-
Configure the Hyper-V environment
-
Hyper-V VM backup best practices
-
Hyper-V backup best practices with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Hyper-V backup best practices FAQs
-
Conclusion
As virtualization technology evolves, more and more organizations are using Microsoft's Hyper-V to manage workloads in their production environments. Hyper-V can not only stand alone, but can also be used in conjunction with other virtualization platforms, such as VMware vSphere, to support a wide range of environmental requirements.
When configuring and managing Hyper-V, it is critical to follow best practices. Here are some key recommendations:
Configure the Hyper-V environment
Optimize resource allocation
Ensure that host resources (e.g., CPU, memory, storage) are allocated appropriately and that VM resources are adjusted according to actual demand to avoid waste or insufficiency. Regular monitoring of resources helps maintain high performance.
Enable high availability features
Configure Hyper-V's high-availability features, such as failover clustering and live migration, to ensure that VMs are automatically migrated during hardware failures or maintenance to reduce downtime.
Enhanced security and isolation
Configure network isolation and access control policies to segregate network traffic through virtual switches and protect VMs from unauthorized access with Hyper-V's security features.
Hyper-V VM backup best practices
Backups are a critical component that cannot be ignored when ensuring the security and stability of your Hyper-V environment. Here are some important backup best practices:
Hyper-V checkpoints are not backups
Checkpoints are mechanisms used in Hyper-V to capture the state of VMs, but they should not be used as a formal backup solution. Checkpoints are dependent on the production environment and do not provide standalone disaster recovery capabilities.
Host or cluster level backups
Employing a modern backup solution that captures backups at the Hyper-V host or cluster level not only backs up VM data, but also its configuration, helping to simplify the restore process.
Using application-aware backups
In VMs running critical applications such as databases, application-aware backups ensure data consistency. With Microsoft's Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS), data prior to backup can be properly flushed to disk, ensuring data consistency when restored.
Encrypted backup data
Encrypting backup data is critical to prevent unauthorized access. Ensure that backup data is encrypted both in transit and in storage to protect sensitive information.
Verify the validity of backups
It is critical to validate backups on a regular basis. An automated validation process can help detect potential problems with your backups and ensure that data can be restored smoothly if it needs to be restored.
Hyper-V backup best practices with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
By implementing Hyper-V VM best practices, organizations can significantly improve the performance, availability and security of their virtualized environments. Especially in the area of backup, choosing the right solution and strategy is critical. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a backup solution designed for a wide range of virtualization platforms, supporting 10+ virtualization platforms including Hyper-V, VMware, Proxmox, XenServer, XCP-ng, oVirt, RHV, and more.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery's operation is very simple, just a few simple steps.
1. Just select VMs on the host
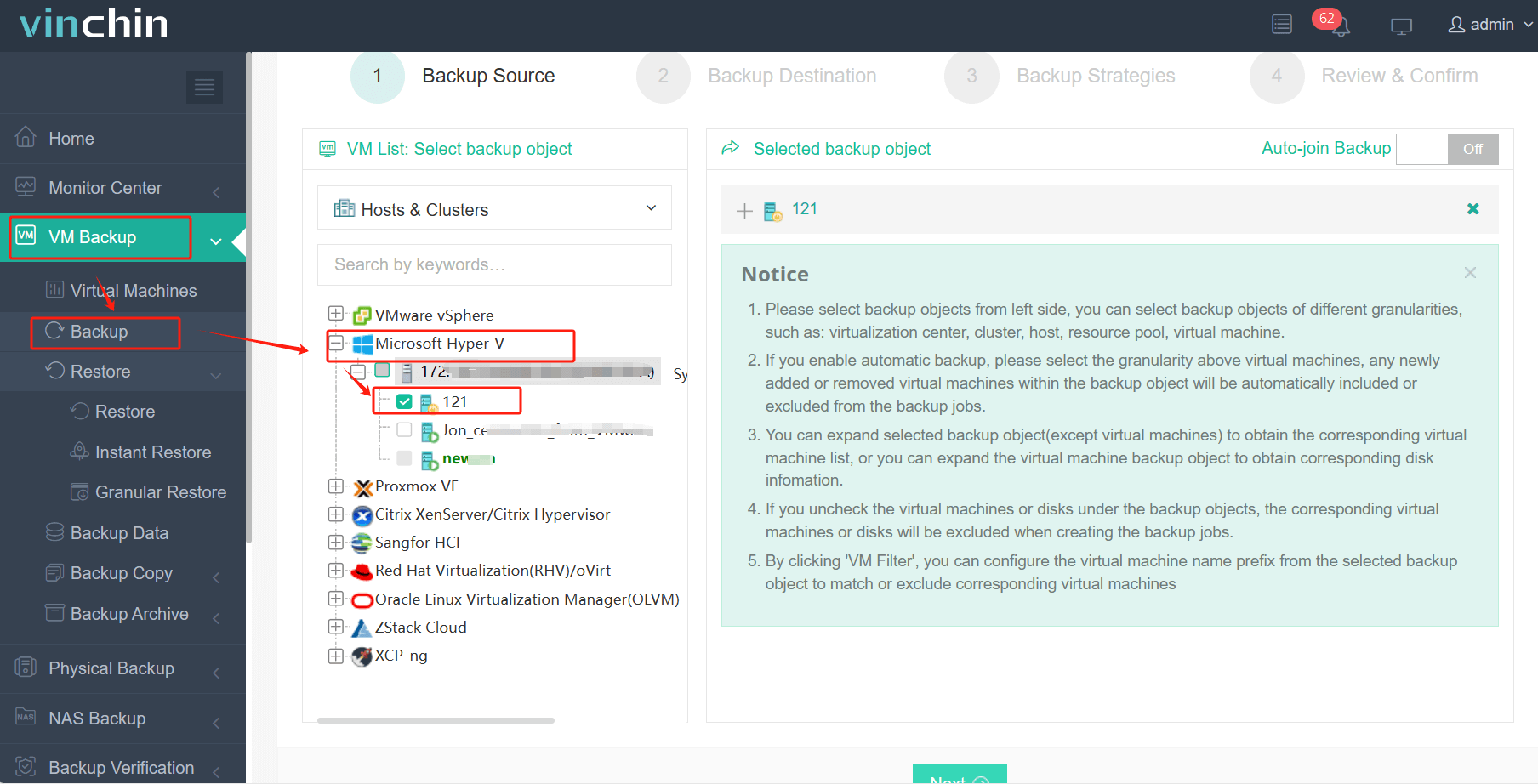
2.Then select backup destination
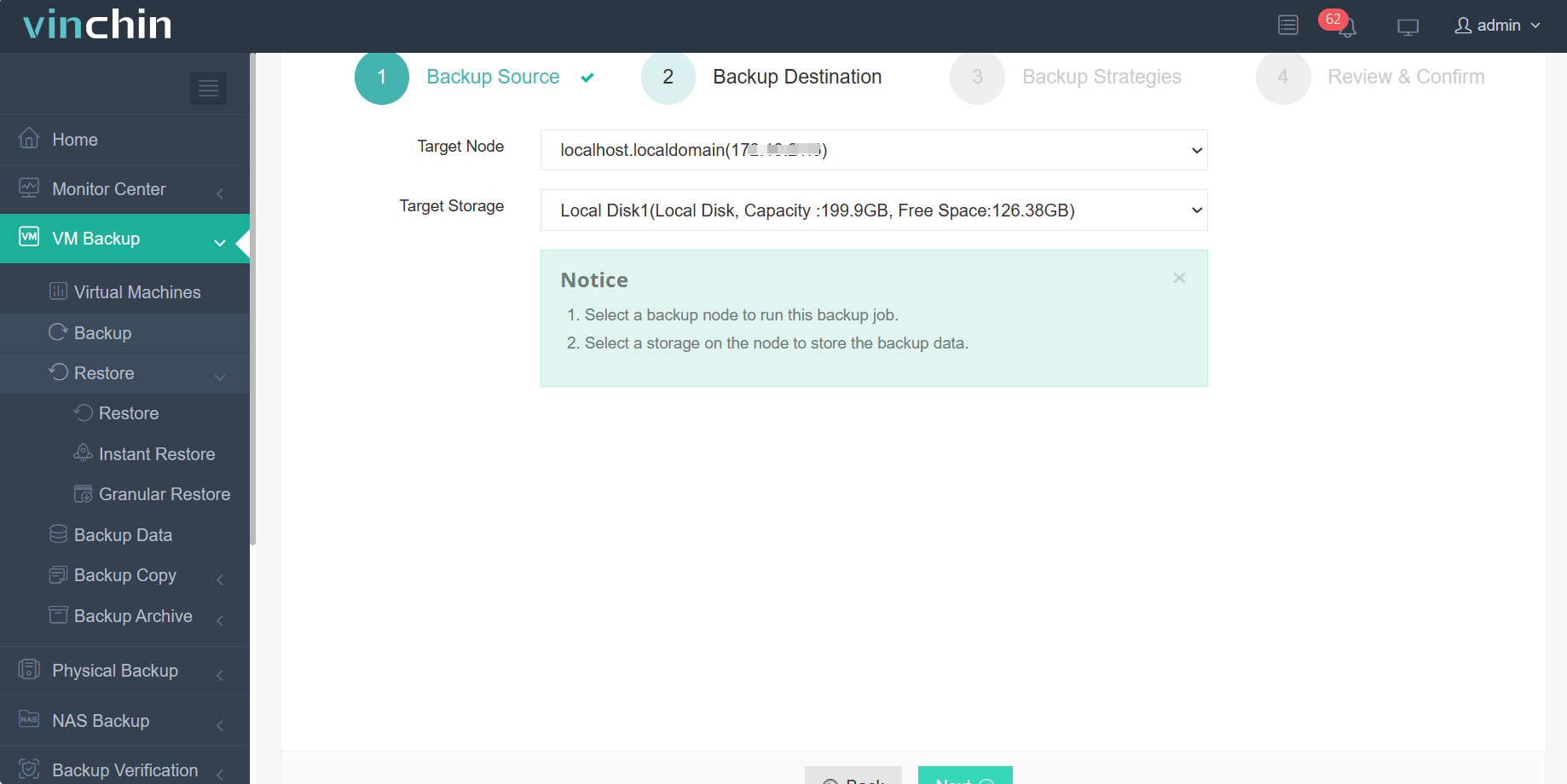
3.Select strategies
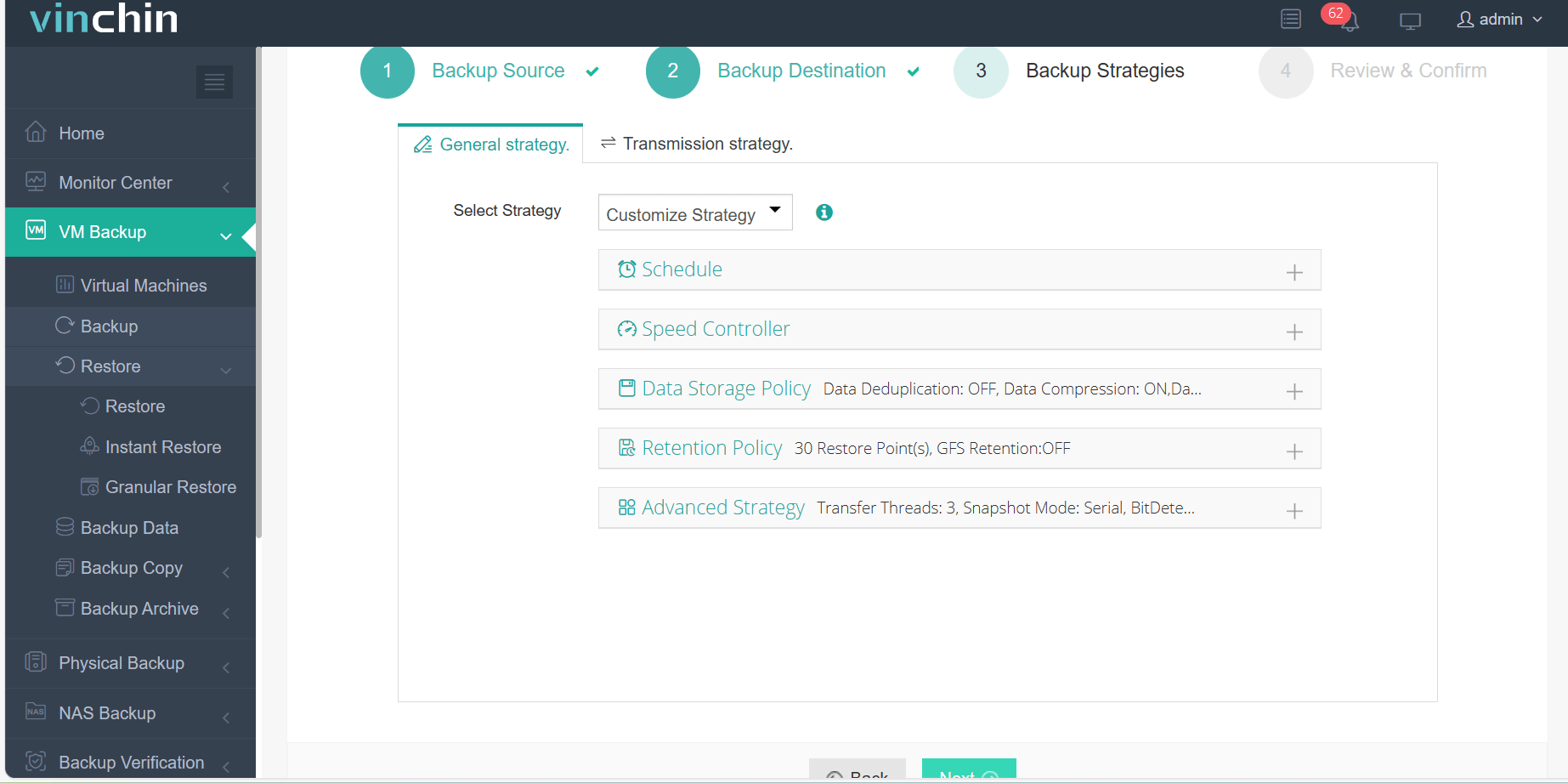
4.Finally submit the job 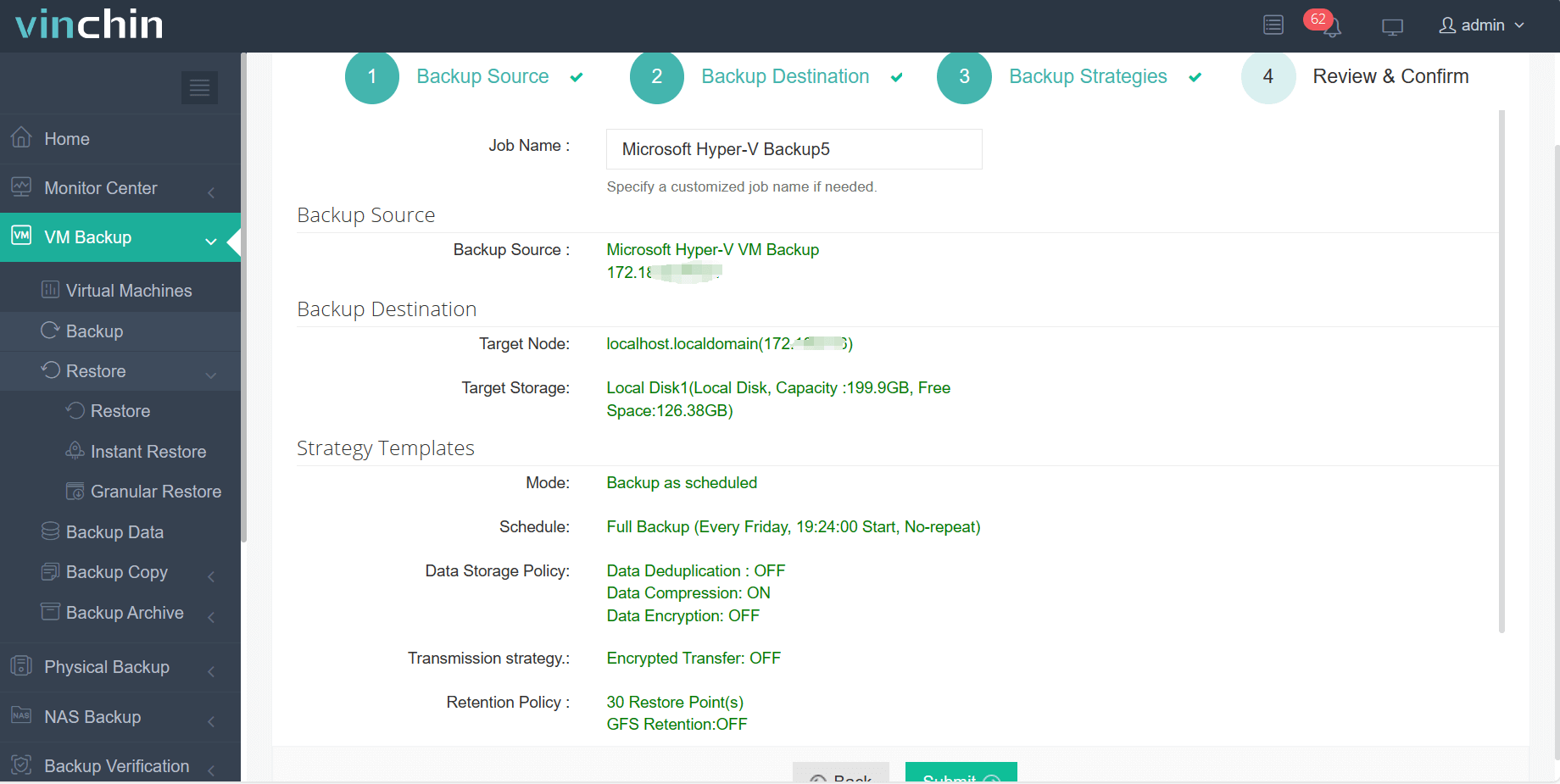
In addition, Vinchin offers powerful VM backup and recovery features, including agentless backup, V2V migration and more, designed to fully protect and efficiently manage critical data in virtualized environments. To help users get hands-on experience with these features, Vinchin is offering a free 60-day trial. For more information, please contact Vinchin directly or consult our local partners.
Hyper-V backup best practices FAQs
Q1: Why is it important to regularly back up Hyper-V virtual machines?
A1: Regular backups are essential to protect your data against hardware failures, ransomware, and accidental deletions. They ensure business continuity by allowing you to restore VMs quickly in the event of a disaster.
Q2: What is the difference between full, incremental, and differential backups in Hyper-V?
A2: Full Backup: Captures all data of the VM, providing a complete restore point. It requires more storage space and time.
Incremental Backup: Only backs up changes since the last backup, saving storage space and time, but requires all previous increments to restore.
Differential Backup: Backs up changes since the last full backup, requiring less storage than full backups but more than incremental backups.
Conclusion
By following Hyper-V VM best practices, organizations can enhance performance, availability, and security in their virtual environments. Implementing proper backup strategies, such as using Vinchin Backup & Recovery, ensures comprehensive protection and efficient management of critical data.
Share on:







