-
What is a SQL Server Database?
-
Method 1: Downloading SQL Server Software
-
Method 2: Downloading Sample Databases
-
Method 3: Exporting and Downloading Existing Databases
-
Effortless Backup & Recovery with Vinchin
-
SQL Server Database Download FAQs
-
Conclusion
Need to perform a SQL Server databases download? Whether you are testing, developing, or migrating data, this task is common in IT operations. Many administrators must download SQL Server software, sample databases, or export existing databases for local use. This guide walks you through every scenario—from beginner basics to advanced automation—using clear steps and trusted resources.
What is a SQL Server Database?
A SQL Server database is a structured set of data managed by Microsoft SQL Server. This relational database management system (RDBMS) stores information in tables and supports transactions. It offers tools for querying, reporting, analytics, and security. Organizations of all sizes rely on SQL Server—from small business applications to large enterprise systems.
SQL Server databases are popular because they combine reliability with advanced features like high availability, encryption, and scalability. Knowing how to download or export databases is essential for IT administrators and developers alike.
Method 1: Downloading SQL Server Software
Before working with any database files or backups, you need the SQL Server engine installed on your system. Microsoft provides several editions—some free—that cover different use cases.
Quick Start with Free Editions
If you need a lightweight or test environment, download the Express or Developer edition from Microsoft’s official site:
Go to the official SQL Server downloads page.
Download SQL Server 2022 Express or SQL Server 2022 Developer.
Run the installer and choose Basic for quick setup or Custom for more control.
Accept license terms and complete installation.
(Optional) Install SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to manage databases via GUI.
Customizing Your Installation
Choose Custom installation if you want control over:
Which components (e.g., Full-Text Search, Reporting Services) are installed
Installation directories
Instance naming
Network configurations
Each feature in the installer includes a description to guide your decisions.
Automating Installation with Command Line or Docker
For repeatable deployments:
Command-line install with configuration files:
setup.exe /ConfigurationFile=MyConfig.ini /Q
Docker install:
docker pull mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest docker run -e 'ACCEPT_EULA=Y' -e 'SA_PASSWORD=YourStrong!Passw0rd' \ -p 1433:1433 --name sql2022 -d mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2022-latest
⚠️ Common issues include missing prerequisites, port conflicts (default TCP 1433), and insufficient permissions. Always run installers as Administrator.
Method 2: Downloading Sample Databases
Sample databases are great for demos, training, and testing without touching production systems. Microsoft provides well-known options such as AdventureWorks and Northwind.
Restore from Backup File
Download the
.bakfile from Microsoft’s sample database page.Copy it to your SQL Server backup directory (find it with:
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('InstanceDefaultDataPath')In SSMS, right-click Databases → Restore Database….
Select Device, add the
.bakfile, and confirm to restore.The database will appear in SSMS after restore completes.
Build with Scripts
Some samples are provided as .sql scripts (e.g., Northwind).
Open the script in SSMS.
Connect to your SQL Server instance.
Run the script with F5 to create schema and insert data.
This method is flexible—you can edit tables or data before execution.
Automating with PowerShell or T-SQL
For large environments, automate restores with scripts:
Invoke-Sqlcmd -Query "RESTORE DATABASE [AdventureWorks] FROM DISK='C:\Backups\AdventureWorks.bak' WITH MOVE 'AdventureWorks_Data' TO 'D:\MSSQL\Data\AdventureWorks.mdf', MOVE 'AdventureWorks_Log' TO 'D:\MSSQL\Data\AdventureWorks.ldf'"
Always verify restored databases with:
DBCC CHECKDB('AdventureWorks')Method 3: Exporting and Downloading Existing Databases
Exporting lets you back up databases, migrate workloads, or move subsets of data between servers.
Full Database Backup with SSMS
Open SSMS, right-click the target database → Tasks → Back Up…
Set Backup type = Full.
Specify destination path (e.g.,
C:\Backups\MyDatabase.bak).Click OK to create the
.bakfile.
The resulting backup file can be restored anywhere.
Selective Data Export
If you only need certain tables or rows:
Right-click the database → Tasks → Export Data…
Select destination format (CSV, Excel, or another DB).
Choose objects and mappings.
This is useful for dev/test data movement without full backups.
Using BACPAC Files & T-SQL Automation
For migrations and schema+data export:
BACPAC file:
Right-click DB → Tasks → Export Data-tier Application…
Save the
.bacpaclocally or to cloud storage.Automated backup:
BACKUP DATABASE [MyDatabase] TO DISK = 'C:\Backups\MyDatabase.bak'RESTORE VERIFYONLY FROM DISK = 'C:\Backups\MyDatabase.bak'
Jobs or scripts can schedule recurring exports for ongoing protection.
Effortless Backup & Recovery with Vinchin
Native SQL Server tools are powerful, but many businesses need more automation, advanced features, and ransomware protection. Vinchin Backup & Recovery provides:
Incremental backup with compression and deduplication
Flexible batch database backup
Automated backup verification
Granular recovery options
The intuitive web console allows database protection in four steps:
Step 1—Select the Microsoft SQL Server instance you wish to back up;
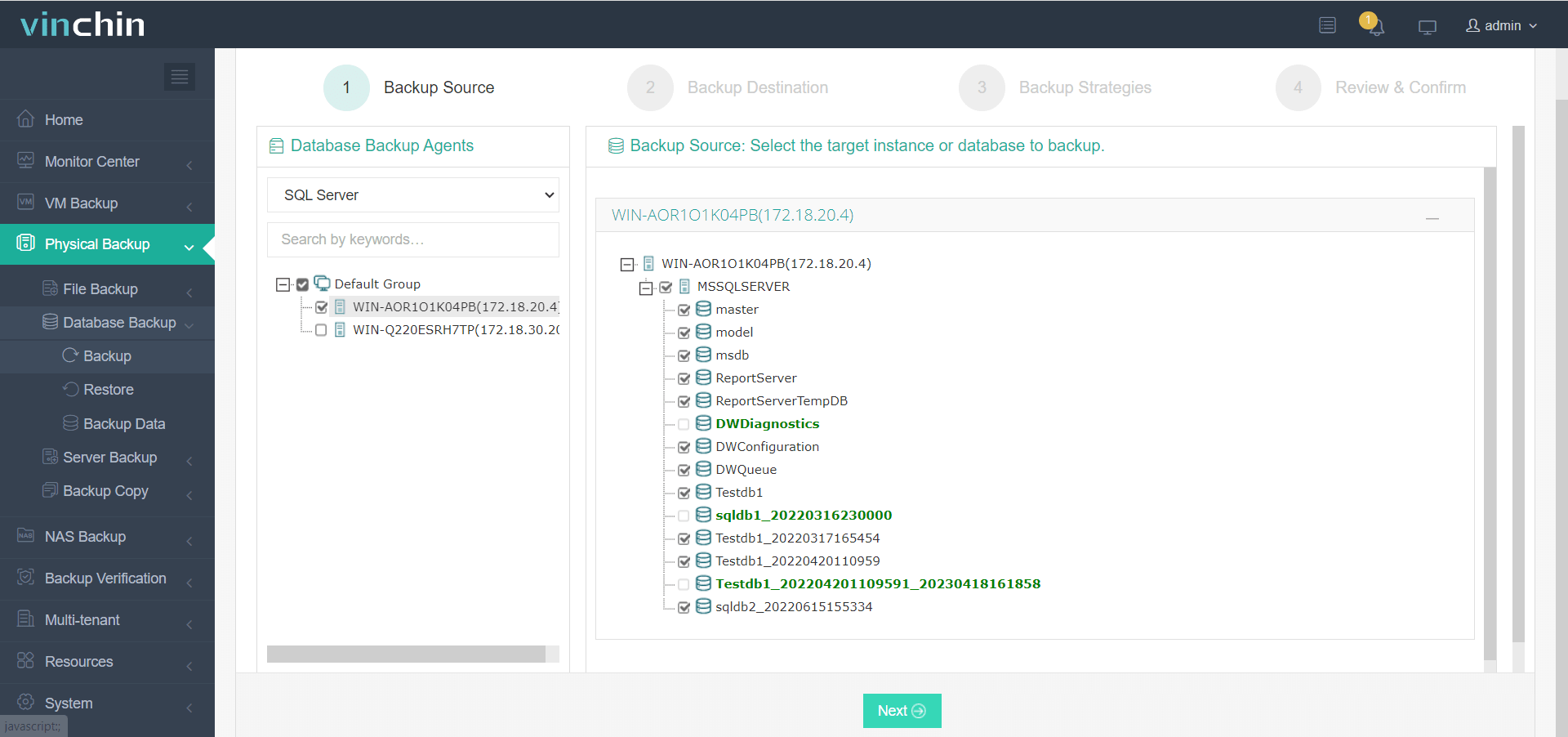
Step 2—Choose the desired storage target;
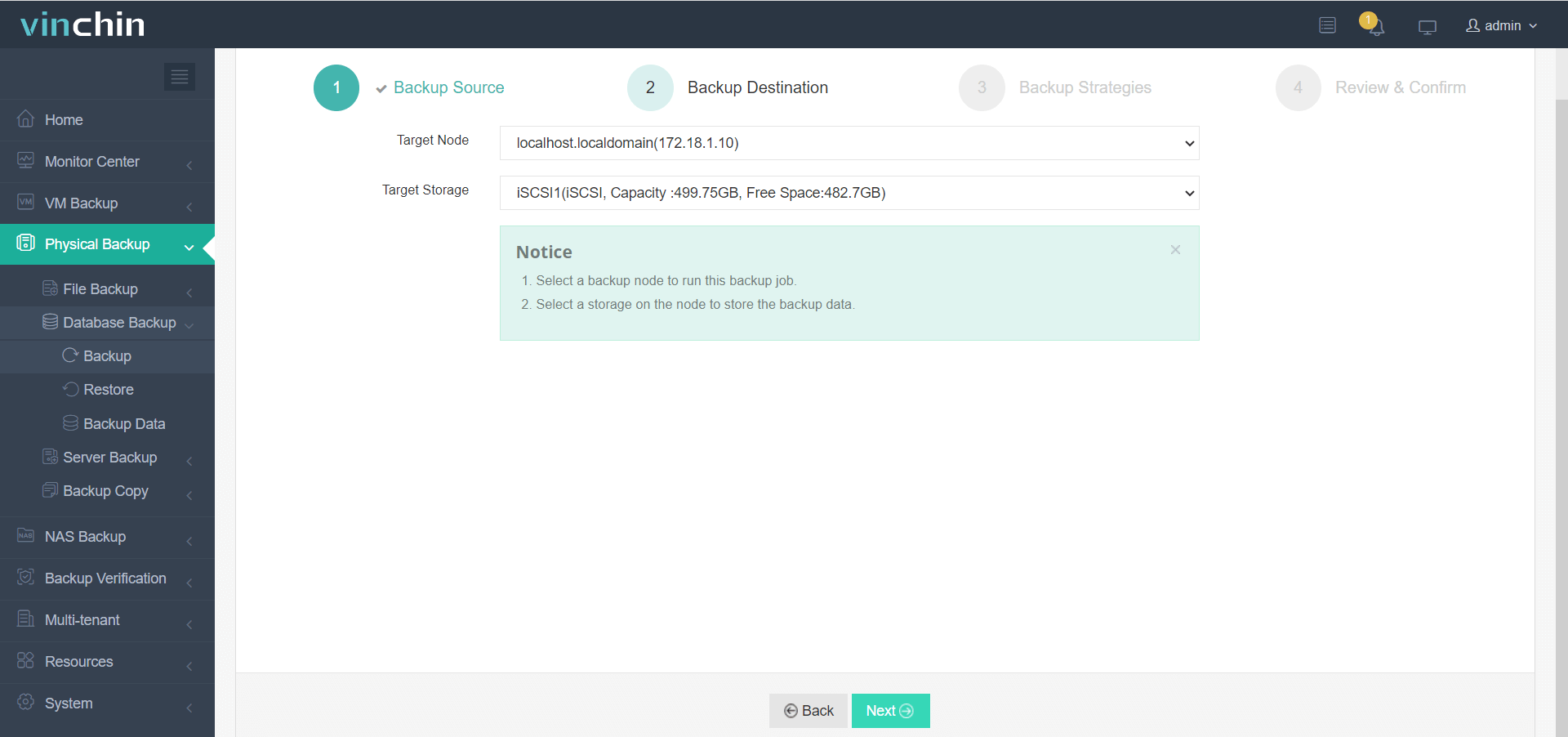
Step 3—Define scheduling and retention strategies according to business requirements;

Step 4—Submit the job.
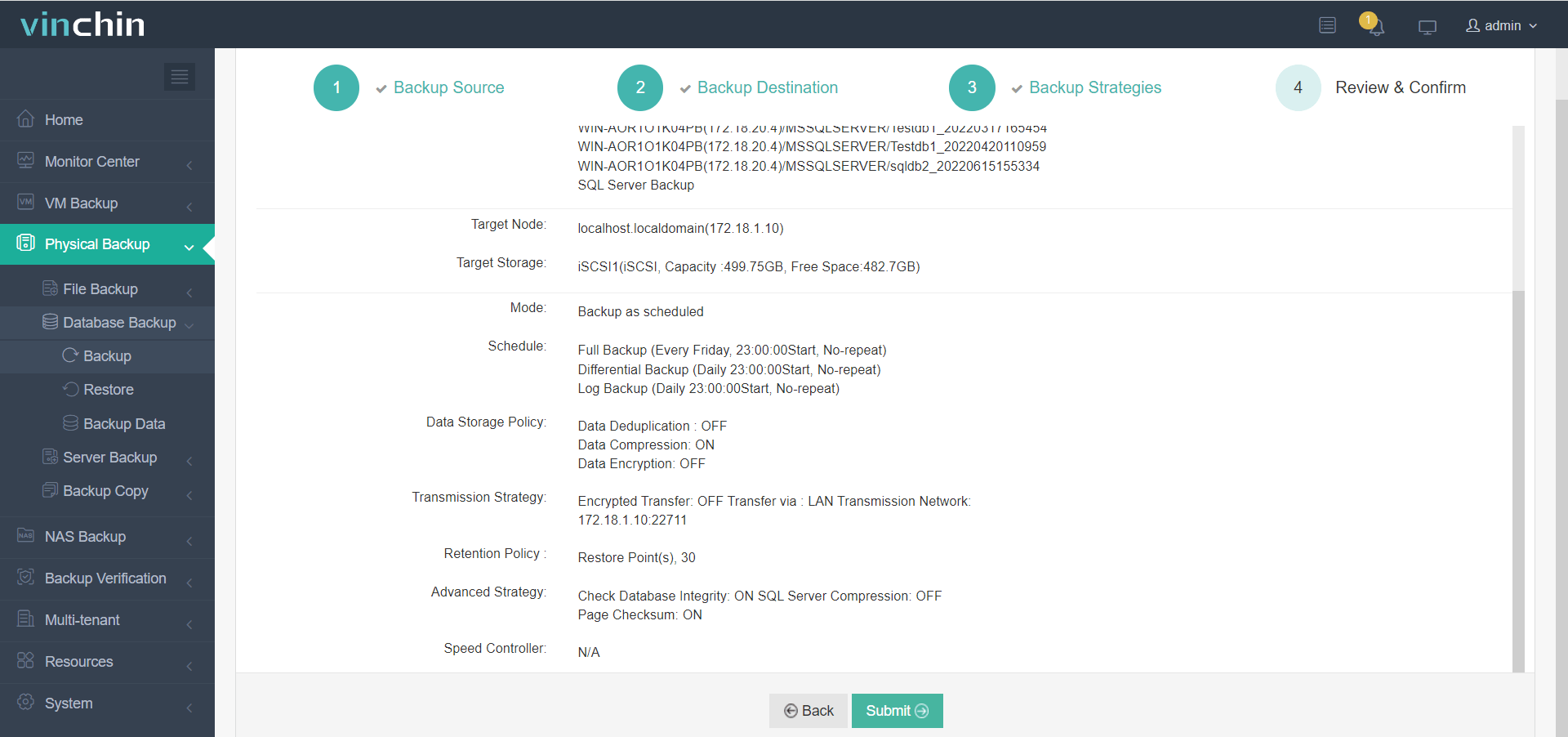
Thousands of enterprises rely on Vinchin worldwide. A 60-day free trial is available to experience the platform.
SQL Server Database Download FAQs
Q1: Can I download older versions of SQL Server if my application requires them?
Yes; visit Microsoft's archive pages linked from their main downloads site—they offer previous releases alongside documentation about end-of-support dates.
Q2: How do I fix permission denied errors when restoring .bak files?
Right-click SSMS shortcut > Run as Administrator > Ensure .bak file resides in accessible folder such as C:\Temp—not user profile directories restricted by UAC policies.
Q3: What should I do if my restored database shows “Suspect” status?
Run DBCC CHECKDB ('YourDatabase') WITH NO_INFOMSGS; If corruption found restore clean backup else consult logs/error messages before attempting repair commands.
Conclusion
Downloading software packages, importing samples—or exporting live data—is straightforward once familiar with these methods! Each step ensures safe handling whether learning new skills/testing code/migrating workloads securely between platforms/environments alike! For robust automated protection look no further than Vinchin's proven solutions tailored specifically toward modern IT operations teams worldwide!
Share on:








