-
What Is Oracle Database SQL?
-
Why Use SQL in Oracle Database?
-
Basic Oracle Database SQL Commands
-
Advanced Query Techniques in Oracle Database SQL
-
Operational Management: Indexes & Privileges
-
Performance Tuning for Operational Efficiency
-
Protecting Your Workloads with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Oracle Database SQL FAQs
-
Conclusion
Oracle Database SQL is at the heart of enterprise data management. For IT operations administrators, it’s more than just a tool for querying data—it’s essential for keeping systems running smoothly, troubleshooting issues fast, ensuring compliance, and protecting business-critical information. Whether you’re new to Oracle or have years of experience under your belt, mastering Oracle Database SQL can make daily tasks easier and help you respond quickly when problems arise. This guide will walk you from beginner basics through advanced techniques used by professionals in real-world environments—and show how to safeguard your Oracle Database SQL workloads using Vinchin.
What Is Oracle Database SQL?
Oracle Database SQL is Oracle’s version of Structured Query Language (SQL), which is the industry standard for working with relational databases. With SQL in Oracle Database, you can create tables, insert or update records, retrieve information on demand, enforce security rules, and automate routine tasks. Every time an application interacts with your database—even if users never see it—SQL statements are running behind the scenes.
For operations teams managing large environments or mission-critical applications, understanding how these statements work is key to maintaining uptime and meeting service level agreements (SLAs).
Why Use SQL in Oracle Database?
SQL provides a universal way to manage data inside Oracle Database. It lets you define structures like tables and indexes; add or change records; pull reports; enforce access controls; and much more—all using clear commands that follow international standards.
But Oracle goes further than basic SQL. Its implementation includes features designed for high performance analytics, scalability across huge datasets, robust security controls, and automation capabilities that simplify complex workflows. This means you can use one language—from simple queries up to advanced business logic—across all your operational needs.
For IT administrators responsible for reliability or compliance audits, knowing how to leverage these features helps ensure both efficiency and peace of mind.
Basic Oracle Database SQL Commands
Getting started with Oracle Database SQL doesn’t require deep technical knowledge. You’ll use straightforward commands every day as part of regular maintenance or troubleshooting.
To create a table in your database environment:
CREATE TABLE employees ( employee_id NUMBER(6), first_name VARCHAR2(20), last_name VARCHAR2(25), hire_date DATE, salary NUMBER(8,2) );
This command sets up an employees table with columns for ID numbers, names, hire dates, and salaries.
When adding new records:
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date, salary)
VALUES (1001,'John','Smith',TO_DATE('2024-06-01','YYYY-MM-DD'),60000);Tip: For bulk inserts during migrations or batch jobs in production scripts use INSERT /+ APPEND / to speed up loading—but only if recent backups exist since this bypasses redo logging.
To pull specific information:
SELECT first_name,last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE salary > 50000;
If you need to adjust existing data:
UPDATE employees SET salary = 65000 WHERE employee_id = 1001;
And when removing outdated entries:
DELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 1001;
Each command follows clear syntax rules documented by Oracle. Mastering these basics lays the groundwork for more advanced administration tasks later on.
Advanced Query Techniques in Oracle Database SQL
Once comfortable with basic commands, operations teams often need more powerful tools to handle complex reporting or analysis requirements.
Joins let you combine information from multiple tables—a common need when building dashboards or investigating incidents:
SELECT e.first_name,e.last_name,d.department_name FROM employees e JOIN departments d ON e.department_id = d.department_id;
Aggregate functions such as SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, and MAX help summarize large volumes of data quickly:
SELECT department_id,SUM(salary) AS total_salary FROM employees GROUP BY department_id;
Subqueries allow nesting one query inside another—for example when comparing individual values against group averages:
SELECT first_name,last_name FROM employees WHERE salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees);
Views provide virtual tables based on saved queries—useful for simplifying access control or creating reusable reports:
CREATE VIEW high_earners AS SELECT first_name,last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE salary > 100000;
Analytic functions like ROW_NUMBER() enable ranking results within partitions—a handy feature when identifying top performers per department without writing complicated procedural code.
Operational Management: Indexes & Privileges
Beyond querying data efficiently lies another layer critical for IT operations: managing performance through indexes and enforcing proper user privileges.
Indexes speed up searches by letting the database find rows faster—especially important as tables grow over time:
CREATE INDEX idx_emp_lastname ON employees(last_name);
However: Too many indexes can slow down inserts/updates due to extra overhead during writes. Regularly review index usage statistics via dynamic views like V$OBJECT_USAGE so you strike the right balance between read speed and write efficiency.
User privileges control who can view or modify sensitive information—a must-have in regulated industries. Grant only what’s needed using roles tailored to job duties:
GRANT SELECT ON employees TO analyst_role; REVOKE UPDATE ON employees FROM analyst_role;
Auditing tracks changes made by users—a requirement under many compliance frameworks such as GDPR or HIPAA. Enable auditing selectively on key tables using commands like:
AUDIT SELECT ON employees BY ACCESS;
Partitioning splits very large tables into smaller segments (“partitions”) based on criteria such as date ranges—making backups faster while improving some types of queries (Partitioning Guide).
Performance Tuning for Operational Efficiency
Performance matters most when end-users are waiting—or when nightly jobs threaten to run past their windows! Here’s how experienced admins tune their environments:
Start by diagnosing slow queries using built-in tools like EXPLAIN PLAN:
EXPLAIN PLAN FOR SELECT * FROM employees WHERE last_name='Smith'; SELECT * FROM TABLE(DBMS_XPLAN.DISPLAY());
This reveals whether full table scans are happening instead of index lookups—a classic sign something needs fixing!
Use bind variables (:salary_limit) rather than hard-coded values in scripts—they reduce parsing overhead while helping prevent accidental exposure through logs (and mitigate some injection risks).
Monitor long-running sessions via dynamic views such as V$SESSION_LONGOPS. If certain jobs always lag behind others? Consider breaking them into smaller batches—or rescheduling outside peak hours where possible.
Regularly review execution plans after schema changes; even small tweaks may shift optimizer choices unexpectedly!
Finally: Keep statistics current using scheduled runs of DBMS_STATS.GATHER_TABLE_STATS. Outdated stats lead directly to poor execution plans—which means slower apps!
Protecting Your Workloads with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
Given the operational demands placed on enterprise databases like Oracle—including backup reliability and rapid recovery—it’s crucial to choose a solution built specifically for these challenges. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as a professional enterprise-level database backup platform supporting today’s mainstream databases such as Oracle (including all core features), MySQL, SQL Server, MariaDB, PostgreSQL/PostgresPro and MongoDB environments found across modern infrastructures.
With Vinchin Backup & Recovery you gain robust protection through features including incremental backup support for fast daily copies; advanced source-side compression tailored especially for Oracle workloads; flexible batch database backup management; granular any-point-in-time recovery options; plus ransomware protection integrated into every deployment scenario—all designed so IT teams maintain business continuity while optimizing storage costs.
The intuitive web console makes safeguarding your critical databases straightforward:
Step 1: Select the Oracle database to back up;
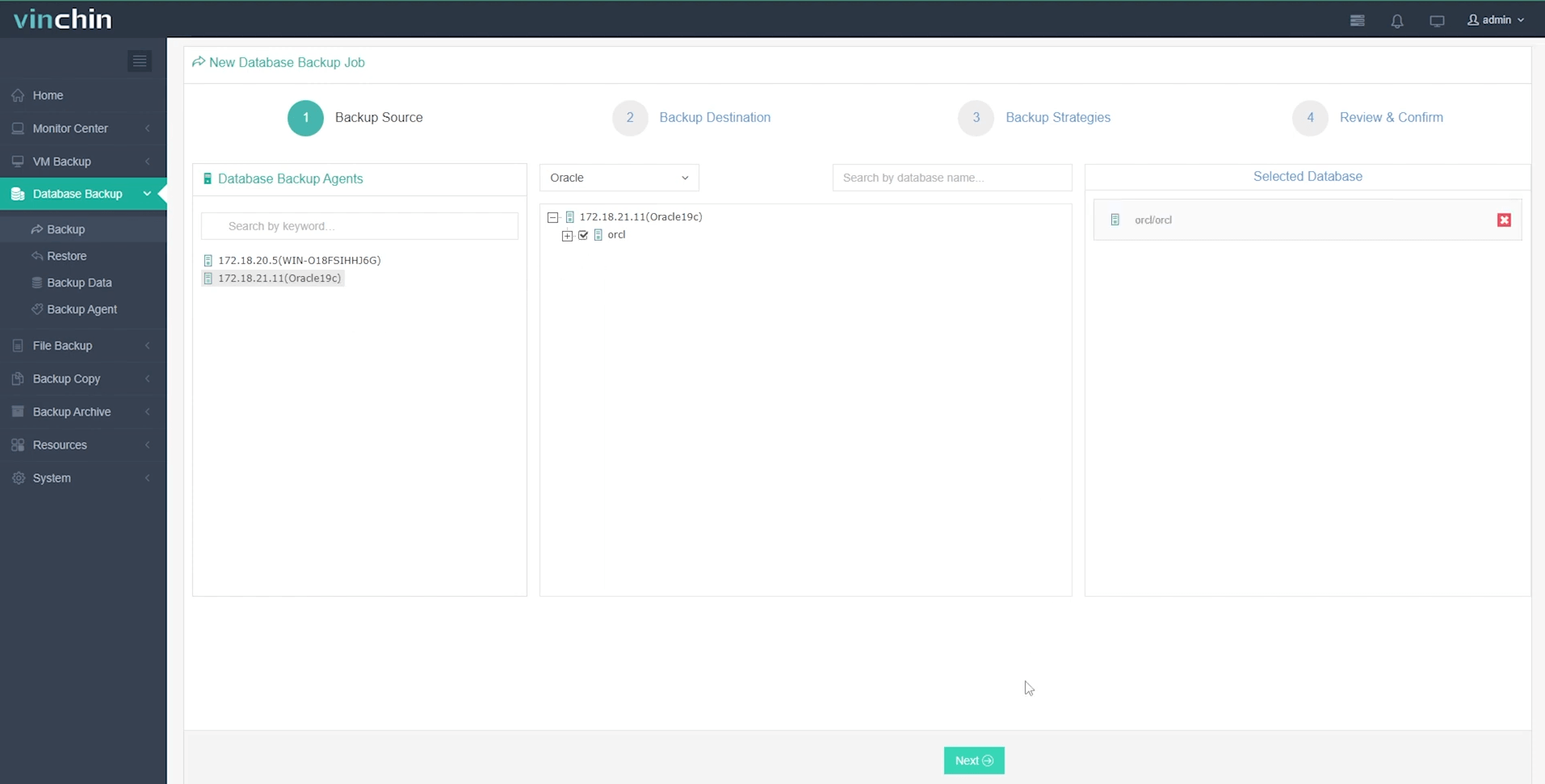
Step 2: Choose backup storage;
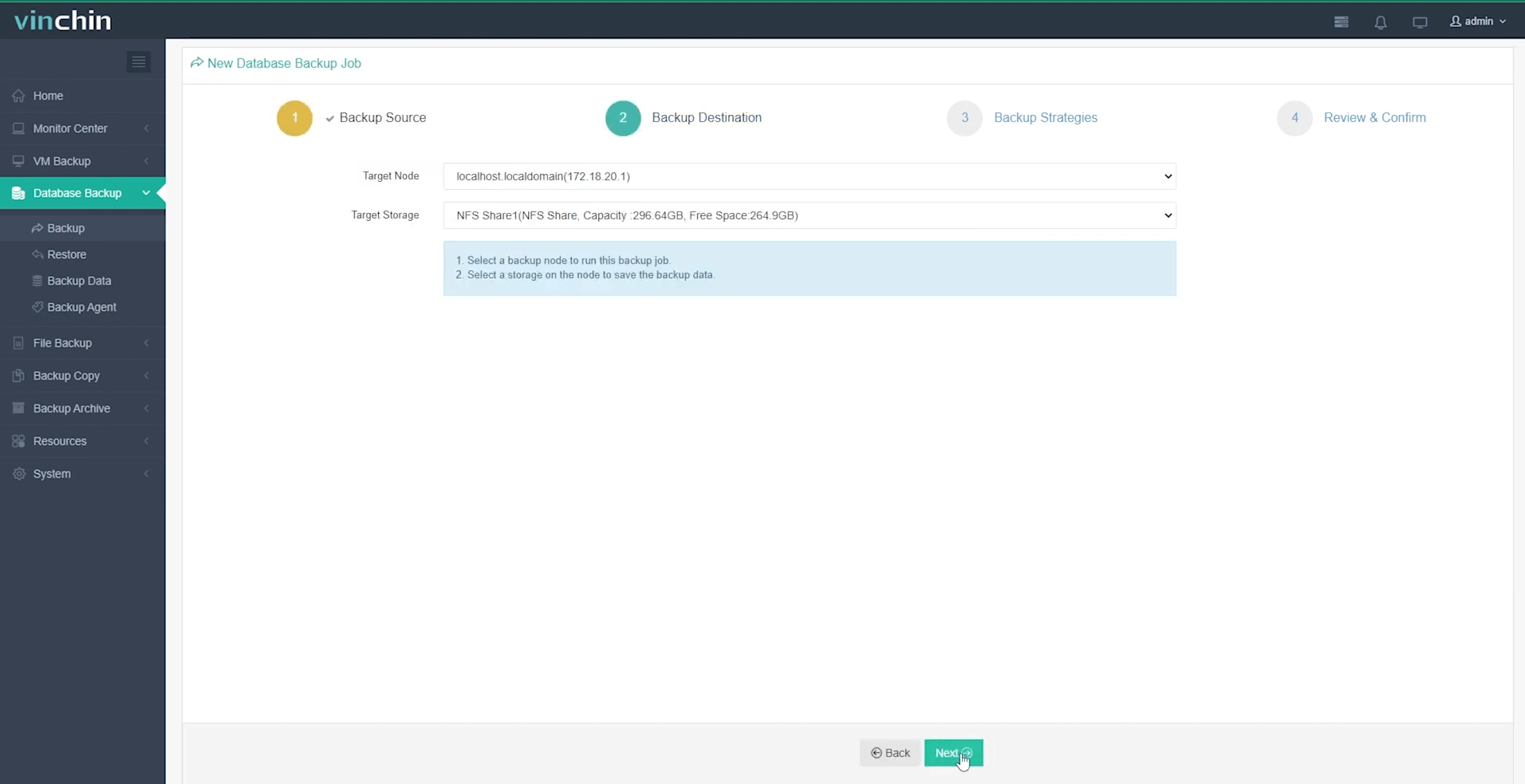
Step 3: Define your backup strategy;
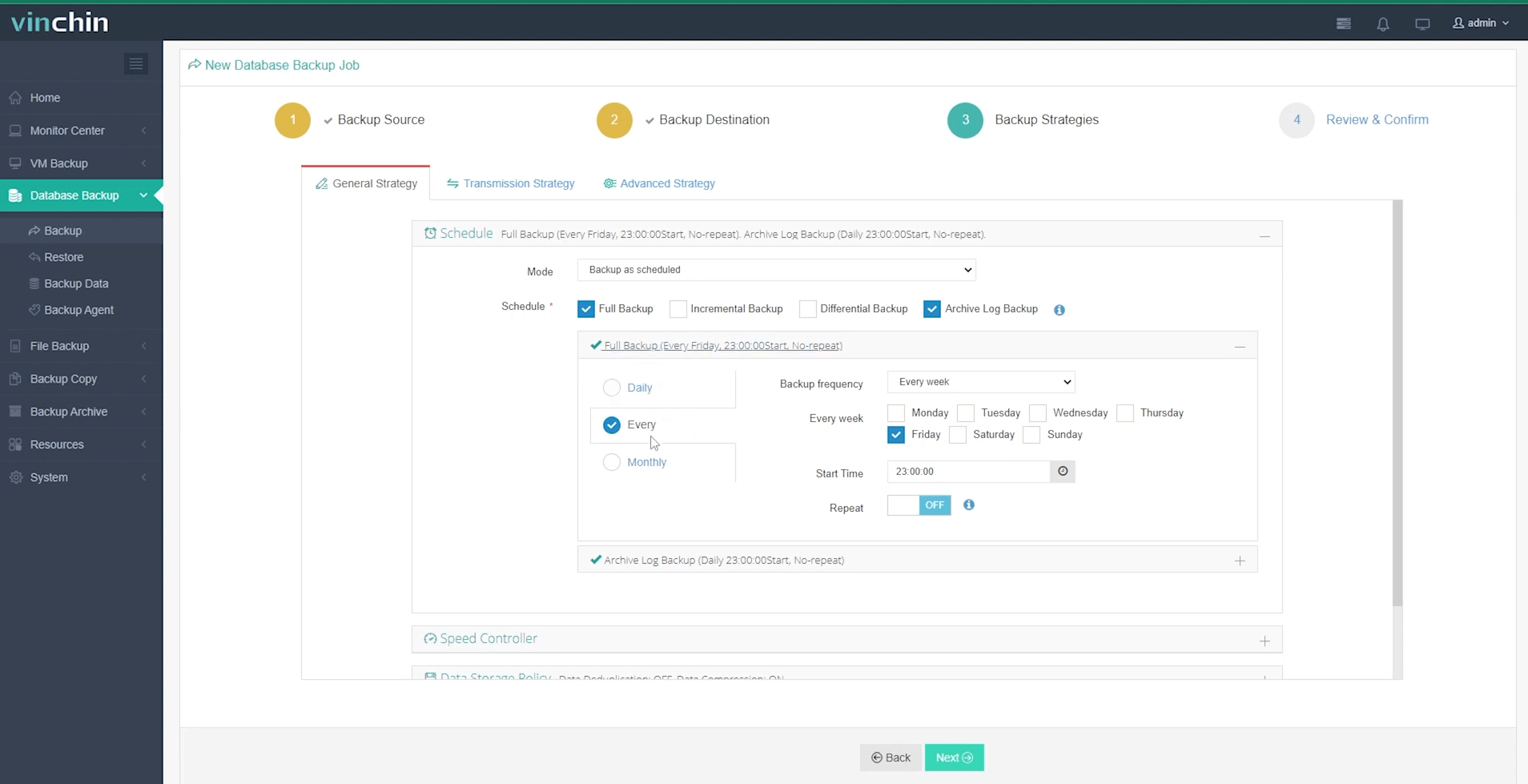
Step 4: Submit the job.
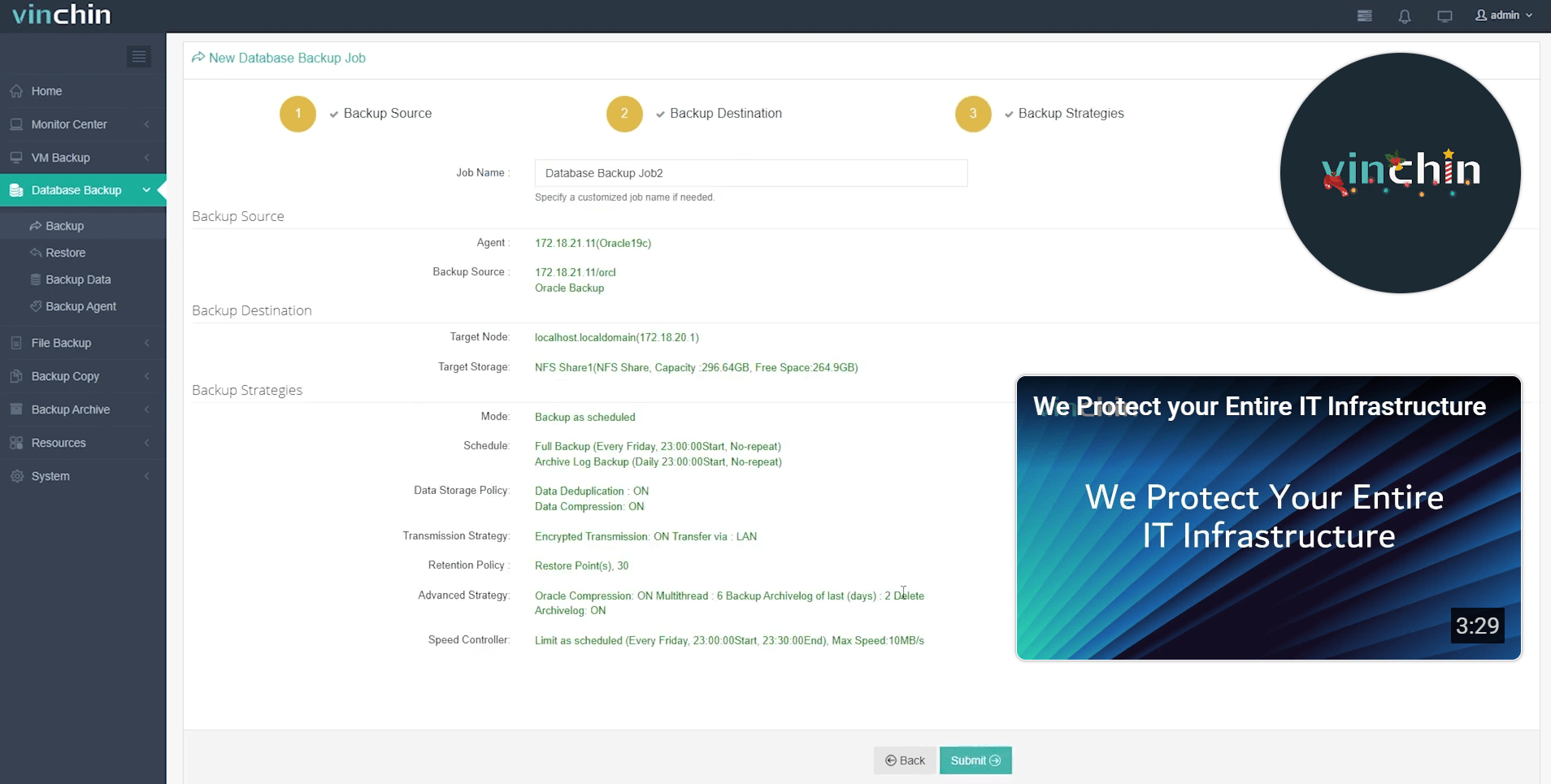
Join thousands worldwide who trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery—an award-winning solution rated highly by enterprises everywhere—with a free 60-day full-featured trial available now! Click below to get started protecting your environment today.
Oracle Database SQL FAQs
Q1: How do I automate regular health checks on my Oracle databases?
Schedule PL/SQL scripts via DBMS_SCHEDULER CREATE JOB ENABLED TRUE MONITOR OUTPUT EMAIL ALERTS SNMP TRAPS
Q2: Can I integrate backup monitoring alerts from Vinchin into my existing NOC dashboard?
Yes configure webhook notifications REST API endpoints SNMP traps supported send alerts directly third-party monitoring platforms
Q3: What steps should I take if unauthorized DML activity appears in audit logs?
Immediately REVOKE suspicious user privileges CHANGE affected passwords REVIEW recent session history NOTIFY security team INITIATE incident response procedures
Conclusion
Mastering Oracle Database SQL empowers IT administrators at every level—from daily maintenance through disaster recovery drills—to deliver reliable service around-the-clock. For secure backups tailored specifically toward enterprise needs consider making Vinchin part of your protection strategy today!
Share on:








