it overrides Virtual Private Database policies too—which means anyone holding this privilege can read any table or view inside your database regardless of row-level security settings. For that reason alone, reserve it only for trusted senior administrators who truly need unrestricted access—for example during major upgrades or troubleshooting root causes after failures.
Giving out SYSDBA widely may violate internal audit rules or compliance standards such as SOX if used solely for routine backups!
Method 2. Granting Specific Privileges Required by RMAN
For tighter security—and easier audits—Oracle recommends assigning only what’s necessary using SYSBACKUP instead of SYSDBA wherever possible.
This privilege was introduced alongside other “least privilege” admin options like SYSDG (Data Guard), SYSKM (Key Management), and SYSRAC (Clusterware). Each one narrows down what an administrator can do based on their actual job function—a win-win for both security teams and operations staff!
Here’s how you create a dedicated backup operator account:
CREATE USER rman_user IDENTIFIED BY strong_password; GRANT SYSBACKUP TO rman_user;
Now connect from command line:
rman target 'rman_user/strong_password@db_service as sysbackup'
Or if relying on operating system authentication:
1. Make sure your Unix/Linux account belongs to the OSBACKUPDBA group (ORA_DBA on Windows).
2. Then simply run:
rman target '/ as sysbackup'
This approach limits what damage could occur if credentials are leaked—the account cannot start up/shut down databases nor change schema objects outside its narrow scope.
After connecting successfully with either method above, try running SHOW ALL; inside RMAN prompt—if it returns configuration details without errors then your setup works!
How to Protect Oracle Database with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
With proper oracle rman user privileges configured, securing reliable backups becomes paramount for business continuity and compliance needs alike. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-grade solution supporting mainstream databases including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with robust capabilities tailored especially for Oracle environments like yours.
Among its extensive feature set are incremental backup support for efficient storage usage; log backup combined with any-point-in-time recovery ensures minimal data loss; scheduled backups automate protection routines; storage protection defends against ransomware threats; and integrity check verifies recoverability before disaster strikes—all designed to streamline operations while maximizing data safety across complex infrastructures.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your Oracle database straightforward:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
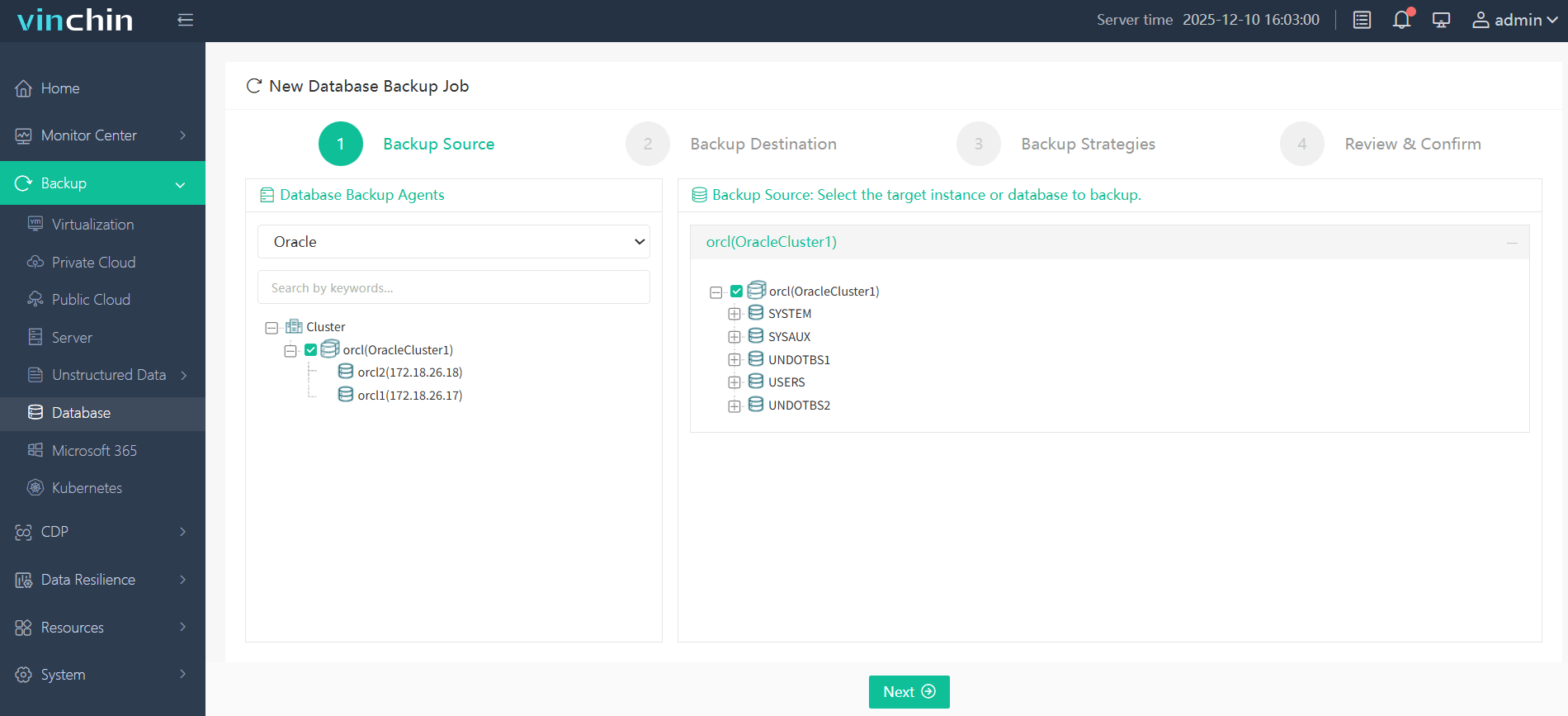
Step 2. Choose backup storage
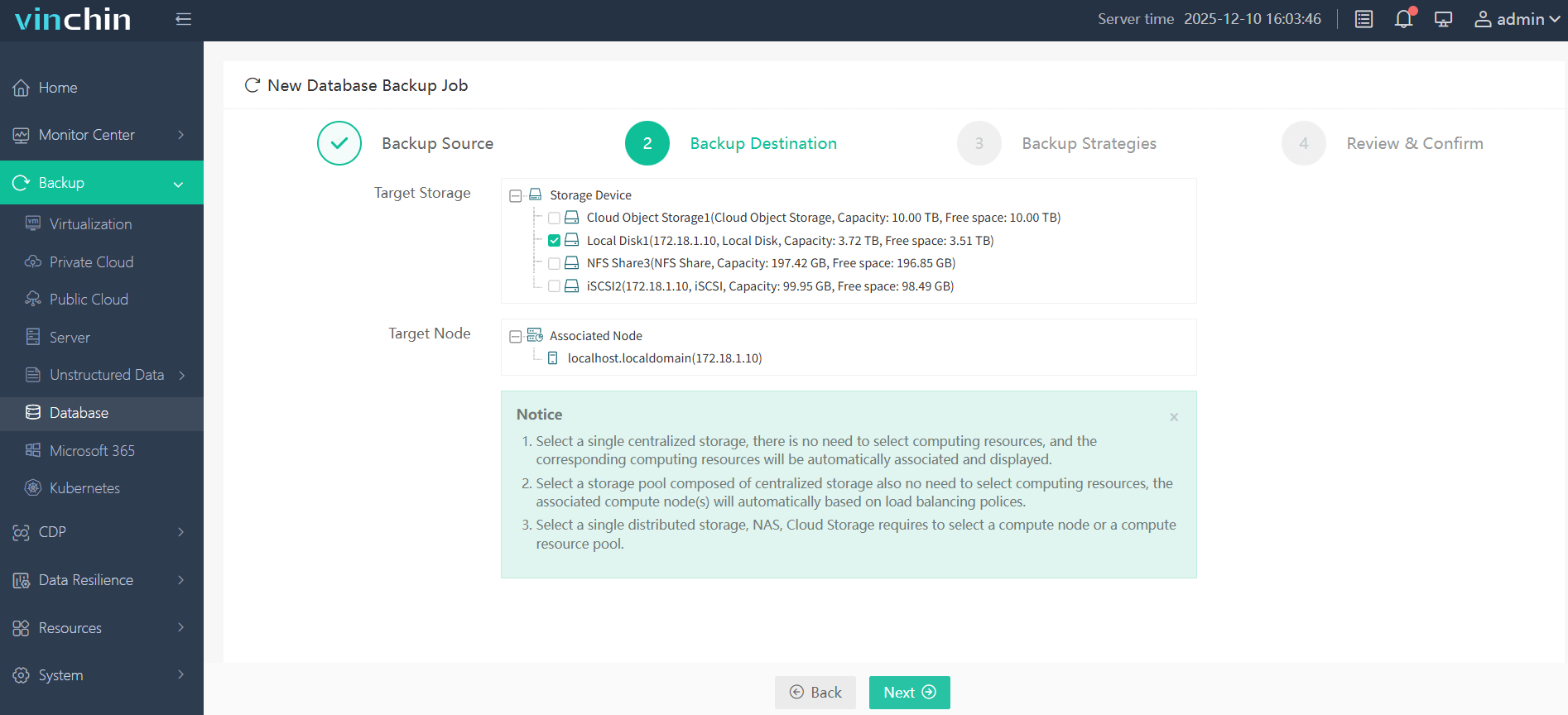
Step 3. Define your backup strategy
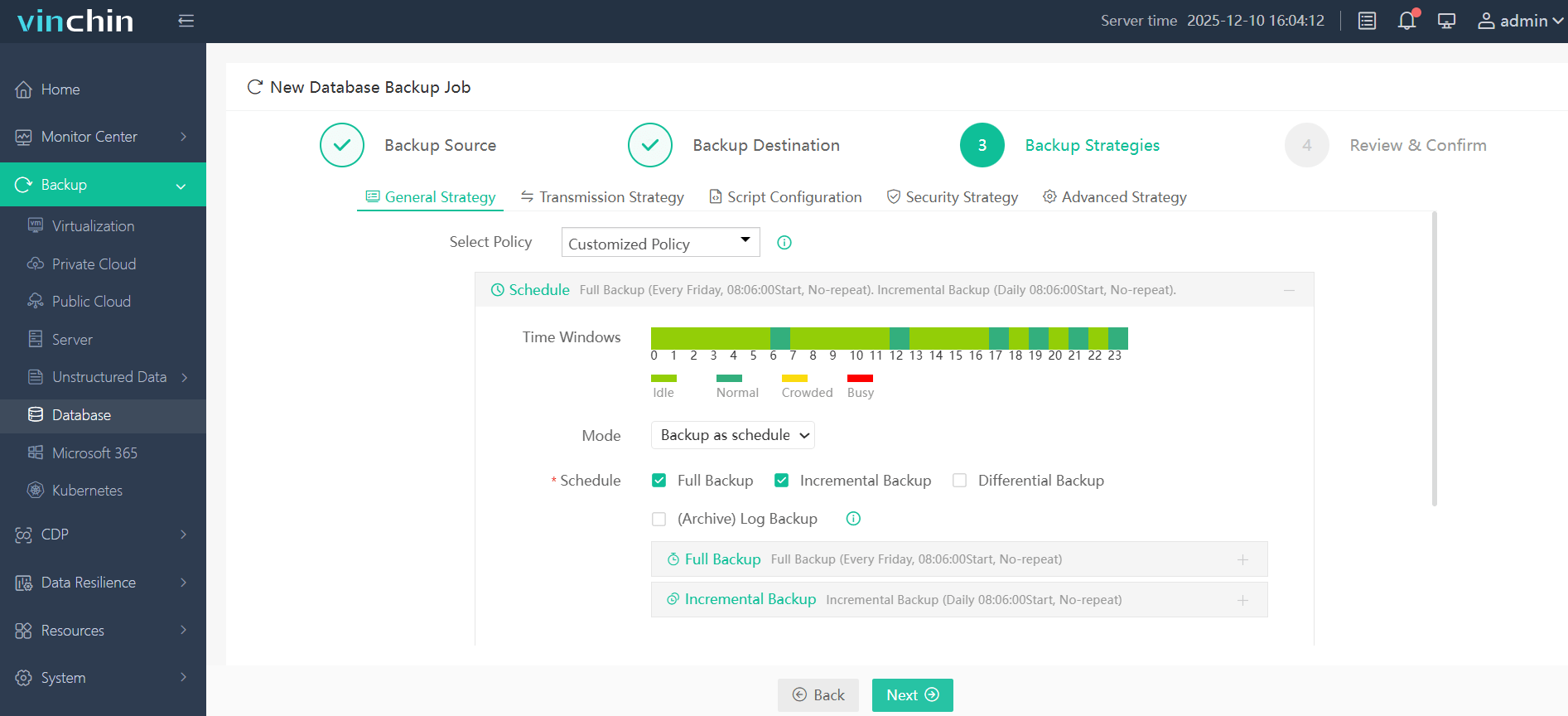
Step 4. Submit the job
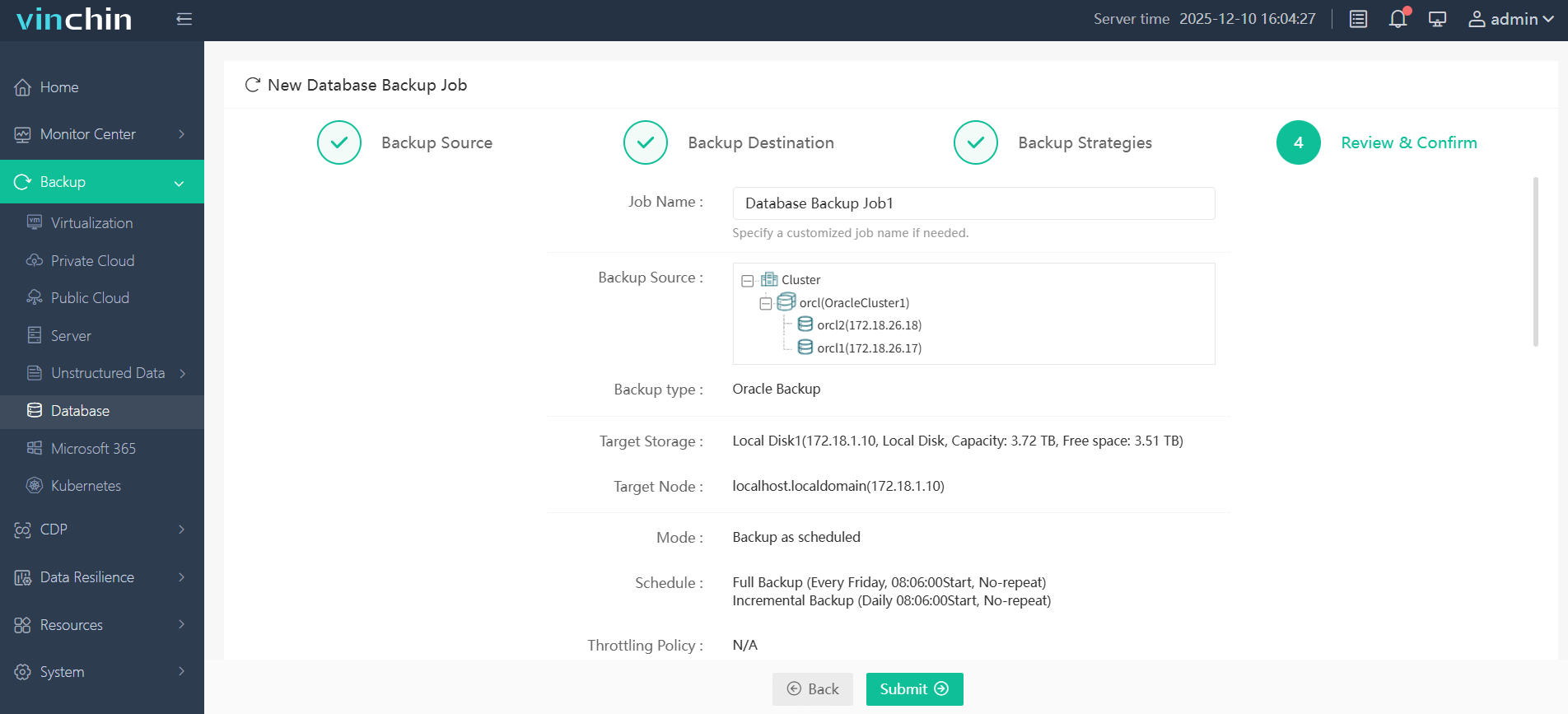
Vinchin Backup & Recovery enjoys global recognition among enterprises large and small—try its top-rated platform free for 60 days with full features enabled by clicking below.
Oracle RMAN User Privileges FAQs
Q1: Can I restrict my automated scripts so they never use full DBA rights?
A1: Yes; assign only SYSBACKUP instead of SYSDBA so scripts cannot perform non-backup administrative actions even if compromised.
Q2: How do I check which accounts have been given powerful system-level rights?
A2: Run SELECT USERNAME,SYSDBA,SYSBACKUP FROM V$PWFILE_USERS AS SYSDBA; this shows current assignments managed via password file authentication mechanisms.
Q3: In multitenant setups how do I allow centralized backups across all pluggable databases?
A3: Create a common user at CDB root then GRANT SYSBACKUP TO user CONTAINER=ALL so they inherit authority everywhere.
Conclusion
Setting correct oracle rman user privileges protects both data integrity and operational efficiency—from single-instance servers through complex multitenant clouds alike! Use least privilege wherever possible; let Vinchin handle automation so every team stays focused on business goals—not manual admin chores.
Share on:







