-
What Is Server Data Backup?
-
Why Server Data Backup Matters?
-
Method 1: Manual Server Data Backup
-
Method 2: Automated Local Server Data Backup (e.g., using Windows Backup or Linux rsync)
-
Method 3: Cloud-Based Server Data Backup (e.g., using AWS Backup or Azure Backup)
-
How to Back Up Server Data with Vinchin?
-
Server Data Backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Server data backup is the backbone of IT resilience. Whether you manage a small business or a large enterprise, losing server data can mean lost revenue, downtime, and even legal trouble. Let’s break down what server data backup is, why it matters, and how to do it right.
What Is Server Data Backup?
Server data backup means making copies of your server’s important files, databases, and system settings. These copies are stored in a separate location—on another disk, a tape, or in the cloud. If your server fails, gets hacked, or someone deletes files by mistake, you can restore your data from these backups. Backups can be full (everything), incremental (just changes), or differential (changes since the last full backup).
Why Server Data Backup Matters?
Why bother with server data backup? Because disasters happen. Hard drives fail, ransomware strikes, and people make mistakes. Without a backup, you risk losing customer records, financial data, or your entire business operation. Backups also help you meet legal and industry rules about data retention. In short, a good backup plan keeps your business running, even when things go wrong.
Method 1: Manual Server Data Backup
Manual server data backup is the simplest way to protect your files. It means copying data by hand from your server to another device, like an external hard drive or USB stick. This method is best for small setups or when you need a quick, one-time backup.
To do a manual backup on Windows Server, use the built-in Backup tool:
1. Click Start, go to All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Backup.
2. In the Backup or Restore Wizard, click Advanced Mode.
3. On the Backup tab, select the files, folders, or drives you want to back up.
4. Choose a Backup destination (File or Tape).
5. Name your backup file and pick a location.
6. Click Start Backup.
On Linux, you can use the cp or tar command to copy files:
To copy a folder:
cp -a /source/folder /backup/location/
To create a compressed archive:
tar czvf /backup/location/backup.tar.gz /source/folder
Manual backups are easy, but they have risks. You might forget to run them, or miss important files. For regular protection, consider automating your backups.
Method 2: Automated Local Server Data Backup (e.g., using Windows Backup or Linux rsync)
Automated local server data backup saves time and reduces errors. You set up a schedule, and the system backs up your data automatically to a local device or network share.
On Windows Server, use Windows Server Backup:
1. Open Server Manager, click Tools > Windows Server Backup.
2. Click Backup Schedule in the right pane.
3. Follow the wizard to select what to back up (full server or custom files).
4. Choose when to run the backup (daily, more often).
5. Select the backup destination (local disk or network share).
6. Review settings and click Finish.
On Linux, rsync is a popular tool for automated backups. To back up /data to /backup:
Run:
rsync -av --delete /data/ /backup/
To automate, add the command to your crontab:
Edit crontab:
crontab -e
Add a line for daily backup at 2am:
0 2 * rsync -av --delete /data/ /backup/
Automated backups reduce human error and ensure regular protection. But remember, local backups can still be lost in a fire or theft. For full safety, add offsite or cloud backups.
Method 3: Cloud-Based Server Data Backup (e.g., using AWS Backup or Azure Backup)
Cloud-based server data backup stores your files on remote servers managed by a cloud provider. This method protects your data from local disasters and makes recovery possible from anywhere.
To back up a Windows Server to AWS using AWS Backup:
1. Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
2. Go to AWS Backup and click Create backup plan.
3. Define your backup schedule and retention rules.
4. Assign resources (like your EC2 instance or on-premises server).
5. Review and activate the plan.
For Azure, use Azure Backup:
1. In the Azure Portal, search for Backup and click Backup center.
2. Click +Backup and select your workload (Azure VM, on-premises server, etc.).
3. Set up a Recovery Services vault.
4. Configure backup policy (frequency, retention).
5. Register your server and start the backup.
On Linux, you can use the AWS CLI or Azure CLI to script backups to the cloud—or use rclone to sync files to cloud storage.
Cloud backups offer offsite protection; scalability; and easy recovery—but they depend on internet connectivity and may have ongoing costs; always encrypt sensitive data before sending it out.
How to Back Up Server Data with Vinchin?
For organizations seeking robust enterprise-grade protection across mainstream operating systems—including Windows servers as well as Ubuntu Linux—Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers comprehensive coverage for environments such as RHEL/SLES/Rocky Linux/Oracle Linux/Debian alongside others commonly found in modern IT infrastructures.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery provides real-time Continuous Data Protection (CDP) that continuously replicates critical information onto standby machines while monitoring heartbeat signals; if failure occurs on any primary machine it triggers automatic failover—and once restored synchronizes all changes seamlessly back again for uninterrupted service continuity.
Among its many features most relevant are forever incremental backups; advanced compression/deduplication; Changed Block Tracking; instant restore/migration of disks; plus bare-metal recovery—collectively ensuring efficient storage usage rapid disaster recovery minimal downtime flexible migration options strong reliability across diverse workloads.
The intuitive Vinchin web console streamlines every step:
1) Select the Windows machine you wish backed up;
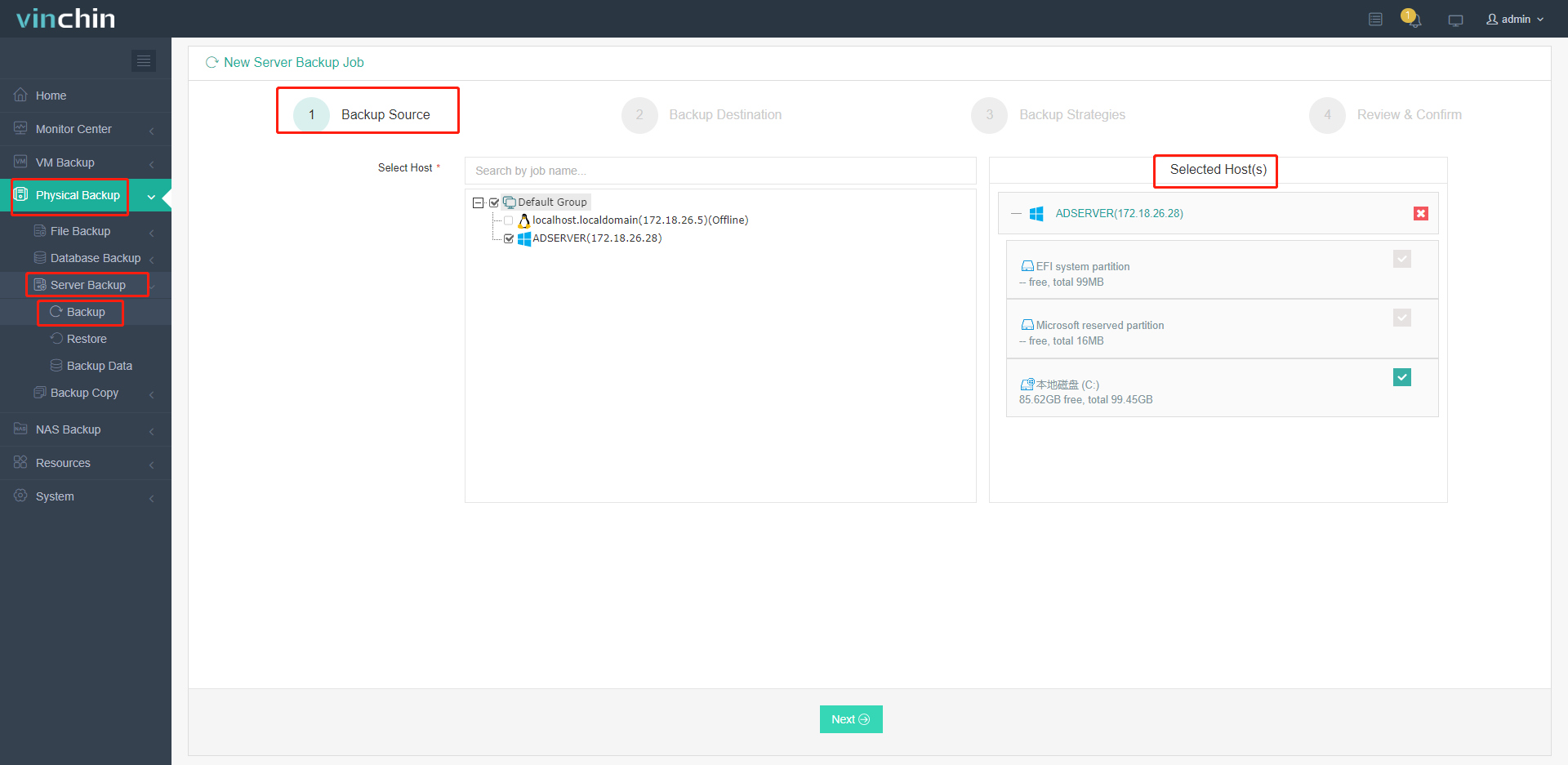
2) Choose where those backups will be stored;
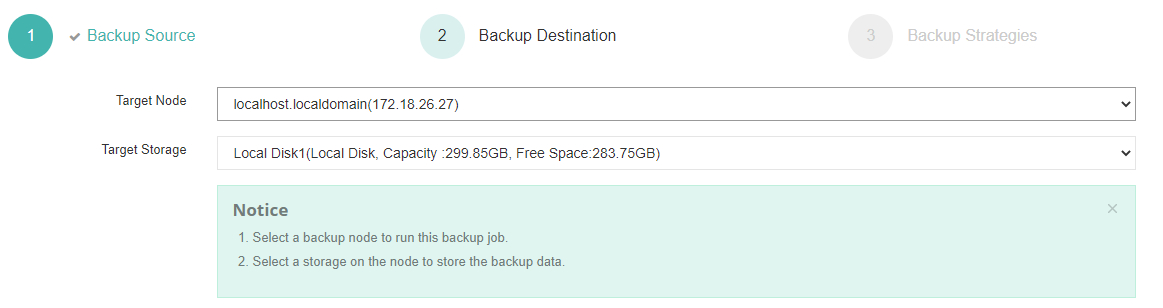
3) Configure strategies like scheduling/compression/deduplication;
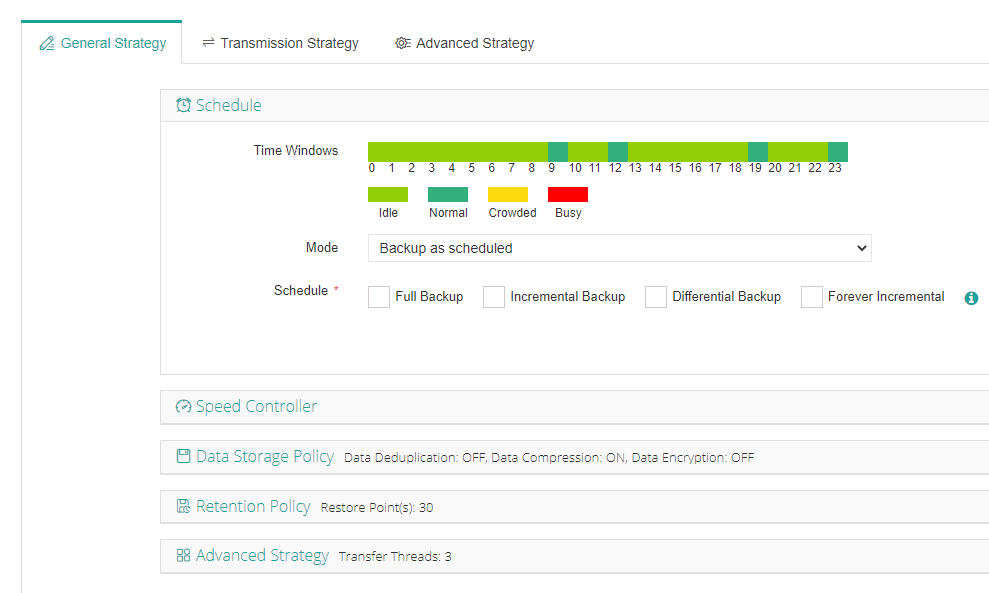
4) Submit—and let Vinchin handle everything else automatically behind-the-scenes.
Recognized globally with top ratings among enterprise users worldwide—Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers all features free for 60 days so you can evaluate without limits; download now via button below!
Server Data Backup FAQs
Q1: How can I test if my backup is restorable?
A1: Restore a small file from your backup to a test location and verify its contents.
Q2: What should I do if my automated backup fails?
A2: Check the backup logs for errors; ensure destination availability; rerun job as needed.
Q3: How do I encrypt my server data backup?
A3: Use built-in encryption options in software—or encrypt beforehand with BitLocker (gpg on Linux).
Q4: Can I back up only certain folders instead of whole server?
A4: Yes—select specific folders during file selection step within most tools’ interfaces.
Q5: How do I schedule a backup in Windows Server?
A5: Open “Windows Server Backup” → “Backup Schedule” → Set schedule → Finish setup process.
Conclusion
Server data backup is essential for business continuity and peace of mind—whether manual automated cloud-based methods suit best regular reliable protection prevents disaster losses every time! Vinchin makes this process simple secure scalable—try their solution free today!
Share on:







