-
What Is Air Gapped Backup?
-
Why Use Air Gapped Backup?
-
Key Considerations Before Implementation
-
Method 1: Offline Storage Devices (Tape Drives, External Hard Drives)
-
Method 2: Network Isolation Techniques
-
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise File Backup Made Simple and Fast
-
Air Gapped Backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Ransomware attacks are more common than ever—and they’re getting smarter. Attackers now target not just your live data but also your backups, hoping to leave you with nothing to restore after an attack. As an operations administrator, you need a strategy that keeps your most important data safe even if everything else fails. That’s where air gapped backup comes in.
What Is Air Gapped Backup?
Air gapped backup means storing copies of your data on systems that are completely isolated from your main network—either physically or logically. There is no direct connection between these backups and your production environment; no wires, no Wi-Fi, no shortcuts for malware or hackers to exploit.
This separation forms a barrier that cyber threats cannot cross easily. Even if ransomware infects every server on your network, it cannot reach an air gapped backup because there’s simply no path to get there. For this reason, air gapping is considered one of the strongest defenses against modern cyberattacks.
Why Use Air Gapped Backup?
Why go through all this trouble? Because attackers know backups are valuable—and they target them first during an attack.
If your backups stay online and connected to the same network as everything else, they can be encrypted or deleted along with production data during a breach. An air gapped backup stands apart as a last line of defense when all other protections fail.
Security agencies recommend air gapping as part of any robust disaster recovery plan because it ensures you always have at least one untouched copy of critical data ready for recovery—even after the worst-case scenario.
Key Considerations Before Implementation
Before setting up an air gapped backup system, take time to think through some key factors that affect both security and daily operations.
First is Recovery Time Objective (RTO)—how quickly do you need systems back online after a failure? Physical media like tape drives often mean longer RTOs due to manual handling, while logical isolation can offer faster restores.
Next is Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—how much recent data can you afford to lose? Manual processes might only allow nightly backups; automated solutions can support more frequent intervals so less data is lost if disaster strikes.
Operational overhead matters too: Are you prepared for regular handling of tapes or drives? Automated network isolation reduces manual work but requires careful setup and monitoring instead.
Finally, consider both cyber and physical security risks: A tape locked in a cabinet may be safe from hackers but could still be lost in a fire or stolen if not protected properly. Your strategy should address both types of threats for true resilience.
Method 1: Offline Storage Devices (Tape Drives, External Hard Drives)
The oldest form of air gapped backup uses offline storage devices such as tape drives or external hard disks—a method trusted by many organizations worldwide.
Here’s how it works: You run your scheduled backup job onto removable media like tapes or USB drives while they’re connected to the system. When finished, you disconnect them physically from all computers and networks—no cables left plugged in anywhere—and store them securely offsite or in a locked room onsite.
Because these devices are unplugged most of the time, there’s no way malware can reach them—even if every machine on your main network gets compromised by ransomware overnight!
However, this method does require discipline:
Someone must remember to disconnect each device after every job
Devices must be stored safely away from theft or disasters
Regular testing is needed so you know those backups actually work when needed
Some teams rotate several sets of tapes/drives so at least one copy always stays offsite—protecting against fire or flood as well as cyberattack.
Method 2: Network Isolation Techniques
Not every organization wants—or has time—for manual processes day after day. Network isolation offers another way to create an air gap using technology rather than just unplugging hardware.
With this approach:
You set up dedicated storage (like NAS appliances) on its own VLAN
Firewalls enforce strict rules so only authorized traffic reaches this storage during scheduled windows
After each backup completes, scripts automatically disable access by shutting down interfaces or removing firewall rules until next time
For example: Place backup storage on its own VLAN with firewall rules set to DENY ALL except specific ports (such as port 445 for SMB) during defined hours when backups run; outside those hours all connections are blocked again automatically.
In cloud environments you might use isolated S3 buckets accessible only via temporary credentials created just-in-time for each job—then revoked immediately afterward so nothing remains open between jobs.
Network isolation reduces human error risk compared with manual methods—but demands careful configuration plus regular audits so gaps don’t appear over time due to overlooked settings changes elsewhere in the environment.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise File Backup Made Simple and Fast
To put these strategies into action efficiently across diverse environments such as NAS appliances, Windows/Linux file servers, and S3-compatible object storage—which are commonly targeted for secure file protection—Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional enterprise-grade solution supporting nearly all mainstream file storage platforms. Its advanced architecture delivers exceptionally fast file backup speeds thanks to proprietary technologies like simultaneous scanning/data transfer and merged file transmission—outpacing typical industry offerings by a wide margin.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery brings together features including incremental backup support for efficient change tracking; wildcard filters for precise selection; multi-level compression options; robust encryption; and seamless cross-platform restore capabilities allowing any file backup—from NAS shares to object storage—to be restored wherever needed. Together these features ensure reliable protection while optimizing performance and flexibility.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding critical files straightforward. For example:
Step 1. Select the NAS files to back up
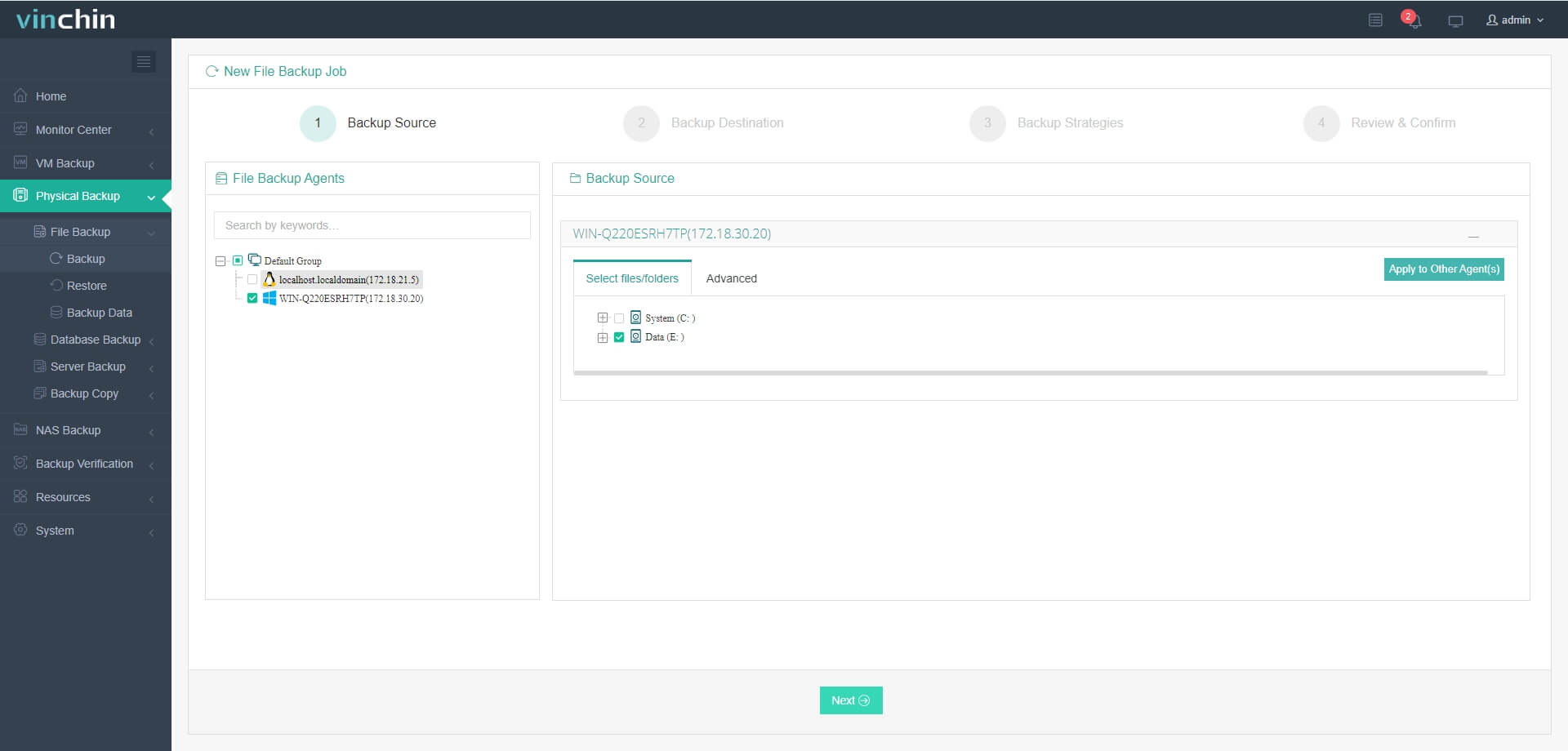
Step 2. Choose the desired backup storage
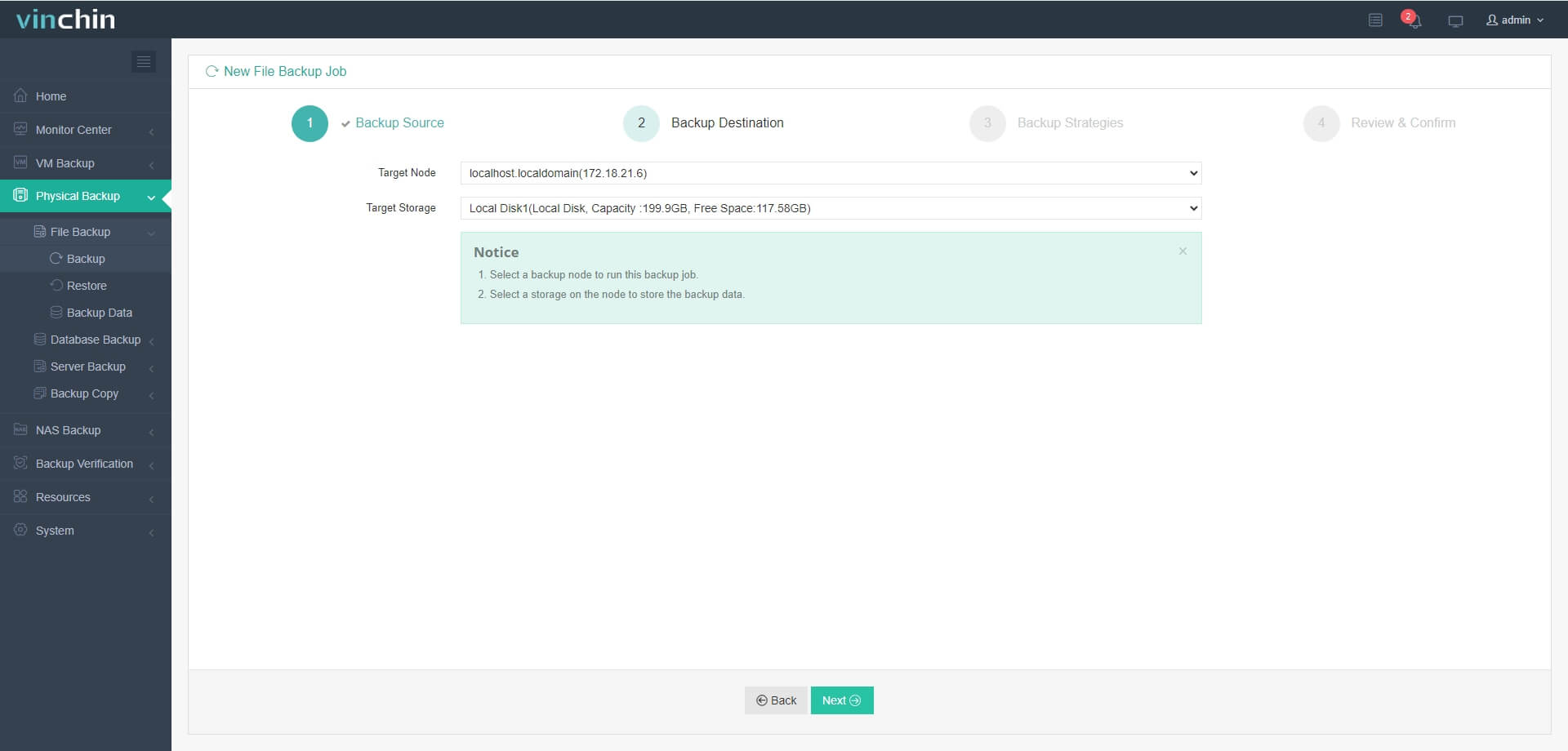
Step 3. Define scheduling and retention strategies
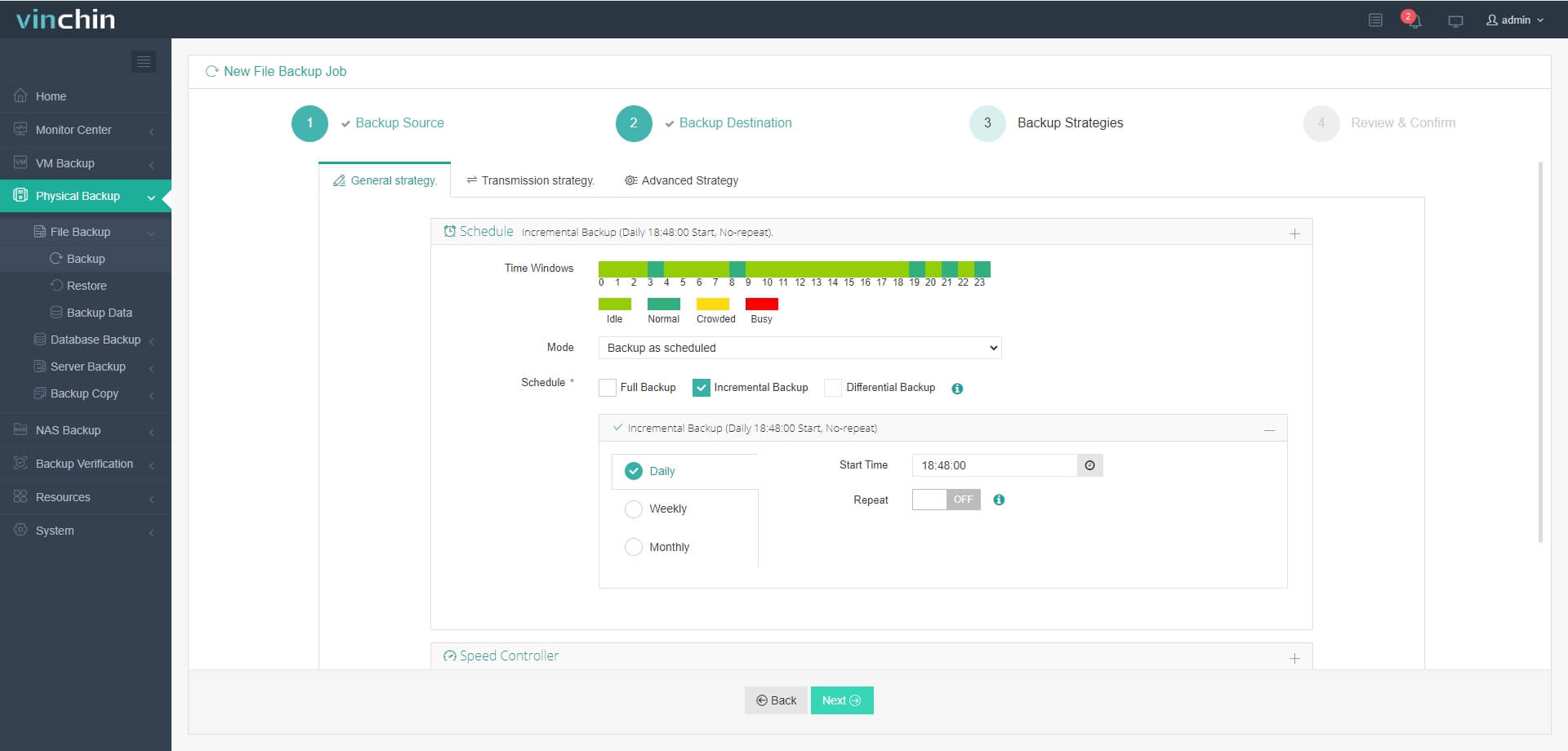
Step 4. Submit the job
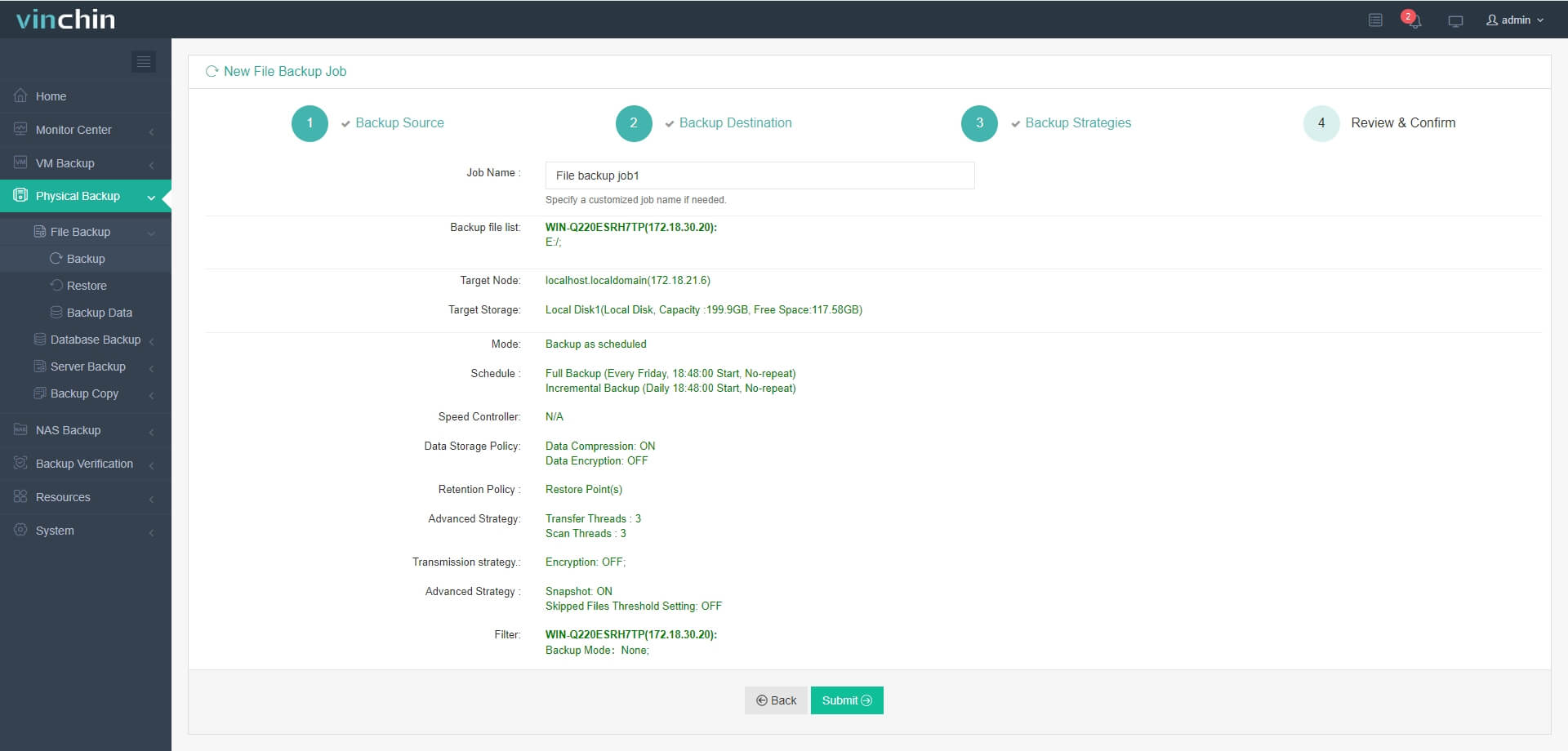
Recognized globally with top ratings among enterprise users across 60+ countries, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured free trial valid for 60 days—experience why thousands trust it for business-critical data protection today.
Air Gapped Backup FAQs
Q1: Can I automate my entire air gapped workflow—including disconnecting storage?
Yes; use scheduled jobs combined with scripts/firewall automation so devices/networks isolate themselves right after each completed job without human intervention required every time.
Q2: How do I balance frequent incremental backups versus hassle moving/removing physical media constantly?
Many admins combine approaches—using automated logical gaps daily then copying full sets weekly/monthly onto removable media taken fully offline/offsite afterward.
Q3: What should I do if my test restores fail unexpectedly?
Check logs/settings immediately; verify source/destination paths match current infrastructure; rerun tests regularly until successful results repeat reliably under varied conditions.
Conclusion
Air gapped backup gives operations administrators powerful protection against ransomware and disasters alike by keeping vital copies truly out-of-reach until needed most—and Vinchin makes building/testing these defenses fast yet simple for any team ready take control today!
Share on:








