-
What Is Hadoop Cloud?
-
Why Choose Hadoop Cloud Solutions?
-
Method 1. Deploying Hadoop on Public Cloud Infrastructure (e.g., AWS EC2)
-
Method 2. Using Managed Hadoop Services (e.g., Amazon EMR, Google Dataproc)
-
Method 3. Running Hadoop on Containers With Kubernetes in the Cloud
-
How to Protect Hadoop Cloud Data With Vinchin?
-
Hadoop Cloud FAQs
-
Conclusion
Big data drives modern business decisions, and Apache Hadoop is a leading tool for processing it at scale. As data volumes grow fast, many organizations look for flexible ways to manage their clusters without heavy hardware investments or complex maintenance tasks. That’s why “hadoop cloud” solutions are gaining momentum worldwide—they combine distributed computing power with the agility of cloud platforms. In this guide, we’ll break down what hadoop cloud means, why it matters, how you can deploy it step by step, and how to protect your valuable data along the way.
What Is Hadoop Cloud?
Hadoop cloud refers to running Apache Hadoop clusters on virtualized cloud infrastructure instead of traditional physical servers. With hadoop cloud deployments, you can spin up clusters using virtual machines or managed services from major providers—scaling resources up or down as your workload changes without buying extra hardware or worrying about server failures.
You have several choices: install open-source Hadoop on your own VMs; use a managed service that handles setup and scaling; or run containerized Hadoop workloads on Kubernetes clusters in the cloud. Each approach offers different levels of control and automation but shares common benefits: pay-as-you-go pricing models, rapid provisioning times, built-in redundancy features, and easier integration with other modern IT tools.
Why Choose Hadoop Cloud Solutions?
Why do so many teams move their big data workloads to hadoop cloud environments? Flexibility is key—you can launch a cluster in minutes instead of weeks and adjust capacity instantly when demand spikes or drops off again.
Cost savings also matter: you only pay for what you use rather than over-provisioning hardware that sits idle much of the time. Plus, most clouds offer advanced security controls like encryption-at-rest and network isolation out-of-the-box—features that would take significant effort to implement yourself on-premises.
Finally, hadoop cloud solutions often integrate seamlessly with other services such as object storage (for scalable file management), analytics engines (for real-time insights), or machine learning platforms (for predictive modeling). For many organizations seeking speed-to-value with big data projects, moving Hadoop workloads into the cloud is an easy win.
Method 1. Deploying Hadoop on Public Cloud Infrastructure (e.g., AWS EC2)
Deploying Hadoop directly onto public cloud VMs gives you maximum flexibility over configuration while leveraging elastic compute resources behind the scenes. You’re responsible for setup—but also get full control over every detail of your environment.
First steps: choose your preferred provider (such as AWS) and create several virtual machines sized appropriately for NameNode(s), DataNodes, ResourceManager(s), NodeManagers—and optionally edge nodes if needed for client access or gateway functions. Select instance types based on expected CPU load and memory requirements; memory-optimized instances work well for HDFS-heavy jobs while compute-optimized ones suit YARN-intensive tasks best.
Set up secure networking using tools like VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) and configure firewall rules via Security Groups so only trusted users can reach cluster nodes remotely—this helps prevent unauthorized access right from day one.
Next comes software installation:
Install Java Development Kit (JDK) since Apache Hadoop depends on it.
Download a stable release from Apache’s official site.
Unpack files onto each VM.
Edit configuration files (core-site.xml, hdfs-site.xml, yarn-site.xml) according to your topology—for example:
<property> <name>fs.defaultFS</name> <value>hdfs://namenode-hostname:9000</value> </property>
Assign one node as primary NameNode; others become DataNodes storing actual blocks of information across disks in redundant fashion.
Format HDFS just once at initial setup:
hdfs namenode -format
Start core daemons:
start-dfs.sh start-yarn.sh
Access monitoring dashboards by visiting http://<NameNode-IP>:9870 if using Hadoop 3.x (50070 applies to older versions).
To submit jobs:
Use
hadoop jarcommand-line interface.Or interact through YARN ResourceManager web UI at port
8088.
Remember: ongoing monitoring is vital! Set up log collection agents or connect metrics output to centralized dashboards so you catch issues early before they impact production workloads.
Optimizing Performance and Cost
Running hadoop cloud clusters efficiently requires tuning both performance settings and spending habits:
Right-size VM types based on job profiles—don’t overspend on high-memory nodes unless truly needed.
Consider spot/preemptible instances for non-critical DataNodes; these save money but may be interrupted unexpectedly.
Store temporary files locally but write critical outputs directly into durable object storage buckets when possible.
Automate cluster shutdown during idle periods using scripts tied into job schedulers—cloud billing stops when VMs are powered off!
Method 2. Using Managed Hadoop Services (e.g., Amazon EMR, Google Dataproc)
Managed services simplify everything by automating provisioning tasks—from spinning up worker nodes to patching software stacks behind the scenes—all accessible through user-friendly web consoles or APIs.
To deploy a hadoop cloud cluster using Amazon EMR:
1. Open the EMR console online.
2. Click Create cluster button.
3. Pick desired software release version (“emr-x.x”), select core applications (Hadoop, plus optional Spark/Hive/Pig).
4. Choose instance types/sizes matching workload needs.
5. Configure networking/security settings including IAM roles for least privilege access control.
6. Click Create cluster again—the platform handles bootstrapping automatically!
For Google Dataproc:
1. Go to the Dataproc dashboard inside Google Cloud Console.
2. Click Create cluster link at top right corner.
3. Specify region/zone preferences plus number/type of worker VMs required.
4. Under Components section check box next to “Hadoop.”
5a.(Optional) Use CLI instead:
gcloud dataproc clusters create my-cluster --region=us-central1 --num-workers=3 --image-version=2.1-debian10 --optional-components=HADOOP
Check Google’s documentation regularly since image versions update frequently.
Once live:
Submit jobs via web UIs, command-line tools, or REST APIs depending on workflow preference; store datasets inside native object stores like S3/GCS which integrate natively with HDFS connectors.
Method 3. Running Hadoop on Containers With Kubernetes in the Cloud
Containerization brings portability, rapid scaling, and easier upgrades compared with classic VM-based deployments— especially useful if your organization already uses microservices architecture elsewhere!
Start by creating a managed Kubernetes cluster via services like GKE (Google), EKS (AWS), or AKS (Azure).
Next, deploy containerized versions of NameNode/DataNode/ResourceManager/NodeManager pods either via maintained Helm charts:
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami helm install my-hadoop bitnami/hadoop
Or apply custom YAML manifests sourced from Apache’s official repository:
kubectl apply -f hadoop-cluster.yaml
Kubernetes orchestrates pod scheduling, health checks, and rolling updates automatically; you define resource limits per pod so no single job starves others out during busy periods.
Handling Persistent Storage in Kubernetes
Persistent storage is crucial since containers are ephemeral by design:
Use PersistentVolumeClaims mapped onto block storage volumes provided by your chosen public cloud;
here’s an example snippet:
apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: datanode-pvc spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 500Gi
Alternatively, connect HDFS directly with S3-compatible endpoints using community-supported connectors—
this enables hybrid workflows spanning both local disks AND remote buckets seamlessly.
How to Protect Hadoop Cloud Data With Vinchin?
While robust storage architectures like Hadoop HDFS provide inherent resilience, comprehensive backup remains essential for true data protection. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-grade solution purpose-built for safeguarding mainstream file storage—including Hadoop HDFS environments—as well as Windows/Linux file servers, NAS devices, and S3-compatible object storage. Specifically optimized for large-scale platforms like Hadoop HDFS, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers exceptionally fast backup speeds that surpass competing products thanks to advanced technologies such as simultaneous scanning/data transfer and merged file transmission.
Among its extensive capabilities, five stand out as particularly valuable for protecting critical big-data assets: incremental backup (capturing only changed files), wildcard filtering (targeting specific datasets), multi-level compression (reducing space usage), cross-platform restore (recovering backups onto any supported target including other file servers/NAS/Hadoop/object storage), and integrity check (verifying backups remain unchanged). Together these features ensure efficient operations while maximizing security and flexibility across diverse infrastructures.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers an intuitive web console designed for simplicity. To back up your Hadoop HDFS files:
Step 1. Select the Hadoop HDFS files you wish to back up
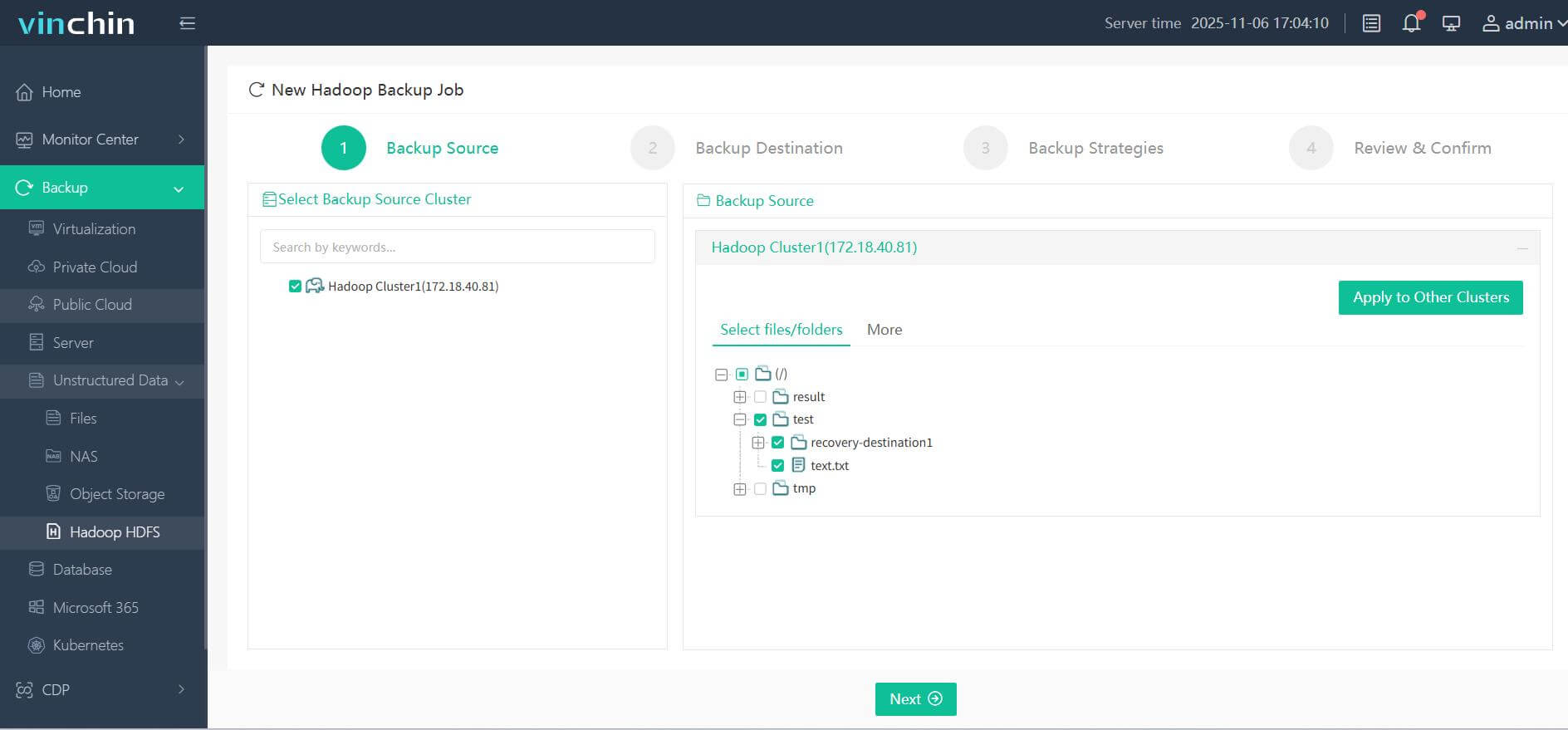
Step 2. Choose your desired backup destination
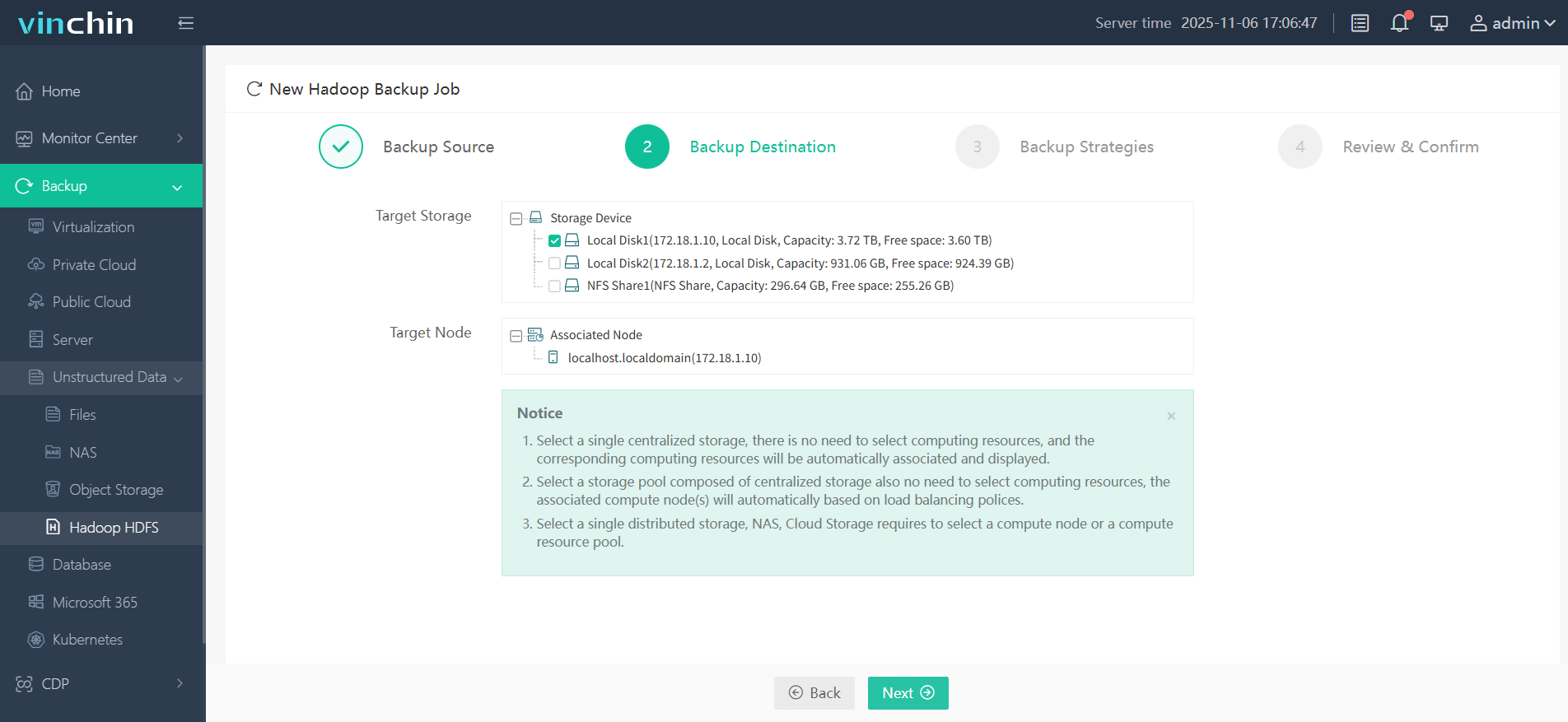
Step 3. Define backup strategies tailored for your needs
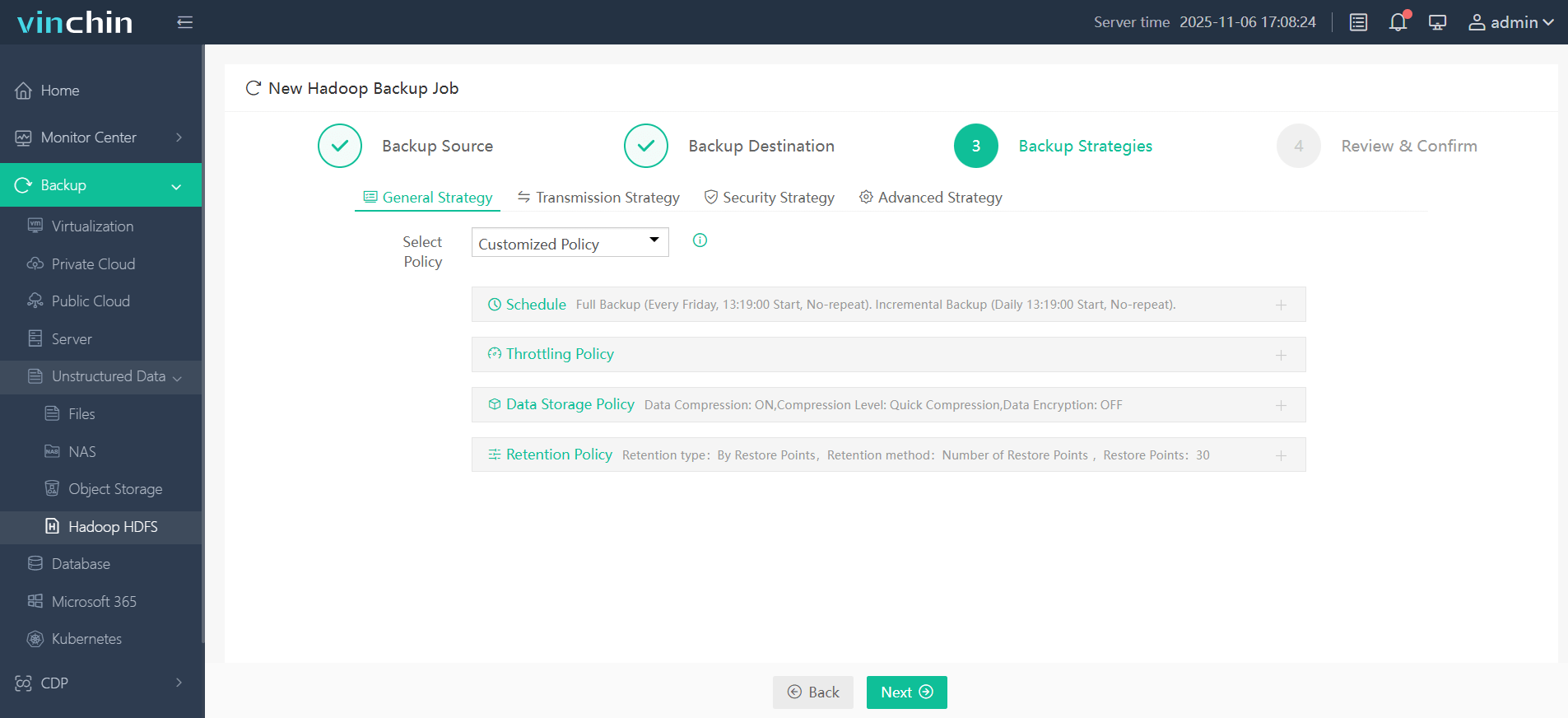
Step 4. Submit the job
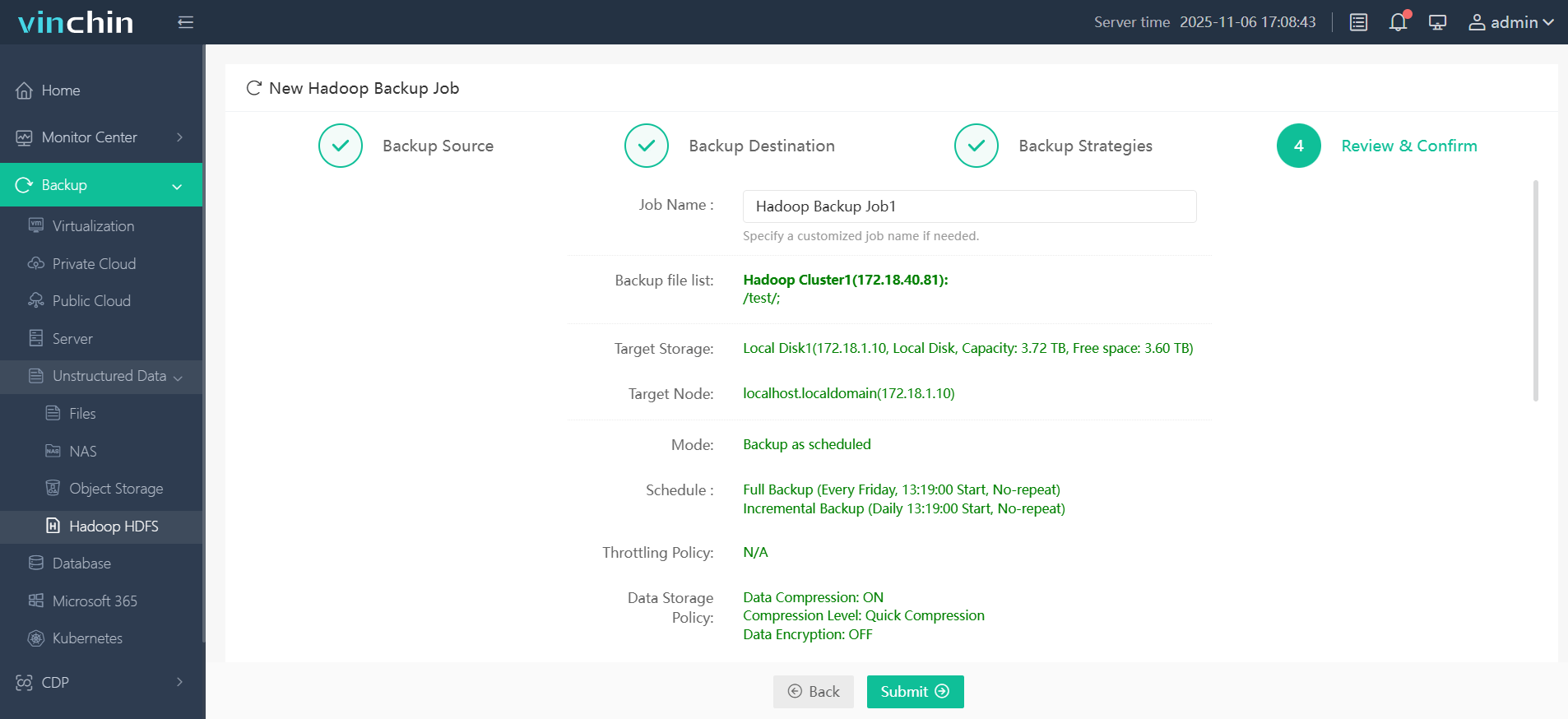
Join thousands of global enterprises who trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery—renowned worldwide with top ratings—for reliable data protection. Try all features free with a 60-day trial; click below to get started!
Hadoop Cloud FAQs
Q1: Can I automate daily health checks across multiple hadoop cloud clusters?
A1: Yes—use cron jobs combined with REST API calls against each platform's monitoring endpoints for scheduled status reporting across all environments.
Q2: What should I do if my managed hadoop service hits its default quota limit?
A2: Request quota increases through your provider's support portal before launching additional nodes/jobs during peak periods.
Q3: How do I enable encryption-at-rest for my hadoop data stored in public clouds?
A3: Activate built-in encryption features within S3/GCS/Azure Blob Storage settings then reference those encrypted buckets within core-site.xml configurations.
Conclusion
Moving Apache Hadoop workloads into the cloud unlocks flexibility, cost savings, and seamless integration opportunities not possible with legacy infrastructure alone. Whether deploying manually, using managed services, or embracing containers/Kubernetes—you gain agility without sacrificing control over big data pipelines. Protect every workload confidently using Vinchin’s robust backup features today!
Share on:









