-
What is Crosscheck Backup?
-
Why Perform Crosscheck Backup?
-
Method 1: Manual Crosscheck Backup Steps
-
Method 2: Using Oracle RMAN CROSSCHECK Command
-
How Vinchin Backup & Recovery Simplifies Database Protection
-
Crosscheck Backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Every backup administrator knows: a backup is only as good as its recoverability. But how do you know if your backup files are still present and usable? This is where "crosscheck backup" comes into play. Crosschecking ensures that what’s recorded in your catalog matches what’s actually stored on disk or tape.
In this article, we’ll explain what crosscheck backup means at every level—from basic definitions to advanced troubleshooting. You’ll learn why it matters for data safety, how to perform it manually or with Oracle RMAN commands, and how to avoid common mistakes along the way. We’ll also show you how Vinchin can help you keep your database backups reliable and easy to manage.
What is Crosscheck Backup?
A crosscheck backup process verifies whether each backup file listed in your catalog or repository truly exists on storage media like disks or tapes. Think of it as an audit: does every record in your system point to a real file? If a file has been deleted outside of your backup software—or moved without updating records—the crosscheck process updates its status so you don’t get caught off guard during recovery.
It’s important to note that crosschecking checks for presence—not internal consistency or corruption within files themselves. For deeper integrity checks (like verifying checksums), you need additional validation steps such as RESTORE VALIDATE commands in Oracle RMAN.
Crosschecking keeps your metadata honest by synchronizing logical records with physical reality—a critical step before any restore operation.
Why Perform Crosscheck Backup?
Performing regular crosscheck backups protects against silent failures in your data protection strategy. Over time, many things can go wrong: files may be moved accidentally; disks might fail; tapes could become unreadable; someone might delete old backups thinking they’re no longer needed.
If your catalog claims a file exists but it’s missing from storage, restores will fail when you need them most—often during emergencies when time matters most! Regularly running crosschecks ensures that what’s available matches what’s recorded so there are no surprises later.
For organizations subject to compliance rules (such as financial services or healthcare), demonstrating regular verification through crosschecks can also help meet audit requirements.
Method 1: Manual Crosscheck Backup Steps
Manual crosschecking gives you direct control over the verification process but requires discipline—and sometimes creativity—to do well.
Start by reviewing your current backup catalog or inventory list. This could be generated by scripts from your database system or even maintained manually if you have a small environment. For example:
On Linux/Unix systems: run
ls -lh /backup/oracle/to list all files in a directory.Export a list of expected backups from your management console if available.
Compare this list against entries shown in any tracking spreadsheet or database table used for recording backups.
Next, physically check each storage location—whether local disk directories or remote tape libraries—to confirm every file listed actually exists where expected:
1. Use OS-level tools like ls, find, or Windows Explorer search functions.
2. For tapes: consult library management interfaces to see which volumes are loaded.
3. If using network-attached storage (NAS): verify mount points are accessible before checking contents.
4. Document any discrepancies immediately—including missing files’ names and paths—for follow-up investigation.
Suppose you find that /backup/oracle/full_bkp_20240601.bak is missing from disk but still appears in your catalog spreadsheet—that’s an inconsistency! Update the catalog entry right away (marking it expired/unavailable) so future restores don’t try using non-existent data.
Manual methods work best for small environments but quickly become error-prone at scale due to human oversight and dynamic changes—especially when multiple admins handle backups across different shifts or sites.
For larger setups—or whenever possible—it’s wise to supplement manual checks with automated scripts:
# Example Bash script snippet: for f in $(cat /path/to/catalog_list.txt); do if [ ! -f "$f" ]; then echo "Missing file: $f" fi done
This approach highlights gaps between expected files versus actual presence on disk—a simple yet effective sanity check!
Always document findings after each manual review session so trends can be spotted over time (e.g., recurring hardware issues).
Method 2: Using Oracle RMAN CROSSCHECK Command
Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) provides built-in automation for performing robust crosschecks—saving time while reducing risk of human error.
The CROSSCHECK command synchronizes physical reality with logical records inside the RMAN repository:
It scans all registered backups—including sets, image copies, proxy copies—and compares their existence on disk/tape.
If any item listed cannot be found at its recorded location (due to deletion/movement/hardware failure), RMAN marks it as EXPIRED.
Expired items signal potential problems needing attention before relying on those backups for restore operations.
Before running these commands:
Make sure RMAN connects successfully both to the target database instance AND recovery catalog if used.
No special maintenance channel is needed for disk-based storage; however,
if using tape devices via SBT interface,
allocate appropriate channels first (ALLOCATE CHANNEL FOR MAINTENANCE DEVICE TYPE 'SBT_TAPE').
To perform a full scan across all types:
RMAN> CROSSCHECK BACKUP;
This covers all known sets/copies/proxies regardless of type/location.
Want more targeted checks?
To focus only on archived logs:
RMAN> CROSSCHECK ARCHIVELOG ALL;
To check image copies specifically:
RMAN> CROSSCHECK DATAFILECOPY ALL;
To narrow down by tablespace:
RMAN> CROSSCHECK BACKUP OF TABLESPACE USERS;
After running these commands,
review output carefully—any item marked EXPIRED should trigger investigation!
Common causes include accidental deletion,
storage unmounts,
or retention policies purging older files outside of RMAN control.
If missing files are restored back into place,
re-running CROSSCHECK BACKUP; updates their status back from EXPIRED to AVAILABLE automatically!
To clean up expired entries from repository:
RMAN> DELETE EXPIRED BACKUP;
This removes stale references so future jobs run cleaner/faster without confusion over unavailable resources.
For large catalogs—or tape-heavy environments—
consider scheduling these tasks during off-hours since scanning slow devices may impact performance temporarily.
Always monitor logs for errors such as RMAN-06172 (“device not ready”) which often indicate permission issues,
hardware faults,
or misconfigured media managers requiring prompt attention.
How Vinchin Backup & Recovery Simplifies Database Protection
Beyond traditional manual and command-line methods, enterprise-grade solutions streamline the entire process of safeguarding critical databases such as Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—all supported by Vinchin Backup & Recovery. As an advanced professional solution designed for modern IT environments, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers comprehensive protection across nearly every mainstream platform mentioned above—including seamless support for Oracle databases featured throughout this article's examples.
Among its extensive capabilities are features like incremental backups options tailored per platform needs, batch database backup scheduling for efficiency at scale, flexible data retention policies including GFS strategies, robust log/archived log management with any-point-in-time recovery assurance, plus cloud/tape archiving integration for long-term resilience. These combined features ensure optimized resource usage while maximizing reliability and simplifying compliance—all through one unified solution built specifically for enterprise demands.
Managing Oracle database protection with Vinchin Backup & Recovery is straightforward thanks to its intuitive web console interface:
Step 1. Select the Oracle database to back up
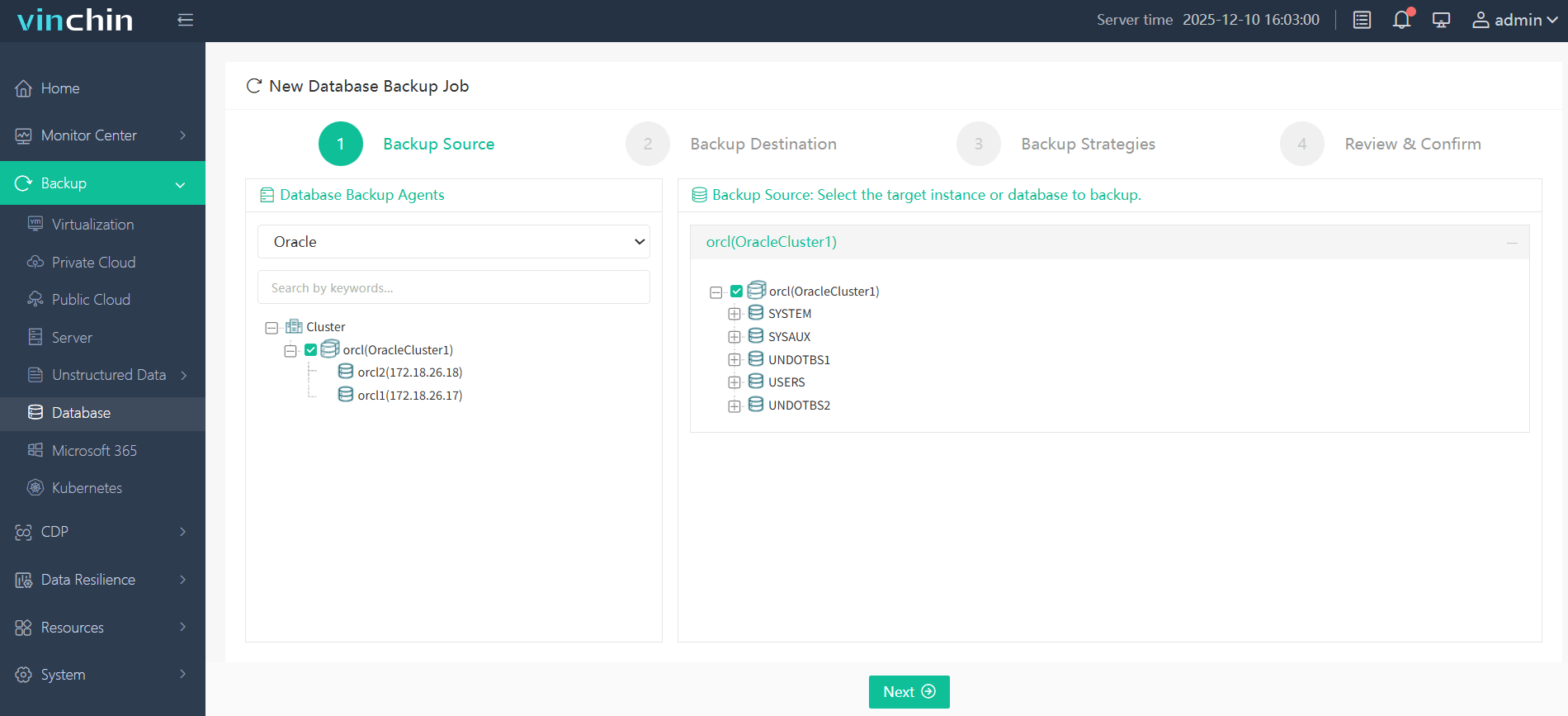
Step 2. Choose backup storage
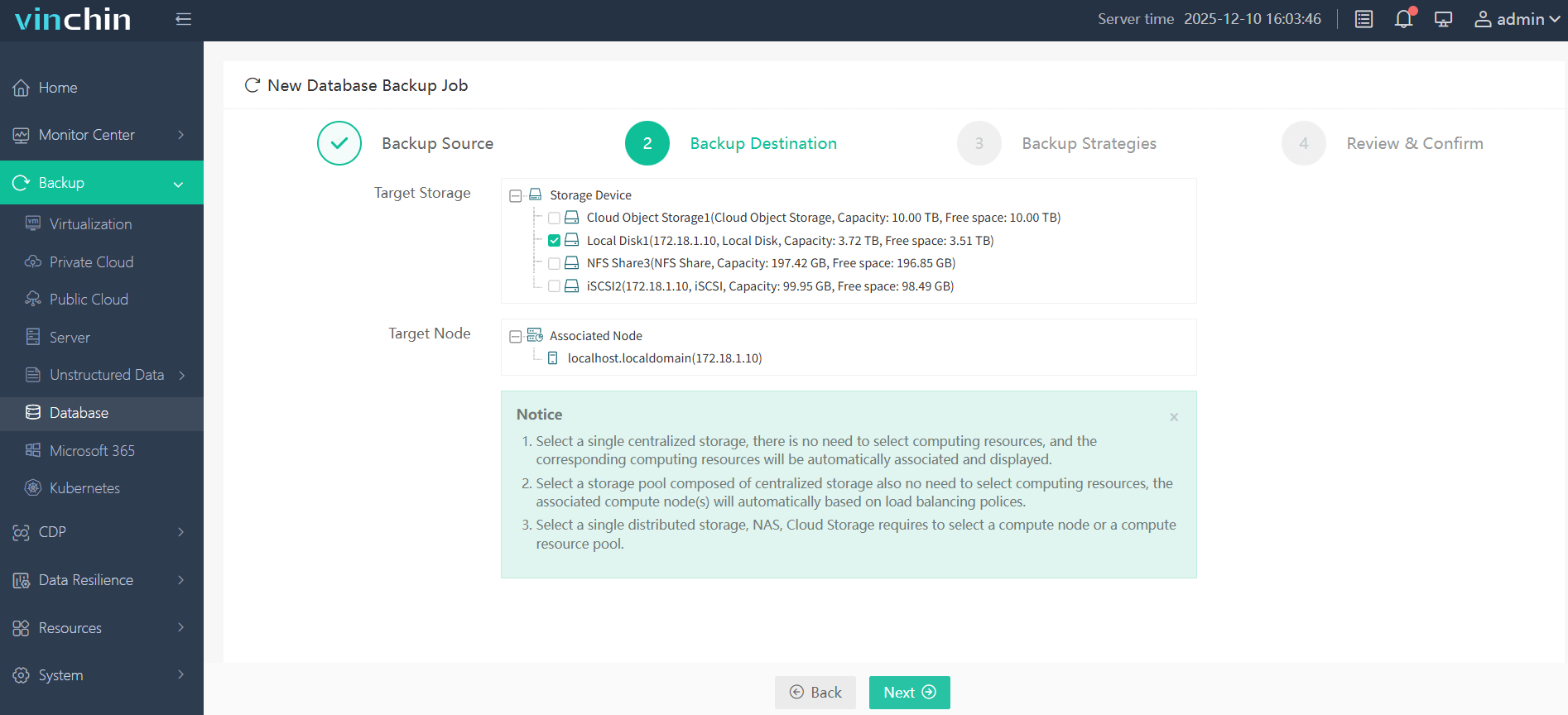
Step 3. Define your backup strategy
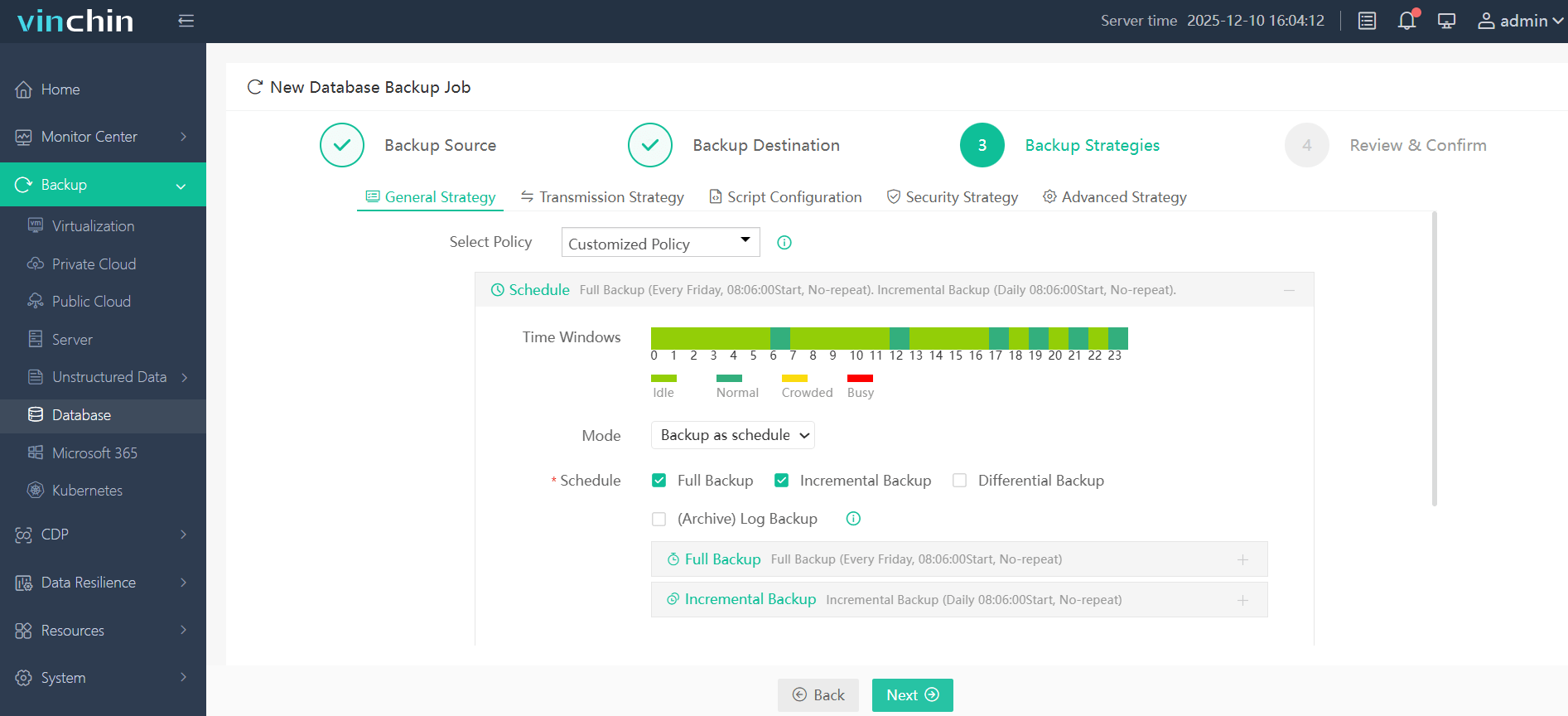
Step 4. Submit the job
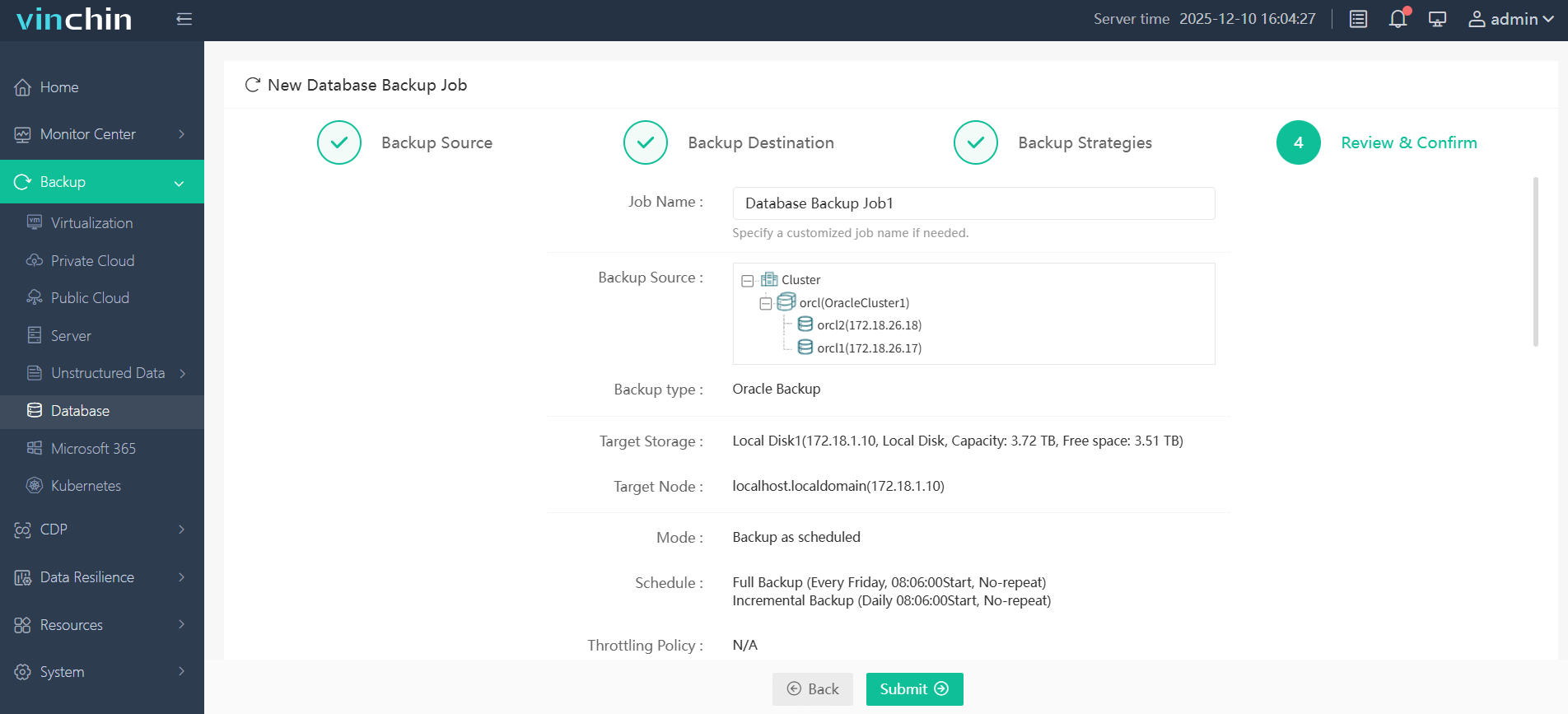
Recognized globally with top customer ratings and trusted by thousands worldwide, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully functional free trial lasting up to 60 days—click below now and experience effortless enterprise data protection firsthand!
Crosscheck Backup FAQs
Q1: Can I automate regular crosschecks without logging into my console each time?
A1: Yes—you can schedule automated scripts using cron jobs (Linux) or Task Scheduler (Windows) calling rman target / @crosscheck_script.rman weekly for hands-off verification.
Q2: Does running CROSSCHECK detect corrupted backup blocks?
A2: No—it only confirms presence/accessibility; use VALIDATE BACKUPSET or RESTORE VALIDATE commands separately for deep integrity testing.
Q3: What should I do if my tape library reports “media not found” during scheduled crosschecks?
A3: Check device connections/logs first then reload affected cartridges before retrying scan via CROSSCHECK BACKUP DEVICE TYPE SBT_TAPE command.
Conclusion
Crosscheck backup keeps catalogs accurate so restores succeed when needed most—no surprises! Whether done manually or through automated tools like Oracle RMAN, regular verification builds trust in business continuity plans long-term. Vinchin makes managing enterprise-grade data protection even simpler—try our free trial today!
Share on:






