-
What Is Zero Downtime?
-
Why Zero Downtime Matters?
-
Method 1: High Availability Solutions for Zero Downtime
-
Method 2: Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies
-
Method 3: Live Migration and Replication for Zero Downtime
-
How to Achieve Zero Downtime Data Protection with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
-
Zero Downtime FAQs
-
Conclusion
In today’s digital world, even a few minutes of downtime can cause big problems—lost revenue, damaged reputation, frustrated users. Businesses now demand their systems stay up around the clock. But is true zero downtime possible? Let’s break down what zero downtime means in IT operations and explore proven ways you can get closer to this ideal goal.
What Is Zero Downtime?
Zero downtime means your systems are always available to users—even during updates or failures—with no visible interruption at any time. In practice, this means customers never notice an outage while using your applications or services. While achieving absolute zero downtime is rare outside of specialized industries like finance or healthcare, most organizations aim for near-zero by combining technology with strong processes.
It’s important to distinguish between “high availability” (which reduces outages) and “zero downtime” (which aims to eliminate them entirely). High availability keeps services running through most failures; zero downtime takes things further by ensuring even planned maintenance doesn’t disrupt users at all.
Why Zero Downtime Matters?
Why do so many businesses chase zero downtime? First: money talks. Even a brief outage can cost thousands—or millions—in lost sales or transactions. E-commerce sites lose customers fast if they can’t check out; banks risk failed payments; service providers see clients switch brands after repeated disruptions.
Second: trust is fragile online. Users expect instant access every time they log in—if you fail them once too often, they may not return. In regulated sectors like healthcare or finance, unplanned outages could also mean legal trouble due to compliance rules on data access and uptime guarantees.
Finally: innovation speeds up when teams aren’t afraid of breaking things during upgrades or deployments because robust zero-downtime strategies are in place (Informatica). That means faster delivery of new features without risking business continuity—a win-win for everyone involved.
Method 1: High Availability Solutions for Zero Downtime
High availability (HA) forms the backbone of any serious attempt at zero downtime. The core idea is simple: design your infrastructure so that if one part fails—hardware or software—another takes over instantly without user impact.
Most HA setups rely on redundancy: multiple servers clustered together so workloads shift automatically if something breaks down behind the scenes. Load balancers distribute traffic across healthy nodes while health checks spot trouble early before it affects end-users’ experience.
Implementing HA in Virtualized Environments
Virtualization platforms make high availability easier than ever by letting you cluster virtual machines across physical hosts—and move them as needed without disruption. For example:
With VMware vSphere HA or Hyper-V Failover Clustering enabled on your hypervisors,
You can set up automatic failover policies,
So when one host fails unexpectedly,
VMs restart quickly elsewhere with minimal delay,
And load balancers keep routing requests smoothly throughout the process.
But beware: not all apps handle failover gracefully! Stateless services adapt better than those storing session data locally; shared storage must be robust enough to avoid bottlenecks; network settings should allow seamless IP reassignment between nodes during switchover events.
Testing matters here too—you don’t want surprises during a real incident! Regularly simulate node failures using built-in tools like vSphere’s “Test Failover” function or PowerShell scripts for Hyper-V clusters so you know everything works as expected under pressure.
Advanced teams might also deploy geo-redundant clusters spanning multiple data centers for extra resilience against site-wide disasters—but this adds complexity around latency management and data consistency that requires careful planning.
Method 2: Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategies
Even with perfect high availability design, disasters still happen—from hardware faults to ransomware attacks that encrypt entire file shares overnight! That’s where backup and disaster recovery (DR) come into play as your safety net against worst-case scenarios.
A solid backup plan starts with regular snapshots stored both onsite—for quick restores—and offsite—for protection against local disasters like fire or flood.
Disaster recovery goes further by defining exactly how you’ll restore full operations after major incidents:
Which systems get priority?
How long until critical apps are back online?
Who coordinates each step?
The key metric here is Recovery Time Objective (RTO)—how fast you must recover—and Recovery Point Objective (RPO)—how much recent data loss is acceptable.
To approach zero downtime goals:
Automate backups using scheduled jobs
Use continuous replication where possible
Test restores frequently—not just backups themselves
Some solutions offer instant VM recovery features that let you boot from backup images directly while production storage gets rebuilt behind the scenes—a huge advantage when every minute counts!
Method 3: Live Migration and Replication for Zero Downtime
Live migration lets administrators move running virtual machines from one host server to another without shutting them down—a powerful tool for performing hardware maintenance or balancing workloads dynamically with no user impact.
Replication complements this by keeping real-time copies of critical VMs ready on standby hosts—or even remote sites—for rapid switchover if primary resources go offline unexpectedly.
These technologies are especially valuable in cloud environments where flexibility matters most—but require careful setup:
Sufficient bandwidth between source/destination hosts
Consistent storage configurations across clusters
Application-level support for handling brief pauses during migration
For example:
If patching underlying hardware supporting dozens of VMs,
You could migrate active workloads live onto other servers first,
Apply updates safely,
Then return VMs afterward—all invisible to end-users!
Replication also enables planned site migrations (“lift-and-shift”) without extended outages since cutover happens almost instantly once sync completes.
How to Achieve Zero Downtime Data Protection with Vinchin Backup & Recovery?
To put these strategies into action within virtualized environments such as VMware, consider Vinchin Backup & Recovery—a professional enterprise-level solution supporting over 15 mainstream virtualization platforms including VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox VE, oVirt/OLVM/RHV family products, XCP-ng/XenServer variants, OpenStack, ZStack, among others. This broad compatibility ensures seamless integration whether your infrastructure relies primarily on VMware or spans multiple hypervisors across hybrid clouds.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers advanced features highly relevant for minimizing operational disruption—including forever incremental backup, instant recovery capabilities, cross-platform V2V migration support, granular restore options, and comprehensive data deduplication/compression technologies—all designed to maximize uptime while optimizing resource usage across diverse environments.
The intuitive web console makes protecting your environment straightforward:
Step 1: Select the VMware VM(s) you wish to back up
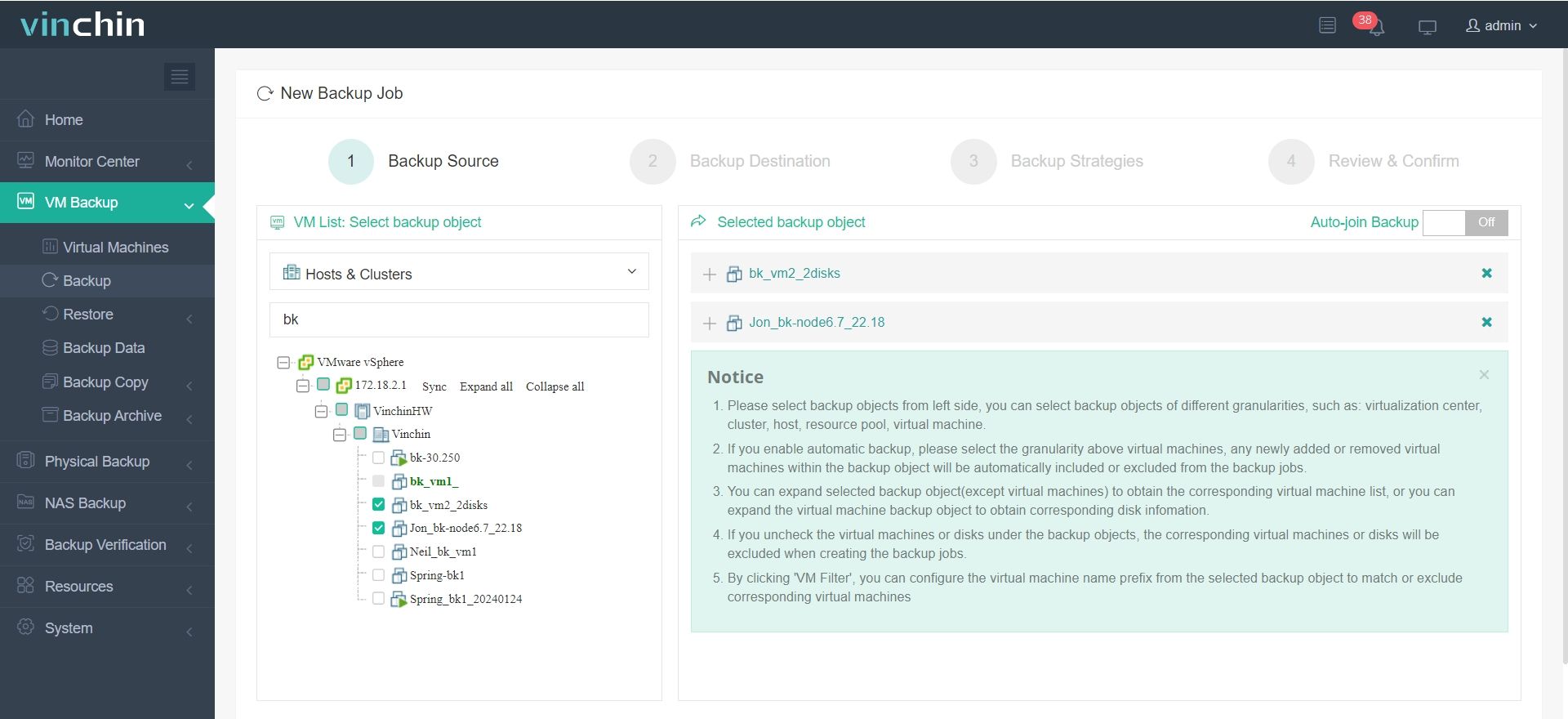
Step 2: Choose appropriate backup storage
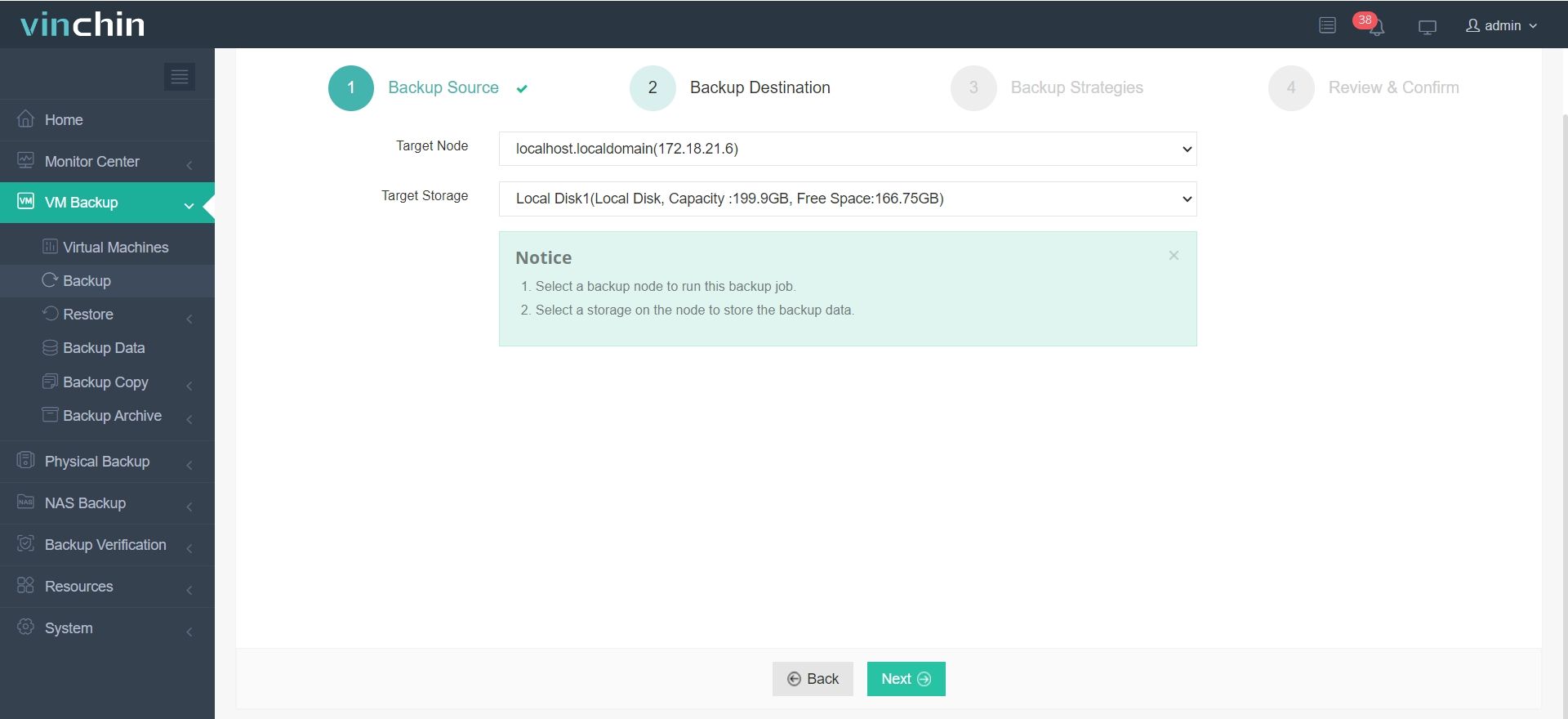
Step 3: Configure an optimal backup strategy tailored for your needs
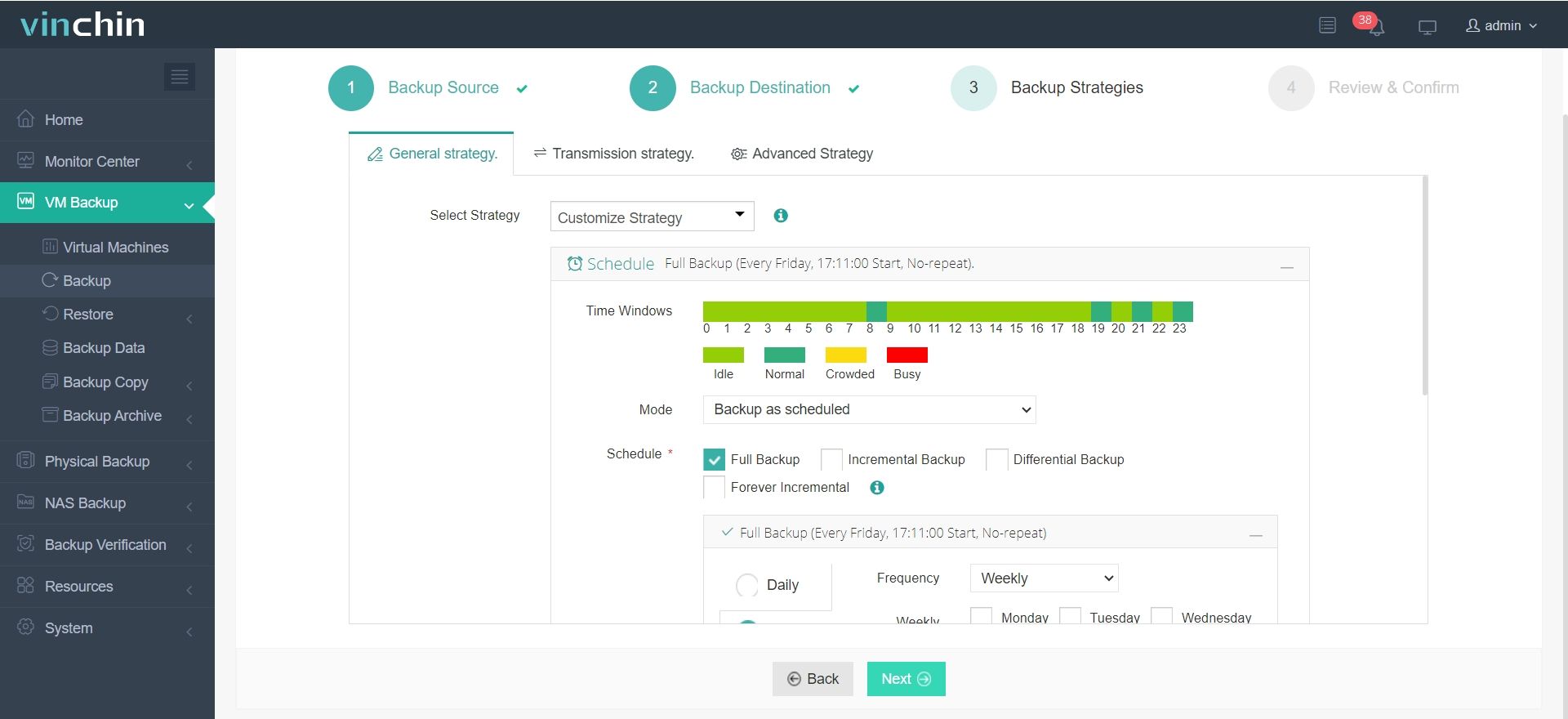
Step 4: Submit the job
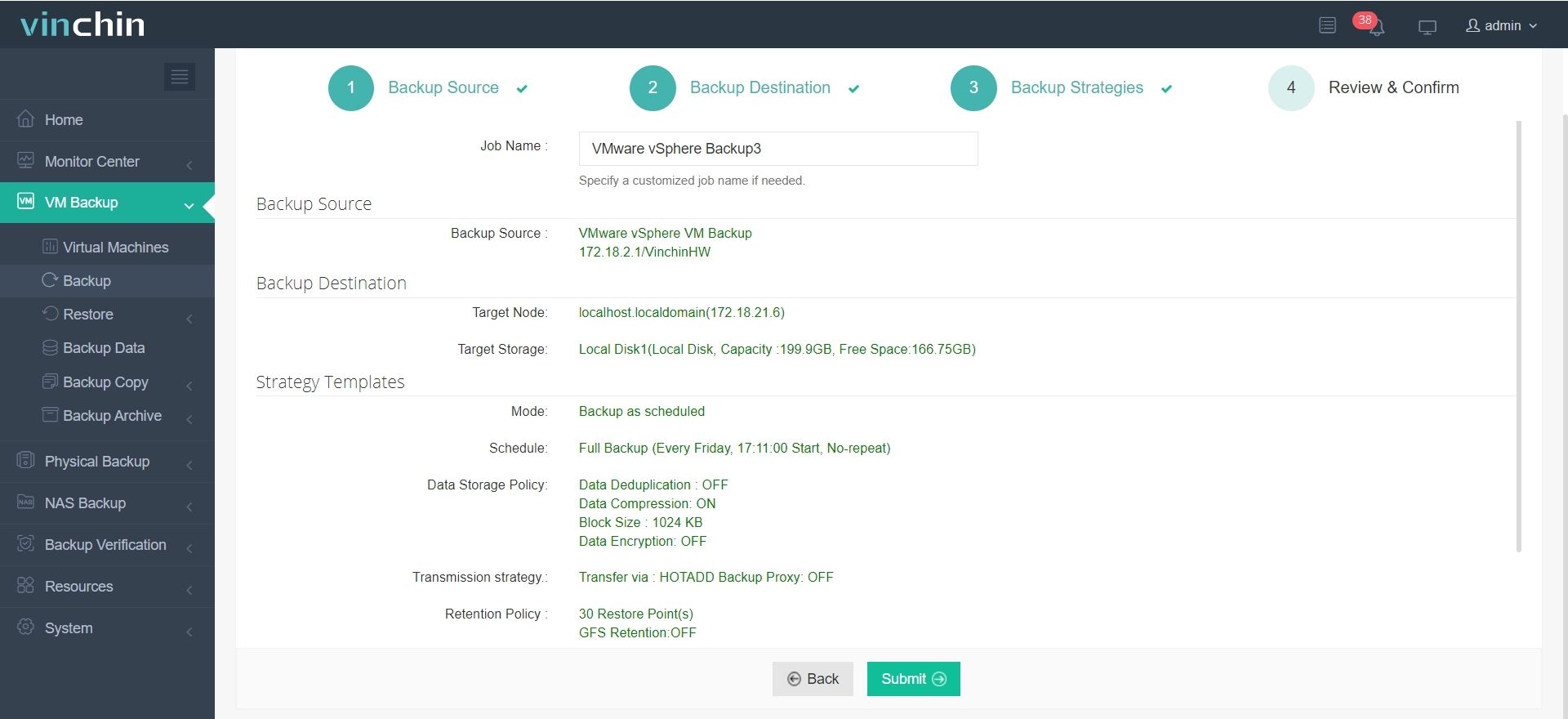
Thousands of enterprises worldwide trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery for reliable data protection—experience its power yourself with a 60-day full-featured free trial today!
Zero Downtime FAQs
Q1: How does zero downtime apply when managing hybrid cloud environments?
A1: By synchronizing workloads across public/private clouds using live migration plus cross-site replication tools while maintaining consistent networking/storage policies everywhere involved.
Q2 : What metrics should I track regularly measure actual system uptime versus planned objectives?
A2 : Monitor Mean Time Between Failures, Mean Time To Repair, total number unplanned incidents per month, percentage successful automated failovers, average RTO/RPO values achieved last quarter.
Q3 : Can my organization recover instantly from ransomware attack without losing productivity?
A3 : Yes — provided frequent immutable backups exist offsite AND tested instant-recovery workflows already established ahead-of-time before threat occurs.
Conclusion
Zero downtime remains the gold standard modern IT operations strive toward daily—it protects revenue streams while building lasting customer trust through uninterrupted service delivery worldwide round-the-clock reliability expected everywhere nowdays alike! With solutions like Vinchin simplifying robust data protection/migration tasks even small teams achieve results previously reserved only largest enterprises alone. Give it try today see difference firsthand yourself!
Share on:







