-
XCP-ng Overview
-
Proxmox Overview
-
XCP-ng vs Proxmox Comparison table
-
How to choose between XCP-ng and Proxmox?
-
How to migrate VM between XCP-ng and Proxmox?
-
XCP-ng vs Proxmox FAQs
-
Conclusion
The landscape of server virtualization is rich with options, and two prominent open-source solutions that have gained significant traction in recent years are XCP-ng and Proxmox. Both offer robust solutions for managing virtual environments, yet they cater to different needs and preferences.
XCP-ng Overview
XCP-ng is an open-source virtualization platform based on XenServer. It is designed to provide a stable, powerful, and enterprise-grade virtualization environment. XCP-ng aims to continue the open-source legacy of XenServer, ensuring that the community has a free alternative that is not limited by commercial restrictions.
Key Features of XCP-ng
1.High Performance and Scalability: XCP-ng offers excellent performance and scalability, supporting large-scale virtual infrastructures.
2. Advanced Networking: It includes advanced networking features such as VLAN, PVLAN, Open vSwitch, and network bonding.
3. Storage Flexibility: Supports various storage options including local storage, NFS, iSCSI, and Fibre Channel.
4. Enterprise-Grade Features: Live migration, high availability, and disaster recovery are available out-of-the-box.
5. Security: Strong focus on security with features like Dom0 isolation and support for Xen hypervisor's robust security mechanisms.
Proxmox Overview
Proxmox VE is an open-source server virtualization management solution based on KVM and LXC. It provides a web-based interface for managing virtual machines, containers, storage, and networking.
Key Features of Proxmox
1. KVM and LXC Integration: Seamlessly integrates KVM for full virtualization and LXC for container-based virtualization.
2. Web-Based Management Interface: Intuitive and powerful web-based interface for managing the entire virtual infrastructure.
3. Backup and Restore: Proxmox includes built-in backup and restore functionalities with support for scheduling and snapshotting. It also integrated Proxmox Backup Server which offers native protection.
4. Storage Support: Versatile storage support, including local storage, ZFS, Ceph, NFS, and iSCSI.
5. High Availability: Features like live migration, high availability clustering, and integrated disaster recovery tools.
XCP-ng vs Proxmox Comparison table
Here is a comparison table that highlights some key differences between XCP-ng and Proxmox.
Feature | XCP-ng | Proxmox |
Hypervisor type | Type 1 (bare-metal) | Type 1 (bare-metal) |
Kernel | Xen Hypervisor | Linux Kernel (Debian-based) |
Storage Management | Local, NFS, iSCSI, Fiber Channel, SMB/CIFS | Local, NFS, iSCSI, ZFS, Ceph, GlusterFS |
High Availability (HA) | Yes | Yes |
Live Migration | Yes | Yes |
Backup Solutions | Integrated with Xen Orchestra, snapshot-based | Integrated, snapshot-based, supports vzdump, Proxmox Backup Server |
Web Management Interface | Xen Orchestra (separate product) | Proxmox VE Web Interface |
How to choose between XCP-ng and Proxmox?
Here are some considerations when choosing between the two virtualization platforms.
Performance
Both XCP-ng and Proxmox offer high performance, but their architecture influences their efficiency in different scenarios. XCP-ng, with its Xen-based hypervisor, excels in scenarios requiring high scalability and strong isolation between virtual machines. Its paravirtualization capabilities also contribute to enhanced performance for certain workloads.
Proxmox, leveraging KVM, is known for its robust performance in handling diverse workloads, including both virtual machines and containers. The integration with LXC makes it particularly efficient for scenarios where lightweight, low-overhead virtualization is beneficial.
Ease of Use
Proxmox stands out for its ease of use, thanks to its comprehensive and user-friendly web interface, which simplifies the management of virtual machines, containers, storage, and networking, making it accessible even for users with limited experience in virtualization.
XCP-ng, while also providing a web-based interface through Xen Orchestra, may require a steeper learning curve. Xen Orchestra is powerful but might not be as intuitive as Proxmox's interface for new users.
Backup and Recovery
XCP-ng supports various backup solutions, including Xen Orchestra, which offers powerful backup and recovery features, including delta backups and continuous replication.
Proxmox VE includes integrated backup and restore capabilities, supporting full and incremental backups. The Proxmox Backup Server enhances these capabilities with efficient data deduplication and compression.
How to migrate VM between XCP-ng and Proxmox?
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is not only a professional backup solution for virtual machine, but also an advanced VM migration solution, supporting VMware vSphere, Hyper-V, Proxmox, XenServer, XCP-ng, oVirt, OLVM, RHV, OpenStack, etc. By adding both virtualized platforms into the backup system, you can perform easy agentless V2V migration with a user-friendly web console.
There is the built-in conversion engine in the backup system, you just need to select the VM you need to move it to another virtualized platform.
It only takes 4 steps to migrate VMs between the two platforms. For example, if you want to migrate VM form Proxmox to XCP-ng, just follow the steps below:
1. Choose the VM from Proxmox you want to migrate.
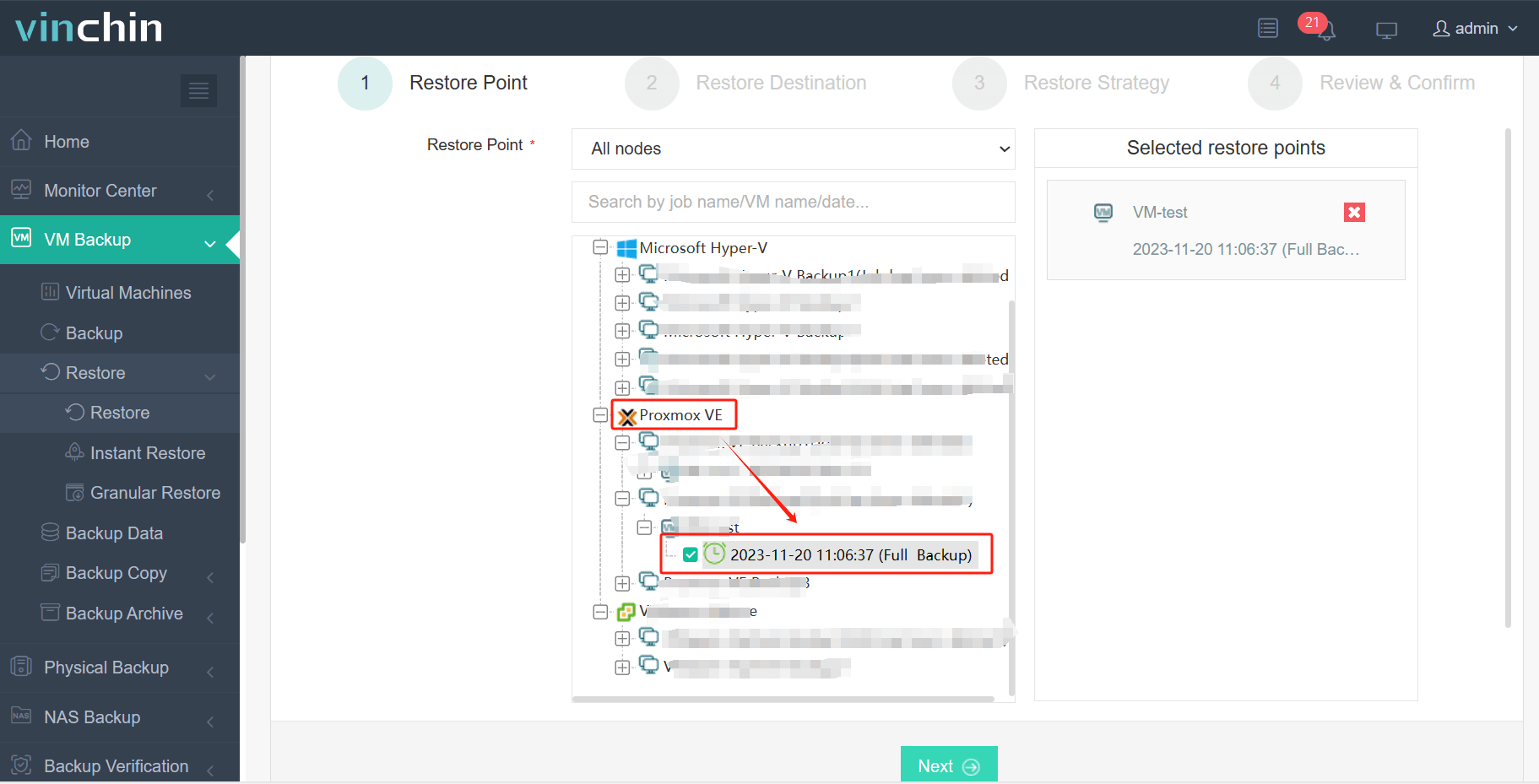
2. Select the XCP-ng host as migration destination.
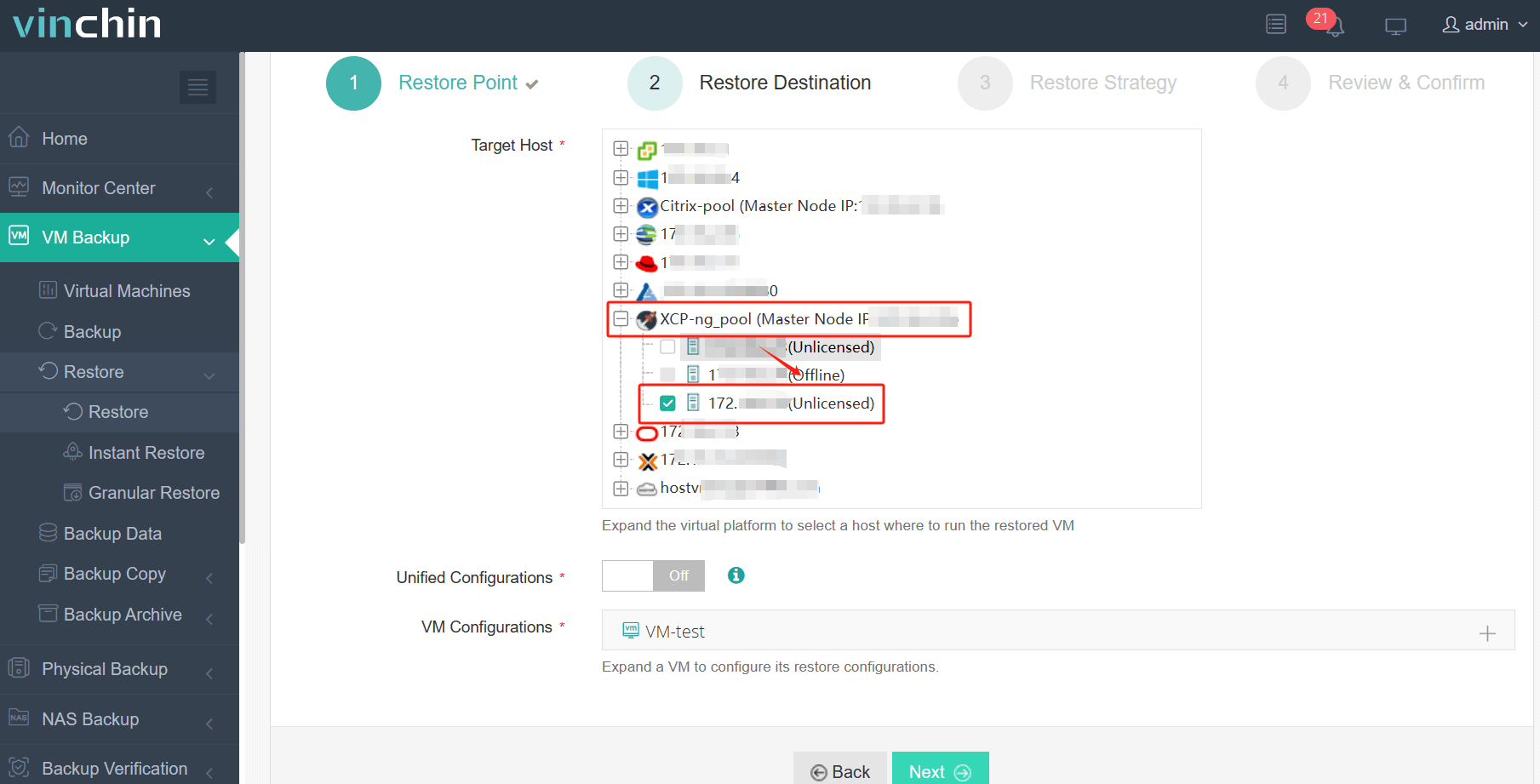
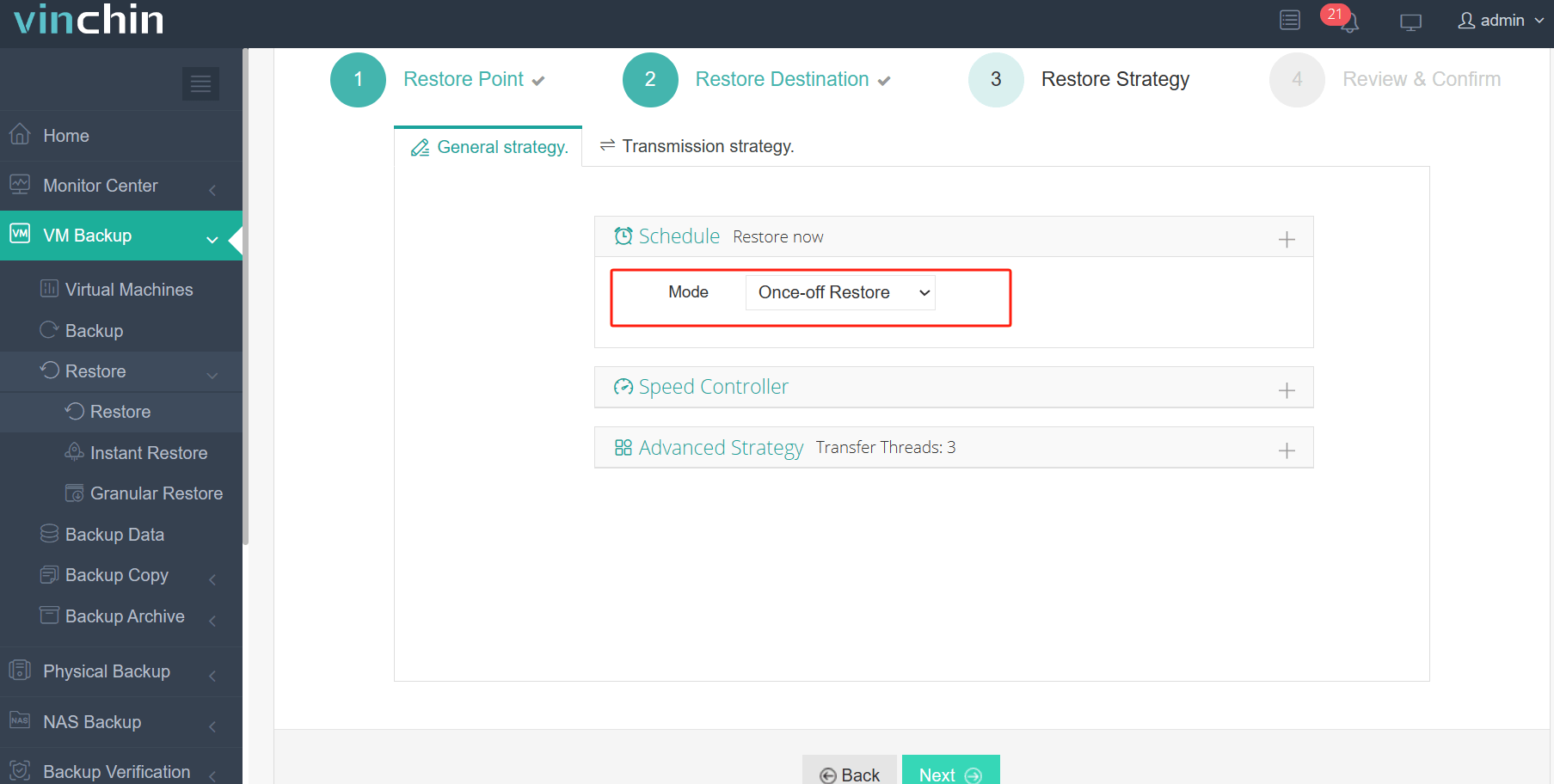
3. Configure the restore strategy.
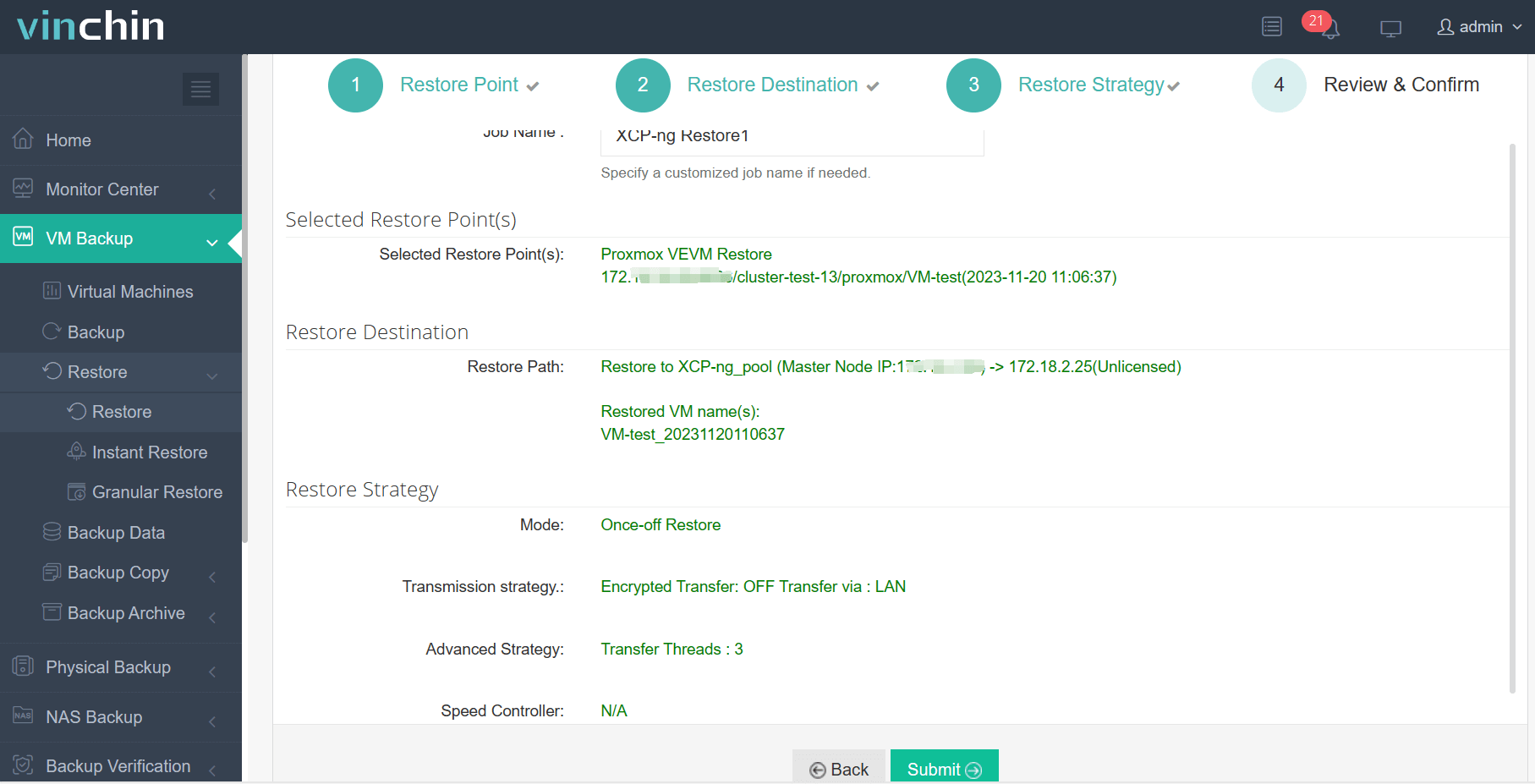
4. Review and submit the job.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery safeguards your virtual environment and facilitates VM migration across hypervisors. Try it fully-featured for 60 days. Share your needs with us for a tailored solution.
XCP-ng vs Proxmox FAQs
1. Q: Can they integrate with cloud services?
A: Both platforms can integrate with cloud services through Vinchin solution. For example, you can migrate those VMs to AWS EC2, or archive backup data to cloud services like Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, Wasabi and MinIO.
2. Q: How do their pricing models compare?
A: XCP-ng is completely free and open-source, with no licensing fees. Proxmox offers a free version and a paid subscription model (Proxmox VE Enterprise) with additional features and support.
Conclusion
Both XCP-ng and Proxmox offer compelling solutions for virtualization needs. XCP-ng stands out for its focus on the Xen hypervisor and its suitability for large-scale deployments, while Proxmox excels in its versatility with support for both VMs and containers. Ultimately, the choice between the two will depend on specific organizational requirements, including existing infrastructure, budget constraints, and technical expertise.
Share on:








