-
What Is Retention Lock?
-
What Is Governance Mode?
-
What Is Compliance Mode?
-
Retention Lock Governance vs Compliance Differences
-
Why Choose Governance or Compliance Mode?
-
Retention Lock Governance vs Compliance Differences Table
-
How Vinchin Backup & Recovery Simplifies File Protection?
-
Retention Lock Governance vs Compliance FAQs
-
Conclusion
Data protection is a top priority for every organization today. With threats ranging from accidental deletion to malicious tampering, keeping your critical files safe has never been more important. Retention lock is a powerful tool that helps you enforce data integrity by making files unchangeable for a set period—but which mode should you choose: governance or compliance? This article explains both options step by step so you can make an informed decision that fits your environment.
What Is Retention Lock?
Retention lock is a feature found in many modern storage systems—including S3 Object Lock and WORM (Write Once Read Many) storage—that prevents data from being altered or deleted until a specified retention period expires. When enabled, it makes files read-only at either the file level or across entire directories or storage volumes depending on your system’s capabilities.
This technology helps organizations meet legal mandates or business policies that require certain records to remain unchanged over time. For example, financial institutions may need to keep transaction logs immutable for years due to regulations like SEC 17a-4(f). By integrating with existing infrastructure—whether cloud object storage or local NAS devices—retention lock ensures that even privileged users cannot bypass these controls without proper authorization or waiting out the retention period.
What Is Governance Mode?
Governance mode offers flexibility while still protecting your data against most risks. When you enable governance mode on files or objects:
Data becomes read-only during the retention period.
Authorized administrators can override or remove locks if necessary—for example, during audits or when correcting mistakes.
Early deletion requires special permissions; unauthorized users cannot simply erase protected data.
This mode suits organizations where internal controls are strong but some operational agility is needed—for instance, when handling evolving business requirements or responding quickly to legitimate exceptions.
Think of governance mode as a safety net: it blocks accidental deletions but allows trusted staff to intervene if business needs change unexpectedly.
What Is Compliance Mode?
Compliance mode enforces strict immutability aligned with regulatory standards such as SEC 17a-4(f) and FDA 21 CFR Part 11. Here’s what sets it apart:
Once enabled on files or objects, no user—including administrators—can modify or delete them before the retention period ends.
There are no exceptions; even system-level overrides are blocked.
Compliance mode often requires extra setup steps like designating security officers who approve policy changes.
It creates detailed audit trails showing all access attempts—a crucial requirement during regulatory reviews.
Industries such as finance, healthcare, government agencies often mandate this level of protection because they must prove their records have not been altered under any circumstances.
If you need absolute assurance that your data remains untouched until its expiration date—and want evidence ready for auditors—compliance mode delivers peace of mind few other features can match.
Retention Lock Governance vs Compliance Differences
Both modes prevent premature changes to critical data—but their differences matter greatly in practice:
The main distinction lies in reversibility:
In governance mode, authorized personnel can unlock files early if needed; this provides flexibility but introduces some risk if permissions aren’t tightly managed.
In compliance mode, once locked down nothing short of waiting out the full retention period will allow changes—even root users cannot override it without violating system integrity checks built into compliant platforms.
Another difference involves administrative overhead:
Governance mode typically integrates with standard role-based access controls already present in most enterprise environments.
Compliance mode may require creating dedicated roles (like Security Officer), implementing multi-factor authentication for policy changes, enforcing stricter logging/auditing practices—and sometimes passing external audits before activation!
Finally: after setting either governance OR compliance on a given dataset (such as an MTree), you cannot switch between modes later without destroying all protected content first—a permanent choice demanding careful planning upfront!
Implementation and Management Overhead
Choosing between these modes isn’t just about security—it affects daily operations too:
Governance mode usually means less paperwork: existing admins manage locks using familiar tools; exceptions can be processed quickly when justified.
Compliance mode increases workload: expect regular audits of access logs; policy updates might require multiple approvals; recovery from mistakes could involve lengthy appeals rather than quick fixes!
Both modes demand robust monitoring so expired locks don’t leave orphaned files consuming precious storage space indefinitely—a common pitfall if automation isn’t set up correctly!
Are you prepared for this extra effort? If not—or if your team lacks experience managing strict regulatory controls—you might prefer starting with governance until processes mature enough for full compliance adoption later on.
Why Choose Governance or Compliance Mode?
How do you decide which approach fits best? Start by asking yourself these questions:
1. Are there explicit legal mandates governing your industry (e.g., GDPR fines for improper deletion)?
2. Does your organization tolerate any risk of early file modification—even by trusted staff?
3. Do you have established workflows for handling urgent requests to unlock protected data?
4. Will auditors expect proof that no one—not even IT admins—could alter records before expiration?
5. Can your team handle increased management complexity required by compliance-grade solutions?
If strict regulations apply—or if audit-readiness trumps convenience—compliance mode is likely mandatory! Otherwise, governance gives enough control while letting you adapt quickly when business priorities shift unexpectedly.
Retention Lock Governance vs Compliance Differences Table
| Feature | Governance Mode | Compliance Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Who Can Remove Locks | Authorized Admins | No One |
| Regulatory Alignment | Internal Policies | External Mandates (SEC/FDA/etc.) |
| Flexibility | High | None |
| Audit Trail Requirements | Standard Logging | Detailed Immutable Logs |
| Change After Activation | Possible With Permission | Impossible Until Expiry |
| Management Overhead | Moderate | High |
Remember: once set per dataset/storage area (like an MTree), switching modes means deleting all current locked content first!
How Vinchin Backup & Recovery Simplifies File Protection?
Given how crucial robust backup strategies are when working with S3 object storage and other mainstream platforms supporting retention lock features, it's essential to use an enterprise-grade solution designed for speed and reliability. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional file backup platform supporting Windows/Linux file servers, NAS appliances, and S3-compatible object storage—with exceptionally fast backup speeds compared to competitors.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery leverages proprietary technologies such as simultaneous scanning/data transfer and merged file transmission to deliver rapid backups far beyond typical vendor performance benchmarks. Key features include incremental backup support, wildcard filtering for flexible job targeting, multi-level compression options to optimize storage usage, cross-platform restore capabilities between file server/NAS/object/S3 destinations, and robust encryption ensuring end-to-end security—all contributing to efficient management and comprehensive protection across diverse environments.
The web console of Vinchin Backup & Recovery is extremely intuitive. To back up S3 object storage files using retention lock policies typically takes just four steps:
Step 1. Select the S3 object storage files to back up
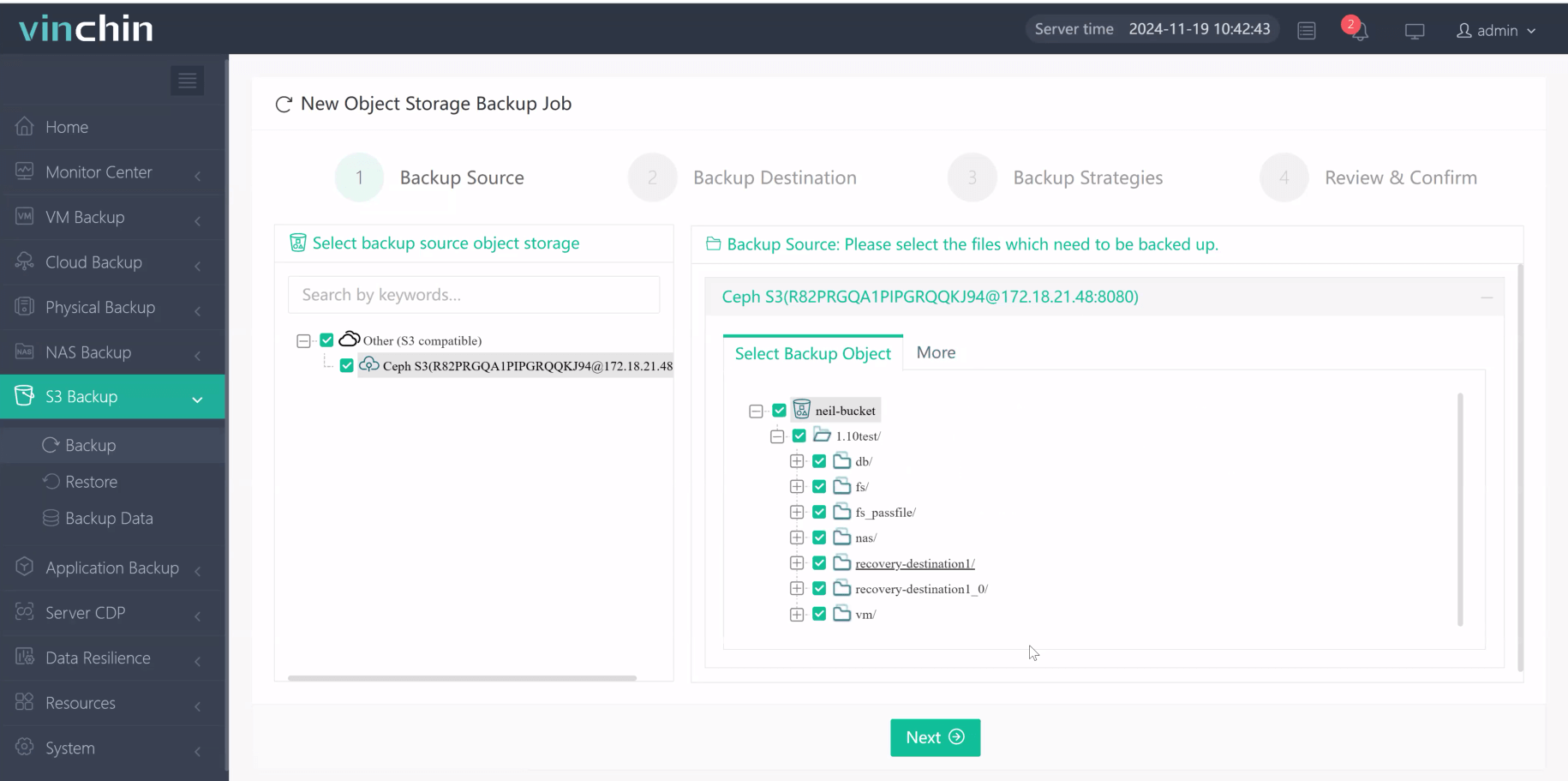
Step 2. Choose the backup destination
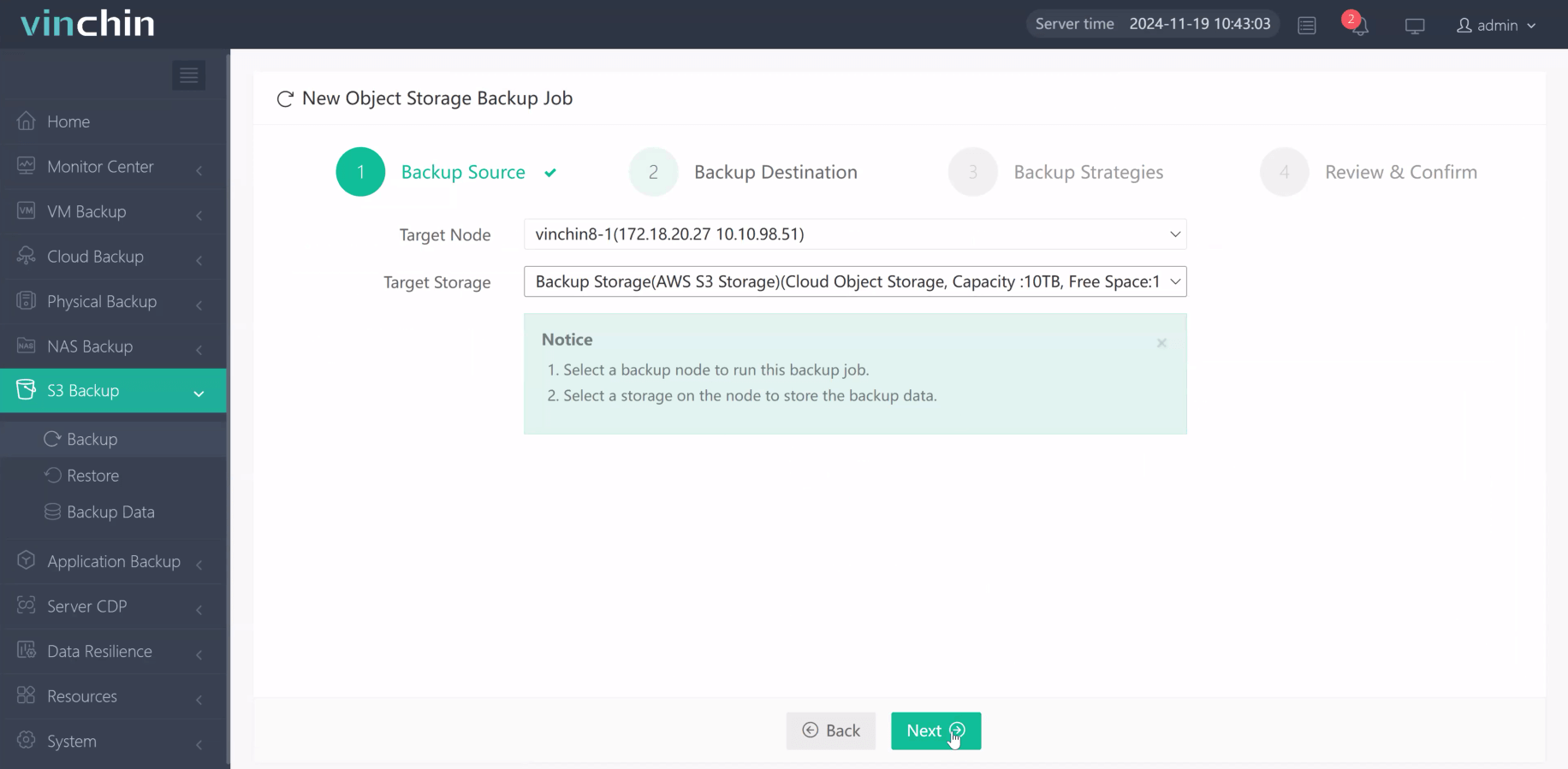
Step 3. Define your backup strategy
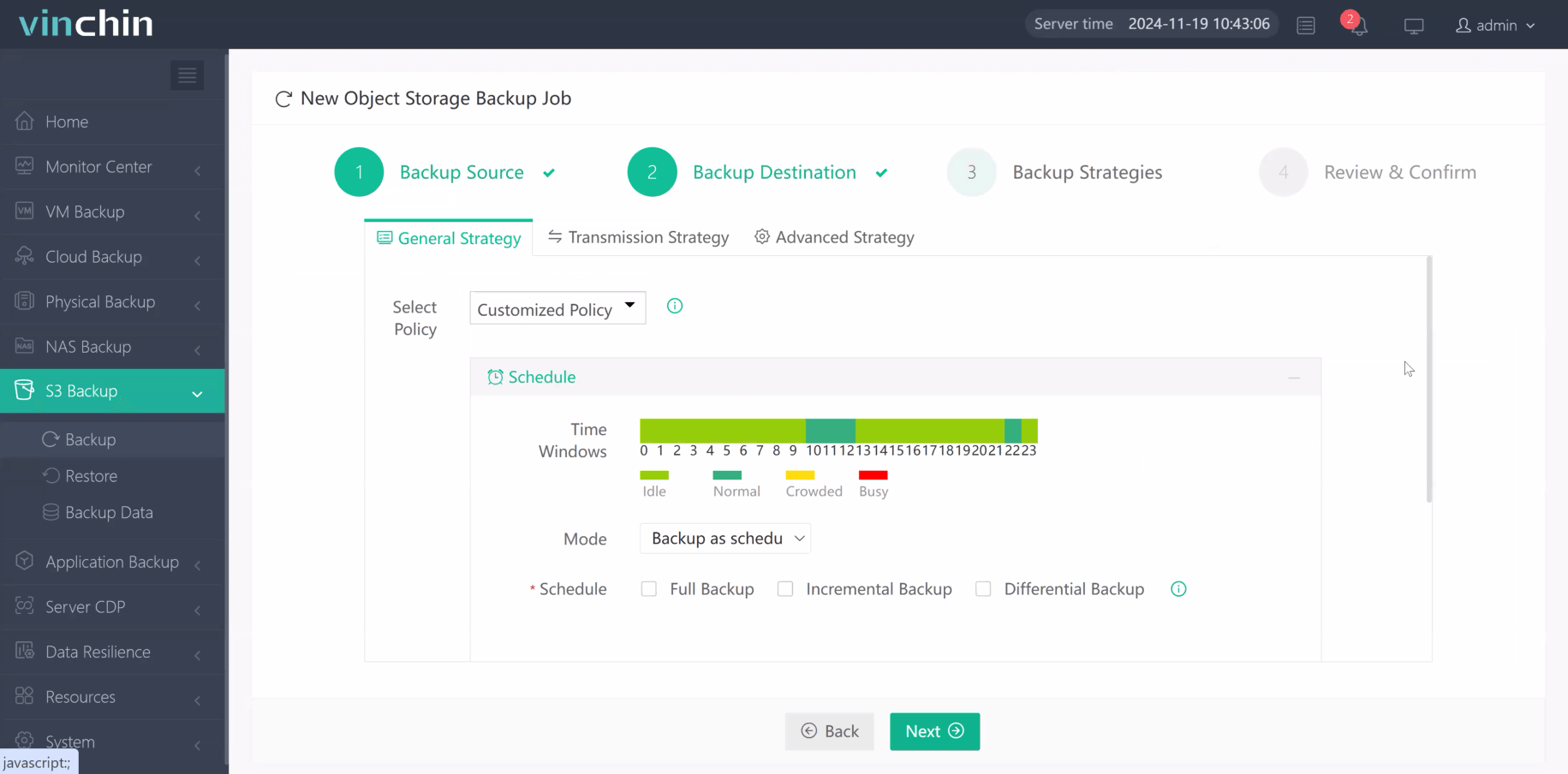
Step 4. Submit the job
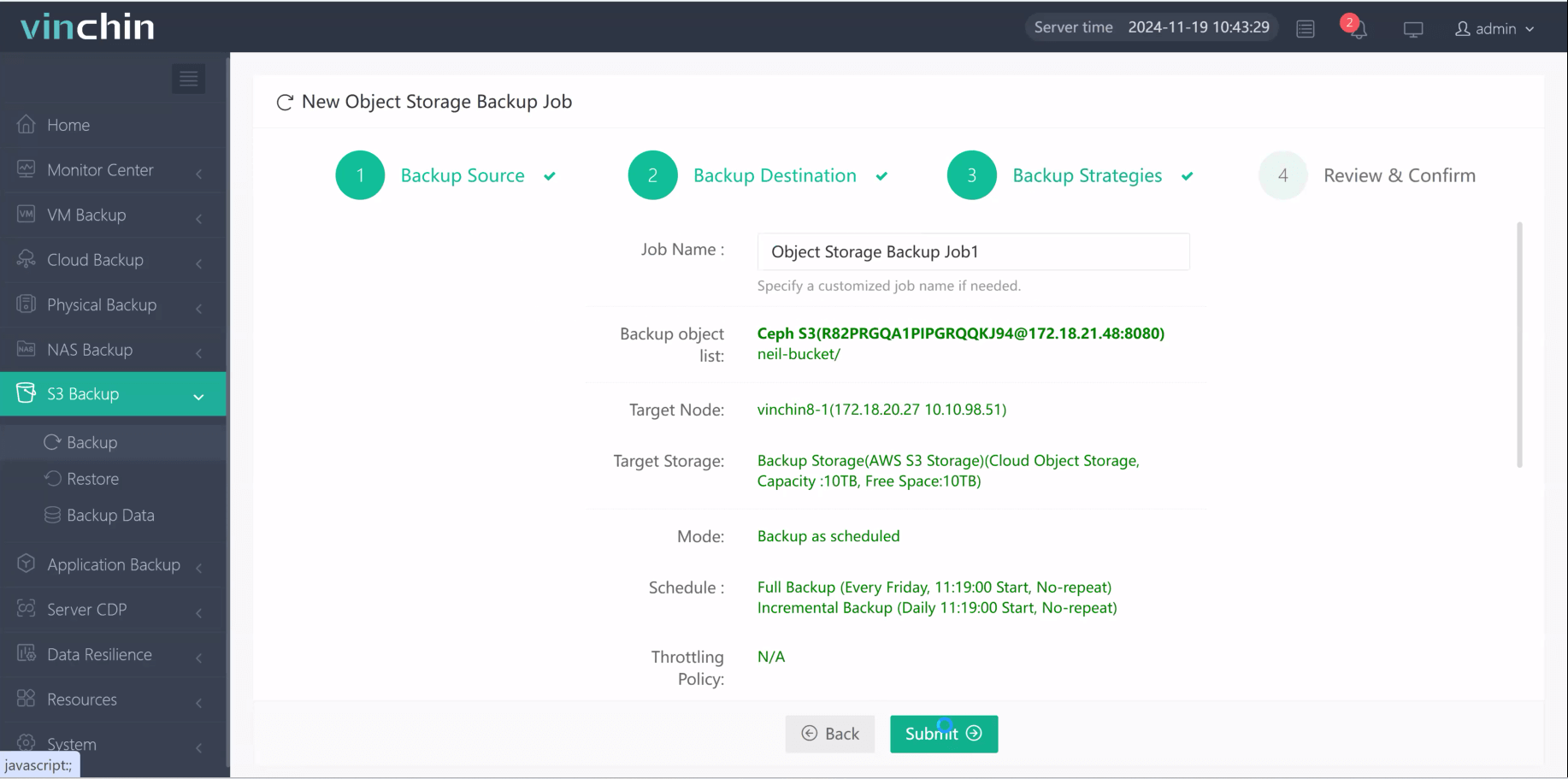
Recognized globally by thousands of enterprises and highly rated by IT professionals worldwide, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers a fully featured free trial valid for 60 days—click below to get started today!
Retention Lock Governance vs Compliance FAQs
Q1: How does retention lock interact with backup lifecycle policies?
Retention lock overrides standard lifecycle rules; locked backups remain undeletable until their set expiry regardless of scheduled cleanup routines.
Q2: Can legal holds extend an active compliance-mode lock beyond its original duration?
Yes; applying a legal hold pauses countdown timers so affected items stay protected indefinitely until released by authorized personnel following documented procedures.
Q3: What format does Vinchin export reports listing currently locked items?
Reports typically generate CSV output viewable in Excel/Notepad++ via EXPORT REPORT button within JOB HISTORY menu.
Conclusion
Retention lock protects vital records against loss or tampering—with governance offering flexibility while compliance guarantees strict immutability demanded by regulators worldwide:
Choose based on risk tolerance/regulatory exposure
Plan implementation carefully since choices are permanent per dataset
Test thoroughly before production rollout
Vinchin makes deploying either approach simple across diverse infrastructures—so safeguarding mission-critical assets has never been easier!
Share on:









