-
What Is Database Backup?
-
Method 1: Manual Database Backup
-
Method 2: How to Back Up Databases Using SQL Server Management Studio
-
Method 3: How to Back Up Databases Using Oracle RMAN
-
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Solution for Reliable Database Bak
-
Database Bak FAQs
-
Conclusion
Every IT administrator knows the pain of lost data. A single mistake or hardware failure can bring business to a halt. That’s why database backup—often called “database bak” in shorthand—is a core part of any data protection plan. But what’s the best way to create and restore these backups? In this guide, you’ll learn what database bak means, why it matters, and how to perform reliable backup and restore operations in SQL Server and Oracle environments.
What Is Database Backup?
A database backup is a copy of your database’s data, structure, and sometimes even its settings, saved to a secure location. This backup can be used to restore the database if it becomes corrupted, deleted, or otherwise unavailable. In SQL Server, these backups are often stored as .bak files, while Oracle uses its own formats.
Types of Database Backups
Not all backups are created equal. You can choose from several types depending on your needs:
Full Backup: Captures all data in the database at a single point in time.
Differential Backup: Saves only changes made since the last full backup.
Incremental backup: Stores changes since the last backup of any type.
Full backups are simple but can be slow and require more storage. Differential and incremental backups are faster and use less space but depend on previous backups for a complete restore.
Method 1: Manual Database Backup
Manual database backup is the most basic approach. It’s often used for small environments or one-off tasks. While it gives you full control, it’s also easy to forget or make mistakes.
For SQL Server, you can use Transact-SQL (T-SQL) commands. Open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), connect to your server, and run:
BACKUP DATABASE [YourDatabase] TO DISK = 'C:\Backup\YourDatabase.bak' WITH FORMAT, INIT, NAME = 'Full Backup of YourDatabase';
This command creates a full backup of your database and saves it as a .bak file. Make sure the path exists and SQL Server has write permissions. The WITH FORMAT option overwrites any existing media set at that location; INIT initializes the backup file.
For Oracle databases, you can use export utilities like expdp or exp for logical exports (schema-level), but for true physical backups—including all data blocks—Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is preferred (see Method 3).
Manual backups are simple but rely on you remembering to run them regularly. They also don’t scale well for large or busy environments.
Method 2: How to Back Up Databases Using SQL Server Management Studio
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is the go-to tool for most SQL Server administrators. It offers a graphical interface for both backup and restore operations, making the process less error-prone.
To create a backup using SSMS:
1. Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to your SQL Server instance.
2. In Object Explorer, right-click the database you want to back up and select Tasks > Back Up....
3. In the Back Up Database window, choose your backup type (Full, Differential, or Transaction Log).
4. Under Destination, click Add and specify the path and filename for your .bak file.
5. Click OK to start the backup.
To restore a database from a .bak file:
1. In Object Explorer, right-click Databases and select Restore Database....
2. Under Source, select Device and click the browse button (...).
3. Click Add and browse to your .bak file.
4. Confirm the destination database name under Destination.
5. On the Options page, you can select Overwrite the existing database (WITH REPLACE) if needed.
6. Click OK to begin restore.
If there are active connections during restore with overwrite enabled, use ALTER DATABASE [YourDatabase] SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE; before starting.
SSMS also allows you to script these actions for automation or documentation purposes.
Scheduling Backups with SQL Server Agent
Automating backups reduces risk by ensuring regular protection without manual intervention.
With SQL Server Agent:
1. Open SSMS and expand your server in Object Explorer.
2. Expand SQL Server Agent, right-click on Jobs, then choose New Job...
3. Enter a job name under General.
4. Go to the Steps page; click New...
5. Enter step details; paste your T-SQL BACKUP DATABASE command in the command box.
6. Set schedules under the Schedules tab—choose frequency as needed.
7. Save with OK.
This approach ensures that backups run consistently—even if you forget—and provides logs for troubleshooting failed jobs.
Method 3: How to Back Up Databases Using Oracle RMAN
Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) is Oracle’s standard tool for physical database backup and recovery tasks in enterprise environments.
To perform a full backup with RMAN:
1. Open a command prompt on your Oracle server.
2. Start RMAN:
rman target /
3. Run:
BACKUP DATABASE;
This creates a full physical backup in your default location set by Oracle configuration parameters like DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST.
To restore a database using RMAN:
1. Start RMAN as above; connect as target user with necessary privileges.
2. If needed (for full restores), mount but do not open:
STARTUP MOUNT;
3. Restore from backup:
RESTORE DATABASE; RECOVER DATABASE;
4. Once complete:
ALTER DATABASE OPEN;
RMAN can also back up archived logs (BACKUP ARCHIVELOG ALL;) which are essential for point-in-time recovery if running in ARCHIVELOG mode.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Solution for Reliable Database Bak
For organizations seeking robust automation beyond native tools like SSMS or RMAN while supporting both Oracle databases—a primary focus here—and other leading platforms such as MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL/PostgresPro and MongoDB, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers comprehensive enterprise-grade protection across heterogeneous environments. With features including incremental backup,sophisticated batch scheduling,data retention policies management,multiple level compression,and ransomware defense, Vinchin Backup & Recovery streamlines complex workflows while maximizing efficiency. These capabilities ensure fast recovery times,minimized storage costs,and regulatory compliance—all within one unified platform. The intuitive web console makes safeguarding critical databases straightforward.
1. Select source SQL Server database(s),
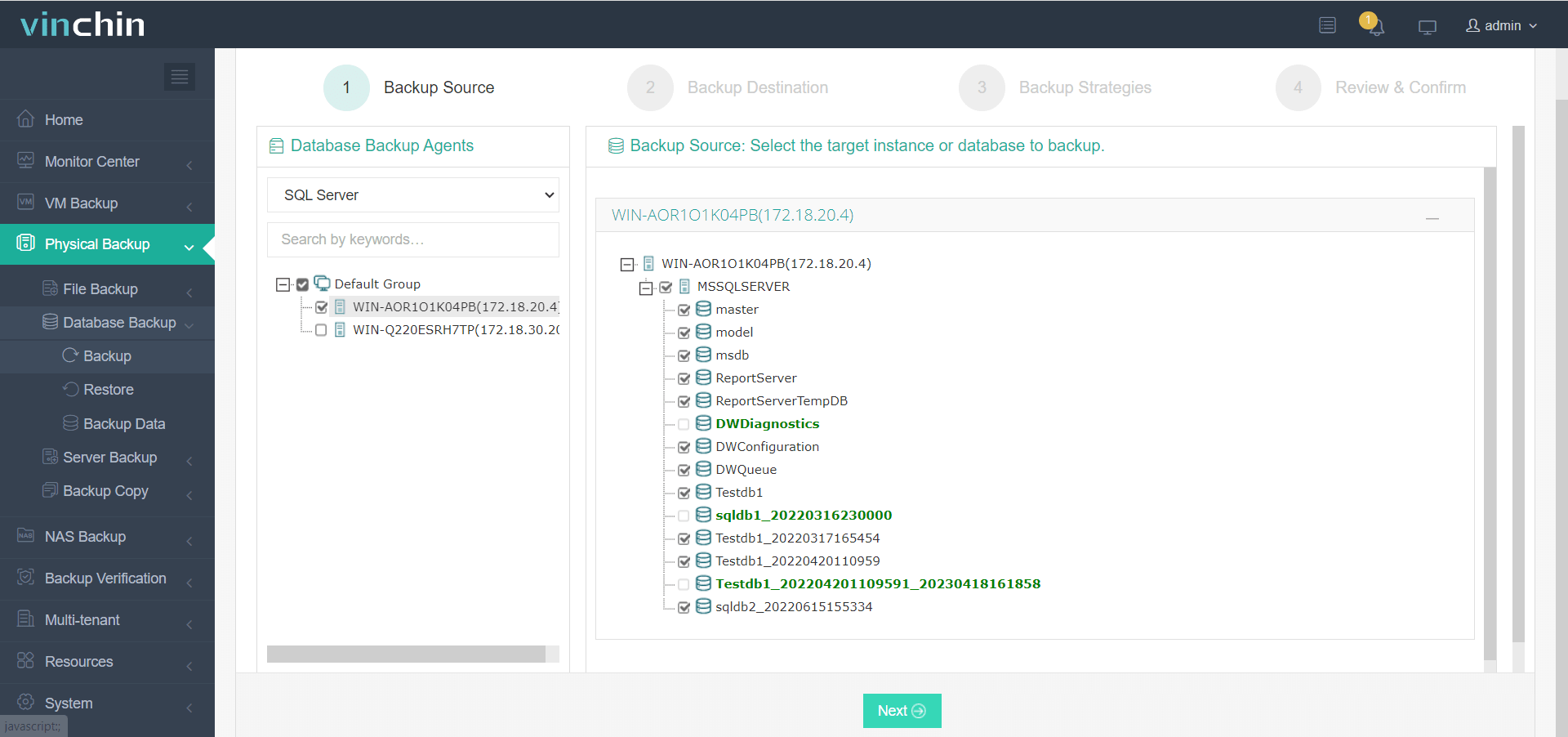
2. Choose target storage location(s),
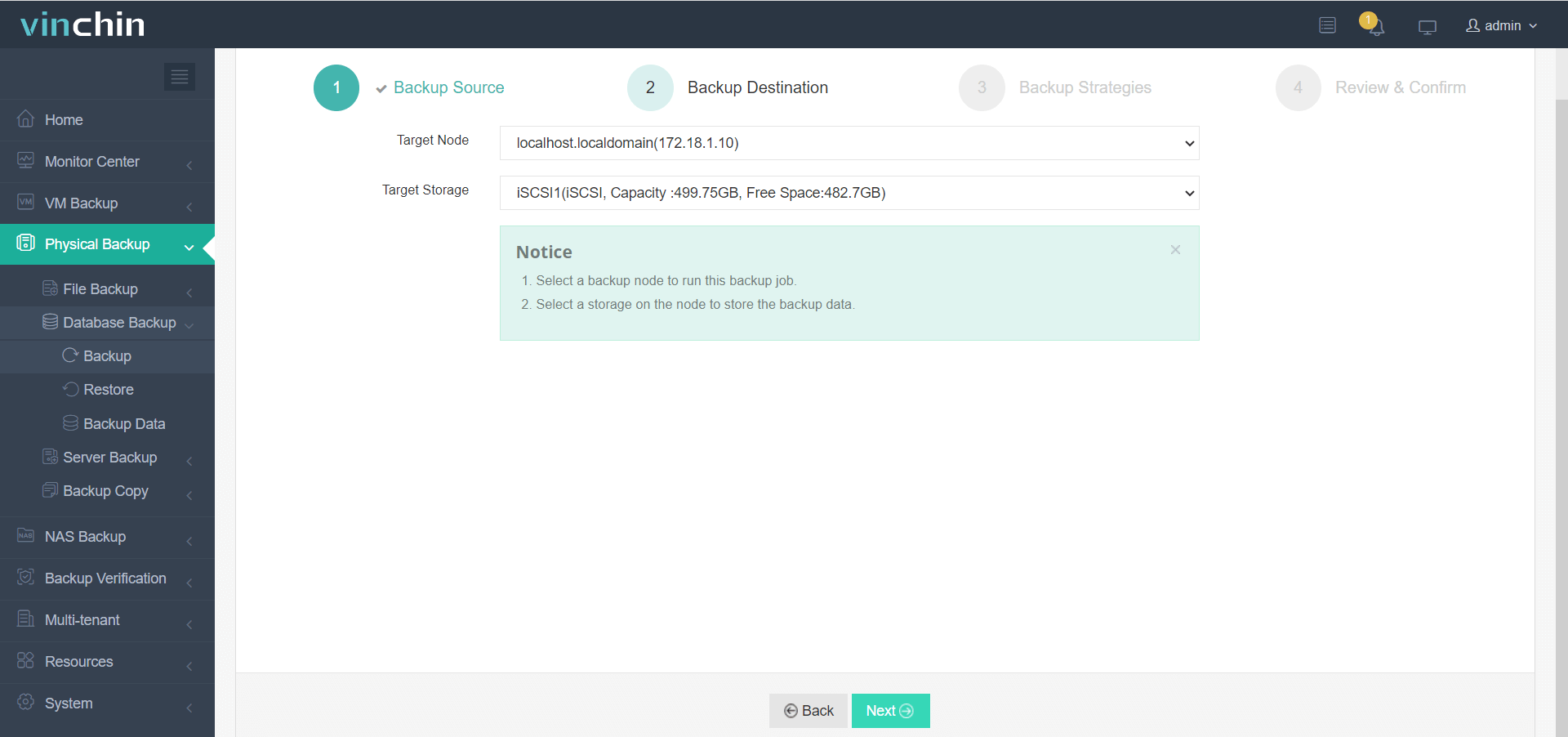
3. Configure backup strategies,

4. Submit the job.
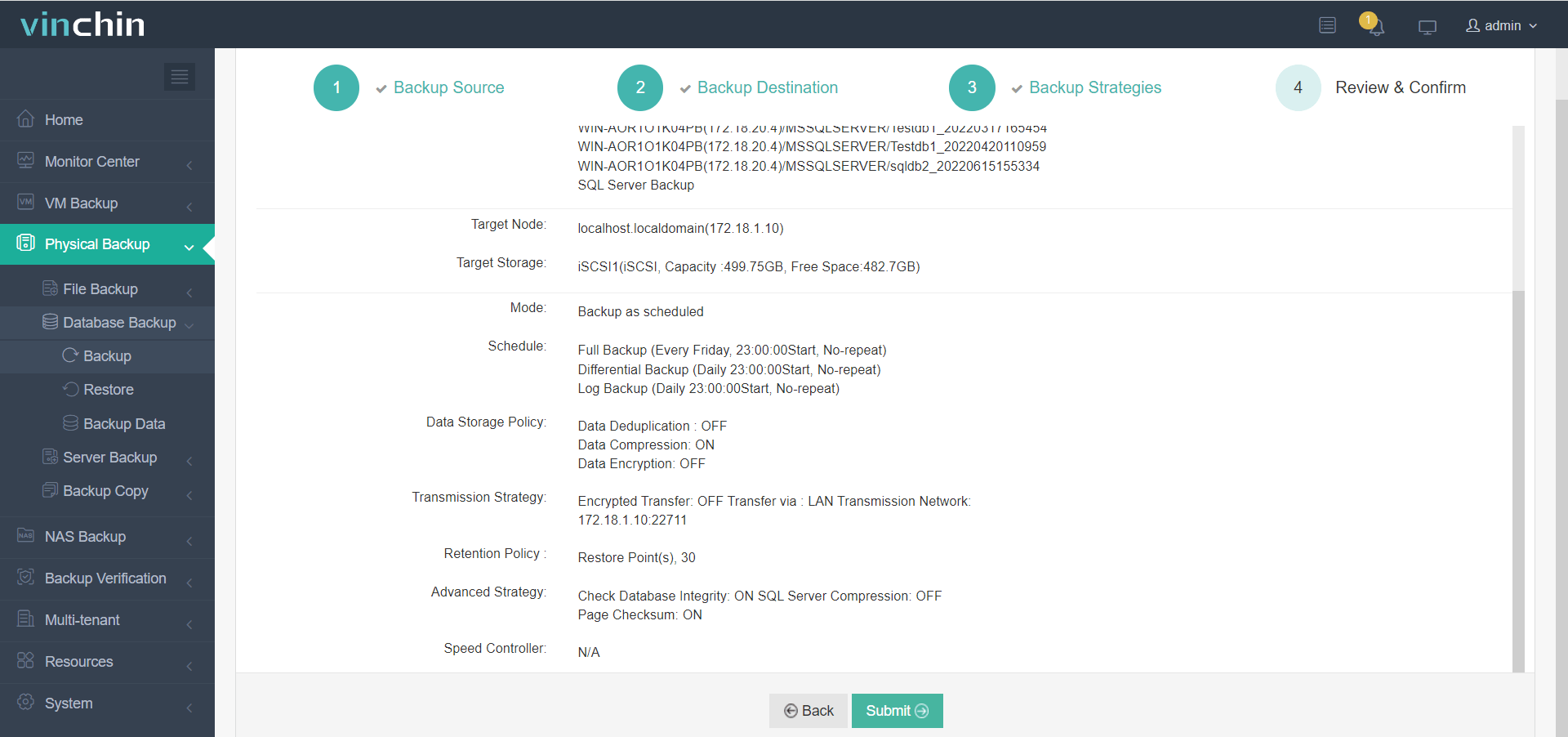
Experience why thousands worldwide trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery's award-winning solution.Download now—for free—with an unrestricted 60-day trial.
Database Bak FAQs
Q1: Can I restore a .bak file from one version of SQL Server onto another?
Check compatibility first—restoring from newer versions onto older servers is not supported without migration steps.
Q2: What should I do if my scheduled SQL Server Agent job fails?
Review job history in SQL Server Agent logs—common causes include permission issues or insufficient disk space.
Q3: How can I encrypt my Oracle RMAN backups?
Before running BACKUP commands in RMAN session: enter CONFIGURE ENCRYPTION FOR DATABASE ON then proceed as usual.
Conclusion
Database bak routines protect against disaster—from accidental deletion to hardware failure—by letting you recover fast when things go wrong.Whether using scripts or tools like SSMS or Oracle RMAN—or automating everything with Vinchin—the key is regular testing of both backups and restores so you're never caught off guard.
Share on:







