-
What is Hadoop Platform?
-
Why Use Hadoop Platform?
-
Main Components of Hadoop Platform
-
Method 1: How to Deploy Hadoop on Virtual Machines?
-
Method 2: How to Deploy Hadoop Using Cloud Services?
-
How to Protect Data on Hadoop Platform with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
Hadoop Platform FAQs
-
Conclusion
The hadoop platform has transformed how organizations handle big data—moving from traditional on-premises clusters to flexible cloud-native solutions. But with this evolution come new operational challenges. Managing complex clusters, ensuring high availability, and protecting critical data are daily concerns for IT administrators like you. How do you keep your systems running smoothly while scaling to meet growing demands? Let’s walk through what makes the hadoop platform unique—and how you can deploy it with confidence.
What is Hadoop Platform?
The hadoop platform is an open-source framework designed for distributed storage and processing of massive datasets across clusters of standard hardware. It began as a solution for web-scale companies but now supports enterprises worldwide in handling everything from logs to machine learning workloads. Its architecture allows you to scale out easily by adding more nodes as your data grows—without major changes to your applications or infrastructure.
Hadoop’s design emphasizes fault tolerance and horizontal scalability. If one node fails, others take over its work automatically. This resilience makes it ideal for mission-critical environments where downtime is not an option.
Why Use Hadoop Platform?
Why do so many organizations rely on the hadoop platform? The answer lies in its ability to process huge volumes of structured or unstructured data quickly using parallel computing techniques.
With Hadoop:
You can analyze petabytes of information without expensive proprietary hardware.
It supports diverse workloads—from real-time analytics to batch processing—on a single cluster.
Its open ecosystem lets you integrate tools like Hive or Spark as your needs evolve.
For operations teams, this means flexibility at lower costs compared to legacy systems. But with great power comes complexity: managing resources efficiently and safeguarding sensitive data require careful planning.
Main Components of Hadoop Platform
At its core, the hadoop platform consists of several main components that work together:
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): Spreads files across multiple nodes so storage is redundant and scalable.
Yet Another Resource Negotiator (YARN): Allocates CPU/memory resources among jobs running on the cluster.
MapReduce: Breaks down large computations into smaller tasks processed in parallel across nodes.
Hadoop Common: Provides libraries shared by all modules.
Beyond these basics are optional ecosystem tools:
Hive enables SQL-like queries; HBase offers NoSQL capabilities; Pig simplifies scripting; Zookeeper coordinates distributed processes. Choosing which components to deploy depends on your business goals—some environments need only HDFS/MapReduce while others benefit from advanced analytics layers.
Method 1: How to Deploy Hadoop on Virtual Machines?
Deploying the hadoop platform on virtual machines gives you full control over every aspect of your environment—a common choice for private clouds or regulated industries.
Before starting:
Make sure each VM runs a supported Linux OS (like CentOS or Ubuntu), has enough CPU/RAM/disk space for expected workloads—and that hostnames resolve correctly across all nodes via DNS or /etc/hosts. Open firewall ports such as 8020 (NameNode), 8088 (ResourceManager), 9864 (DataNode Web UI). Consider enabling Kerberos if strong authentication is required.
Here’s how you can set up a basic multi-node cluster:
1. Provision VMs—assign one as master (NameNode) plus several workers (DataNodes)
2. Install Java Development Kit on each VM
3. Download official Apache Hadoop release from hadoop.apache.org then extract files
4. Set up passwordless SSH from master node using ssh-keygen/ssh-copy-id
5. Edit config files (core-site.xml, hdfs-site.xml, yarn-site.xml, mapred-site.xml) with correct paths/IPs
6. Format NameNode metadata using hdfs namenode -format
7. Start services via start-dfs.sh (for HDFS) then start-yarn.sh (for YARN)
8. Check cluster status at web UI (http://<master-node>:9870/)
If SSH connections fail during setup:
Double-check network settings; ensure firewalls allow traffic between nodes; verify keys were copied correctly; try manual login before automating scripts.
Once running smoothly:
You can submit MapReduce jobs directly—or layer higher-level tools like Hive/Pig atop your base install.
Method 2: How to Deploy Hadoop Using Cloud Services?
Cloud-based deployments make it easy to launch scalable clusters fast—with minimal hardware management overhead.
Popular managed services include AWS Elastic MapReduce (EMR) and Azure HDInsight—but always review current documentation before starting production projects.
To deploy using AWS EMR or Azure HDInsight:
1. Log in to AWS/Azure console
2. Launch new cluster via EMR (Create cluster) or HDInsight (+ New)
3. Select “Hadoop” as primary application stack—you may also add Spark/Hive if needed
4. Configure number/type of worker nodes based on workload size
5. Set IAM roles/policies carefully so only authorized users access sensitive data
6. Enable auto-scaling policies where possible—to optimize costs during peak/off hours
7. Consider spot/preemptible instances if budget matters more than uptime guarantees
8. Review settings then create cluster—the service provisions VMs/configures software automatically
9. Access web UIs/SSH endpoints provided by cloud dashboard
Managed platforms handle patching/failover behind the scenes—but always monitor usage closely! Unused resources drive up costs quickly unless auto-shutdown rules are enforced.
Cloud deployments suit organizations needing rapid elasticity—or those lacking dedicated datacenter staff. Still, secure access controls remain vital even when infrastructure is abstracted away.
How to Protect Data on Hadoop Platform with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
While robust storage architectures like Hadoop HDFS provide inherent resilience, comprehensive backup remains essential for true data protection. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-grade solution purpose-built for safeguarding mainstream file storage—including Hadoop HDFS environments—as well as Windows/Linux file servers, NAS devices, and S3-compatible object storage. Specifically optimized for large-scale platforms like Hadoop HDFS, Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers exceptionally fast backup speeds that surpass competing products thanks to advanced technologies such as simultaneous scanning/data transfer and merged file transmission.
Among its extensive capabilities, five stand out as particularly valuable for protecting critical big-data assets: incremental backup (capturing only changed files), wildcard filtering (targeting specific datasets), multi-level compression (reducing space usage), cross-platform restore (recovering backups onto any supported target including other file servers/NAS/Hadoop/object storage), and integrity check (verifying backups remain unchanged). Together these features ensure efficient operations while maximizing security and flexibility across diverse infrastructures.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers an intuitive web console designed for simplicity. To back up your Hadoop HDFS files:
Step 1. Select the Hadoop HDFS files you wish to back up
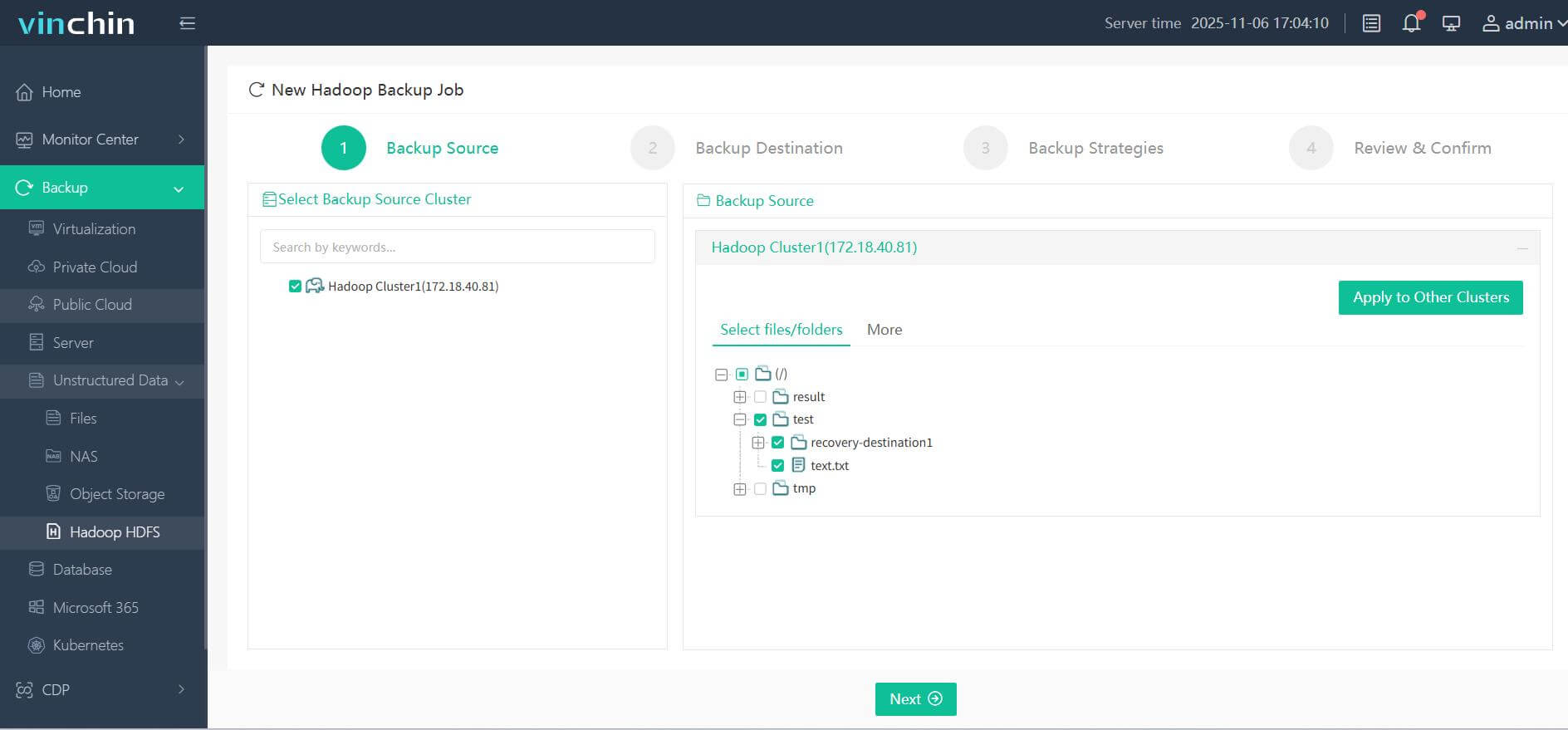
Step 2. Choose your desired backup destination
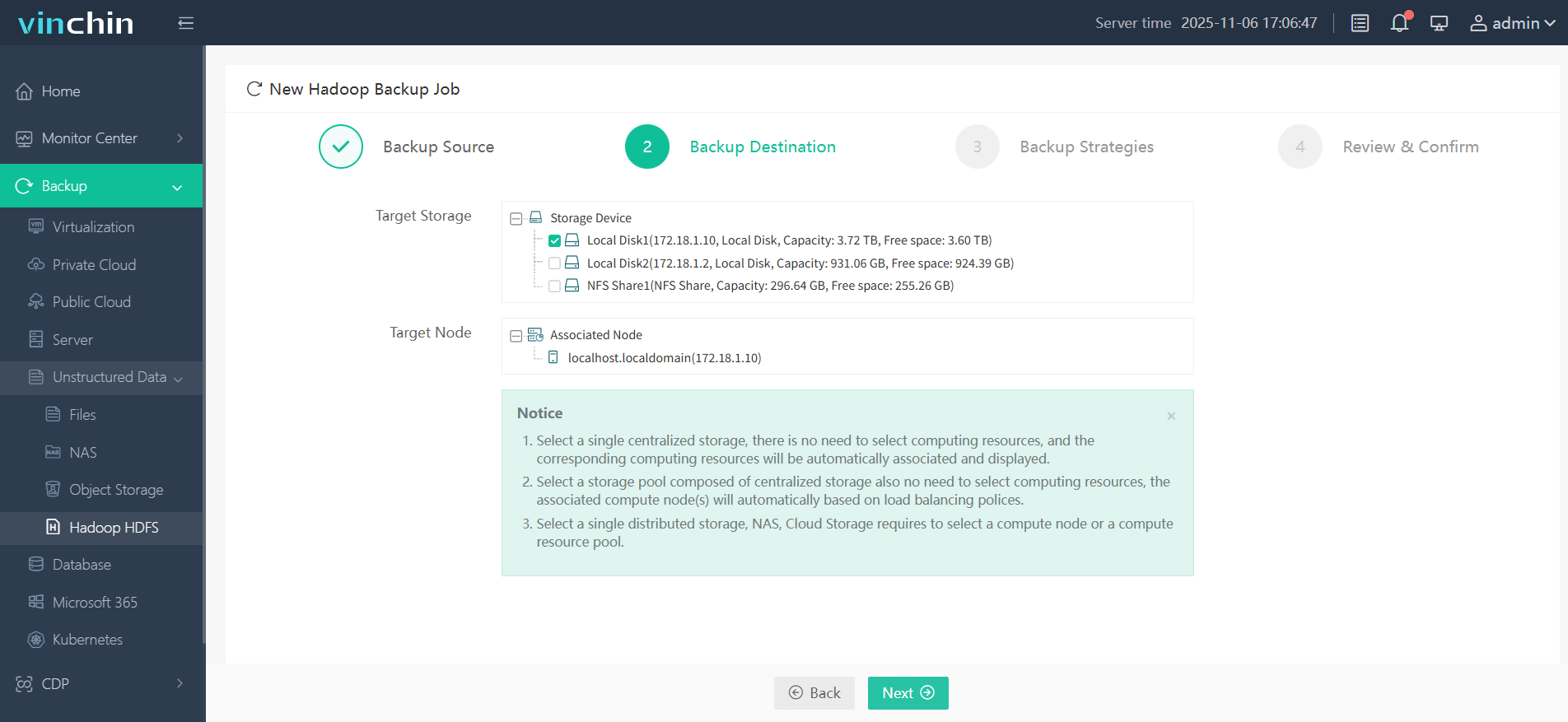
Step 3. Define backup strategies tailored for your needs
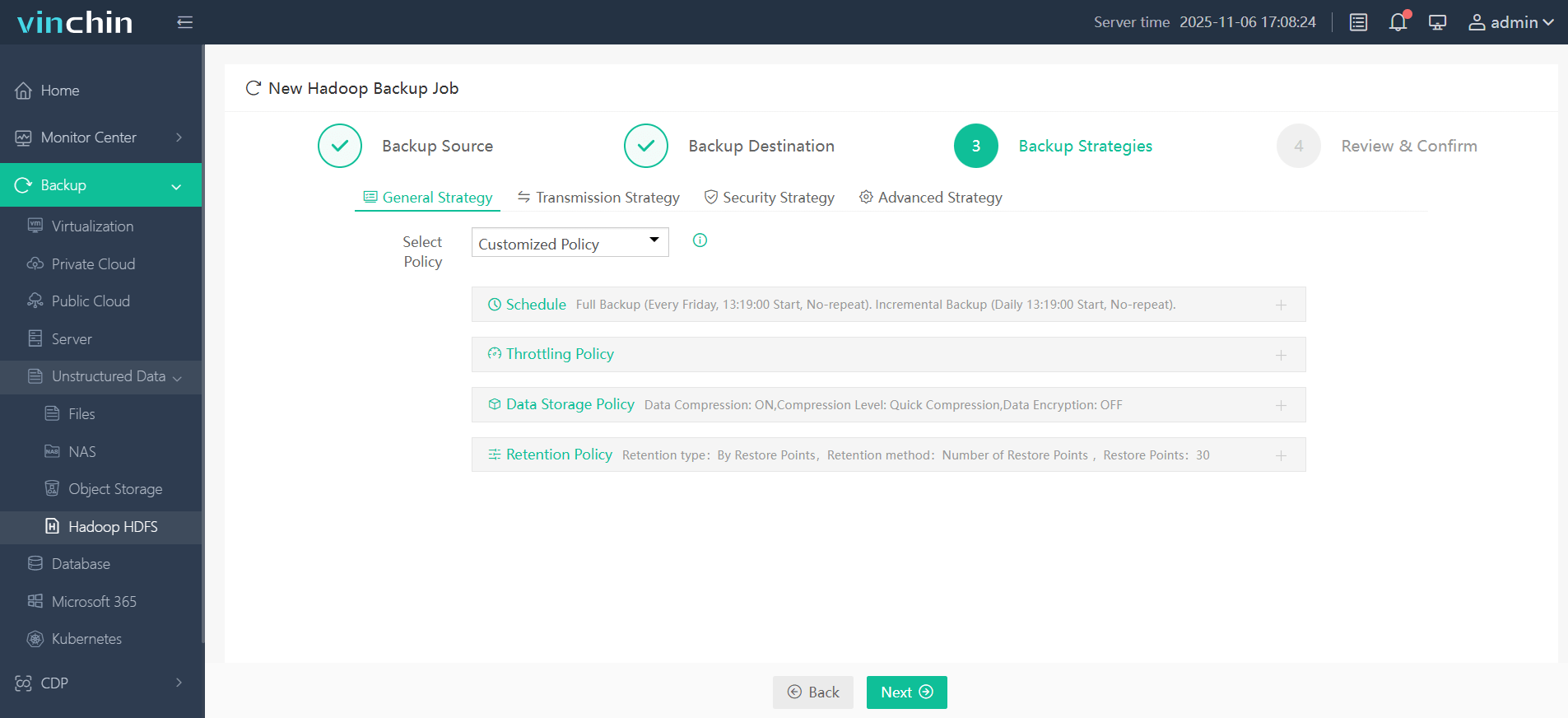
Step 4. Submit the job
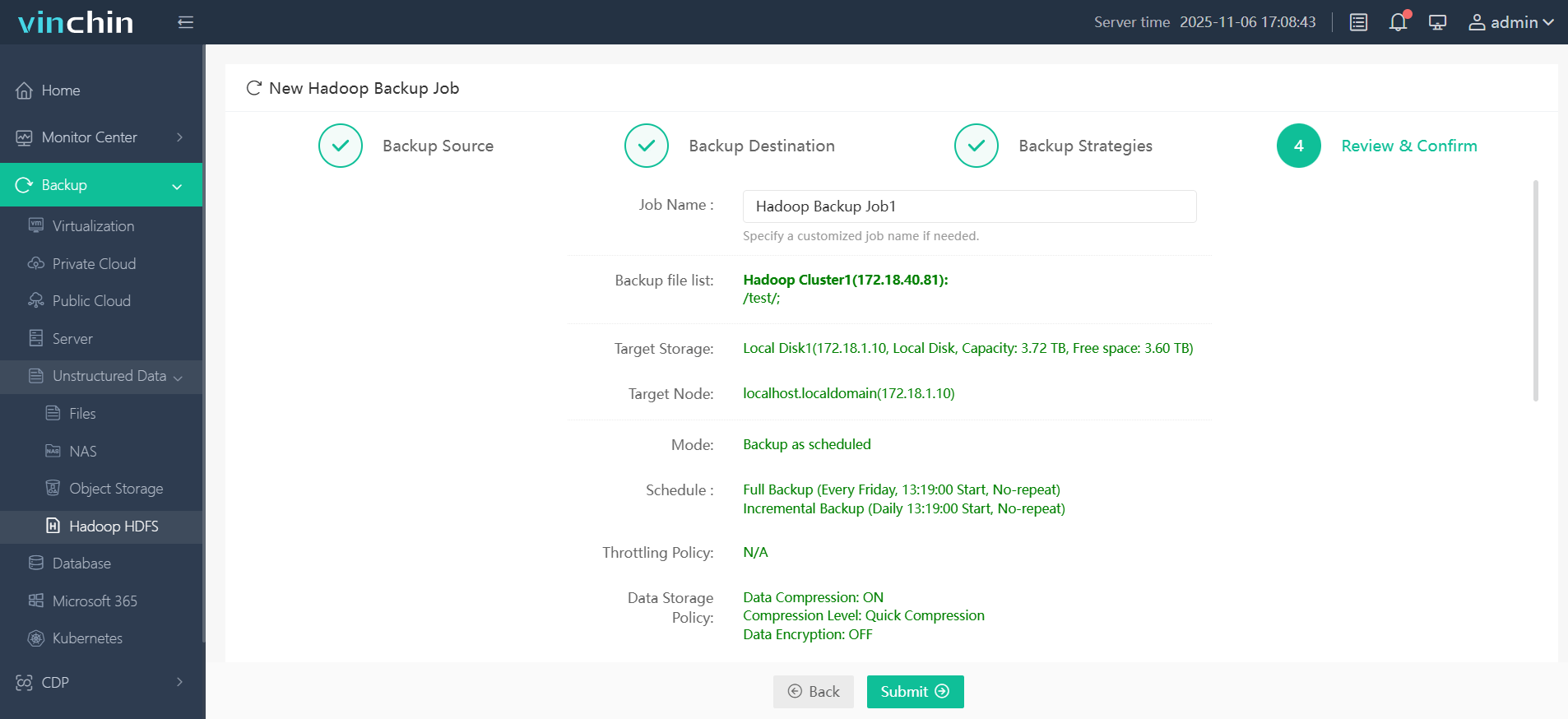
Join thousands of global enterprises who trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery—renowned worldwide with top ratings—for reliable data protection. Try all features free with a 60-day trial; click below to get started!
Hadoop Platform FAQs
Q1: How do I expand my existing hadoop cluster?
A1: Add new worker nodes physically/logically,set them up identically,and update configuration files before restarting affected services—the system rebalances data automatically afterward.
Q2: What steps help reduce cloud deployment costs?
A2: Enable auto-scaling,use spot/preemptible instances when possible,and shut down idle clusters promptly via provider dashboards/scripts.
Q3: How do I monitor overall health of my hadoop environment?
A3: Check NameNode/YARN ResourceManager UIs regularly—track disk usage,node heartbeats,and job queue lengths for early warning signs of trouble.
Conclusion
The hadoop platform empowers organizations everywhere with scalable big-data processing—whether deployed onsite or in the cloud.Protecting those investments is easy thanks to Vinchin’s advanced backup features.Start your free trial now—and keep critical workloads resilient no matter what tomorrow brings.
Share on:







