-
What is CBT Technology?
-
How CBT Works
-
Common Causes Why CBT Cannot Be Enabled
-
How to Confirm Whether CBT is Enabled?
-
How to Disable CBT?
-
Enterprise-level Backup Solution that Efficiently Integrates CBT
-
Changed Block Tracking Cannot be Enabled FAQs
-
Conclusion
Due to VMware's convenient Changed Block Tracking (CBT) technology, a foundation is provided for incremental backups of virtual machines. Except for the first backup, which must be a full backup and transfer of the entire VM data, subsequent backups only need to query the CBT records to obtain which blocks have changed, and then back up only those changed blocks. This not only saves time scanning the disk and determining changed blocks, but also significantly reduces the amount of data that needs to be transferred.
However, by default, the CBT feature is disabled because it causes a small but measurable performance degradation. Typically, CBT needs to be enabled before the first snapshot. By querying the virtual machine configuration, it is possible to determine whether Changed Block Tracking is enabled.
What is CBT Technology?
VMware Changed Block Tracking (CBT) is a core feature provided by VMware vSphere that records changes to disk blocks of virtual machines. CBT was first introduced in VMware vSphere 4.0 as part of the VMware vSphere Storage APIs–Data Protection framework. It allows third-party data protection applications to use this technology to perform more efficient backup and replication operations.
CBT works at the ESXi storage stack level and allows third-party backup solutions to back up only the blocks of data that have changed since the last backup, thereby enabling incremental backups instead of full backups of the entire virtual machine. This not only greatly reduces the size of the backup data, but also speeds up the backup process, especially in large environments with hundreds of VMs.
How CBT Works
The working principle of CBT is that the VMKernel monitors which blocks of data have been changed since the last snapshot point and records the offsets of these changed blocks. Based on these offsets, the modified data in the data blocks can be retrieved.
CBT identifies the modified disk sectors by comparing the last and current change set IDs. In addition, CBT can identify all in-use VMFS (Virtual Machine File System) blocks on the virtual disk. This tracking process is performed by the hypervisor itself and takes place outside the VM.
Requirements for Using CBT
✨VMware vSphere (ESXi 4.0 or later)
✨CBT must be enabled for the virtual machine (enabled by default)
✨Virtual hardware version 7 or later
✨Local VMFS datastore, NFS or iSCSI datastore
✨Physical compatibility mode Raw Device Mapping (RDM) is not supported
✨The virtual machine storage cannot be an independent disk (persistent or non-persistent), which means it must be affected by snapshots.
If CBT is not enabled during backup, the following errors will occur:
■ Changed block tracking is not configured correctly
■ Changed block tracking is not configured correctly for disk "Hard disk #"
■ Changed block tracking is not configured correctly for one or more virtual machine disks
Common Causes Why CBT Cannot Be Enabled
1. Existing Snapshots
One of the most frequent causes of the error is the presence of snapshots on the virtual machine. VMware does not allow CBT to be enabled on a VM with active snapshots; attempting to do so results in the warning “one or more snapshots present”. This limitation exists because snapshots alter the virtual disk chain, preventing VMware from accurately tracking changes.
2. Virtual Hardware Version and Configuration
CBT requires the VM to be running on virtual hardware version 7 or later and the host to be ESXi 4.0 or higher. Additionally, the VM’s disks must use supported storage modes—CBT is not supported on RDM in physical compatibility mode.
3. Backup-Tool and Transport Mode Limitations
Certain backup solutions and transport modes inherently disable or prevent enabling CBT. It may disable CBT by default when using the Virtual Appliance (HotAdd) transport mode and does not support re-enabling it. Likewise, some third-party tools warn that CBT cannot be enabled if the VM shows no snapshots (indicating a stale or corrupt state) or when VMware Tools are outdated.
How to Confirm Whether CBT is Enabled?
To check whether CBT is enabled for a virtual disk, perform the following steps:
1. Open vSphere Client and select a powered-off virtual machine.
2. Right-click the virtual machine, then navigate to Edit Settings > Options > Advanced/General > Configuration Parameters.
3. The virtual machine's configuration file (.vmx) contains the following entry:
ctkEnabled = “TRUE”
Note: To disable CBT, set the value to False.
4. In each virtual disk's configuration, the .vmx file will contain an entry like the following:
scsix:x.ctkEnabled = “TRUE”
5. Each virtual disk and its corresponding snapshot disk will be associated with a .ctk file.
vmname.vmdk
vmname-flat.vmdk
vmname-ctk.vmdk
vmname-000001.vmdk
vmname-000001-delta.vmdk
vmname-000001-ctk.vmdk
6. Power on the virtual machine.
7. In the virtual machine's home directory, verify that each disk with CBT enabled also has a vmname-ctk.vmdk file.
How to Disable CBT?
To turn off CBT (Changed Block Tracking), follow these steps:
1. Power off the virtual machine.
2. Right-click the virtual machine and select “Edit Settings.”
3. Click the “Options” tab.
4. In the “Advanced” section, click “General,” then select “Configuration Parameters.” This will open the Configuration Parameters dialog box.
5. For the specified SCSI disk, change the ctkEnabled parameter to false.
6. Power the virtual machine back on.
Enterprise-level Backup Solution that Efficiently Integrates CBT
After a deep understanding of VMware CBT functions and common problems, you may need a tool that can provide efficient and stable incremental backup capabilities for virtual machines.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is such an enterprise-level virtualization data protection solution that widely supports mainstream virtualization platforms such as VMware vSphere, Citrix Hypervisor (XenServer), XCP-ng, Proxmox, Red Hat Virtualization (RHV), oVirt, etc. Vinchin Backup & Recovery now had implemented CBT support for: VMware vSphere, Citrix Hypervisor (XenServer 7.3 and higher), XCP-ng, RHV (4.4.7 or newer), oVirt (4.4.7 or newer), OLVM (4.4.8 or newer) and Huawei FusionCompute (KVM), significantly improving the efficiency and reliability of incremental backup.
For platforms that do not support CBT, Vinchin provides its own SpeedKit technology as an alternative to achieve similar incremental backup acceleration effects.
It is very easy to enable CBT backup in Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1. Select the backup object
2. Specify the backup destination
3. Set the backup policy. Here in the "Advanced Strategy", check the "CBT" option.
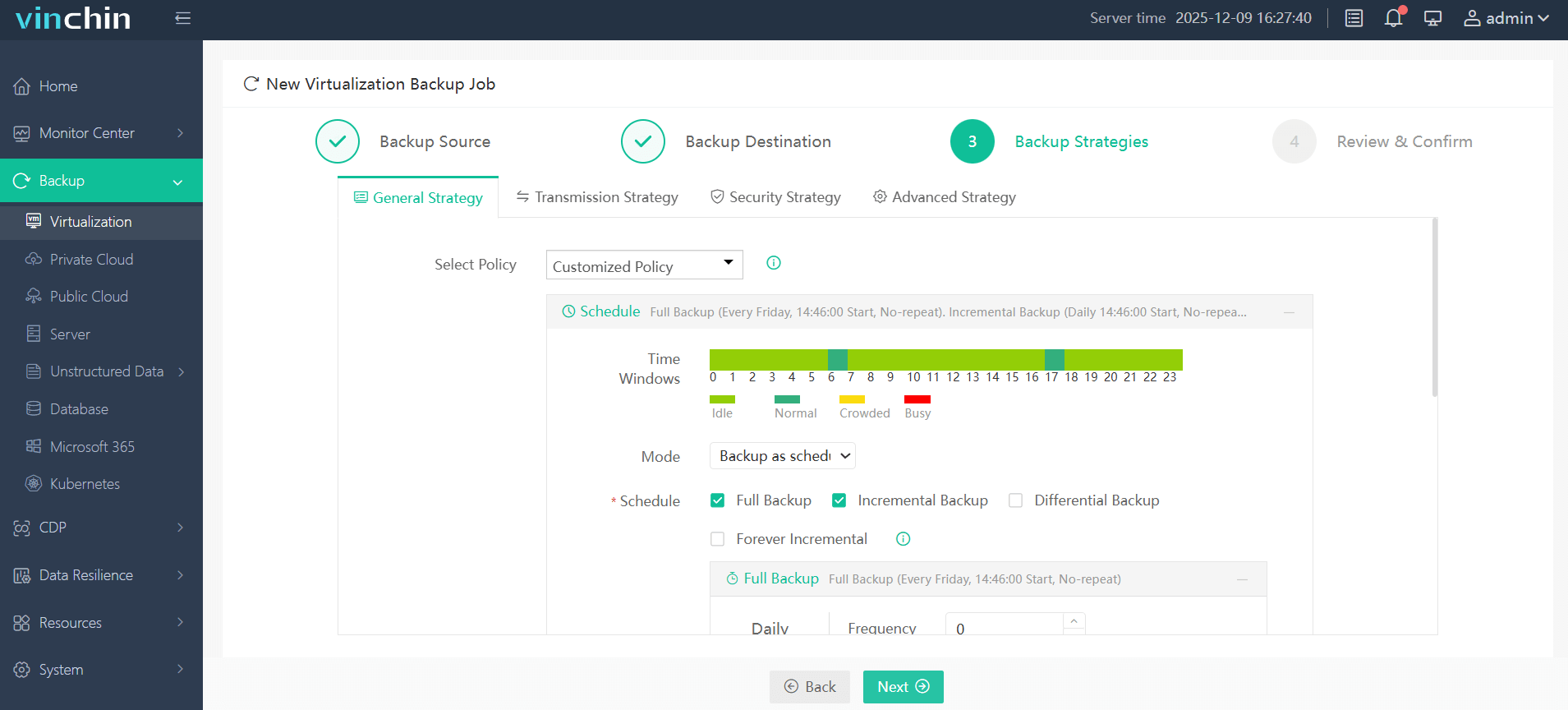
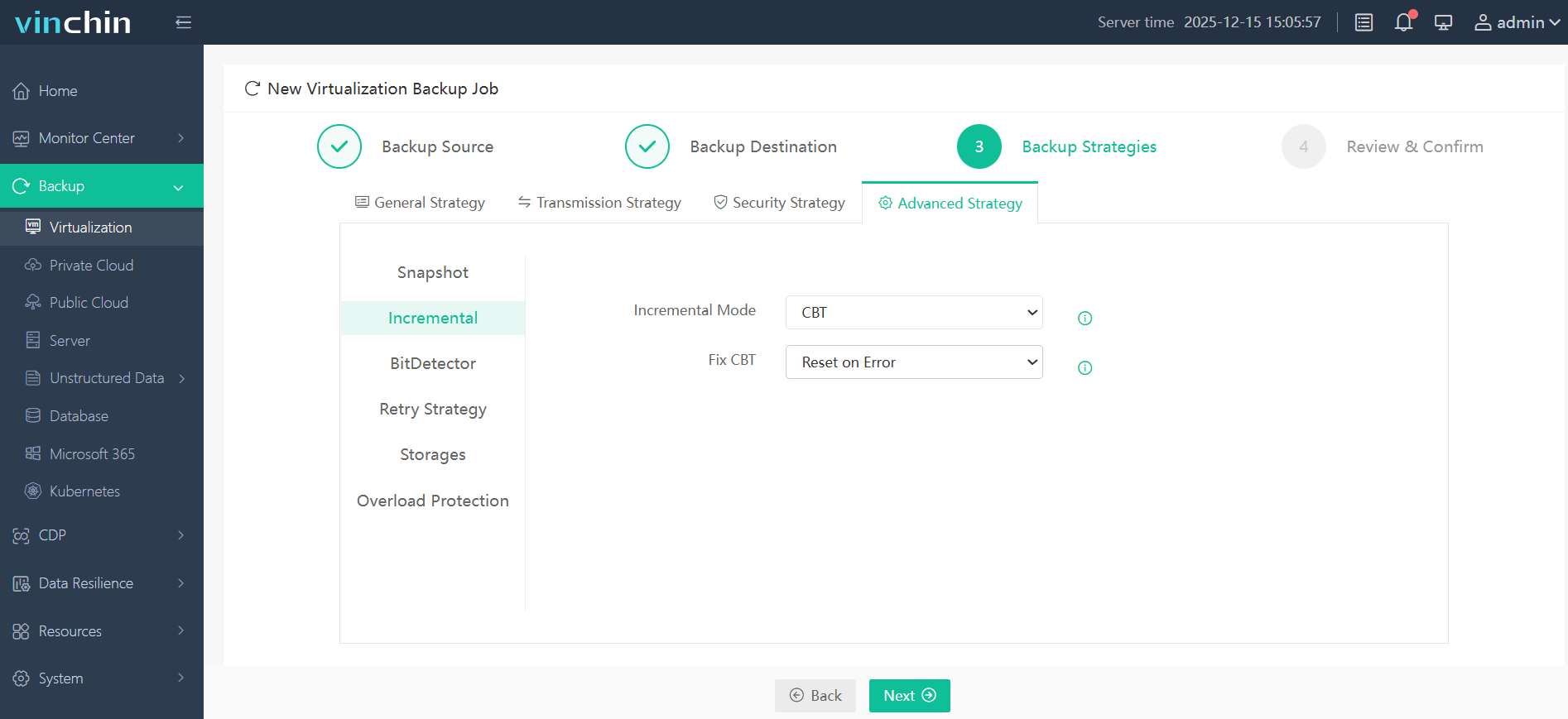
4. Submit the task
In addition to CBT, Vinchin also provides a number of advanced features to further enhance data protection capabilities, such as instant recovery, file-level recovery, backup verification, multi-platform V2V migration, etc. For enterprise users who want to improve backup efficiency and reduce storage costs, Vinchin is a professional choice worth considering. You can try it for free for 60 days to experience the full functionality.
Changed Block Tracking Cannot be Enabled FAQs
1. Where is CBT metadata stored, and can it be manually removed?
CBT uses .ctk files stored alongside the VM's VMDK files in the datastore. You can delete them manually only when the VM is powered off, but be sure to disable CBT first to avoid corruption.
Conclusion
VMware's CBT technology is a powerful tool that enhances the efficiency and speed of virtual machine backups by enabling incremental backups. While it requires proper configuration and is subject to certain limitations—such as compatibility and snapshot constraints—its benefits in reducing backup time and storage usage make it invaluable in enterprise environments. Ensuring CBT is correctly enabled and maintained helps avoid common backup issues and optimizes data protection workflows.
Share on:






