-
Why choose endpoint backup?
-
How does Endpoint backup work?
-
Types of endpoint backup
-
Unified data protection for virtual environments with Vinchin
-
Endpoint backup solutions FAQs
-
Conclusion
With the widespread adoption of hybrid work and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) models, endpoint devices such as laptops, tablets, and mobile workstations have become high-risk vectors for corporate data breaches and loss. According to reports from multiple cybersecurity organizations, the complexity and frequency of ransomware attacks continue to rise throughout 2024–2025. Due to their distributed nature and management challenges, endpoint devices are often the primary targets for attackers.
In this security landscape, relying solely on traditional server or data center-level backups is no longer sufficient to mitigate risks. Enterprises must implement more granular data protection strategies, with endpoint backup emerging as a critical component in ensuring data recoverability and maintaining business continuity.
Why choose endpoint backup?
Endpoint backup solutions effectively guard against various data loss scenarios, including:
Hardware Failure: When a device fails, backups enable fast restoration of data and system configurations to a new device.
Ransomware Attacks: Timely backups are the most reliable way to recover encrypted data and resist cyber extortion.
Natural Disasters: If backups are stored offsite, data can be recovered even when primary locations are impacted.
Human Error: Accidental deletion or overwriting of files can be easily undone with a backup in place.
Lost or Stolen Devices: Backups ensure that data can be restored on a new device, minimizing operational disruption.
These real-world threats highlight the need for proactive protection rather than reactive remedies.
How does Endpoint backup work?
1. Installation and Setup
The process begins by installing a dedicated backup client on each endpoint. IT administrators or users configure which files, folders, and applications to back up, and define preferences such as backup frequency, retention policies, and encryption options.
2. Data Capture and Backup Methods
Once configured, the backup software runs silently in the background, monitoring for changes and initiating backups accordingly. Common backup methods include:
Incremental Backup: Only the changes made since the last backup are saved, minimizing bandwidth and storage usage.
Differential Backup: Captures all changes since the last full backup, creating progressively larger files until the next full backup.
Full Backup: Periodically copies all selected data, providing comprehensive protection at the cost of more storage and network usage.
3. Secure Data Transfer and Storage
Backups are securely transmitted to designated storage targets, such as:
On-premise storage (e.g., NAS or backup servers): Ideal for organizations with strict data sovereignty or compliance needs.
Cloud storage (e.g., AWS, Azure, third-party providers): Offers scalability, accessibility, and reduced infrastructure overhead.
To ensure data safety, endpoint backup solutions implement encryption, access controls, and advanced security mechanisms during transfer and storage.
4. Restoration and Recovery
In the event of data loss, cyberattack, or device failure, the true value of endpoint backup is realized during recovery. Users can initiate restoration via an intuitive interface, choosing to recover individual files, folders, or entire system images to their original state.
Types of endpoint backup
Depending on business needs, different backup strategies may be applied to different endpoints:
File-Level Backup: Suitable for protecting sensitive documents like legal, financial, or research data, particularly in isolated or high-risk systems.
Image-Based Backup: Captures a snapshot of the entire OS, settings, applications, and data, ideal for quickly deploying new workstations.
Continuous Data Protection (CDP): Captures real-time or frequent changes to minimize data loss between scheduled backups. This approach is especially effective against threats like ransomware or accidental deletion.
Unified data protection for virtual environments with Vinchin
In addition to endpoint devices, critical business systems running on virtualized platforms also face serious data security challenges. Traditional physical backup tools often fall short in terms of adaptability and efficiency within virtual environments, making it essential for enterprises to adopt purpose-built backup solutions tailored for virtualization.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is designed to meet this need. It supports major virtualization platforms including VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, KVM, and Proxmox, and offers features such as agentless backup, incremental and snapshot-based CDP, file-level and full VM recovery, and cross-platform (heterogeneous) migration. These capabilities help enterprises build a unified data protection framework that ensures comprehensive coverage—from endpoints to data centers. It supports all major hypervisors and offers key benefits such as:
Agentless Backup: No need to install agents inside each VM, simplifying deployment and reducing resource consumption.
Flexible Backup Strategies: Supports full, incremental, and snapshot-based CDP backups to match various use cases.
Granular and Full Recovery: Restore individual files or entire virtual machines to a previous state with ease.
Cross-Platform Recovery: Enables VM migration and heterogeneous recovery (e.g., from VMware to Proxmox).
Strong Security and Central Management: Protects data through encryption and role-based access, with centralized control for efficient operations.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery's operation is very simple, just a few simple steps.
1.Just select VMs on the host
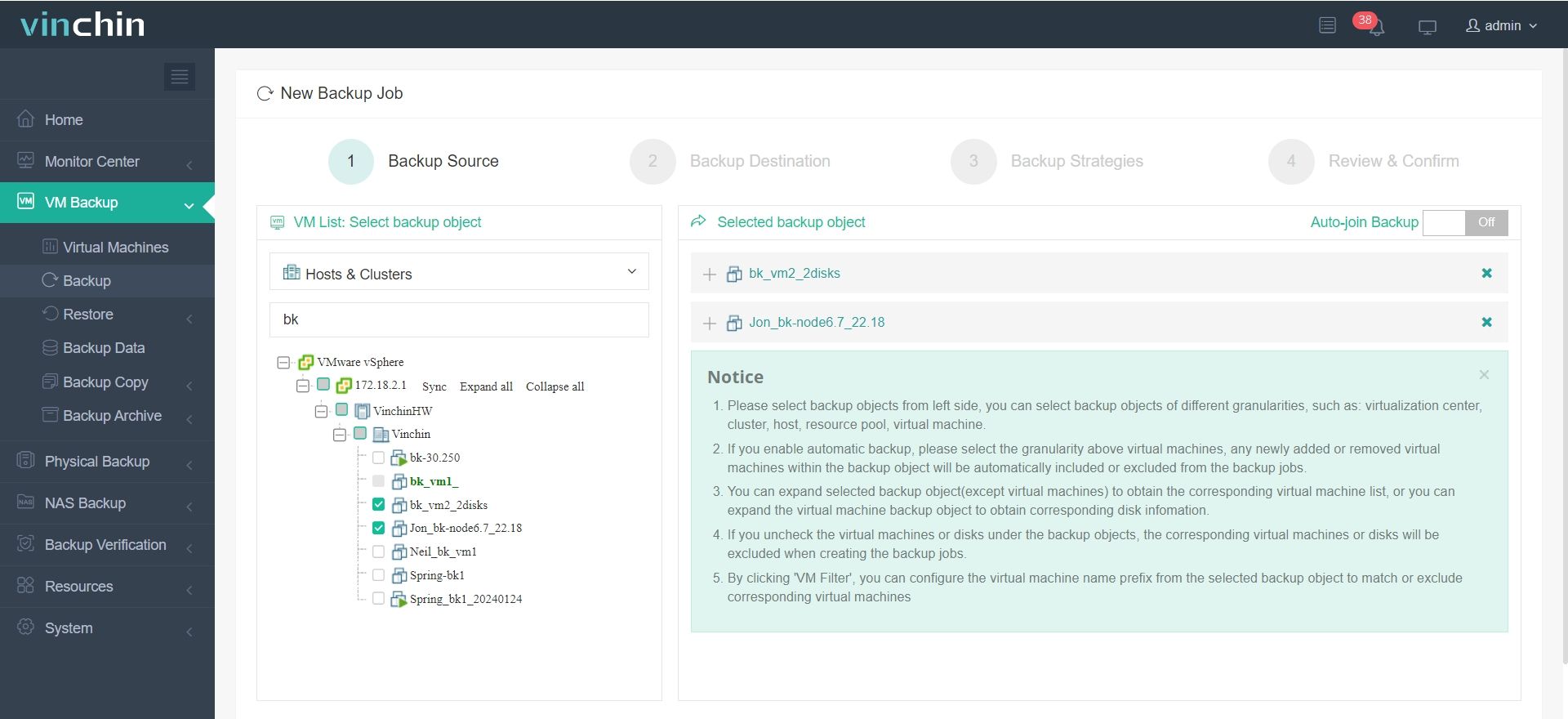
2.Then select backup destination
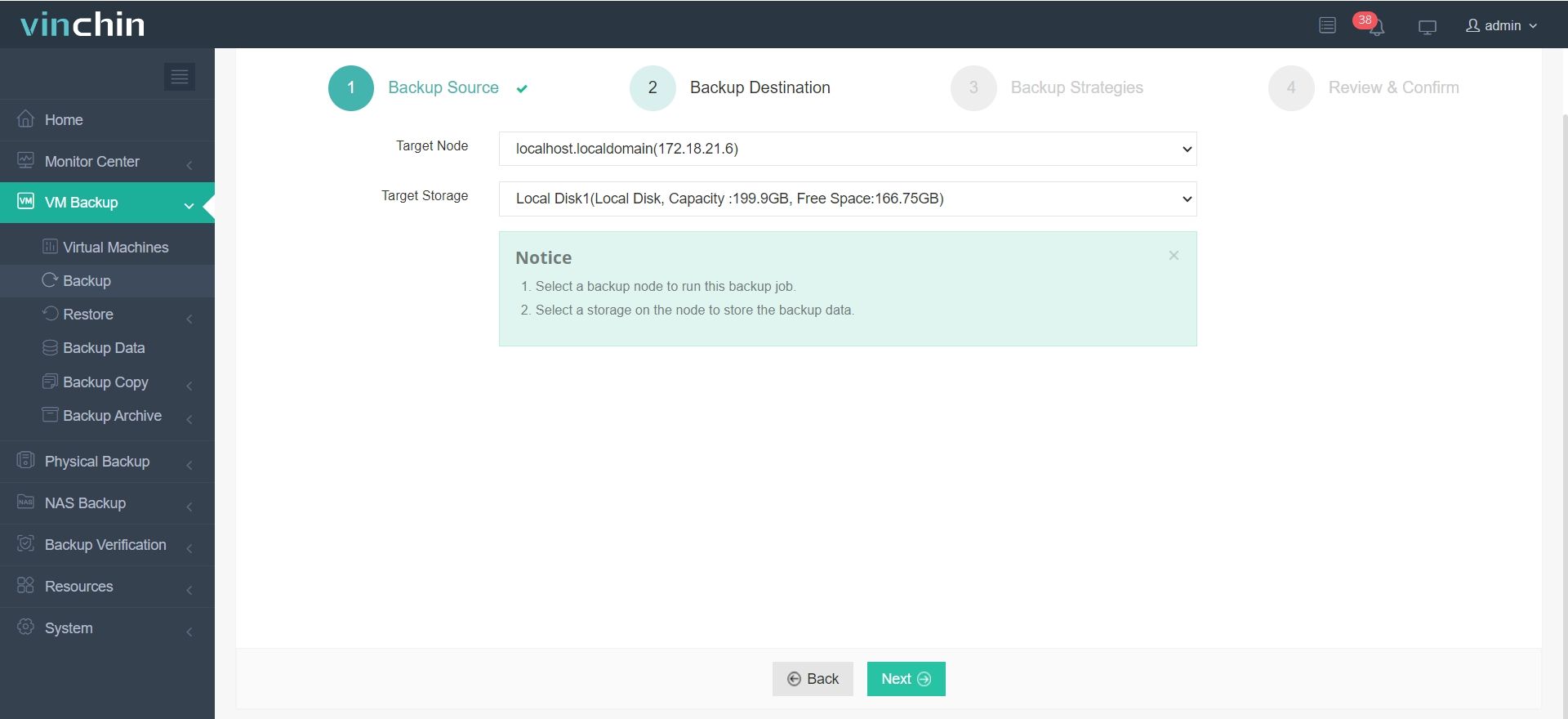
3.Select strategies
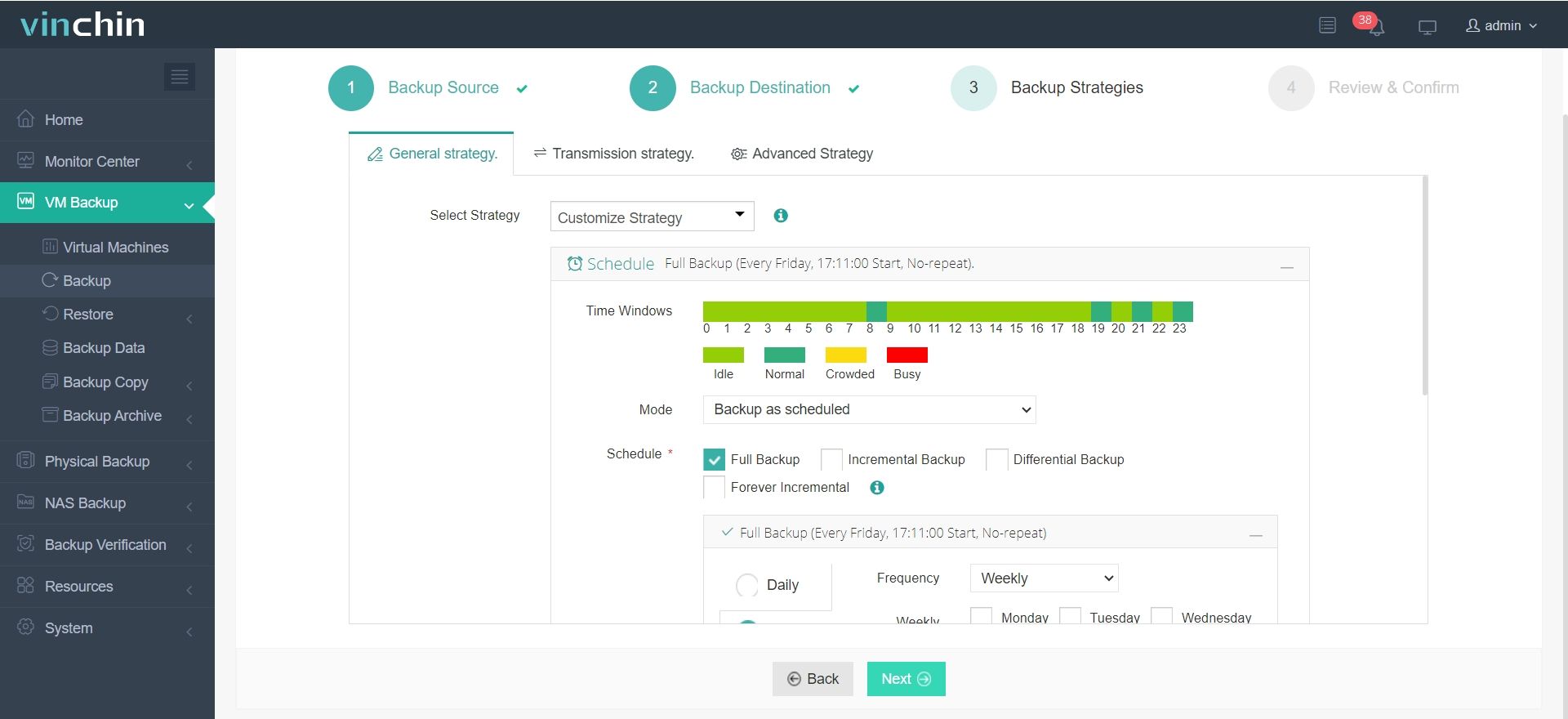
4.Finally submit the job
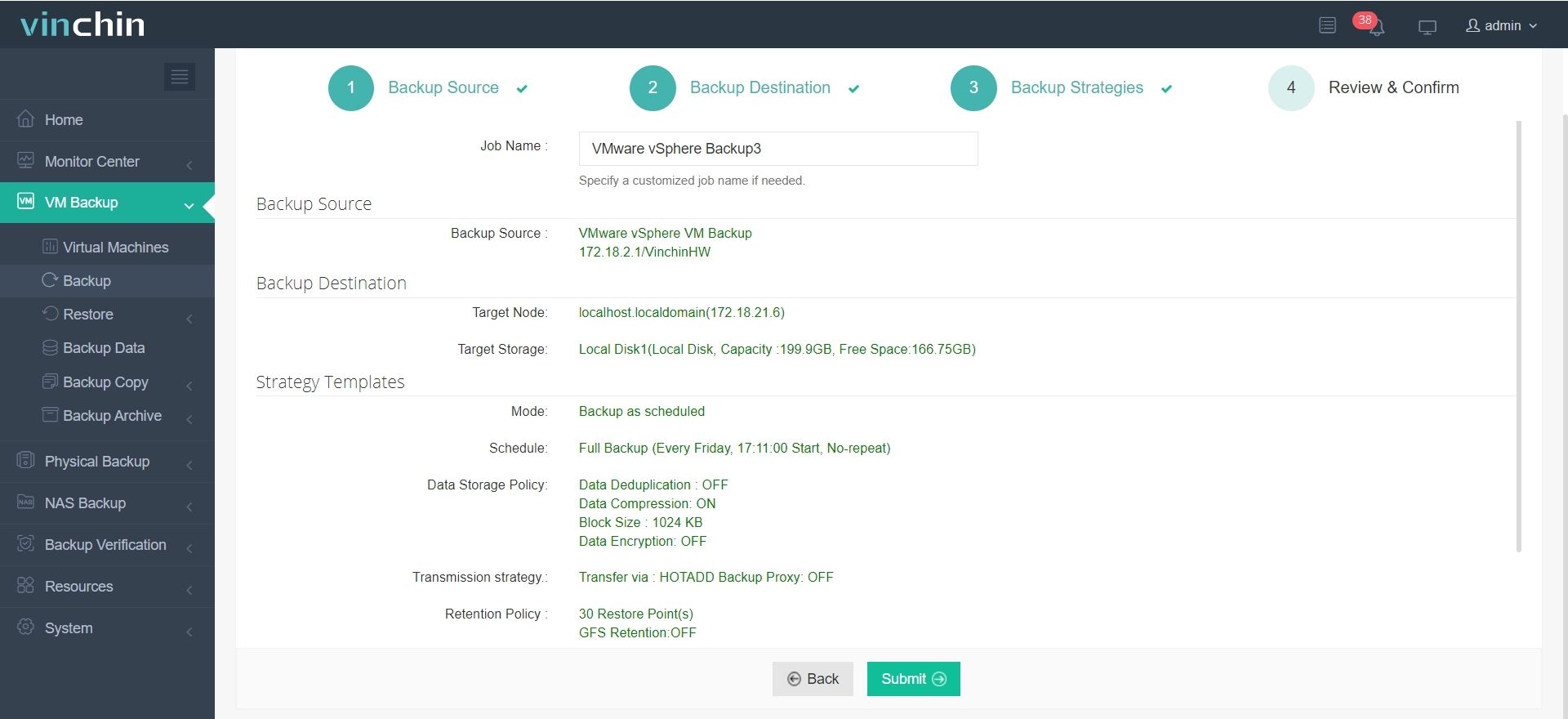
With Vinchin, organizations can safeguard endpoint systems hosted on virtual platforms and build an integrated backup framework that unifies physical and virtual protection. Vinchin offers a free 60-day trial for users to experience the functionality in a real-world environment. For more information, please contact Vinchin directly.
Endpoint backup solutions FAQs
Q1: Is endpoint backup data encrypted?
A1: Most solutions use:
In-transit encryption (TLS/SSL).
At-rest encryption (AES-256).
Q2: How long are backups retained?
A2: Depends on company policy, but common retention options include:
30 days (short-term)
1 year (mid-term)
7+ years (compliance/legal requirements)
Conclusion
Endpoint backup solutions is vital for protecting distributed data in today’s hybrid work environments. It defends against threats like ransomware, hardware failure, and data loss. Solutions like Vinchin ensure unified, secure, and efficient protection for both physical and virtual systems.
Share on:





