-
What is Physical Server Backup Software?
-
Why Use Physical Server Backup Software?
-
Features of Physical Server Backup Software
-
Method 1: Using Built-in Tools (Windows Server Backup and Linux Utilities)
-
How Vinchin Backup & Recovery Secures Your Physical Servers?
-
Physical Server Backup Software FAQs
-
Conclusion
Physical servers are the backbone of many IT environments. Even as virtualization grows, many businesses still rely on physical machines for critical workloads. Protecting these servers from data loss is essential. That’s where physical server backup software comes in. Let’s explore what it is, why you need it, and how to use it—step by step.
What is Physical Server Backup Software?
Physical server backup software is a tool that copies data, system files, and configurations from a physical server to a safe location. This backup can be used to restore the server after hardware failure, cyberattack, or accidental deletion. Unlike virtual server backup, which often uses snapshots and agentless methods, physical server backup usually works at the disk or file level and may require an agent on the server.
Physical server backup software supports a range of operating systems, including Windows Server, Ubuntu, RHEL, SLES, Rocky Linux, Oracle Linux, and Debian. It is designed to handle the unique challenges of protecting real hardware, such as driver dependencies and hardware-specific configurations.
Why Use Physical Server Backup Software?
Physical servers face many risks. Hardware can fail without warning. Ransomware can encrypt files and demand payment. Human error can wipe out important data. When a physical server goes down, the impact can be severe—lost productivity, missed deadlines, and even lost revenue.
A good backup solution helps you recover quickly. It lets you restore files, applications, or even the entire system to the same or new hardware. This reduces downtime and keeps your business running. For compliance, regular backups are often required by law or industry standards.
Features of Physical Server Backup Software
Modern physical server backup software offers a range of features to make data protection easy and reliable. Here are some of the most important:
Full and Incremental Backups:
Full backups copy everything, while incremental backups only copy changes since the last backup. This saves time and storage.
Scheduling and Automation:
You can set backups to run at night or during low-traffic periods, so they don’t disrupt business.
Encryption and Security:
Backups can be encrypted to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Deduplication and Compression:
These features reduce the size of backups, saving storage space and speeding up transfers.
Centralized Management:
Many solutions offer a web console or dashboard to manage backups across multiple servers.
Flexible Recovery Options:
Restore a single file, a folder, or the entire system as needed.
Application Awareness:
Some tools can back up databases and applications in a consistent state, using technologies like Microsoft VSS.
These features help ensure that your backups are reliable, secure, and easy to manage.
Method 1: Using Built-in Tools (Windows Server Backup and Linux Utilities)
Many administrators start with built-in tools. These are free and included with most operating systems but they have limitations.
For Windows Servers:
Windows Server Backup is the standard tool for backing up physical Windows servers. It supports full server, system state, and file-level backups.
To use Windows Server Backup:
1. Open Server Manager and click Add roles and features.
2. In the wizard, select Windows Server Backup under Features and install it.
3. After installation, open Windows Server Backup from the Tools menu.
4. Click Local Backup and then Backup Once or Backup Schedule to start the wizard.
5. Choose Full server or Custom to select specific volumes or files.
6. Select the backup destination (local disk, external drive, or network share).
7. Review the settings and click Finish to start the backup.
Restoring is just as simple. Use the Recover option in the same console; select the backup; follow prompts to restore files or entire server.
For Linux Servers:
Linux does not have a single built-in backup tool but utilities like rsync & tar are widely used.
To back up with rsync:
rsync -avh /source/directory/ /backup/directory/
This command copies files from source to backup directory preserving permissions/timestamps.
To create compressed archive with tar:
tar -czvf backup.tar.gz /directory/to/backup
This creates compressed file containing all data from specified directory.
Restoring is reverse: use rsync/tar -xzvf accordingly.
While powerful these tools require manual setup/scripting for automation/monitoring/retention policies & lack deduplication/centralized management features.
How Vinchin Backup & Recovery Secures Your Physical Servers?
For organizations seeking robust enterprise-grade protection beyond built-in utilities—especially those running mainstream platforms like Windows Server—Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers comprehensive coverage for both Windows (including Windows Server) as well as major Linux distributions such as Ubuntu®, RHEL®, SLES®, Rocky Linux®, Oracle Linux®, Debian® among others commonly found in today’s datacenters.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery provides continuous data protection (CDP), replicating changes in real time from your production machine directly onto a standby host while monitoring heartbeat status; if failure occurs on primary hardware it automatically fails over operations then resynchronizes once healthy again—ensuring minimal disruption during outages.
When configuring standard jobs you gain granular control over policies including forever incremental mode for efficient storage usage; advanced compression/deduplication; Changed Block Tracking (CBT); automatic reconnection; instant recovery/migration capabilities—and more—all designed for speedier restores plus operational flexibility without complexity.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your environment 1.straightforward:Select the Windows machine to protect
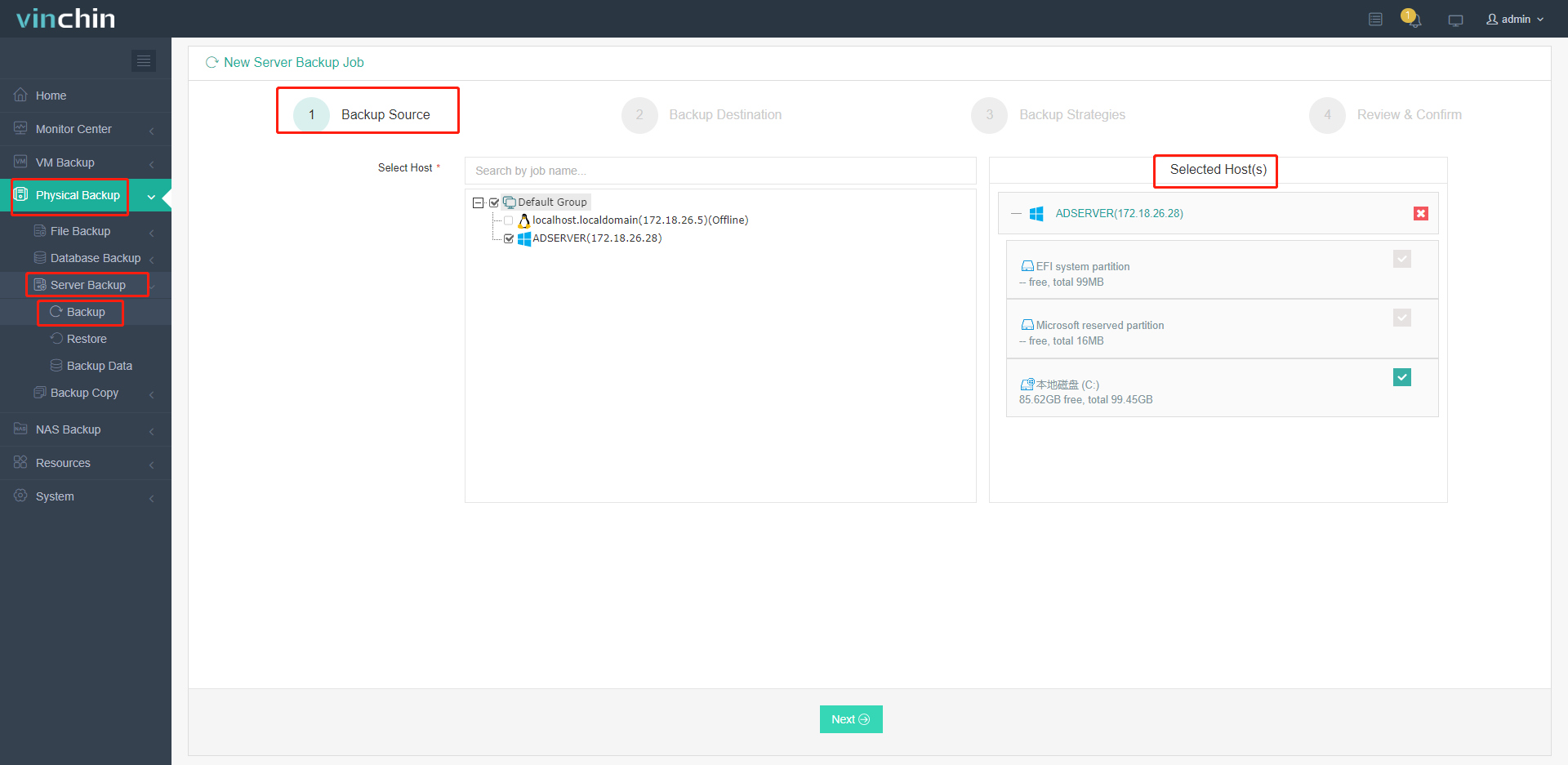
2. Choose your preferred storage target
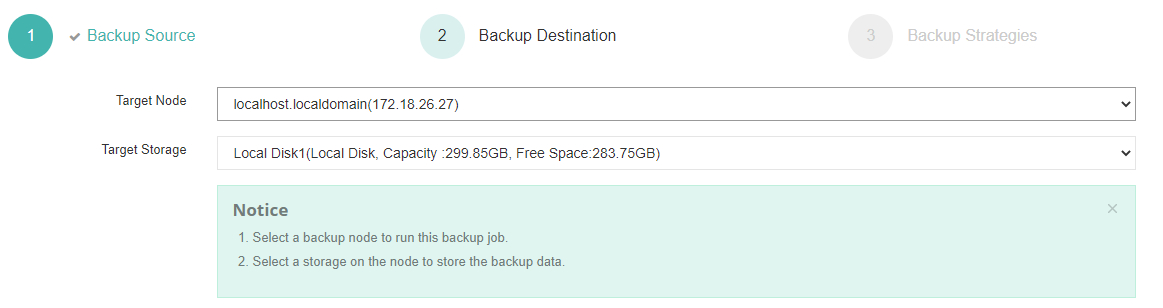
3. Define scheduling/compression/incremental strategies per requirements
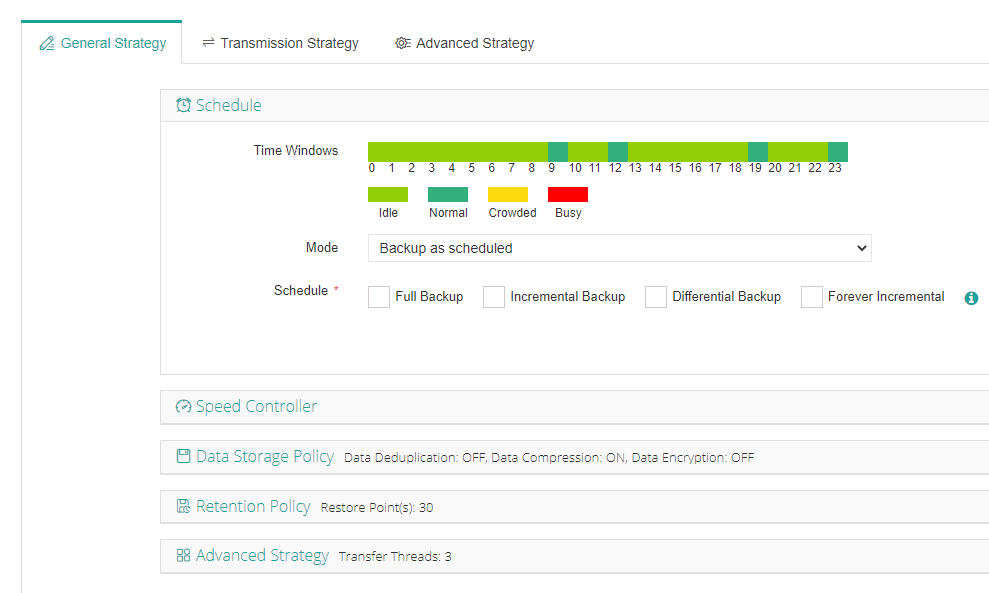
4. Submit job
Recognized globally by thousands of enterprises—with top ratings for reliability—you can experience every feature risk-free via Vinchin's full-featured 60-day trial; click below now to get started.
Physical Server Backup Software FAQs
Q1: How do I restore a single file from a backup?
A1: Open your backup software; select desired job/version/file then click Restore—it’s that simple!
Q2: Can I schedule backups outside business hours?
A2: Yes—most solutions let you customize schedules within their Settings/Schedule menus easily.
Q3: What should I do if my backup fails?
A3: Check logs/storage space/network connectivity first then retry job—or contact vendor support if unresolved issues persist.
Q4: How can I encrypt my backups?
A4: Enable encryption when creating/editing jobs—set strong password/key per policy guidelines provided by your solution vendor!
Q5: Can I back up to cloud storage?
A5: Absolutely! Many modern products—including Vinchin—support direct-to-cloud targets via integrated connectors.
Conclusion
Backing up physical servers is vital for business continuity. Whether you use built-in tools or a professional solution like Vinchin Backup & Recovery regular backups protect you from data loss/downtime—try it free for 60 days & see difference yourself!
Share on:






