-
What Is Oracle RMAN Incremental Backup?
-
Why Use Incremental Backups in Oracle?
-
How to Perform a Level 0 Incremental Backup with RMAN?
-
How to Perform a Level 1 Incremental Backup with RMAN?
-
Vinchin Backup & Recovery for Oracle Database Protection
-
Oracle RMAN Incremental Backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Protecting your Oracle database is one of the most important jobs for any operations administrator. But do you really need to back up every data block every time? Not always. With Oracle RMAN incremental backup, you only save what has changed since your last backup. This approach saves time, storage space, and network resources compared to full-only or archive log shipping strategies.
In this article, you'll learn what Oracle RMAN incremental backup is, why it matters for modern database environments, how to use it step by step—from beginner basics to advanced options—and which best practices can help you get the most out of this powerful tool.
What Is Oracle RMAN Incremental Backup?
Oracle RMAN (Recovery Manager) incremental backup is a method that copies only those data blocks that have changed since a previous backup was taken. Unlike a full backup—which includes every used block in your database—an incremental backup focuses on efficiency by targeting just the changes.
You can run an incremental backup on the whole database or narrow it down to specific tablespaces or even single datafiles. RMAN tracks all changes using system change numbers (SCNs), so it knows exactly which blocks need protection each time you run a job.
This targeted approach reduces both the size of your backups and how long they take to complete—a big advantage when working with large or busy databases where downtime must be kept short.
Why Use Incremental Backups in Oracle?
Incremental backups offer several advantages over traditional full backups:
First, they save storage space because only changed blocks are backed up after your initial baseline copy. Second, they reduce your overall backup window—meaning users have more access time while maintenance runs quietly in the background. Third, they use less network bandwidth during remote or cloud-based backups.
Another key benefit: faster recovery times. Since RMAN applies changes at the block level instead of replaying every transaction from archived logs alone, restores can finish much quicker after an incident.
When should you choose incremental backups? If your database handles frequent updates or grows rapidly—or if minimizing resource usage is critical—increments help keep infrastructure demands under control without sacrificing safety.
For very small databases with little daily change or where simplicity is preferred over optimization, frequent full backups might still make sense; but as complexity grows so does the value of incrementals.
How to Perform a Level 0 Incremental Backup with RMAN?
A level 0 incremental backup forms the foundation of any effective incremental strategy in Oracle RMAN. Think of it as your baseline image—all future increments build upon this snapshot.
Without a recent level 0 backup available for reference, you cannot perform valid level 1 incrementals; if you try anyway, RMAN will create one automatically before proceeding.
To perform a level 0 incremental backup with RMAN:
1. Start RMAN and connect to your target database
Open a terminal window and enter:
rman TARGET /
Or connect remotely using:
rman TARGET sys@yourdb
2. Run the level 0 incremental backup command
At the prompt type:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 DATABASE;
This command backs up all used blocks across your entire database into a new set.
3. (Optional) Add tags for easier management
You can label this base copy for tracking purposes:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 DATABASE TAG 'MONTHLY_BASE';
4. (Optional) Include archived logs
To capture both datafiles and all archived redo logs together:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;
5. (Optional) Target specific tablespaces or datafiles
For focused protection:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 TABLESPACE users; BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 DATAFILE 4;
6. Monitor progress
Watch output messages as files are processed; review logs afterward for errors or warnings.
A well-timed level 0 ensures that subsequent incrementals remain efficient—and keeps restore chains simple when disaster strikes later on.
How to Perform a Level 1 Incremental Backup with RMAN?
Level 1 incrementals are where real savings begin—they copy only those blocks changed since either your last level 0 (baseline) or another recent level 1 (depending on type).
There are two main types: differential and cumulative increments.
By default, running BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 creates differential increments unless specified otherwise.
Let’s break down both approaches:
Differential Level 1 Incremental Backup
A differential level 1 captures all changes made since either your last successful level 0 or another differential/cumulative level 1—whichever came most recently.
This method keeps each individual job small but may require applying multiple increments during recovery if many exist between failures.
Here’s how:
1. Start RMAN and connect
2. Run differential command
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 DATABASE;
3. (Optional) Focus on tablespace/datafile
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 TABLESPACE users; BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 DATAFILE 4;
Cumulative Level 1 Incremental Backup
Cumulative increments gather all changes made since just the last baseline (level 0)—ignoring any intermediate differentials.
The result? Slightly larger jobs each time but simpler/faster restores later because only one increment needs application after restoring from baseline.
Steps:
1. Start RMAN and connect
2. Run cumulative command
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 CUMULATIVE DATABASE;
3. (Optional) Focus on tablespace/datafile
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 CUMULATIVE TABLESPACE users; BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 CUMULATIVE DATAFILE 4;
Which should you choose? Differential backups minimize daily storage impact but may slow down recovery if many must be applied sequentially; cumulative ones write more upfront yet streamline disaster response by reducing restore steps. Consider workload patterns: high-change environments often favor differentials; mission-critical systems needing rapid restores may prefer cumulatives despite their size.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery for Oracle Database Protection
For organizations seeking streamlined enterprise-grade protection beyond native tools like RMAN, Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers robust support for today’s leading databases—including Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, PostgresPro, and TiDB—with special emphasis on comprehensive Oracle coverage featured here. Key capabilities include advanced source-side compression and incremental backup tailored specifically for Oracle workloads alongside batch database operations, flexible retention policies such as GFS retention policy integration, and multi-level data compression options—all designed to optimize storage use while ensuring fast recoverability across complex environments.
Among its many features relevant to enterprise deployments are log/archived log backups with any-point-in-time recovery support; scheduled cloud/tape archiving; strong storage protection against ransomware alteration; WORM compliance safeguards; integrity checks plus automated recovery verification via SQL scripts—delivering reliability without added complexity through unified management workflows that simplify compliance and operational assurance alike.
The intuitive web console makes protecting an Oracle environment straightforward:
Step 1—Select the Oracle database to back up;
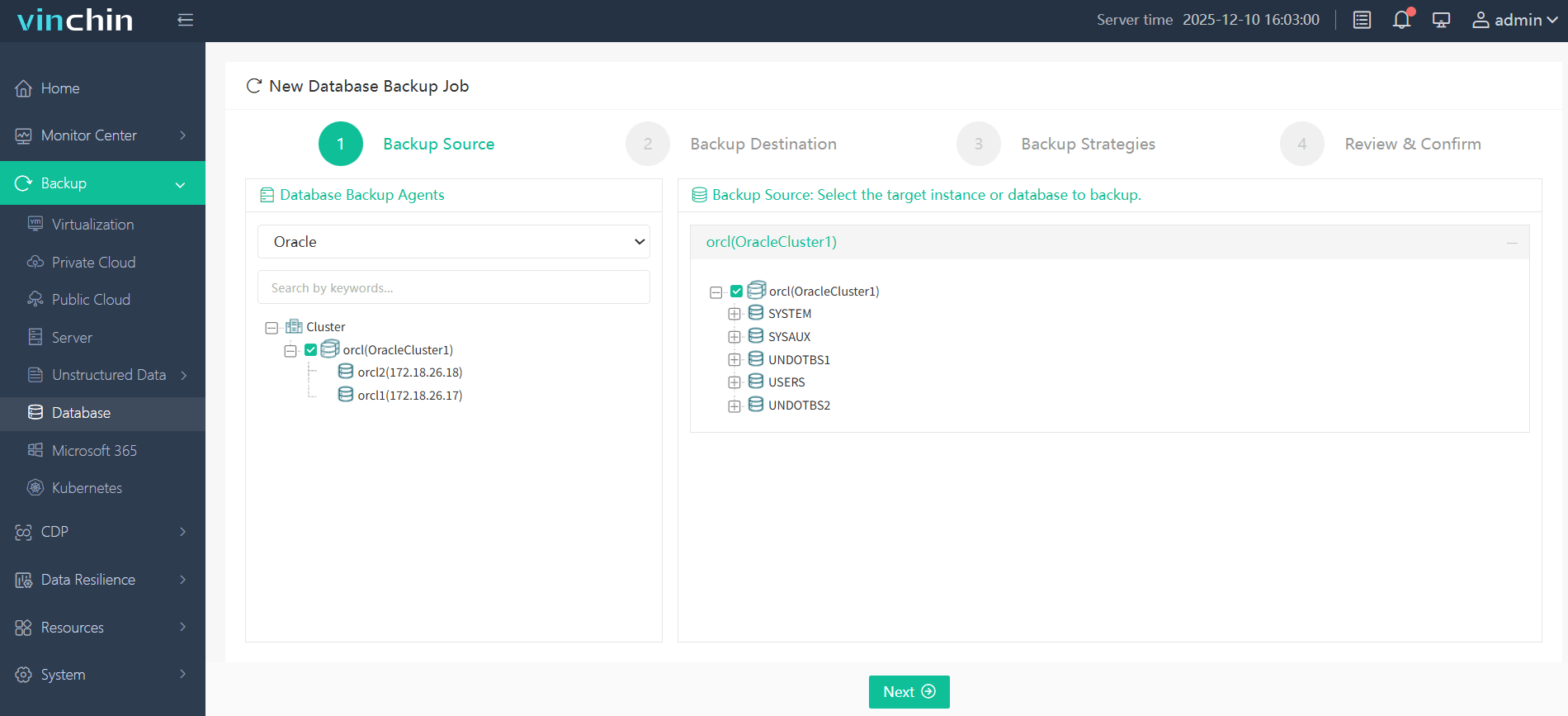
Step 2—Choose the backup storage location;
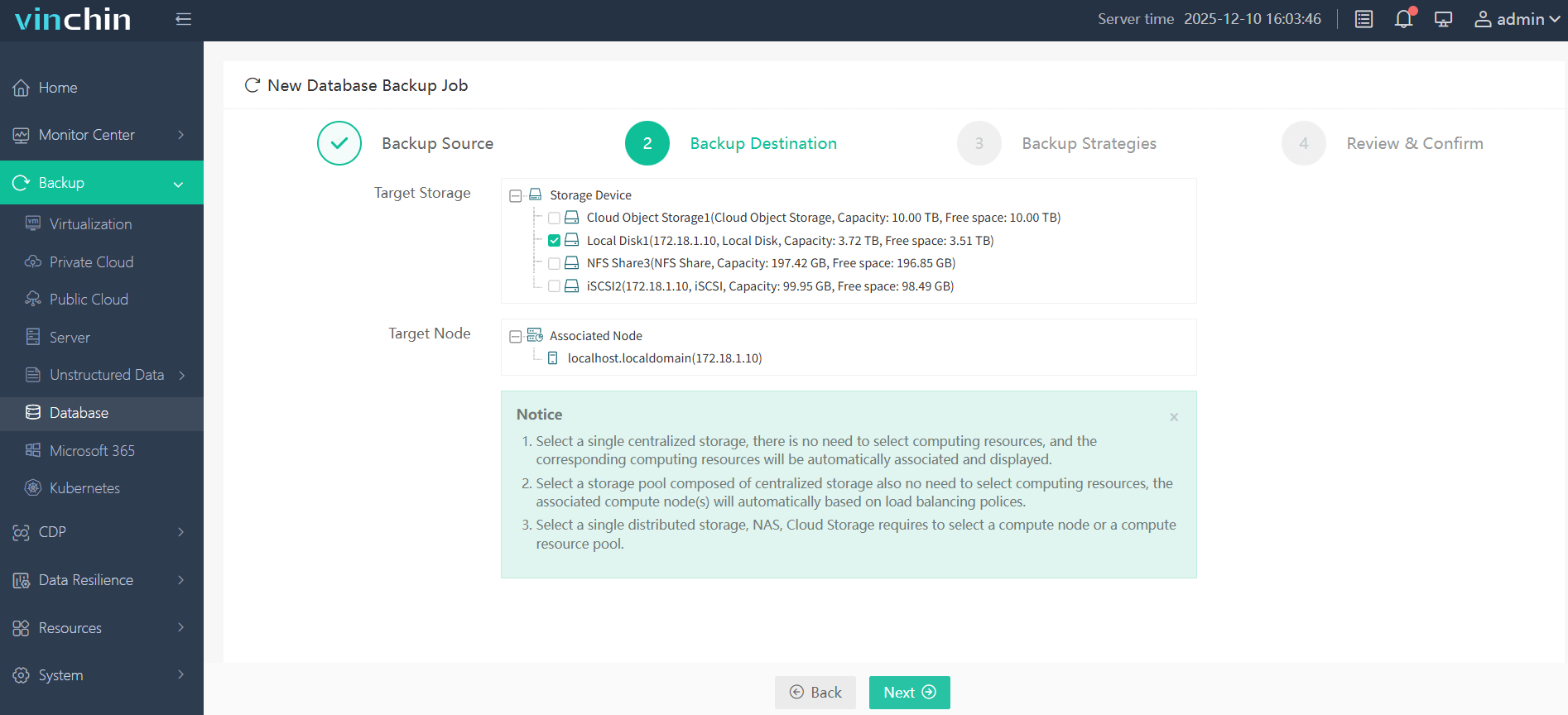
Step 3—Define the backup strategy according to business needs;
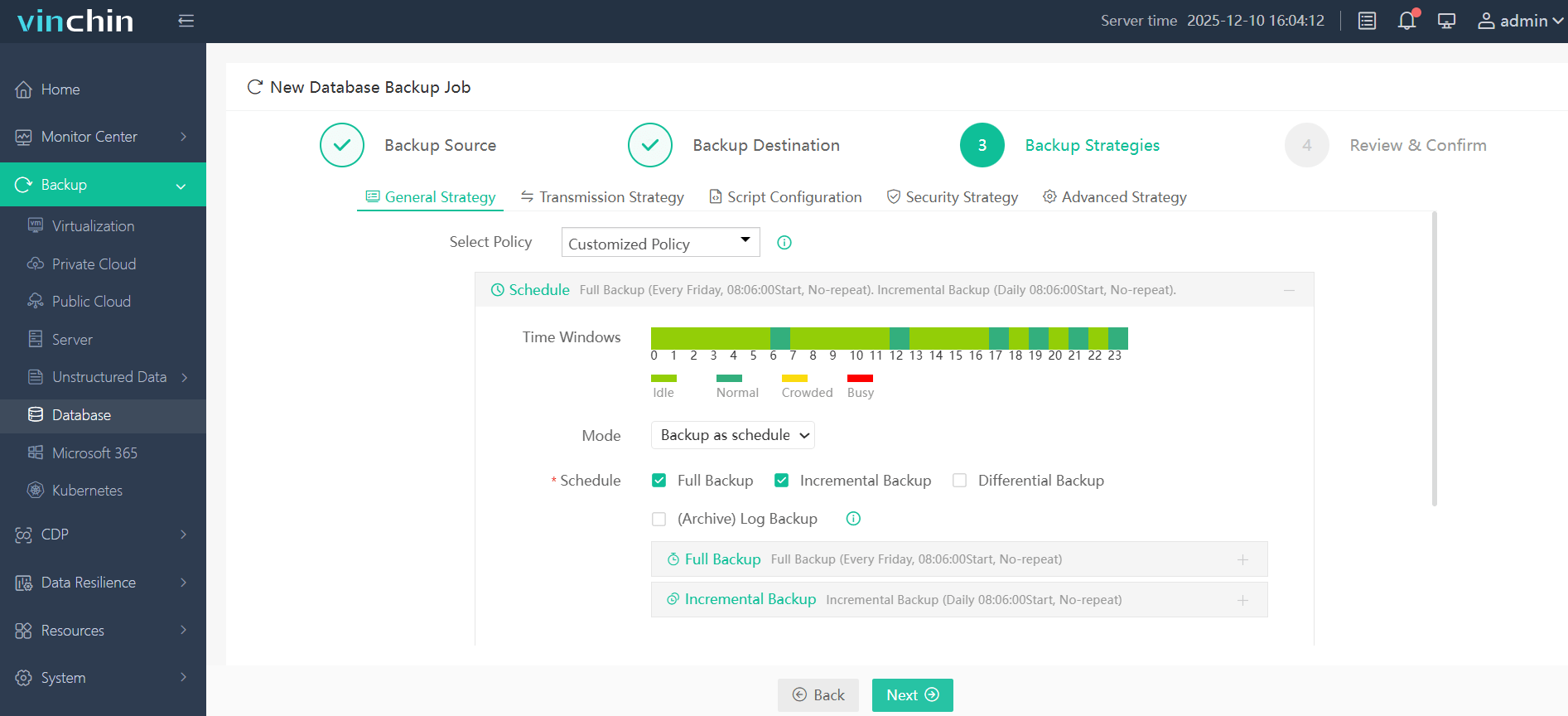
Step 4—Submit the job with just a few clicks for fully automated execution end-to-end.
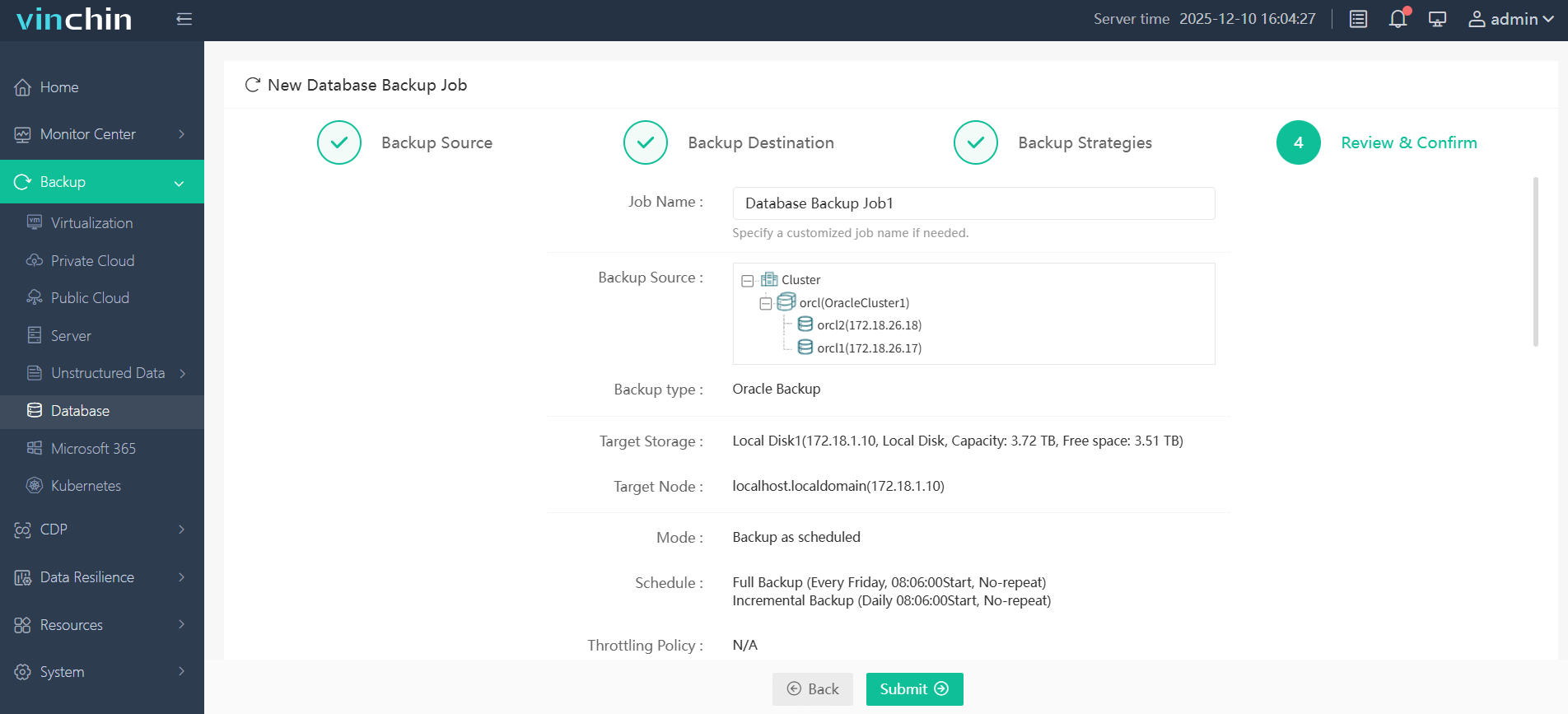
Vinchin Backup & Recovery enjoys global recognition among enterprises seeking trusted data-protection software solutions—with thousands of satisfied customers worldwide and top industry ratings. Try our fully featured free trial now (60 days)—click download below!
Oracle RMAN Incremental Backup FAQs
Q1: Can I schedule automatic daily incremental backups with RMAN?
Yes—you can use cron jobs or Windows Task Scheduler combined with shell scripts calling appropriate rman commands for automation.
Q2: What happens if my Block Change Tracking file becomes corrupted?
Disable BCT using ALTER DATABASE DISABLE BLOCK CHANGE TRACKING, then re-enable it—the next full scan rebuilds tracking info automatically without affecting existing backups.
Q3: How do I verify my latest incremental chain covers all necessary changes?
Use REPORT NEED BACKUP in RMAN—it highlights gaps requiring attention so nothing gets missed during planned recoveries.
Conclusion
Oracle RMAN incremental backup helps administrators save time and storage while protecting vital business data efficiently. For even greater convenience, Vinchin delivers powerful,easy-to-use solutions supporting advanced features.Download our free trial now—and simplify enterprise-grade protection today!
Share on:








