-
What Is a XenServer Pool?
-
Why Use a XenServer Pool?
-
Method 1: Creating a XenServer Pool
-
Method 2: Managing Hosts in a XenServer Pool
-
Method 3: Migrating Virtual Machines Within a XenServer Pool
-
Backup XenServer Pool VMs With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
XenServer Pool FAQs
-
Conclusion
Managing virtual infrastructure can be complex. A XenServer pool helps you organize multiple hosts into one logical unit for easier control and flexibility. In this guide, you’ll learn what a XenServer pool is, why it matters, how to create and manage pools at every level of expertise—and how to protect your environment with reliable backups.
What Is a XenServer Pool?
A XenServer pool is a group of physical servers running Citrix Hypervisor (formerly known as XenServer) that are managed together as one resource. Each pool has a single pool master that coordinates tasks across all member hosts (sometimes called slaves). With shared storage configured between hosts, you can move virtual machines between them without downtime—a feature called live migration.
This setup makes your environment more flexible because resources are pooled together rather than isolated on individual servers. It also simplifies management since you can perform most actions from one interface instead of logging into each server separately.
Why Use a XenServer Pool?
Using a xenserver pool offers several key benefits:
You manage many hosts through one interface.
High availability features let VMs restart automatically on another host if hardware fails.
Load balancing spreads workloads evenly across available resources.
Live migration allows moving VMs between hosts without shutting them down.
Maintenance becomes easier since you can evacuate VMs from one host before updating or repairing it.
These advantages help keep your services running smoothly—even during planned maintenance or unexpected failures—while reducing administrative overhead.
Method 1: Creating a XenServer Pool
Setting up your first xenserver pool is straightforward using XenCenter—the official management console for Citrix Hypervisor environments. Before starting:
Make sure all hosts run the same version of Citrix Hypervisor.
Hardware should be similar across all hosts (CPU type/model especially).
Shared storage must be accessible by every host you plan to include in the pool.
To create a new xenserver pool:
1. Open XenCenter and connect to each server you want in the pool.
2. In the Navigation pane, right-click at the top node or click the Pool menu.
3. Select New Pool.
4. Enter a name and optional description for your new pool.
5. Choose which server should act as the initial pool master—pick carefully; changing masters later requires extra steps like host evacuation.
6. Select additional servers to join this new pool.
7. Click Create Pool to finish setup.
Your new xenserver pool appears in the interface within moments—ready for further configuration or VM deployment.
Method 2: Managing Hosts in a XenServer Pool
Once your xenserver pool exists, managing its membership becomes part of daily operations—from adding capacity to handling hardware failures or upgrades.
Adding a Host
When scaling out your environment:
1. Confirm that any new server matches both software version and hardware profile of existing members.
2. In XenCenter, right-click on your target xenserver pool name.
3. Select Add Server from the context menu.
4. Enter IP address plus credentials for the new host; follow prompts until completion.
The system checks compatibility before joining; mismatched versions or CPUs may block addition—or limit live migration support later on.
Removing a Host
Sometimes you need to decommission old hardware or rebalance resources:
1. First migrate or shut down all VMs running on that host—you cannot remove active workloads safely otherwise!
2. Right-click on target host inside your xenserver pool tree view.
3. Select Enter Maintenance Mode so no new VMs start there by accident during removal prep.
4. Once empty/idle, right-click again then choose Remove from Pool; confirm when prompted.
If issues arise due to lingering connections or failed migrations, check logs under each VM’s properties tab for clues before retrying removal steps.
Handling Pool Master Failures
The designated master manages metadata updates across all members—so if it goes offline unexpectedly:
If current master remains online:
1. Right-click on your xenserver pool name in navigation pane
2.Select Designate New Master
3.Pick another healthy member as replacement
If current master is unreachable:
1.Log into any slave via SSH terminal
2.Run xe pool-emergency-transition-to-master
3.On other remaining slaves run xe pool-recover-slaves sequentially
For catastrophic failures where original master cannot return at all:
Use xe pool-emergency-reset-master then rejoin surviving nodes manually per Citrix CTX138338.
Method 3: Migrating Virtual Machines Within a XenServer Pool
One major advantage of pooling is seamless workload mobility—but successful migrations depend on proper prerequisites being met first!
Prerequisites for Live Migration
Before attempting live migration:
All participating hosts must have access to shared storage repositories such as NFS or iSCSI targets.
Verify shared storage visibility by checking under the Storage tab > Repositories within XenCenter; every intended destination should see identical volumes listed here.
If any VM still uses local disks attached only to its current host: migrate those disks onto shared repositories first using built-in disk move tools inside VM properties dialog box—otherwise live migration won’t work!
Note: Some advanced configurations like GPU passthrough require shutdown-based moves instead; check each VM’s settings under its properties’ “GPU” section before proceeding with migrations involving specialized hardware attachments.
How To Migrate A Virtual Machine Between Hosts?
Once prerequisites above are satisfied:
1.Open up XenCenter
2.Select desired VM from list view
3.Click bolded toolbar button labeled "Move" OR right-click then select "Move VM"
4.In resulting dialog pick destination host within same xenserver pool
5.Click "Move" again—the process begins instantly while keeping guest OS online throughout transfer!
Migration progress appears onscreen; if errors occur review logs under affected VM’s details panel for troubleshooting tips related either network latency/storage access issues etc.
Backup XenServer Pool VMs With Vinchin Backup & Recovery
To ensure robust data protection across diverse virtualization platforms—including XCP-ng and Citrix Hypervisor/XenServer—a comprehensive solution is essential. Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an enterprise-level backup platform supporting over 15 mainstream environments such as VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, oVirt, OLVM, RHV, XCP-ng, OpenStack, ZStack, and more—with full compatibility for both XCP-ng and Citrix Hypervisor/XenServer pools.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers powerful features including forever-incremental backup for fast data capture with minimal impact; granular restore capabilities enabling file-level recovery within VMs; advanced data deduplication/compression to reduce backup footprint; and secure multi-thread transmission ensuring efficient performance even at scale—all designed to maximize reliability while minimizing operational overhead.
With an intuitive web console interface, takes just four streamlined steps:
1.Just select XenServer VMs on the host

2.Then select backup destination

3.Select strategies
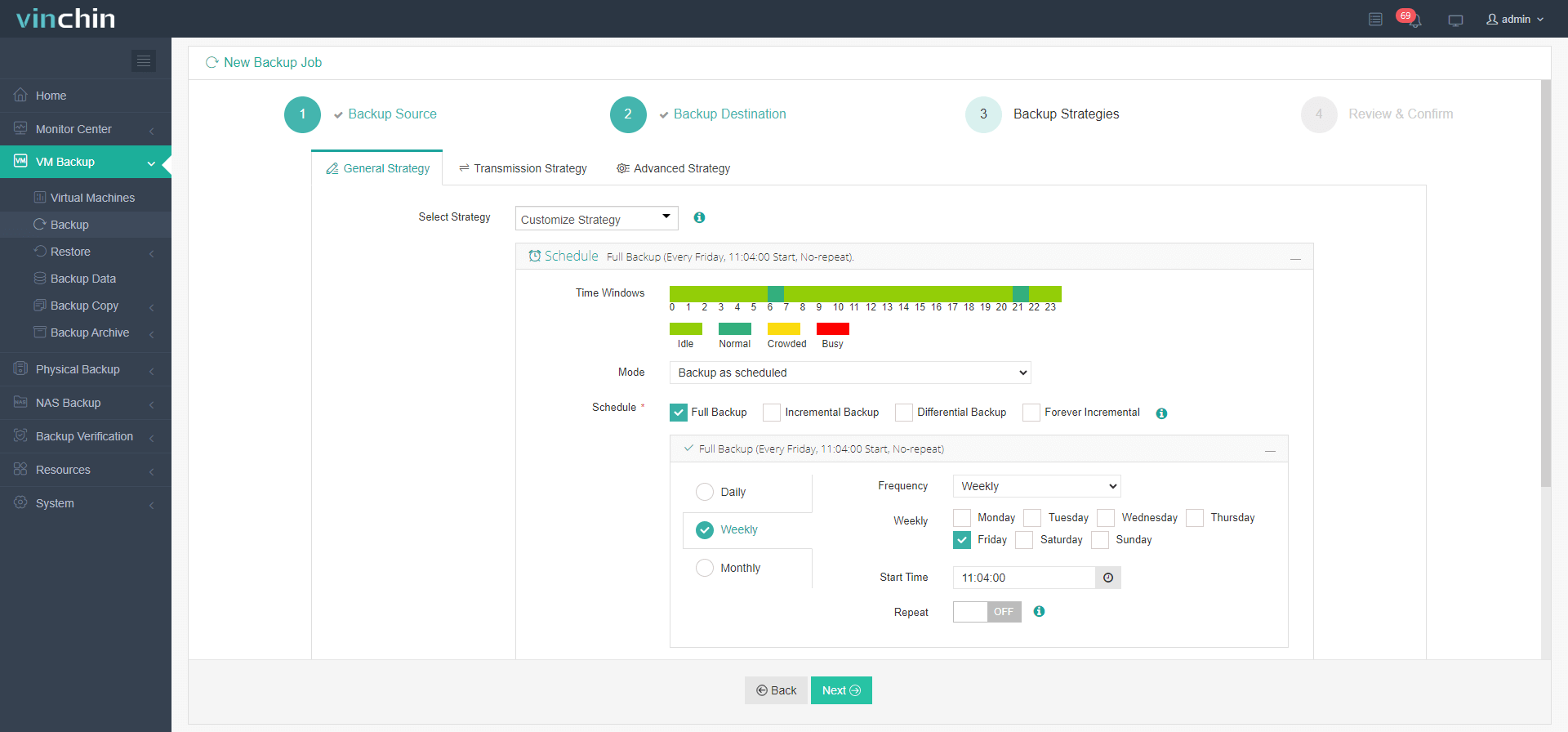
4.Finally submit the job

Thousands of organizations worldwide trust Vinchin Backup & Recovery for enterprise-grade data protection—try it risk-free with their 60-day full-featured free trial by clicking below!
XenServer Pool FAQs
Q1: Can I add servers with different CPU models into my existing xenserver pools?
A1: For best results always match CPU types/models across members—mixed setups may block live migrations due incompatibility features like EVC masking aren’t supported natively yet.
Q2: What happens if my designated master fails suddenly overnight?
A2: Promote another healthy member using SSH command line tool xe pool-emergency-transition-to-master then recover remaining nodes sequentially with xe pool-recover-slaves.
Q3: How do I safely remove an old server still hosting active workloads?
A3: Migrate/shutdown all resident VMs first > enter Maintenance Mode > right-click > Remove From Pool
Q4: Why does my live migration fail even though both source/destination appear healthy?
A4: Check network latency (<5ms), verify identical NIC configs per guest OS settings & confirm both ends see same shared storage repositories via Storage tab.
Conclusion
A well-managed xenserver pool streamlines virtualization administration while boosting uptime through load balancing/live migrations/high availability features alike! With proven tools like Vinchin backing up critical workloads becomes effortless too—try it today!
Share on:








